当前位置:网站首页>Software modeling and analysis
Software modeling and analysis
2022-07-07 09:44:00 【Not enough to eat】
Software modeling and analysis
List of articles
- Software modeling and analysis
- One 、 The introduction
- Two 、 Object oriented methods
- 3、 ... and 、UML Unified modeling language
- Four 、RUP Unified process
- 5、 ... and 、 Software modeling tools
- 6、 ... and 、 Demand acquisition
- 7、 ... and 、 Demand analysis
- 1. Three analysis models
- 2. UML The view of
- 3. Demand analysis method
- 3.1 Object oriented analysis method
- 3.2 The modeling and analysis steps of class diagram are as follows
- 3.3 Establish the object model structure of the system
- 3.4 Build process model
- 3.5 Modeling and analysis steps of state machine diagram
- 3.6 Modeling and analysis steps of activity diagram
- 3.7 Modeling and analysis steps of sequence diagram
- 3.8 Modeling and analysis steps of communication diagram
- 4. Demand analysis roadmap
- 8、 ... and 、 Design
- Nine 、 Design patterns
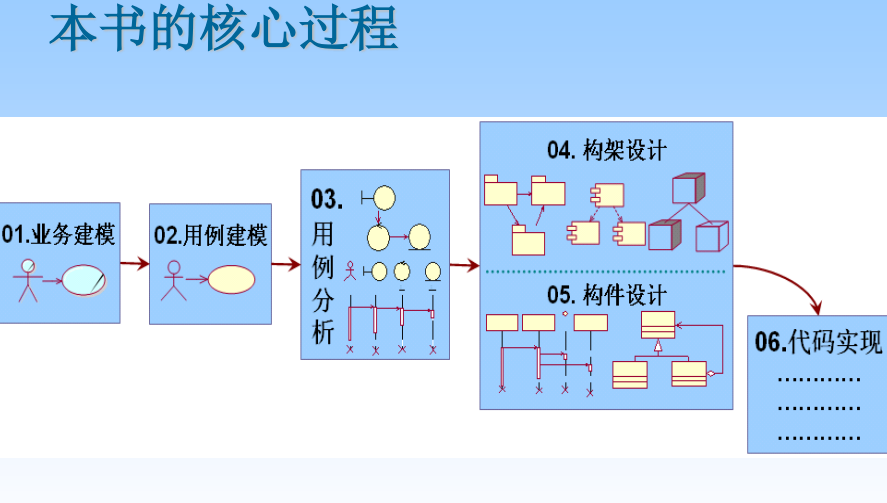
One 、 The introduction
Model It refers to using a relatively simple thing to represent another thing , It is the abstraction of the system from a specific point of view
Two 、 Object oriented methods
object : The object is anything to study . From a book to a library , Single integer to huge database 、 An extremely complex automated chemical plant 、 The space shuttle can be regarded as an object , It's not just a tangible entity , It can also mean invisible ( In the abstract ) The rules 、 Plan or event . object By data ( Describe the properties of things ) And operations on data ( body The act of showing things ) Form an independent whole .
class : Class is a template for an object . That is, a class has the same data and operations for a group Definition of the object made , The methods and data contained in a class describe a set of pairs The common attributes and behaviors of elephants . Classes are abstractions above objects , The object is Class materialization , Is an instance of a class . Class can have subclasses , It can also have its parent , Form a class hierarchy .
news : A message is a specification for communicating between objects . General it It's made up of three parts : The object receiving the message 、 Message name and actual arguments
3、 ... and 、UML Unified modeling language
1. Three categories of modeling languages
Informal 、 Semi formalization 、 formalization
UML Is a semi formal modeling language , It's the standard of system modeling .
2. Software modeling principles
accuracy 、 Standard specification 、 Subsystem division 、 layered
3.UML Characteristics
(1) Unified Booch、OMT and OOSE And so on .
(2) UML It also absorbs the advantages of object-oriented technology , Of course, there are also non aspects Influence on the object .
(3) UML Many new ideas have also been put forward . Added template 、 duty 、 expand Development mechanism 、 Threads 、 The process 、 Distributed 、 Concurrent 、 Pattern 、 cooperation 、 Concepts such as activities , And clearly distinguish the types 、 Classes and instances 、 elaboration 、 Concepts such as interfaces and components .
4.UML Make up the structure
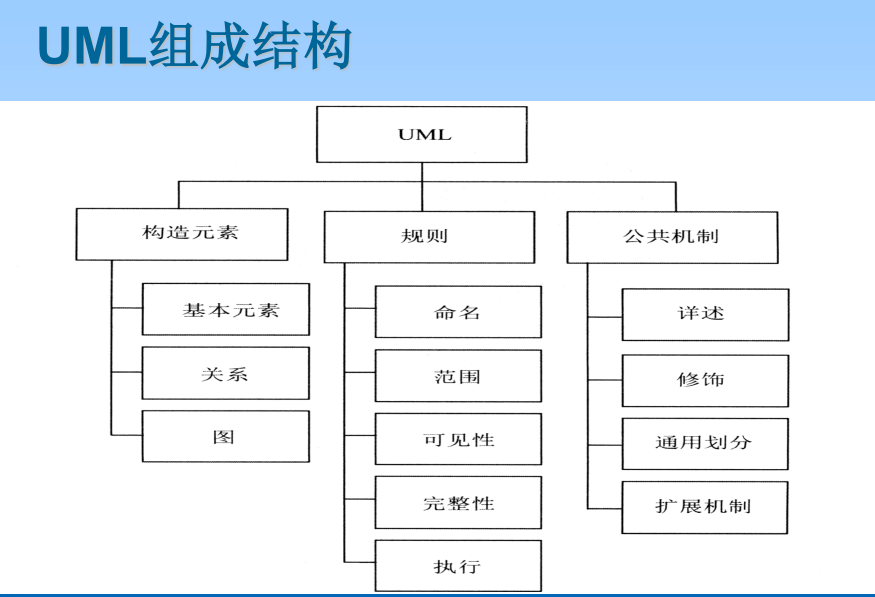
5.UML The basic elements
5.1 Structural elements
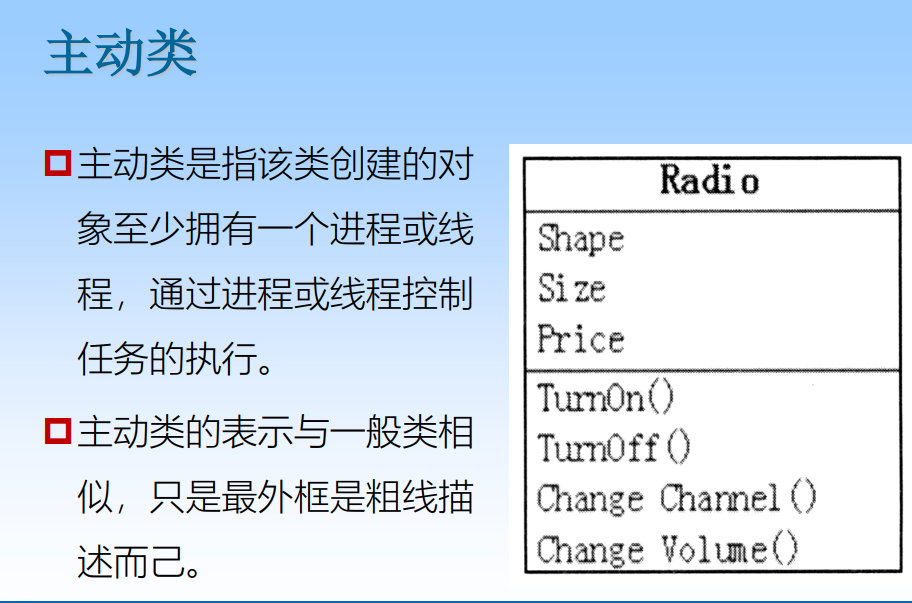
A structural element defines a physical in a business or software system Elements , Describes the static characteristics of things . Structural element Plain Use nouns to express . There are seven structural elements , Namely : Classes and objects 、 Interface 、 Active class 、 Use cases 、 Collaboration 、 Components 、 node .




