当前位置:网站首页>MySQL - SQL execution process
MySQL - SQL execution process
2022-06-23 00:53:00 【Fried cat】
List of articles
One 、 Component is introduced
1、 The connector
1) Responsible for communication with clients , It's half duplex mode , This means that the client can only request from the server or the server can send data to the client at a fixed time , Not at the same time .
2) Verify that the user name and password are correct ( database mysql Of user Verify in the table ), If an error occurs, an error notification is returned (deAcess nied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’(using password:YES)), If correct , Will go mysql Permission table for (mysql Medium user、db、columns_priv、Host surface , The global level is stored separately 、 Database level 、 Table level 、 Column level 、 coordination db Database level for ) Query the permissions of the current user .
2、 cache (Cache)
Also known as query caching , The stored data is stored in the form of key value pairs , If caching is turned on , So in a query sql Statement will first determine whether the cache contains the current sql Statement key value pairs , If there is, return the corresponding result directly , If it doesn't exist, perform the next series of operations . If it is not turned on, skip it directly .
3、 analyzer
From the client sql Analyze , This will include preprocessing and parsing , And the keyword extraction 、 analysis , And make up a parse tree . Specific analytic words include but are not limited to select/update/delete/or/in/where/group by/having/count/limit etc. , If we analyze grammatical errors , Will directly throw the client exception :ERROR:You have an error in your SQL syntax.
such as :select * from user where userId =1234;
In the parser, we use the semantic rules to select from where These keywords are extracted and matched ,mysql Will automatically determine keywords and non keywords , Identify the user's matching fields and custom statements . There will also be some checks at this stage : For example, check whether the current database exists user surface , At the same time, if User There is no userId This field will also report an error :unknown column in field list.
4、 Optimizer
Enter the optimizer description sql The statement conforms to the standard semantic rules and can be executed . The optimizer selects the best choice based on the execution plan , Match the appropriate index , Choose the best solution . For example, a typical example is :
surface T, Yes A、B、C Columns are federated (A,B,C), During the query , When sql The query condition is :select xx where B=x and A=x and C=x. A lot of people think it's useless to use indexes , But it actually uses , Although the index must conform to the leftmost principle to be used , But in essence , The optimizer will automatically send this sql Optimize to :where A=x and B=x and C=X, This optimization will be for the underlying to match the index , At the same time, in this stage, preprocessing is performed automatically according to the execution plan ,mysql Accounting calculates the best time for each method of execution , To finalize an executive sql To the last actuator .
The optimizer will be based on Number of scanning lines 、 Whether to use temporary table 、 Whether to sort, etc. to determine whether to use an index , The number of scanning lines can be estimated through statistical information , Statistics can be regarded as the number of unique indexes , Partial sampling can be used to estimate , Specifically, choice N Data pages , Count the different values of the data on these pages , Get an average of , Then multiply by the number of pages in this index , Got it. . But because the index data will change , So the statistics of the index will also change . When the number of data lines changed exceeds 1/M When , The statistics will be recalculated .
5、 actuator
The executor will call the corresponding storage engine to execute sql. The mainstream is MyISAM and Innodb.
MyISAM and Innodb The index data structure is B+ Trees
memory The index data structure is hash surface

