当前位置:网站首页>pytorch学习记录(六):循环神经网络 RNN & LSTM
pytorch学习记录(六):循环神经网络 RNN & LSTM
2022-07-30 13:25:00 【狸狸Arina】
文章目录
1. 时间序列表示
1.1 word embedding
- pytorch只支持数值类型,不能支持string类型,那必须把string类型表示为数值类型,这种方法就叫做representation或者word embedding;

1.2 one-hot编码

1.3 word2vec
- one-hot 编码稀疏;
- 考虑到单词之间的相似性;常用的方法有word2vec, glove;

1.4 序列的batch表示
- [word num, b, word vec] 以时间戳表示;
- [b, word num. word vec] 以句子表示;

2. 循环神经网络
2.1 RNN 的形式


2.2 RNN Layer

2.2.1 nn.RNN


import torch
import torch.nn as nn
rnn = nn.RNN(50, 10)
print(rnn._parameters.keys())
print(rnn.weight_hh_l0.shape)
print(rnn.weight_ih_l0.shape)
print(rnn.bias_hh_l0.shape)
print(rnn.bias_ih_l0.shape)
''' odict_keys(['weight_ih_l0', 'weight_hh_l0', 'bias_ih_l0', 'bias_hh_l0']) torch.Size([10, 10]) torch.Size([10, 50]) torch.Size([10]) torch.Size([10]) '''
2.2.2 nn.RNNCell
- nn.RNNCell完成单个时间戳的单层的数据传递、预测;功能和n n.RNN一样,只是没有堆叠层和stack所有out的功能;


import torch
import torch.nn as nn
cell1 = nn.RNNCell(100, 50,)
cell2 = nn.RNNCell(50, 30)
input = torch.randn(3,3,100)
ht1 = torch.zeros(3,50)
ht2 = torch.zeros(3,30)
for x_cell in input:
ht1 = cell1(x_cell, ht1)
ht2 = cell2(ht1, ht2)
print(ht1.shape)
print(ht2.shape)
''' torch.Size([3, 50]) torch.Size([3, 30]) '''
2.3 时间序列预测
from cProfile import label
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
def generate_data():
num_time_steps = 60
#生成一个随机时间点开始的样本
start = np.random.randint(3, size = 1)[0] #随机初始化一个开始点
time_steps = np.linspace(start, start+10, num_time_steps)
data = np.sin(time_steps)
data = data.reshape(num_time_steps, 1) #数据长度为1
x = torch.tensor(data[:-1]).float().view(1, num_time_steps-1, 1) #添加一个batch维度为1
y = torch.tensor(data[1:]).float().view(1, num_time_steps-1, 1)
return x,y,time_steps
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, output_size):
super().__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.output_size = output_size
self.rnn = nn.RNN(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, batch_first = True)
self.linear = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
def forward(self, x, hidden_pre):
b = x.size(0)
out, hidden_pre = self.rnn(x, hidden_pre) # out[b, seq, hidden_size] hidden_pre = [b, num_layer, hidden_size]
out = out.view(-1, self.hidden_size) #[b*seq, hidden_size]
out = self.linear(out)#[b*seq, 1]
out = out.view(b, -1, self.output_size) #[b, seq, 1]
return out, hidden_pre
if __name__ == '__main__':
batch_size = 1
num_layers = 2
hidden_size = 10
model = Net(1, hidden_size, num_layers, 1)
criteron = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr = 0.5e-2)
hidden_pre = torch.zeros(num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size)
for iter in range(6000):
x,y,_ = generate_data()
out, hidden_pre = model(x, hidden_pre)
hidden_pre = hidden_pre.detach()
loss = criteron(out, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if iter %100 == 0:
print('iteration:{} loss:{}'.format(iter, loss.item()))
x,y,time_steps = generate_data()
input = x[:,0,:].unsqueeze(1) #取所有batch的序列的第一个数据 [b, 1, word_dim]
h = torch.zeros(num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size)
predictions = []
for _ in range(x.shape[1]): #遍历序列
pred, h = model(input, h)
input = pred
predictions.append(pred.detach().numpy().ravel()[0])
figure = plt.figure(figsize=(20,20), dpi = 80)
plt.scatter(time_steps[1:], predictions, label='pred')
plt.scatter(time_steps[1:], y.view(-1).numpy(), label = 'sin')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
''' iteration:0 loss:0.6097927689552307 iteration:100 loss:0.007763191591948271 iteration:200 loss:0.0011507287854328752 iteration:300 loss:0.00087575992802158 iteration:400 loss:0.0005032330518588424 iteration:500 loss:0.0004986028652638197 iteration:600 loss:0.0009817895479500294 iteration:700 loss:0.00040510689723305404 iteration:800 loss:0.0010686117457225919 '''
2.4 RNN训练难题
- 对于长序列数据,会出现梯度爆炸,或者梯度弥散的情况;