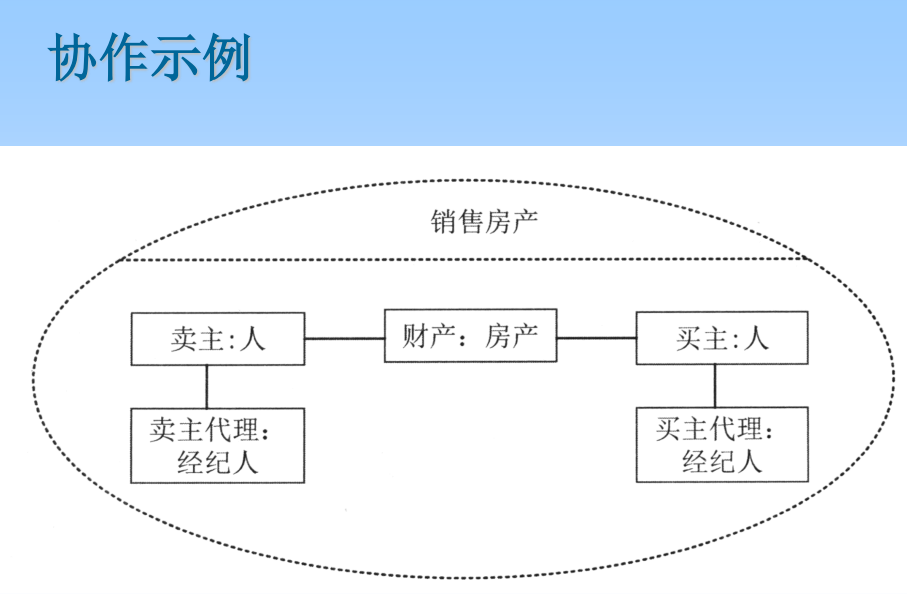
** Collaboration ** Collaboration refers to meaningful interaction , That is, a group of objects in order to complete The interaction between certain tasks .
Implementation of use cases : Between a group of objects that implement a use case Interaction , That is, a use case is represented as the interaction between multiple objects ( Collaboration ). essentially , Collaboration is the realization of use cases .
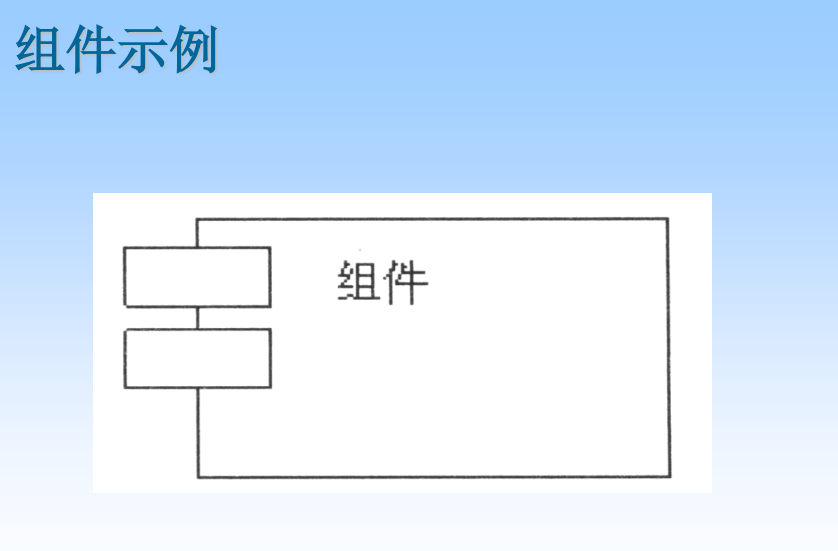
Components Also called component , It is a relatively independent software department in system design Pieces of , It hides the function realization part inside , Announced a group of Interface ( Including supply interface and demand interface ). therefore , Two have Components with the same interface can be replaced with each other .

5.2 Behavioral elements
Behavior elements are used to describe things in business systems or software systems The interaction between things or the state change of things . Behavioral elements describe the dynamic characteristics of things , Use verbs to express . Including interaction and state machines


5.3 Grouping elements

5.4 Comments Elements

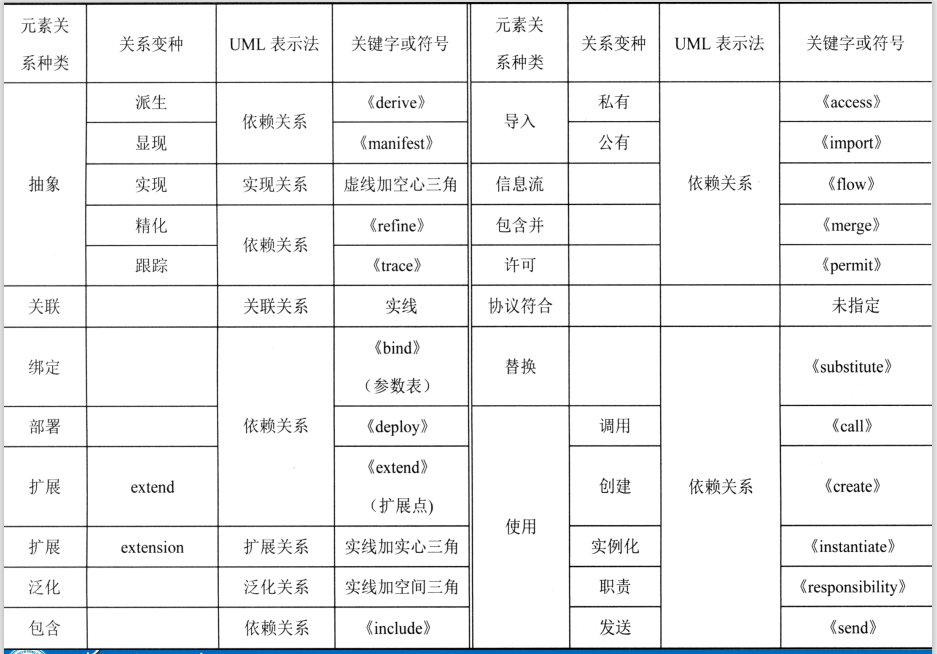
5.5 Relational element
