当前位置:网站首页>樹結構---二叉樹2非遞歸遍曆
樹結構---二叉樹2非遞歸遍曆
2022-07-01 09:10:00 【遨遊的laugh哥】
目錄
完整代碼(binTree.h)
#include"seqQueue.h"
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
class binTree{
friend void printTree(const binTree<T>& t,T flag){
//由於要輸出值,所以隊列存值
//為了檢驗函數功能,直接調用已實現函數
if(t.root==NULL) return;
seqQueue<T> s;
s.enQueue(t.root->data);//值
T tmp,lc,rc;
while(!s.is_empty()){
tmp=s.deQueue();
//調用左右孩子
lc=t.lchild(tmp,flag);
rc=t.rchild(tmp,flag);
cout<<"("<<tmp<<" "<<lc<<" "<<rc<<")"<<endl;
if(lc!=flag) s.enQueue(lc);
if(rc!=flag) s.enQueue(rc);}
}
private:
struct node{
T data;
node *lchild,*rchild;
node():lchild(NULL),rchild(NULL){}
node(const T& x,node* p=NULL,node* q=NULL):data(x),lchild(p),rchild(q){}
~node(){}
};
node* root;
//為公有無參函數傳參
void preTraverse(node* t) const;
void midTraverse(node* t) const;
void postTraverse(node* t) const;
int nodeSize(node* t) const;
int treeHigh(node* t) const;
void clear(node* &t);
//輔助函數---找給定結點值的結點指針
node* find(T x,node* t) const{//傳值x和要返回的指針t
node* tmp;
if(t==NULL) return NULL;
//根左右
if(t->data==x) return t;
tmp=find(x,t->lchild);
if(tmp) return tmp;
else return find(x,t->rchild);
}
public:
/*構造函數*/
binTree(){ root=NULL;}
/*層次遍曆創建樹+層次遍曆已有樹*/
void createTree(T flag);//用flag錶示空結點
void levelTraverse() const;//層次遍曆
/*遞歸實現前中後序遍曆*/
void preTraverse() const;
void midTraverse() const;
void postTraverse() const;
/*求樹的高度+葉子結點個數*/
int nodeSize() const;
int treeHigh() const;
/*求左右孩子結點值---傳參x和錶示空的flag*/
T lchild(T x,T flag) const;
T rchild(T x,T flag) const;
//清空+剪枝
void clear();
void defLeft(T x);
void defRight(T x);
};
//創建樹+層次遍曆
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::createTree(T flag){
seqQueue<node*> s;//創建裝有結點指針的隊列
//輸入根節點並入隊
T x;
cout<<"輸入根節點:";
cin>>x;
s.enQueue(root=new node(x));
//訪問結點,並將非空左右孩子入隊
node* tmp;
T ldata,rdata;
while(!s.is_empty()){
tmp=s.deQueue();
cout<<"輸入結點"<<tmp->data<<"的左右孩子:";
cin>>ldata>>rdata;
if(ldata!=flag) s.enQueue(tmp->lchild=new node(ldata));
if(rdata!=flag) s.enQueue(tmp->rchild=new node(rdata));
}
cout<<"create successful!\n";
}
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::levelTraverse() const{
cout<<"\n層次遍曆:";
if(root==NULL) return;
seqQueue<node*> s;
s.enQueue(root);
while(!s.is_empty()){
node* tmp=s.deQueue();
cout<<tmp->data<<" ";//輸出
if(tmp->lchild) s.enQueue(tmp->lchild);
if(tmp->rchild) s.enQueue(tmp->rchild);
}
}
//遞歸實現前中後序遍曆
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::preTraverse(node* t) const{
if(t==NULL) return;
cout<<t->data<<" ";
preTraverse(t->lchild);
preTraverse(t->rchild);
}
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::preTraverse() const{
cout<<"\n前序遍曆:";
preTraverse(root);
}
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::midTraverse(node* t) const{
if(t==NULL) return;
midTraverse(t->lchild);
cout<<t->data<<" ";
midTraverse(t->rchild);
}
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::midTraverse() const{
cout<<"\n中序遍曆:";
midTraverse(root);
}
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::postTraverse(node* t) const{
if(t==NULL) return;
postTraverse(t->lchild);
postTraverse(t->rchild);
cout<<t->data<<" ";
}
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::postTraverse() const{
cout<<"\n後序遍曆:";
postTraverse(root);
}
//求結點數+樹高
template<class T>
int binTree<T>::nodeSize(node* t) const{
if(t==NULL) return 0;
//結點數=根+左子樹+右子樹
else return nodeSize(t->lchild)+nodeSize(t->rchild)+1;
}
template<class T>
int binTree<T>::nodeSize() const{
return nodeSize(root);
}
template<class T>
int binTree<T>::treeHigh(node* t) const{
if(t==NULL) return 0;
int L,R;
L=treeHigh(t->lchild);
R=treeHigh(t->rchild);
return 1+(L>R?L:R);//根+max(左子樹高度,右子樹高度)
}
template<class T>
int binTree<T>::treeHigh() const{
return treeHigh(root);
}
//求左右孩子
template<class T>
T binTree<T>::lchild(T x,T flag) const{
node* tmp=find(x,root);
if(tmp==NULL||tmp->lchild==NULL) return flag;
else return tmp->lchild->data;
}
template<class T>
T binTree<T>::rchild(T x,T flag) const{
node* tmp=find(x,root);
if(tmp==NULL||tmp->rchild==NULL) return flag;
else return tmp->rchild->data;
}
//清空+剪枝
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::clear(node* &t){
if(t==NULL) return;
clear(t->lchild);
clear(t->rchild);
delete t;
t=NULL;//把根節點置空
}
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::clear(){
clear(root);
}
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::defLeft(T x){
node* tmp=find(x,root);
if(tmp==NULL) return;
clear(tmp->lchild);
}
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::defRight(T x){
node* tmp=find(x,root);
if(tmp==NULL) return;
clear(tmp->rchild);
}主函數測試