2.4.1 梯度爆炸
- Cliping:梯度大于阈值的时候,除以它自己的范数,使得梯度范数变为1;
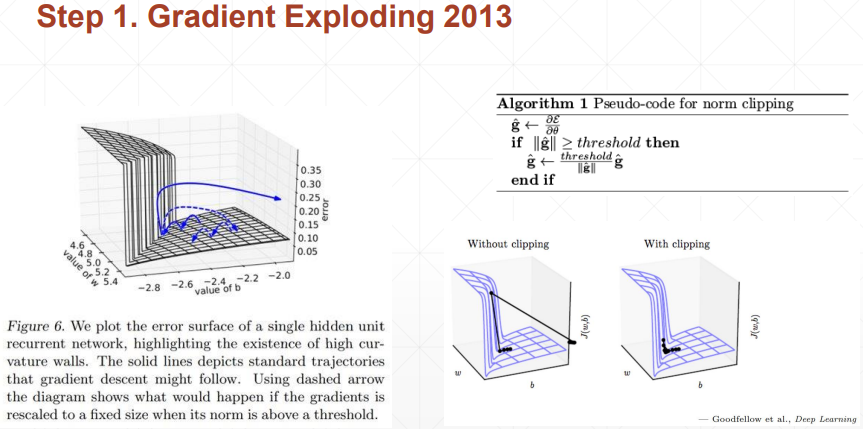
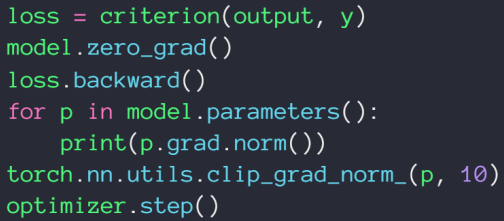
2.4.2 梯度弥散

- LSTM 解决梯度弥散;
2.5 LSTM
- RNN只能保存当前单词的附近的语境,对于离得远的单词或者前面的一些单词就给忘记了(short-term menmory);
- LSTM可以记住特别长的时间序列,所以叫long-short-term menmory;

- RNN 展开形式

- LSTM 展开形式


- 梯度更计算的时候不会出现w^k 的情况,并且梯度计算是几项累加,几乎不会同时出现都很小,或者都很大的情况,所以避免了梯度等于0,也就是梯度弥散;
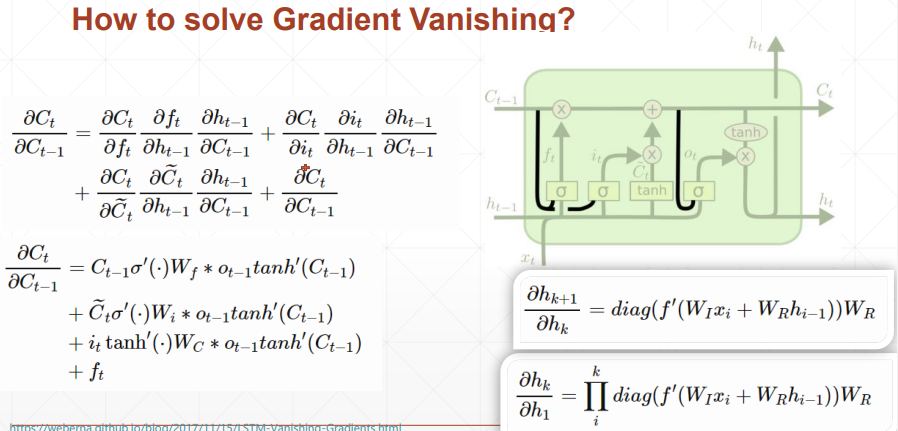
2.6 LSTM使用
2.6.1 nn.LSTM