UML The Communist Party of China defines 24 Kind of relationship . this 24 Relationship in When modeling the representation, it can be classified as Connections 、 Realization relationship 、 Generalization relation 、 Expand relationships and Dependency relationship
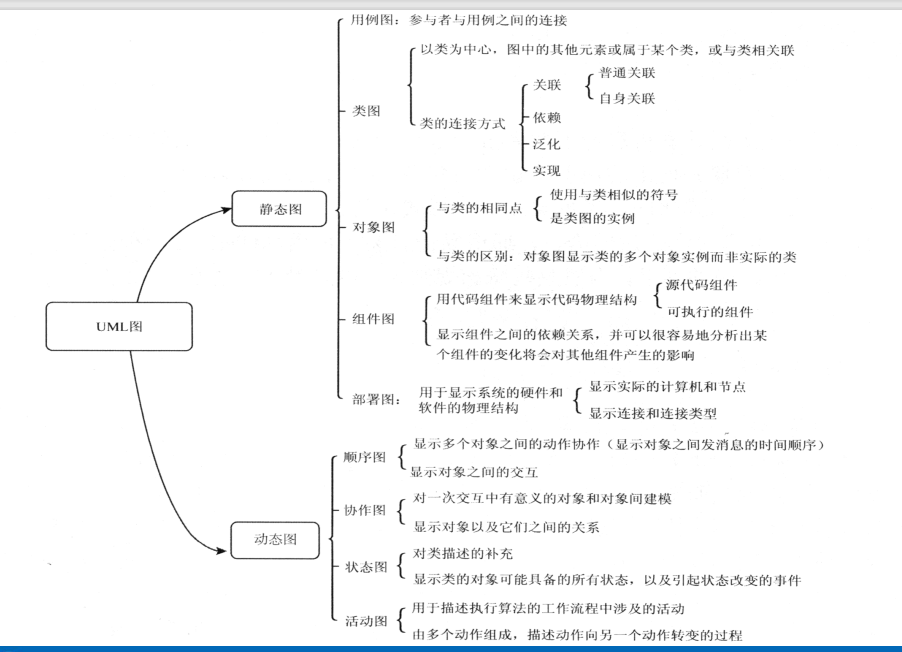
6. common 9 in UML chart
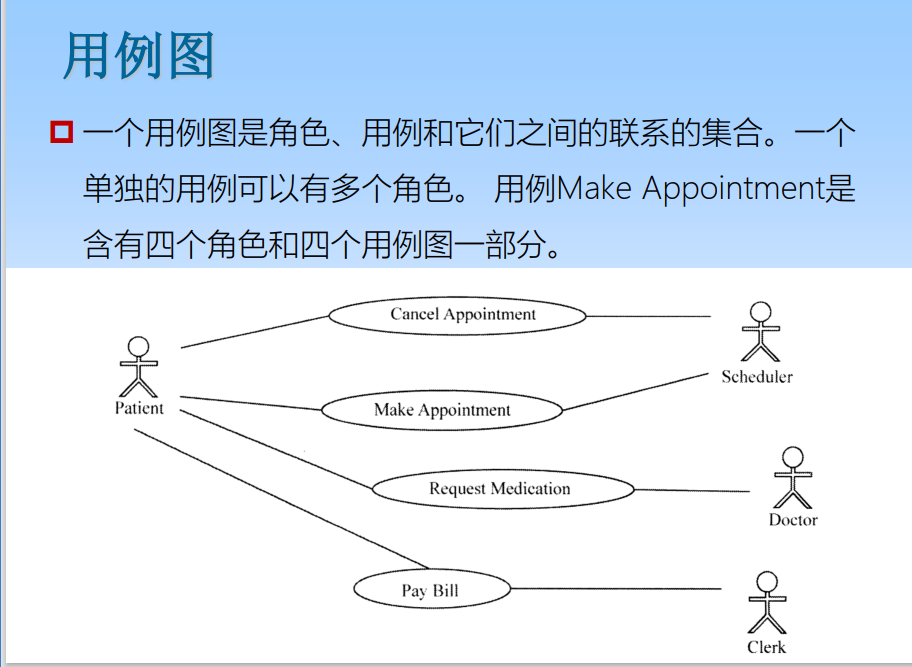
6.1 Use case diagram
Hierarchy of use cases : generalization (generalization)、 contain (include) And extend (extend)
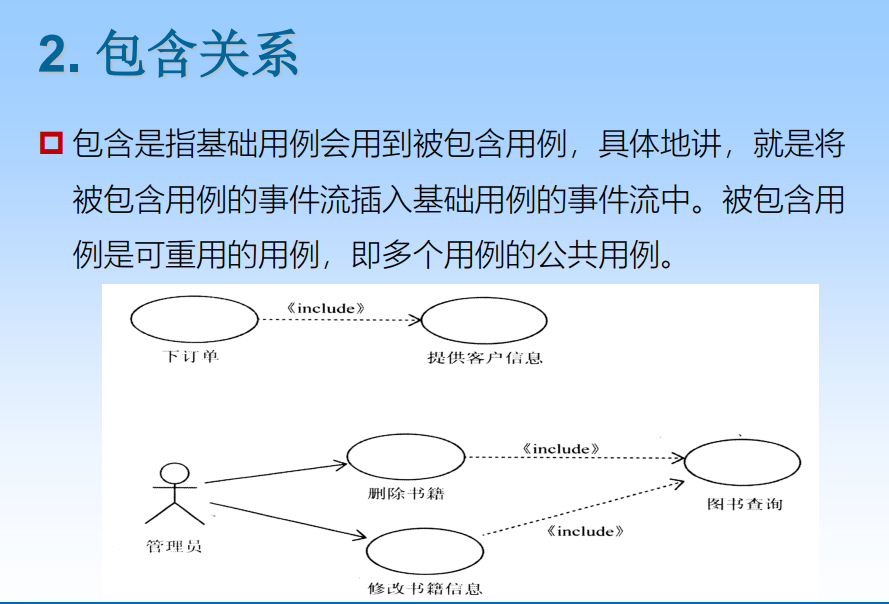
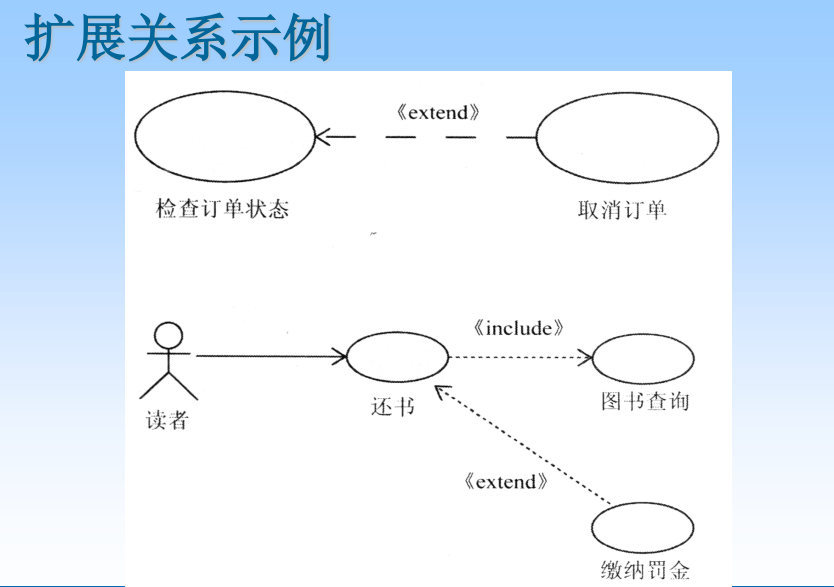
Extended relation refers to the flow of events of extended use cases under certain conditions Next, insert into the basic use case according to the corresponding extension points .
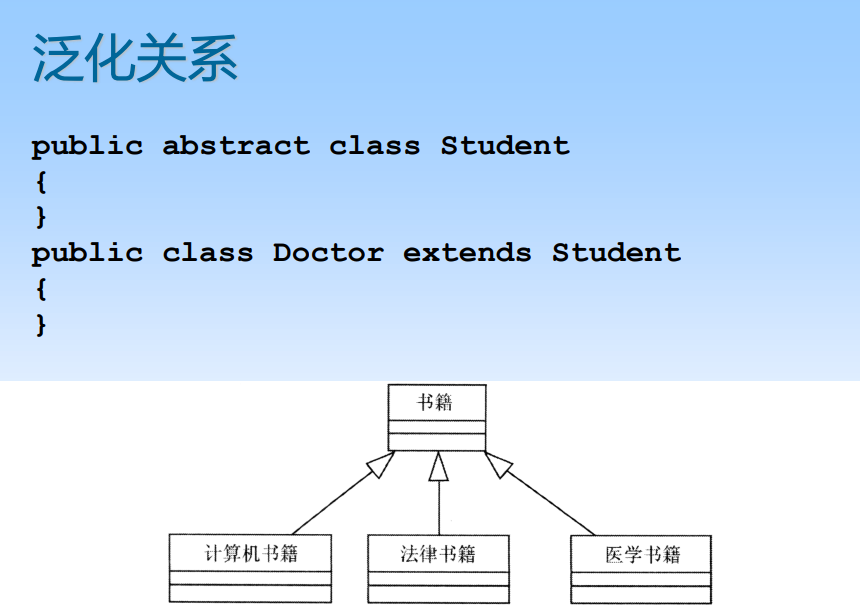
6.2 Class diagram
The writing of class names should be standardized : Orthographic characters are instantiated , Italics Words are abstractions .

Relationships between classes
Connections Generalization relation Realization relationship Dependency relationship
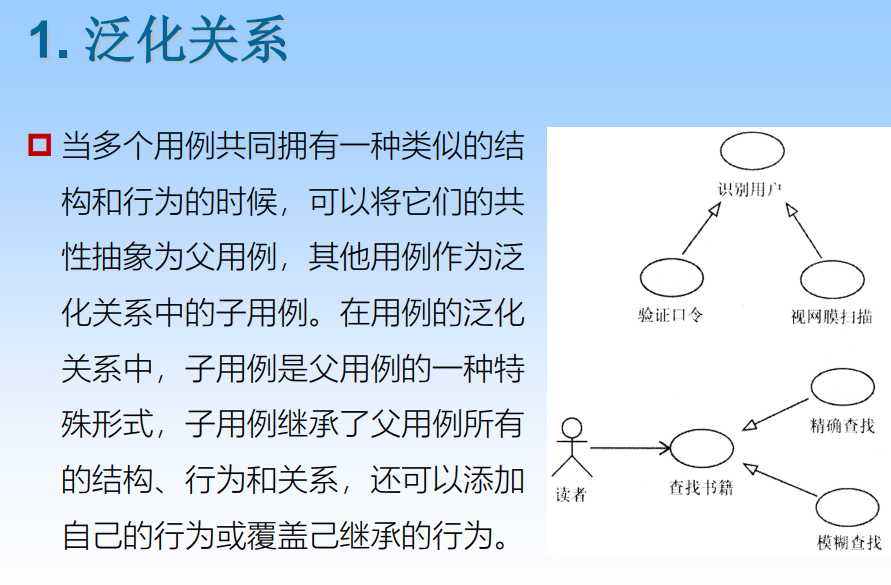
Generalization relation (generalization) It is a special and general relationship , It's one General things ( Parent class ) And the more special kind of the thing ( Subclass ) Between Relationship , Subclasses inherit the properties and operations of the parent class , besides , Subclasses usually Also add new properties and operations .