Two 、 Execution process
1、 Write operations
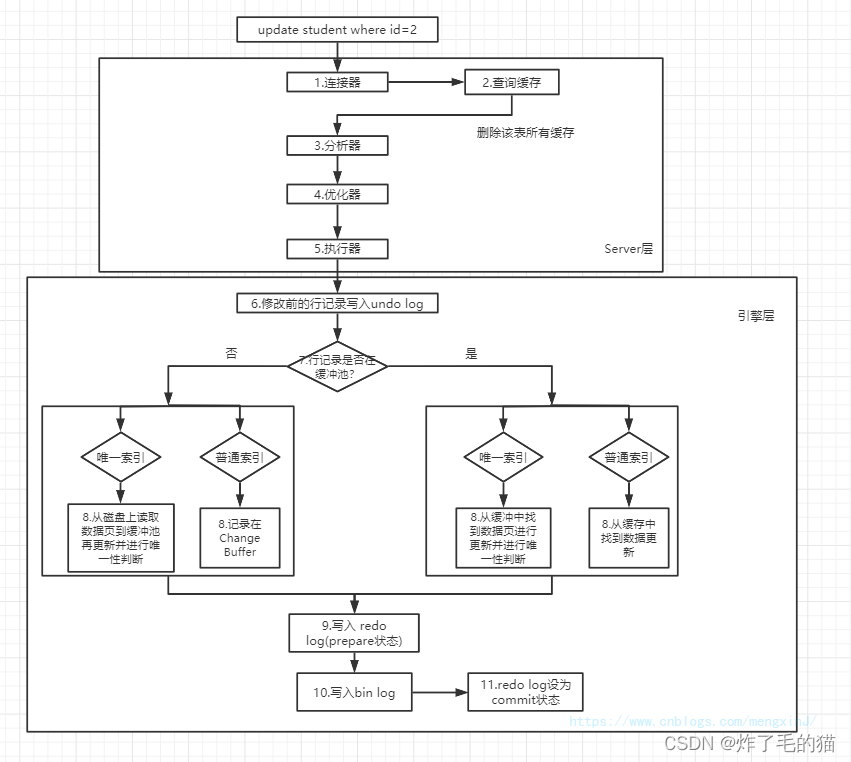
2、 Read operations
The process of query is similar to that of update , But it's a little different , This is mainly due to the differences in their search and filtering , Update because it will be updated after searching , So the query is always in the buffer pool ( The data page that uses the index and contains the data in the buffer pool ). And the query is more complex .
Create table :
create table tbl_test (a int primary key, b int, c int, d int, e varchar(50));
create index idx_bcd on tbl_test(b, c, d);
insert into tbl_test values (4,3,1,1,'a');
insert into tbl_test values (1,1,1,2,'d');
insert into tbl_test values (8,8,7,8,'h');
insert into tbl_test values (2,2,1,2,'g');
insert into tbl_test values (5,2,2,5,'e');
insert into tbl_test values (3,3,2,1,'c');
insert into tbl_test values (7,4,0,5,'b');
insert into tbl_test values (6,5,2,4,'f');
In execution select * from tbl_test where b >= 2 and b < 7 and c > 0 and d != 2 and e != ‘a’; At the time of extraction , Will Where The condition is split into Index Key(First Key & Last Key)、Index Filter And Table Filter.
1、Index Key
Used to determine the SQL The sequential range of queries in the index ( The starting point + Termination point ) Query criteria for , It's called Index Key; Because of a range , It contains at least one starting condition and one ending condition , therefore Index Key Also split into Index First Key and Index Last Key, Respectively used to locate the starting point of index search to the ending point .
Index First Key
Used to determine the starting point of index query range ; Extract rules : Start with the first key value of the index , Check that it's in where Is there... In the condition , If it exists and the condition is =、>=, Then add the corresponding conditions to Index First Key In , Continue reading the next key value of the index , Use the same extraction rules ; If it exists and the condition is >, Then add the corresponding conditions to Index First Key in , To terminate at the same time Index First Key Extraction of ; If it does not exist , Also terminate Index First Key Extraction of .
in the light of SQL:select * from tbl_test where b >= 2 and b < 7 and c > 0 and d != 2 and e != ‘a’, Apply this extraction rule , extracted Index First Key by b >= 2, c > 0 , because c On the condition that >, End of extraction
Index Last Key
The endpoint used to determine the scope of the index query , And Index First Key Just the opposite ; Extract rules : Start with the first key value of the index , Check that it's in where Is there... In the condition , If it exists and the condition is =、<=, Then add the corresponding condition to Index Last Key in , Continue to extract the next key value of the index , Use the same extraction rules ; If it exists and the condition is < , Then add the condition to Index Last Key in , At the same time terminate extraction ; If it does not exist , Also terminate Index Last Key Extraction of
in the light of SQL:select * from tbl_test where b >= 2 and b < 7 and c > 0 and d != 2 and e != ‘a’, Apply this extraction rule , extracted Index Last Key by b < 7 , Because it is < Symbol , End of extraction