lstm = nn.LSTM(100, 20, 4)
c = torch.zeros(4, 30, 20)
h = torch.zeros(4, 30, 20)
x = torch.rand(80, 30, 100)
out, (h,c) = lstm(x, (h,c))
print(out.shape)
print(h.shape)
print(c.shape)
''' torch.Size([80, 30, 20]) torch.Size([4, 30, 20]) torch.Size([4, 30, 20]) '''
2.6.2 nn.LSTMCell




边栏推荐
- [Go]四、模块和包、流程控制、结构体
- 程序员修炼之道:务以己任,实则明心——通向务实的最高境界
- CF780G Andryusha and Nervous Barriers
- R语言向前或者向后移动时间序列数据(自定义滞后或者超前的期数):使用dplyr包中的lag函数将时间序列数据向后移动一天(设置参数n为负值)
- ENVI Image Processing (6): NDVI and Vegetation Index
- ENVI图像处理(6):NDVI和植被指数
- R语言ggplot2可视化:使用ggpubr包的ggboxplot函数可视化分组箱图、使用ggpar函数改变图形化参数(xlab、ylab、改变可视化图像的坐标轴标签内容)
- 树形dp小总结(换根,基环树,杂七杂八的dp)
- Learning notes - 7 weeks as data analyst "in the first week: data analysis of thinking"
- 正确处理页面控制器woopagecontroller.php,当提交表单时是否跳转正确的页面
猜你喜欢

元宇宙的六大支撑技术

【自校正控制】自校正PID

学习笔记——七周成为数据分析师《第一周:数据分析思维》

leetcode207.课程表(判断有向图是否有环)

ML之PDP:基于FIFA 2018 Statistics(2018年俄罗斯世界杯足球赛)球队比赛之星分类预测数据集利用DT决策树&RF随机森林+PDP部分依赖图可视化实现模型可解释性之详细攻略

腾讯称电竞人才缺口200万;华为鸿蒙3.0正式发布;乐视推行每周工作4天半?...丨黑马头条...

自从外包干了四年,基本废了...

cpu/CS and IP

无代码开发平台全部应用设置入门教程
el-table中el-table-column下的操作切换class样式
随机推荐
Anaconda\Scripts\pip-script.py is not present ? 解决方案
qq udp tcp机制
创意loadingjs特效小点跳跃动画
腾讯称电竞人才缺口200万;华为鸿蒙3.0正式发布;乐视推行每周工作4天半?...丨黑马头条...
Hand tearing read-write lock performance test
R语言ggplot2可视化时间序列数据(默认时间中断部分前后自动连接起来)、创建时间分组、使用分面图(faceting)可视化时间序列数据
dolphinscheduler adds hana support
How to solve the problem that the page does not display the channel configuration after the EasyNVR is updated to (V5.3.0)?
大手笔!两所“双一流”大学,获75亿元重点支持!
Study Notes - Becoming a Data Analyst in Seven Weeks "Week 2: Business": Business Analysis Metrics
Current and voltage acquisition module DAM-6160
【软考软件评测师】自动化测试章节下篇
jsArray array copy method performance test 2207292307
打破原则引入SQL,MongoDB到底想要干啥???
jsArray array copy method performance test 2207300040
PyQt5快速开发与实战 8.6 设置样式
【Pytorch】如何在关闭batch-norm的同时保持Dropout的开启
展厅全息投影所具备的三大应用特点
EasyNVS云管理平台功能重构:支持新增用户、修改信息等
matlab画图,仅显示部分图例