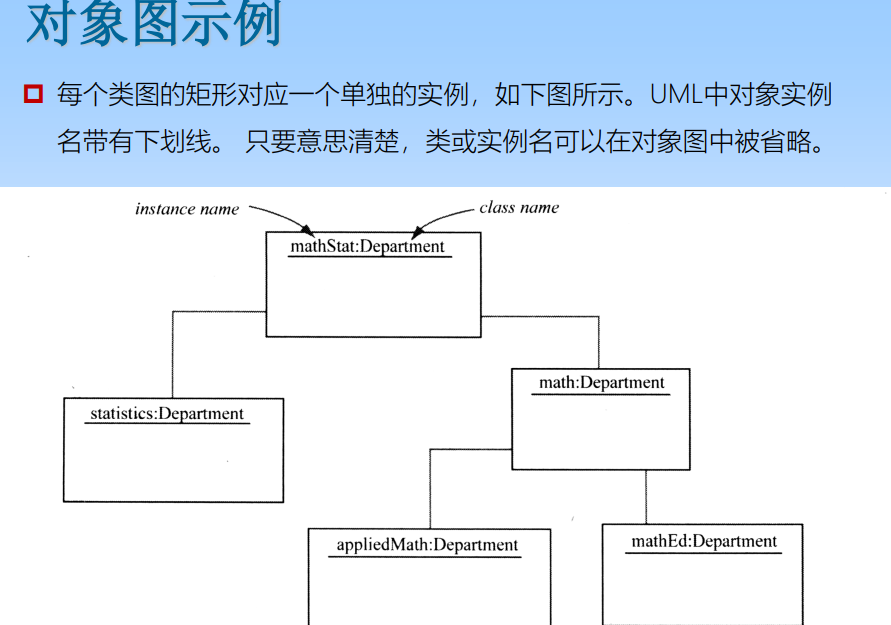
6.3 Object graph
Object reflects an instance of a class . The object graph represents the system in a particular The possible specific contents of each category are timed , Help understand class diagrams .
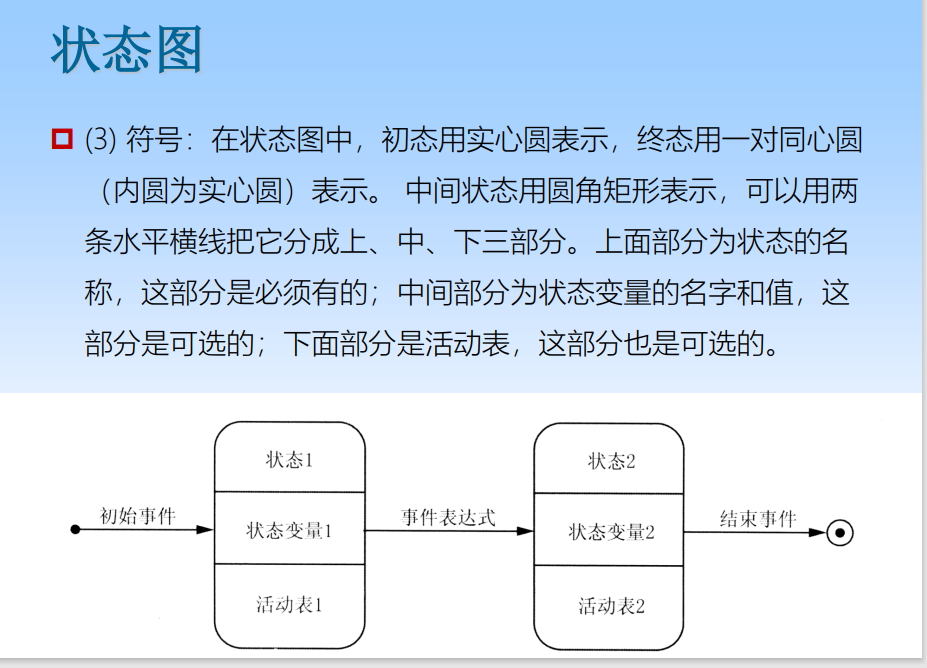
6.4 State diagram
A state diagram is a model diagram of all the processes that a class object may experience . state The diagram consists of the states of the object and the transition events connecting these States .
The states defined in the state diagram are mainly Initial state ( The initial state )、 Terminal state ( Final state ) And the intermediate state . There can only be one initial state in a state diagram , And finally States can have 0 At most . The initial state is the virtual beginning of the action , The final state is action Virtual end of .
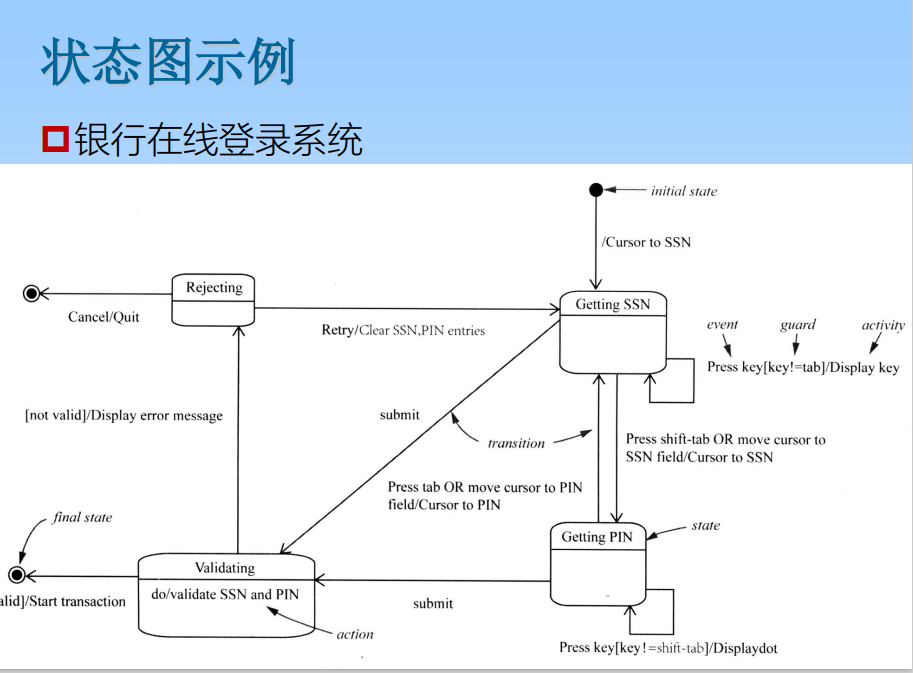
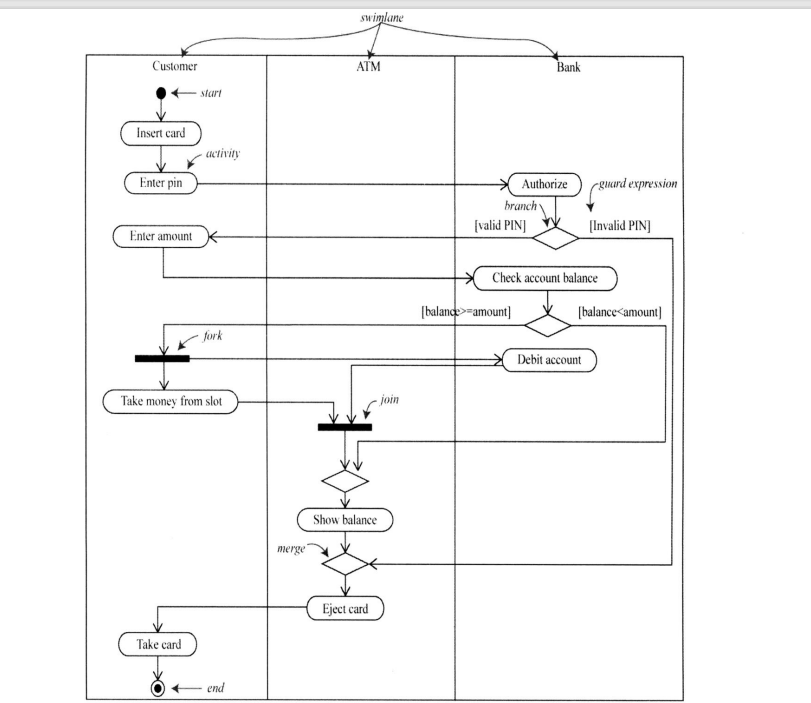
6.5 Activity diagrams
Activity diagram is a variant of state diagram , Used to describe workflow and functions Activities involved . The state diagram focuses on the objects in the process , and Activity diagrams focus on a single process action flow . The activity diagram shows activities Dependencies between .
Activities represent the execution of a workflow step or an operation . Activity diagram description A set of sequential or concurrent activities .