#include"binTree.h"
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
binTree<char> bt;
bt.createTree('#');
printTree(bt,'#');
cout<<bt.nodeSize()<<" "<<bt.treeHigh()<<endl;
bt.defLeft('D');
printTree(bt,'#');
cout<<endl;
cout<<bt.nodeSize()<<" "<<bt.treeHigh()<<endl;
bt.defRight('B');
printTree(bt,'#');
cout<<endl;
cout<<bt.nodeSize()<<" "<<bt.treeHigh()<<endl;
return 0;
}

非遞歸的前中後遍曆
引入棧文件----stack.h
template<class elemType>
class seqStack{
private:
elemType* data;
int maxsize;
int top_s;
void doublespace();//擴容
public:
//構造+析構
seqStack(int initszie=10){
data=new elemType[initszie];
maxsize=initszie;
top_s=-1;
}
~seqStack(){ delete[] data;}
//函數操作
bool is_empty() const{ return top_s==-1;}
elemType top() const{ return data[top_s];}
elemType pop(){
return data[top_s--];
}
void push(const elemType& x){
data[++top_s]=x;
}
};
//擴容
template<class elemType>
void seqStack<elemType>::doublespace(){
elemType* tmp;
maxsize*=2;
data=new elemType[maxsize];
for(int i=0;i<=top_s;i++){
data[i]=tmp[i];
}
delete[] tmp;
}前序實現:
void preTraverse() const{ seqStack<node*> s; if(root==NULL) return; cout<<"前序遍曆:"; s.push(root); node* tmp; while(!s.is_empty()){ tmp=s.pop(); cout<<tmp->data<<" "; //由於棧後進先出,一定要先右後左 if(tmp->rchild) s.push(tmp->rchild); if(tmp->lchild) s.push(tmp->lchild); } }比較簡單,類似層次遍曆,只是一定要先右孩子進棧,然後左孩子進棧
中序
void midTraverse() const{//非遞歸中序 /*由於要記錄出棧次數,所以引入結構elem*/ if(root==NULL) return; struct elem{ node* cur; int time; elem(node* p=NULL):cur(p),time(0){ }//構造函數 }; cout<<"非遞歸中序遍曆:"; //初始化---裝有elem的棧和elem變量 seqStack<elem> s; elem bt(root); s.push(bt); elem tmp;//記錄出棧 while(!s.is_empty()){ tmp=s.pop(); if(tmp.time==1){ //錶明已經出棧過一次了,也就是左結點訪問結束 cout<<tmp.cur->data<<" "; //接下來訪問右孩子節點 if(tmp.cur->rchild) s.push(tmp.cur->rchild); } else{ tmp.time+=1; s.push(tmp);//自己是第一次訪問,入棧,time+1 //左孩子進棧 if(tmp.cur->lchild) s.push(tmp.cur->lchild); } } cout<<endl; }注意:elem(tmp.cur->lchild)-----是elem類型,沒有指定變量名,類似臨時變量
注意:如果出棧過一次,那麼time+1,而且在訪問左結點,一定要:再進棧push一次
後序
void postTraverse() const{//非遞歸後序 /*由於要記錄出棧次數,所以引入結構elem*/ if(root==NULL) return; struct elem{ node* cur; int time; elem(node* p=NULL):cur(p),time(0){ }//構造函數 }; cout<<"非遞歸後序遍曆:"; //初始化---裝有elem的棧和elem變量 seqStack<elem> s; elem bt(root); s.push(bt); elem tmp;//記錄出棧 //以上和中序遍曆代碼一致 while(!s.is_empty()){ tmp=s.pop(); if(tmp.time==2){ //已訪問兩次,也就是左右孩子都遍曆了,輸出結果 cout<<tmp.cur->data<<" "; } else{ if(tmp.time==1){ //左孩子已訪問,右孩子進棧 tmp.time+=1; s.push(tmp);//一定別忘了,右孩子進棧時,自己再進一次棧 if(tmp.cur->rchild) s.push(elem(tmp.cur->rchild));//注意類型 } else{ tmp.time+=1; s.push(tmp);//自己進棧,然後遍曆左孩子 if(tmp.cur->lchild) s.push(elem(tmp.cur->lchild)); } } } }與中序區別只在:
while(!s.is_empty()){
//區別
}
if(tmp.time==2){ //已訪問兩次,也就是左右孩子都遍曆了,輸出結果 cout<<tmp.cur->data<<" "; } else{ if(tmp.time==1){ //左孩子已訪問,右孩子進棧 tmp.time+=1; s.push(tmp);//一定別忘了,右孩子進棧時,自己再進一次棧 if(tmp.cur->rchild) s.push(elem(tmp.cur->rchild));//注意類型 } else{ tmp.time+=1; s.push(tmp);//自己進棧,然後遍曆左孩子 if(tmp.cur->lchild) s.push(elem(tmp.cur->lchild)); } }注意這個根左右過程:
if 訪問根
else if 第一次---左孩子
else 第二次---右孩子
完整程序
#include<stdlib.h>