2、Index Filter
At the completion of Index Key After the extraction of , We according to the where Conditions fix the index's query range , So is it that every index item in the range satisfies WHERE The conditions are ? Obviously 4,0,5 , 2,1,2 All belong to the scope , But they are not satisfied SQL Query criteria for
therefore Index Filter Used after index range determination , determine SQL What other conditions in can be filtered using indexes ; Extract rules : Start with the first column of the index column , Check that it's in where Is there... In the condition , If it exists and where The condition is only =, Then skip the first column and continue to check the index next column , The next index column takes the same extraction rules as the first one ; if where Condition is >=、>、<、<= Some of them , Skip the first column of the index , Put the rest where All index related columns in the condition are added to Index Filter In ; If the first column of the index where Conditions include =、>=、>、<、<= Other conditions , Then this condition and the rest where All index related columns in the condition are added to Index Filter In ; If the first column does not contain query criteria , All index related conditions are added to Index Filter In
in the light of SQL:select * from tbl_test where b >= 2 and b < 7 and c > 0 and d != 2 and e != ‘a’, Apply this extraction rule , extracted Index Filter by c > 0 and d != 2 , Because the first column of the index only contains >=、< Two conditions , So the first column skips , Put the rest of c、d Add two columns to Index Filter in , End of extraction
3、Table Filter
This is a little bit easier ,where All the conditions that can't be filtered by index are included in this ; Extract rules : All queries that do not belong to index columns , All belong to Table Filter In
in the light of SQL:select * from tbl_test where b >= 2 and b < 7 and c > 0 and d != 2 and e != ‘a’, Apply this extraction rule , that Table Filter for e != ‘a’
stay 5.6 Before , It doesn't matter Table Filter And Index Filter Of , These two conditions are directly assigned to Server Layer to filter . The screening process is based on Index Key The conditions of the engine layer are initially screened , Then get the corresponding primary key value, and query back to the table to get the row records initially screened , Pass in Server Layer for subsequent filtering , stay Server Because the index is not used in layer filtering, the whole table scan will be performed . And the optimization of index push down is to make Index Filter Push to the engine layer , In the use of Index First Key And Index Last Key When screening , Take it Index Filter The conditions are screened again , In this way, we can filter out the primary key values corresponding to unqualified records , Reduce the number of times to return to the table , At the same time Server There will also be fewer layers to record , The efficiency of full table scanning and filtering will also be improved .
Here is not used Schematic diagram of index push down and using index push down :
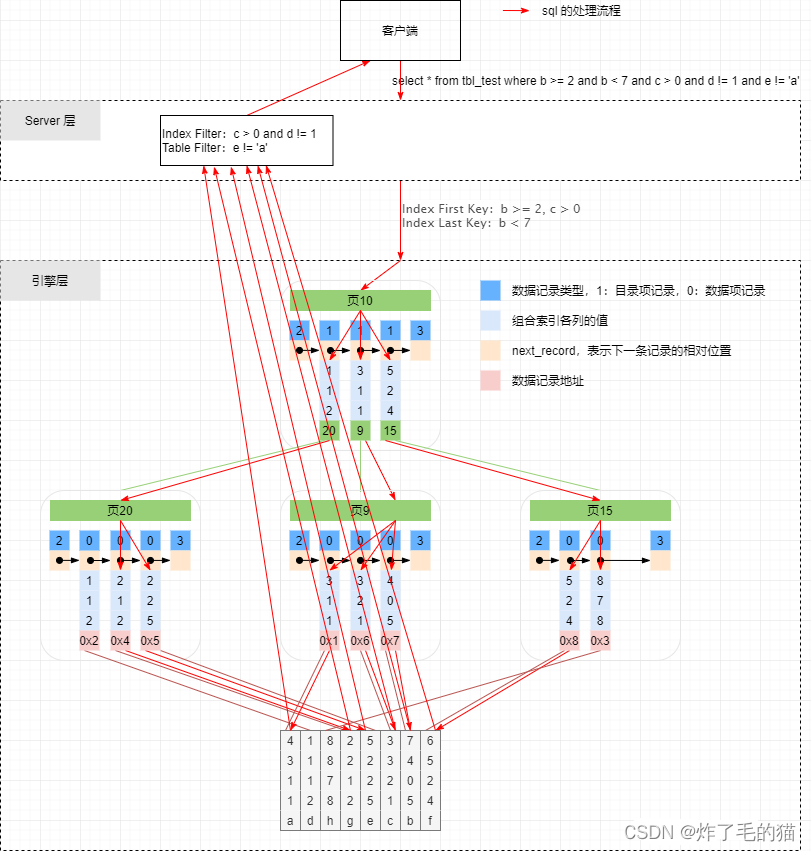
Here is Use Schematic diagram of index push down and using index push down :