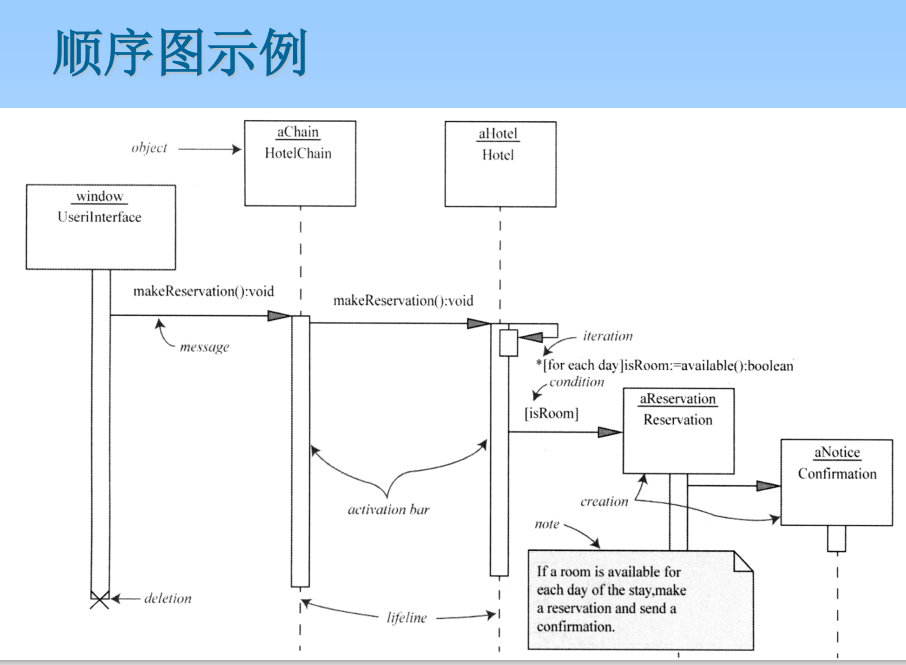
6.6 Sequence diagram
Sequence diagram can be used to represent a scenario description , That is, the history of a transaction cheng . The sequence diagram represents the interaction relationship as a two-dimensional diagram . The vertical is the time axis , when The room extends downward along the vertical line ; The horizontal axis represents the roles of independent objects in collaboration . Object roles are represented by lifelines , When an object exists , The character uses a dotted line Express : When the process of an object is active , The lifeline is a two-way line .
6.7 Collaboration map
The collaboration graph models the meaningful objects and the chains between objects in an interaction . The collaboration diagram uses geometric arrangement to represent the roles in the interaction . The arrows attached to the category roles represent messages . The order of occurrence of messages is messages The number at the arrow indicates .
Collaboration charts are also interactive charts . It also conveys the same message like a sequence diagram Rest , But it doesn't care when the message is delivered , Only care about the role of the object
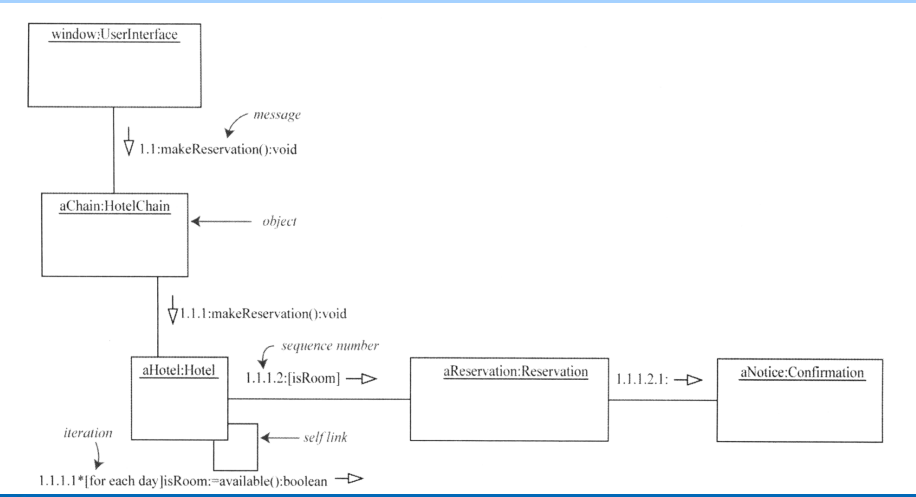
6.8 Component diagram
Component diagram is a physical view that models the implementation structure of the application itself
Components for implementing views Figure to show . Components are code modules . Component diagram is the physical implementation of class diagram .
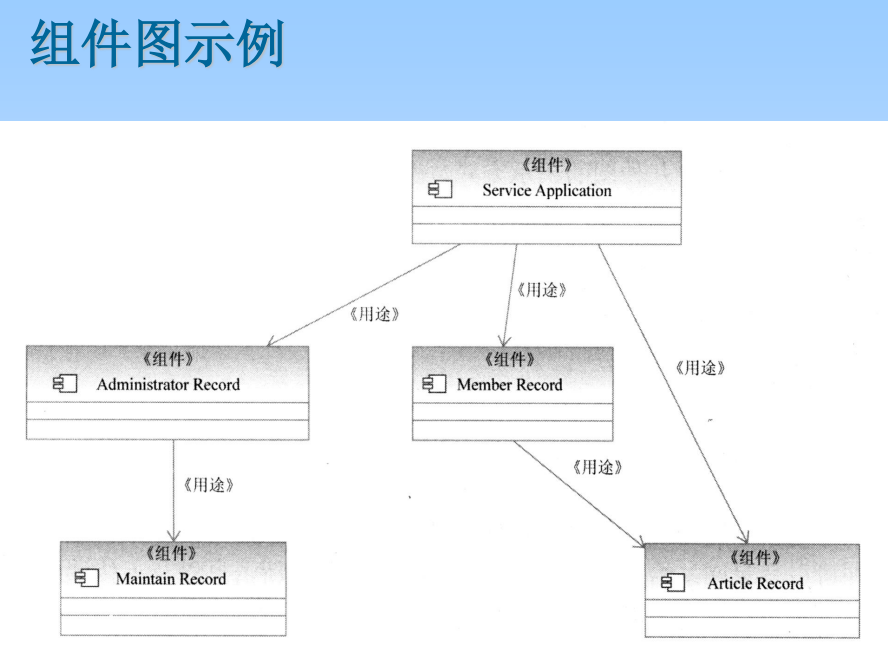
6.9 Deployment diagram
The deployment view describes the arrangement of running component instances located on node instances . Node is A set of running resources , Like a computer 、 Device or memory . This view allows you to evaluate Allocation results and resource allocation .
Four 、RUP Unified process
1. Software development model
Linear : Waterfall model 、 Prototypes
Iterative : Spiral model 、 Fountain model 、 Evolutionary tree model and Iterative incremental model
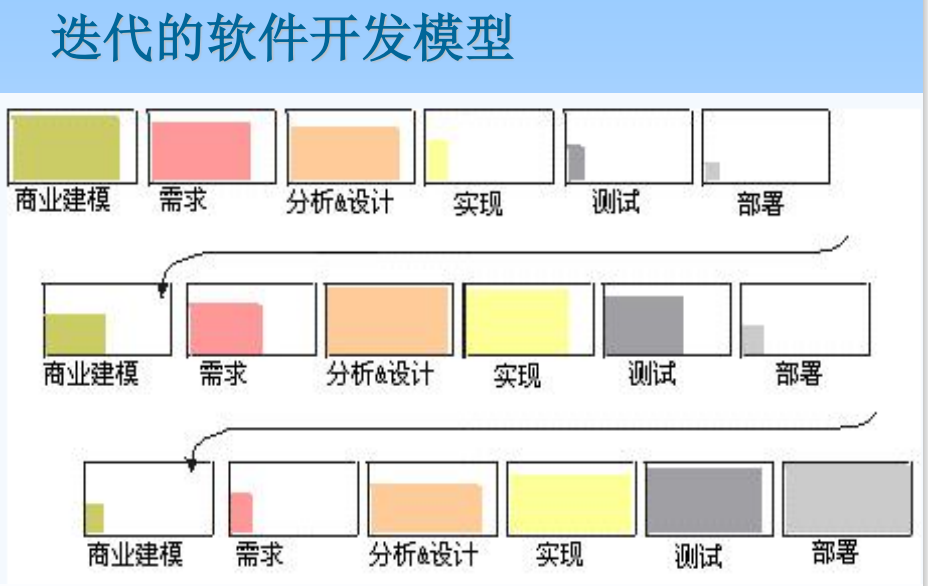
2. RUP Characteristics
Unified software process (RUP) Is the iterative model .
① Software development is an iterative process ;
② Software development is driven by use cases ;
③ Software development is centered on architecture design .
advantage
(1) Reduces the risk of spending on an incremental basis .