#include"seqStack.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
class binTree{
private:
struct node{
T data;
node *lchild,*rchild;
node():lchild(NULL),rchild(NULL){}
node(const T& x,node* p=NULL,node* q=NULL):data(x),lchild(p),rchild(q){}
~node(){}
};
node* root;
public:
binTree(){ root=NULL;}
void createTree();//靜態初始化樹
void preTraverse() const{//非遞歸前序
if(root==NULL) return;
cout<<"非遞歸前序遍曆:";
//將根節點入棧
seqStack<node*> s;//棧的元素類型是--node*
s.push(root);
node* tmp;//記錄出棧元素
while(!s.is_empty()){
tmp=s.pop();//棧頂元素出棧
cout<<tmp->data<<" ";//前序遍曆--先訪問根
//由於棧的後進先出,右孩子先於左孩子進棧
if(tmp->rchild) s.push(tmp->rchild);
if(tmp->lchild) s.push(tmp->lchild);
}
cout<<endl;
}
void midTraverse() const{//非遞歸中序
/*由於要記錄出棧次數,所以引入結構elem*/
if(root==NULL) return;
struct elem{
node* cur;
int time;
elem(node* p=NULL):cur(p),time(0){ }//構造函數
};
cout<<"非遞歸中序遍曆:";
//初始化---裝有elem的棧和elem變量
seqStack<elem> s;
elem bt(root);
s.push(bt);
elem tmp;//記錄出棧
while(!s.is_empty()){
tmp=s.pop();
if(tmp.time==1){
//錶明已經出棧過一次了,也就是左結點訪問結束
cout<<tmp.cur->data<<" ";
//接下來訪問右孩子節點
if(tmp.cur->rchild) s.push(tmp.cur->rchild);
}
else{
tmp.time+=1;
s.push(tmp);//自己是第一次訪問,入棧,time+1
//左孩子進棧
if(tmp.cur->lchild) s.push(tmp.cur->lchild);
}
}
cout<<endl;
}
void postTraverse() const{//非遞歸後序
/*由於要記錄出棧次數,所以引入結構elem*/
if(root==NULL) return;
struct elem{
node* cur;
int time;
elem(node* p=NULL):cur(p),time(0){ }//構造函數
};
cout<<"非遞歸後序遍曆:";
//初始化---裝有elem的棧和elem變量
seqStack<elem> s;
elem bt(root);
s.push(bt);
elem tmp;//記錄出棧
//以上和中序遍曆代碼一致
while(!s.is_empty()){
tmp=s.pop();
if(tmp.time==2){
//已訪問兩次,也就是左右孩子都遍曆了,輸出結果
cout<<tmp.cur->data<<" ";
}
else{
if(tmp.time==1){
//左孩子已訪問,右孩子進棧
tmp.time+=1;
s.push(tmp);//一定別忘了,右孩子進棧時,自己再進一次棧
if(tmp.cur->rchild) s.push(elem(tmp.cur->rchild));//注意類型
}
else{
tmp.time+=1;
s.push(tmp);//自己進棧,然後遍曆左孩子
if(tmp.cur->lchild) s.push(elem(tmp.cur->lchild));
}
}
}
}
};
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::createTree(){
node* f=new node('f');
node* g=new node('g');
node* k=new node('k');
node* h=new node('h');
node* e=new node('e',f,g);
node* j=new node('j',NULL,k);
node* d=new node('d',NULL,e);
node* i=new node('i',j,NULL);
node* b=new node('b',d,NULL);
node* c=new node('c',h,i);
root=new node('a',b,c);
}測試主函數
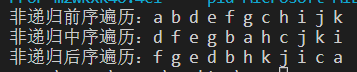
int main(){
binTree<char> bt;
bt.createTree();
bt.preTraverse();
bt.midTraverse();
bt.postTraverse();
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- Principle and application of single chip microcomputer timer, serial communication and interrupt system
- Shell script -for loop and for int loop
- Shell脚本-echo命令 转义符
- [ESP nanny level tutorial] crazy completion chapter - Case: gy906 infrared temperature measurement access card swiping system based on the Internet of things
- In the middle of the year, where should fixed asset management go?
- How to manage fixed assets efficiently in one stop?
- Design and manufacture of simple digital display electronic scale
- It technology ebook collection
- 【pytorch】transforms. Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
- Personal decoration notes
猜你喜欢