3、 summary

Note here that if you don't use the index in the beginning , The data pages on the disk will be read to the buffer pool for query in turn .
Original address :https://www.cnblogs.com/mengxinJ/p/14045520.html#_label2
边栏推荐
- #yyds干货盘点#尾递归比递归好在哪儿
- 62. 不同路径
- New progress in the construction of meituan's Flink based real-time data warehouse platform
- Read Amazon memorydb database based on redis
- EasyCVR使用RTMP推流时不显示界面如何解决?
- Flowable global listener monitors the start and end of a process
- What is the storage structure and mode of data in the database?
- 【滑动窗口】leetcode992. Subarrays with K Different Integers
- leetcode 91. Decode Ways 解码方法(中等)
- 數據庫中數據的儲存結構和方式是什麼?
猜你喜欢

SAP mm me27 create intra company sto order

图神经网络有哪些用途和应用?

#yyds干货盘点# 解决剑指offer:把二叉树打印成多行

New progress in the construction of meituan's Flink based real-time data warehouse platform
3 big questions! Redis cache exceptions and handling scheme summary

SAP UI5 应用开发教程之一百零三 - 如何在 SAP UI5 应用中消费第三方库试读版

層次選擇器
62. 不同路径

MySQL-Seconds_ behind_ Master accuracy error

Yyds dry inventory solution sword finger offer: print the binary tree into multiple lines
随机推荐
How about precious metal spot silver?
SAP ui5 application development tutorial 103 - how to consume third-party libraries in SAP ui5 applications
Isolation level of transaction system
中金证券开户安全吗?它和中金银行是什么关系呢?
OSPF综合实验
初学者如何快速入门深度学习?
Ros2 summer school 2022 transfer-
华为云招募工业智能领域合作伙伴,强力扶持+商业变现
MySQL-Seconds_ behind_ Master accuracy error
BGP federal comprehensive experiment
LINQ 查詢
Flowable global listener monitors the start and end of a process
Hello, is the securities account presented by the Business School of qiniu business school safe? How can I open a safe stock account to speculate in stocks
Software construction course ADT and OOP understanding
SAP UI5 应用开发教程之一百零二 - SAP UI5 应用的打印(Print)功能实现详解
一文读懂基于Redis的Amazon MemoryDB数据库
Ansible learning summary (7) -- ansible state management related knowledge summary
Quelle est la structure et la façon dont les données sont stockées dans la base de données?
How to use enum data types
Is Ruida futures safe? What are the procedures for opening futures accounts? How to reduce the futures commission?