(2) Reduce the risk that the product can not enter the market according to the established schedule .
(3) Accelerate the progress of the whole development work .
3. Based on unified process UML system modeling
RUP It is a process definition platform , It is a process framework . Can target RUP Customize the specified process , Make a plan that suits your organization Practical software flow .
RUP You can use UML To build various models required by the software system .
4. RUP The development process

5. RUP Core workflow
RUP There are nine core workflows , It is divided into six core process workflows and three A core support workflow .
(1) Business modeling workflows describe how to organize development for new goals An idea , And based on this idea in business use case model and business The process of defining an organization in the business object model 、 Roles and responsibilities .
(2) The goal of requirements workflow is to describe what the system should do , And make Developers and users agree on this description .
(3) The analysis and design workflow transforms requirements into the design of future systems , Develop a health for the system Strengthen the structure and adjust the design , Match it to the implementation environment , Optimize its performance .
(4) The purpose of realizing workflow includes defining in the form of hierarchical subsystem Organization structure of semantic code ; In the form of components ( Source file 、 Two Base file 、 Executable file ) Implement classes and objects ; Will develop Components of are tested as units , And integration developed by a single person ( Or groups ) The result is , Make it executable System .
(5) The test workflow should verify the interaction between objects , Verify all groups in the software Correct integration of components , Verify that all requirements have been correctly implemented , Identify and confirm Recognize that defects are raised and dealt with before software deployment .
(6) The purpose of deploying workflow is to successfully generate the version and distribute the software Send to end users . Deployment workflows describe those that are related to ensuring software Activities related to the availability of products to end users , Include Software packaging 、 Generate products other than the software itself 、 Install the software 、 Help users .
(7) The configuration and change management workflow depicts how a project is composed of multiple members Control a large number of products . Provides guidelines to manage multiple in an evolving system Variants , Track the version during software creation .
(8) Software project management balances various goals that may conflict , To manage risk , Overcome various constraints and successfully deliver products that satisfy users .
(9) The purpose of environmental workflow is to provide software development organization with software development Development environment , Including processes and tools .
6. RUP Elements and experience
RUP The ten elements include : Development prospects 、 Reach a plan 、 identification And risk reduction 、 Assign and track tasks 、 Check business reasons 、 Design component architecture 、 Build and test products incrementally 、 Verification and evaluation results 、 Manage and control change 、 Provide user support a .
RUP Six experiences : Iterative development Manage requirements Architecture Visual modeling Verify software quality Control software changes
5、 ... and 、 Software modeling tools
1. PowerDesigner
Baidu SkyDrive :PowerDesigner165.rar_ Free high speed download | Baidu SkyDrive - Share unlimited (baidu.com)
Extraction code :b9mc
2. IBM RSA
Baidu SkyDrive :RSA_9.0_Setup.rar_ Free high speed download | Baidu SkyDrive - Share unlimited (baidu.com)
Extraction code :fut0
6、 ... and 、 Demand acquisition
1. Three levels of software requirements
Business needs (business requirement) Describe the high level of the organization or customer The goal is ( That is, the macro goal ).
The user needs (user requirement) Describe the micro goals of the organization or customers , namely Describes the tasks that users must complete when using the product , This is in use cases (use case) It is explained in the document
functional requirement (functional requirement) Defines what developers must implement software function , Enable users to complete their tasks , To meet business needs ( That is, the software functions that meet the requirements ).
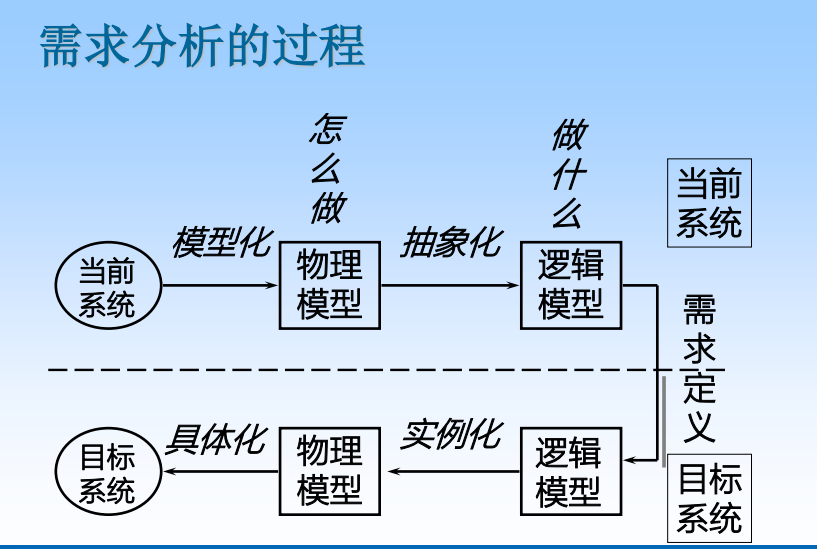
2. Requirements engineering process
Demand acquisition 、 Demand analysis 、 Requirements description and requirements verification .
3. Requirements acquisition method
Field investigation Internet Research Complex networks and data mining
4. Complex network requirements acquisition method of complex system
- Scenario based approach
- Knowledge based approach
- Prototype based approach
- Viewpoint based approach
- Methods of obtaining the characteristics of Complex Networks
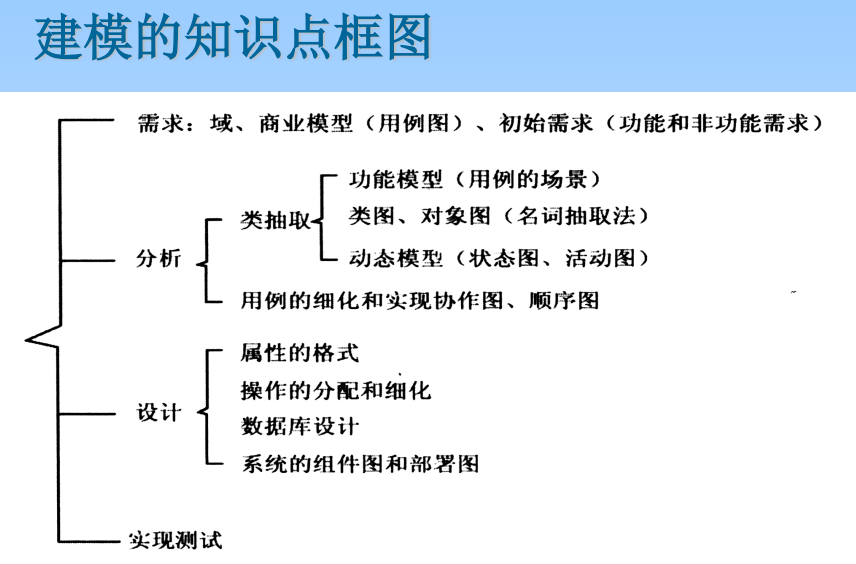
7、 ... and 、 Demand analysis
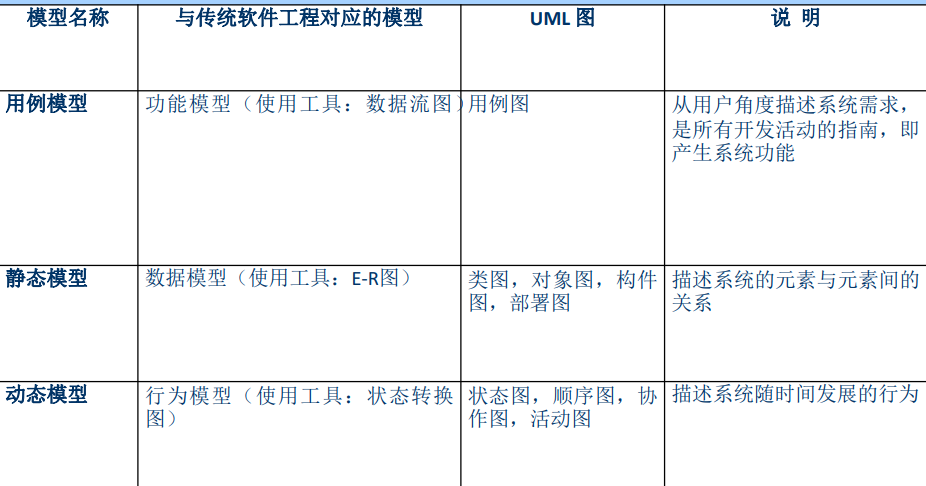
1. Three analysis models
Functional model : Translate the functional requirements of users into what developers and users can understand A way of expressing , The result is a use case model .