猿人学第20题(题目会不定时更新)

2.3 【pytorch】数据预处理 torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder

Jetson nano installs tensorflow GPU and problem solving

安装Oracle EE

2.4 激活函数

How to solve the problem of fixed assets management and inventory?

足球篮球体育比赛比分直播平台源码/app开发建设项目

如何做好固定资产管理?易点易动提供智能化方案

2.4 activation function

Performance improvement 2-3 times! The second generation Kunlun core server of Baidu AI Cloud was launched
随机推荐
【pytorch学习】torch.device
Redis source code learning (29), compressed list learning, ziplist C (II)
【pytorch】nn. AdaptiveMaxPool2d
R language observation log (part24) -- initialization settings
An overview of the design of royalties and service fees of mainstream NFT market platforms
树结构---二叉树1
Personal decoration notes
Summary of reptile knowledge points
Meituan machine test in 2022
Reproduced Xray - cve-2017-7921 (unauthorized access by Hikvision)
Shell脚本-变量的定义、赋值和删除
Performance improvement 2-3 times! The second generation Kunlun core server of Baidu AI Cloud was launched
Pain points and solutions of fixed assets management of group companies
毕业季,我想对你说
Installing Oracle EE
Daily practice of C language - day 80: currency change
Ape anthropology topic 20 (the topic will be updated from time to time)
【ESP 保姆级教程】疯狂毕设篇 —— 案例:基于阿里云和Arduino的化学环境系统检测,支持钉钉机器人告警
Shell脚本-特殊变量:Shell $#、$*、[email protected]、$?、$$
Which method is good for the management of fixed assets of small and medium-sized enterprises?