The object model : Through the analysis of use case model , Decompose the system into cooperative parts Class analysis . In general , Class diagram and object diagram are used to describe All objects of 、 The attributes of objects and the relationship between objects .
dynamic model : Describe the dynamic behavior of the system . Generally, it is described by sequence diagram and communication diagram Describe the interaction between objects in the system , To reveal how all objects Realize each specific use case through division of labor and cooperation : Through the state machine diagram Describe the state change of a single object in the system , To reveal a single pair The dynamic behavior of the elephant . Get the execution description of the event flow through the activity diagram Statement .
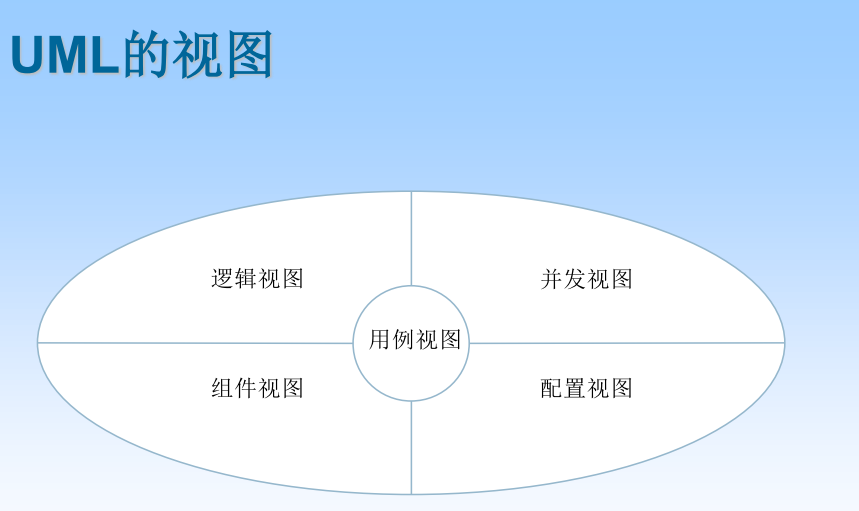
2. UML The view of
(1) Use case views emphasize systems that are seen or needed from external actors in the system System function .
(2) The logical view shows how... From the perspective of the static structure and dynamic behavior of the system Realize the functions of the system . It is mainly for designers and developers , It mainly focuses on the specific implementation within the system .
(3) The component view shows the organization of code components .
(4) The concurrency view shows the concurrency of the system , Solve in and Communication and synchronization problems in the transmission system
(5) The configuration view shows the specific deployment of the system .
3. Demand analysis method
3.1 Object oriented analysis method
(1) Determine the logical model of the system .① Identify objects and classes .② To determine the structure .
(2) Determine the process model of the system : The state machine diagram 、 Activity diagrams 、 Sequence diagram 、 Communication diagrams .
3.2 The modeling and analysis steps of class diagram are as follows
(1) Find out the terms in the requirements ( Candidates ).
(2) Merge nouns with the same meaning , Exclude names outside the scope word , And look for implied nouns .
(3) Remove nouns that can only be used as class attributes .
(4) The remaining nouns are the analysis class you are looking for ( Candidate classes ).
(5) According to common sense 、 Problem domain 、 System responsibility determines which of these attribute .
(6) Supplement the dynamic properties of this class , Like the state 、 Connections between objects ( Such as polymerization 、 relation ) Equal attribute .
(7) Supplement the analysis documents of each class , For the further design of the class Lay the foundation .
3.3 Establish the object model structure of the system
(1) Identify and identify classes
Select relevant nouns from the requirement description Set some classes , Then analyze these classes , Filter out the unqualified class .
(2) Prepare data dictionary
The data dictionary should accurately describe the precise meaning of each class , describe The range of classes in the current problem , Including members of classes 、 Usage side Face assumptions or limitations, etc .
(3) Determine the association
Association refers to the interdependence between two or more classes . A dependency represents a Species association , Associations can be implemented in various ways .
(4) Determine properties
Only consider and be specific Use directly related attributes , Don't consider attributes that go beyond the problem domain .
(5) Use inheritance to refine classes
Use inheritance to share public properties , To organize classes
(6) Improve the object model
3.4 Build process model
(1) Prepare the scene
(2) Identify events
(3) Prepare event tracking table
(4) Construct a state machine diagram 、 Activity diagrams 、 Sequence diagram 、 Communication diagrams
3.5 Modeling and analysis steps of state machine diagram
(1) Determine the object of system control , You can also find it in the sequence diagram
(2) Determine the start state and end state of the object .
(3) Look for meaningful control states throughout the life cycle of an object .
(4) Look for transitions between States .
(5) Add the event that caused the conversion .
(6) use UML Modeling tools draw state machine diagrams . (7) Supplement necessary documents .
3.6 Modeling and analysis steps of activity diagram
(1) Select key processes from the collected original requirements .
(2) Determine whether the activity diagram to be designed is for business processes or use cases .
(3) The beginning and end of the design activity process .
(4) Determine all execution objects of the activity diagram .
(5) Determine the active node , And group activities according to the execution object :① Such as Create activity diagrams for use cases , Then the horn Every action of color changes Is the active node ;② If you create an activity diagram for a business process , Then put each Process steps ( Or fragments ) Become an active node .
(6) Determine the transfer between active nodes .
(7) Handle branching and merging between active nodes .
(8) Handle bifurcation and convergence between active nodes .
(9) use UML Modeling tools for activity diagram modeling .
(10) Prepare necessary supplementary documents .
3.7 Modeling and analysis steps of sequence diagram
(1) Complete the detailed analysis of the use case diagram .
(2) For each use case , Identify the objects involved in the basic event flow ( Including connection mouth 、 Subsystem 、 Roles, etc ).
(3) Identify whether these objects are active objects or passive objects .
(4) Identify whether the messages sent by these objects are synchronous messages or asynchronous messages .
(5) Start from the active object and send messages to the receiving object .
(6) The receiving object calls its own service to return results for the active object .
(7) If the receiving object needs to call the services of other objects , You need to ask them He sends a message to the object .
(8) So again and again , Finally, it returns meaningful results to the active object .
(9) use UML Modeling tools draw sequence diagrams .
(10) Supplement the sequence diagram with necessary explanatory documents .
3.8 Modeling and analysis steps of communication diagram
(1) Complete the detailed analysis of the use case diagram .
(2) For each use case , Identify the objects involved in the basic event flow ( Including connection mouth 、 Subsystem 、 Roles, etc ).
(3) Identify the connection relationship between objects
(4) Identify the order of messages sent by these objects
(5) Start from the active object and send messages to the receiving object .
(6) The receiving object calls its own service to return results for the active object .
(7) If the receiving object needs to call the services of other objects , You need to ask them He sends a message to the object .
(8) So again and again , Finally, it returns meaningful results to the active object .
(9) use UML Modeling tools draw communication diagrams .
(10) Supplement the sequence diagram with necessary explanatory documents .
4. Demand analysis roadmap
(1) Class extraction :
① Further refine and analyze the functional model of the system ( Scenario analysis of use cases )
② Draw a class diagram 、 Yes Image map
③ Draw a dynamic model ( Use state machine diagram or activity diagram to represent ).
(2) Refine and implement use cases , Draw a sequence diagram or communication diagram .
8、 ... and 、 Design
1. summary
Start from the software requirements specification , Form the specific design scheme of the software
2. Object oriented design
Object-oriented design is to transform the requirements obtained in the analysis stage into cost and quality Quantity required 、 The process of abstract system implementation scheme . From object-oriented analysis to Object oriented design is a process of gradually expanding the model .
3. Guidelines for object-oriented design
(1) modularization
(2) abstract : It not only supports process abstraction , And support data abstraction
(3) Information hiding : Information hiding is realized by encapsulation of objects
(4) Low coupling Reduce coupling between classes ( relation / Gather / rely on ), Make the modification of a class right The scope of influence of other categories has been reduced , Thus the system becomes easier to maintain
Coupling mainly refers to the closeness of the correlation between different objects
(5) High cohesion Improve the versatility of classes , And control the complexity of the class , Efforts to decompose classes make Classes have independent responsibilities
4. Design patterns
** Create pattern :** The singleton pattern 、 Abstract factory pattern 、 Builder pattern 、 factory Pattern 、 Archetypal model .
** Structural mode :** Adapter pattern 、 Bridging mode 、 Decoration mode 、 Portfolio model 、 Appearance mode 、 The flyweight pattern 、 The proxy pattern .
** Behavioral patterns :** Template method pattern 、 Command mode 、 Iterator pattern 、 Observe Person mode 、 Intermediary model 、 Memo mode 、 Interpreter mode 、 The state pattern 、 The strategy pattern 、 Responsibility chain pattern 、 Visitor mode .
5. Six principles of design patterns
(1) Opening and closing principle Open to expansion , Turn off for changes
(2) Richter substitution principle (LSP) Any place where a base class can appear , Subclasses must appear .
(3) Dependence Inversion Principle For interface programming cheng , It depends on the abstract and not on the concrete
(4) Interface isolation principle Using multiple isolated interfaces is better than using a single The interface is better .
(5) Dimitar's law An entity should have as little contact with other entities as possible There is interaction , Make the system function modules relatively simple Independent
(6) Synthetic multiplexing principle Use composition whenever possible / Way of aggregation , Instead of using Inherit
5. Design roadmap
(1) The structure design Refine the attribute format of the class 、 Operation and relationship constraints .
(2) Database design According to the class diagram E-R chart , And further refine the design of the database table .
(3) Component and deployment design In large and medium-sized systems , We also need to complete the deployment design of the system , Draw component diagram and deployment diagram .
(4) Detailed design Refine relevant algorithms in class operations according to use case diagrams and activity diagrams .
Nine 、 Design patterns
1. The four basic elements of the model
(1) Schema name
(2) problem Describes when patterns should be used
(3) Solution Describe the components of the design , The relationship between them and Their responsibilities and ways of cooperation .
(4) effect This paper describes the effect of pattern application and the problems that should be weighed in using pattern
2. Observer( The observer ) Pattern
Separate objects , Make an object change Change can affect other objects , And this object doesn't know The details of those affected objects
3. Composite Pattern ( Portfolio model )
Put some objects Group together , And treat this group of objects as an object to use
4. Strategy Pattern ( The strategy pattern )
To implement different response strategies, just use different kinds Of Controller Just replace the instance
5. Proxy Pattern ( The proxy pattern )
Provide a proxy for other objects to Control access to this object .
边栏推荐
- Integer or int? How to select data types for entity classes in ORM
- 如何使用clipboard.js库实现复制剪切功能
- 大佬们,有没有遇到过flink cdc读MySQLbinlog丢数据的情况,每次任务重启就有概率丢数
- VSCode+mingw64+cmake
- [Frida practice] "one line" code teaches you to obtain all Lua scripts in wegame platform
- Over 100000 words_ Ultra detailed SSM integration practice_ Manually implement permission management
- flink. CDC sqlserver. 可以再次写入sqlserver中么 有连接器的 dem
- 牛客网——华为题库(61~70)
- Elaborate on MySQL mvcc multi version control
- How to become a senior digital IC Design Engineer (5-2) theory: ULP low power design technology (Part 1)
猜你喜欢

Strategic cooperation subquery becomes the secret weapon of Octopus web browser
Unity3d interface is embedded in WPF interface (mouse and keyboard can respond normally)
Netease cloud wechat applet

战略合作|SubQuery 成为章鱼网络浏览器的秘密武器
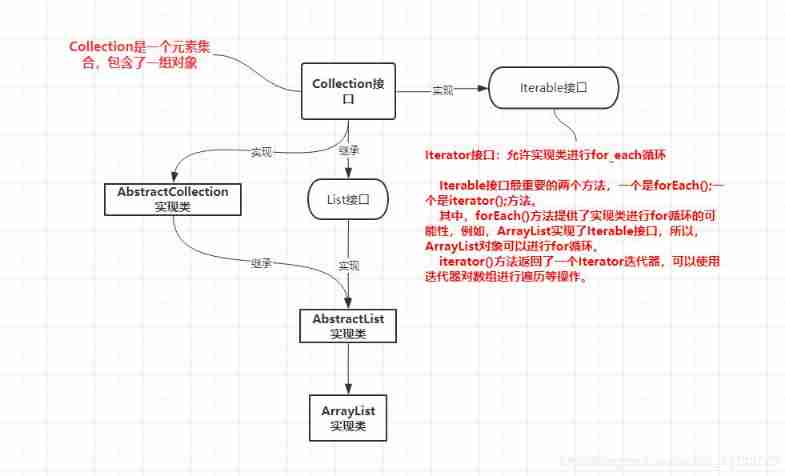
Difference between interface iterator and iteratable
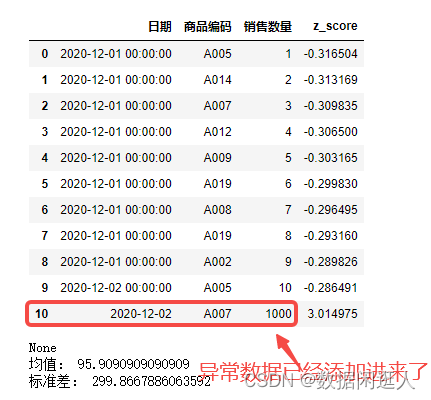
Use 3 in data modeling σ Eliminate outliers for data cleaning
First issue of JS reverse tutorial
![[4G/5G/6G专题基础-146]: 6G总体愿景与潜在关键技术白皮书解读-1-总体愿景](/img/fd/5e8f74da25d9c5f7bd69dd1cfdcd61.png)
[4G/5G/6G专题基础-146]: 6G总体愿景与潜在关键技术白皮书解读-1-总体愿景
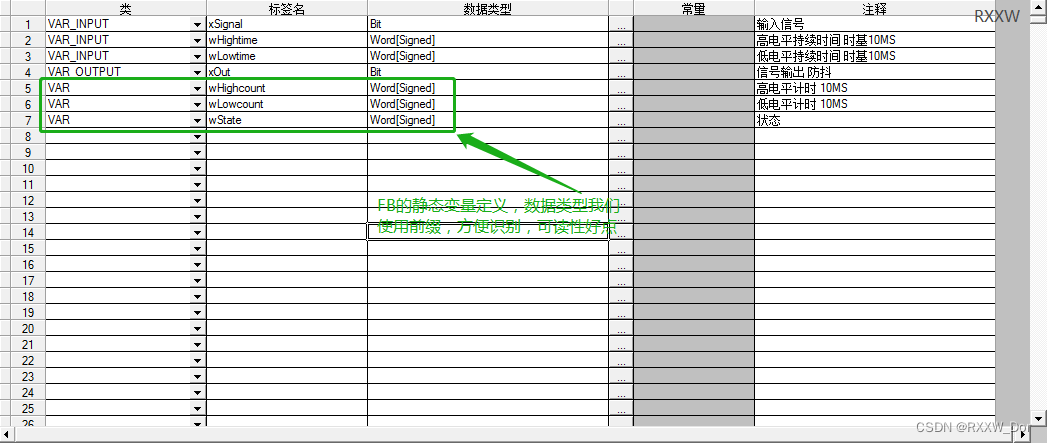
Switching value signal anti shake FB of PLC signal processing series
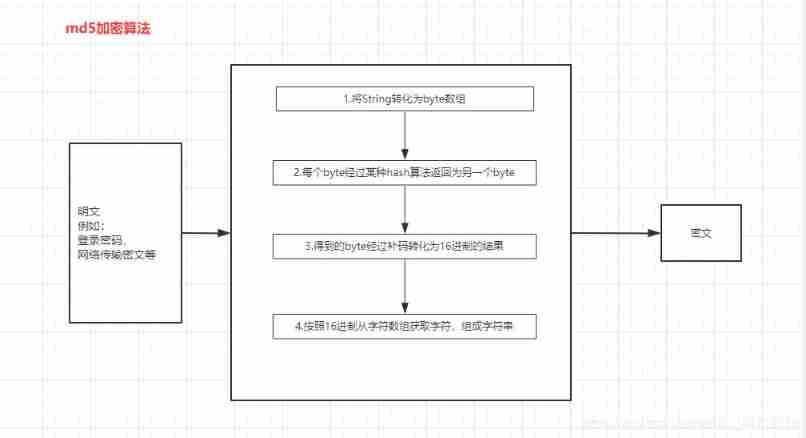
What is MD5
随机推荐
scrapy爬虫mysql,Django等
AI从感知走向智能认知
MongoDB怎么实现创建删除数据库、创建删除表、数据增删改查
Difference between interface iterator and iteratable
沙龙预告|GameFi 领域的瓶颈和解决方案
【无标题】
剑指 Offer II 107. 矩阵中的距离
其实特简单,教你轻松实现酷炫的数据可视化大屏
[cloud native] Devops (I): introduction to Devops and use of code tool
NATAPP内网穿透
What is MD5
Kubernetes cluster capacity expansion to add node nodes
Communication mode between processes
Mysql:select ... for update
nlohmann json
La différence entre viewpager 2 et viewpager et la mise en œuvre de la rotation viewpager 2
js逆向教程第二发-猿人学第一题
Vs2013 generate solutions super slow solutions
VSCode+mingw64+cmake
JS inheritance prototype