当前位置:网站首页>First acquaintance with string+ simple usage (I)
First acquaintance with string+ simple usage (I)
2022-06-24 10:51:00 【I running】
Catalog
c++98 in string Common constructors
1. Construct an empty class object -- An empty string
2. Constant string initialization
3. Copy structure initialization
4. Specified length initialization .
5. Specify the characters and their number to initialize
6. Initializes the substring of an existing object
3. Iterator traverses backwards
1. Subscript access modification
2. In access object at Function to modify
string Reference and reference
string The capacity of the object
string What is it? :
string It's a class
string Class is basic_string An instance of the template class
Use char To instantiate basic_string Template class
The instantiated object is an array of characters that manages dynamic growth , With ‘\0’ ending
You need to include the header file when using string
#include <string>
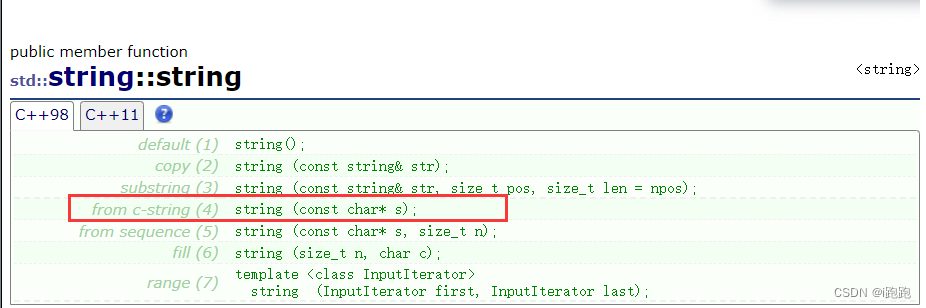
c++98 in string Common constructors
1. Construct an empty class object -- An empty string
string + ( Object name )
string s1;
2. Constant string initialization
string + Object name (“ initialization ”)
string s2("hello csdn");
3. Copy structure initialization
string + Object name ( Object already exists )
string + Object name = Object already exists
string s3(s2); string s4 = s3;
The above three are the most commonly used initialization methods
4. Specified length initialization .
string + Object name (" Initialize content , Initialization length ")
string s5("asdfghjkl", 4);
5. Specify the characters and their number to initialize
string + Object name ( Number , character )
string s6(5,'c');
6. Initializes the substring of an existing object
string + Object name ( Object already exists , Specify starting position , Specify the length )
string s7(s2,3,5);
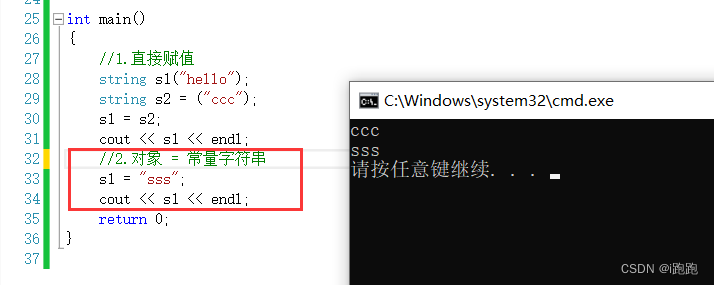
string Assignment
1. object 1= object 2

2. object = character string
3. object = character
string Object traversal
1.[ Subscript ] Traverse
void test3() { string s1("abcdefg"); //1.[ Subscript ] Traverse // It's used here size() function , The length of the string is returned , It doesn't contain \0 cout << s1.size() << endl; for (size_t i = 0;i < s1.size();i++) { // Here we use [], It's essentially function overloading : s1.operator[](i); cout << s1[i] << " "; } cout << endl; }
string Class is a custom type , use [] You need to find its operator overloaded function to call
2. Iterator forward traversal
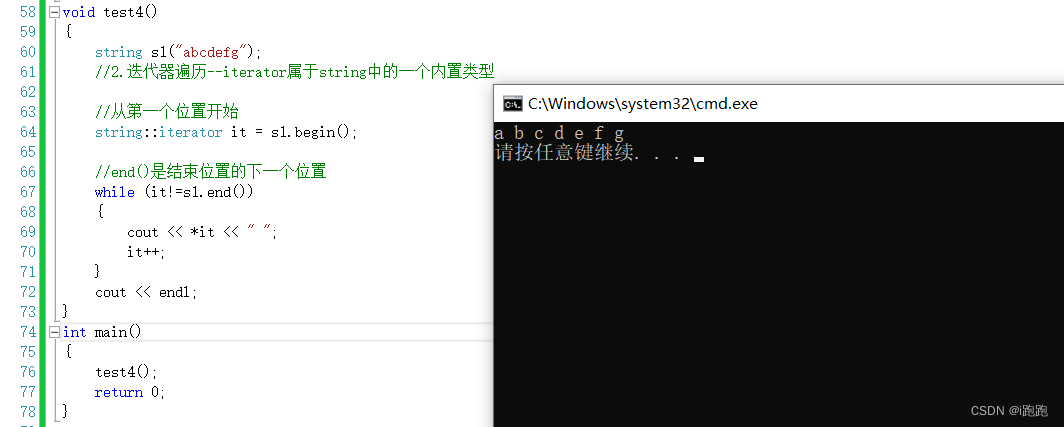
void test4() { string s1("abcdefg"); //2. Iterator traversal --iterator Belong to string A built-in type in // This method can be used to solve some problems with large number of combinations string::iterator it = s1.begin(); //end() Is the next position of the end position while (it!=s1.end()) { cout << *it << " "; it++; } cout << endl; }We're just getting started with iterators , It can be understood as a pointer first ,begin() Point to the first character ,end() Points to the next... Of the last character , Generally point to '\0', The next step is to operate in pointer mode .
3. Iterator traverses backwards
void test7() { string s1("abcdefg"); //3. Iterator traverses backwards --reverse_iterator // This method can be used to solve some problems with large number of combinations string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin(); //end() Is the next position of the end position while (rit != s1.rend()) { cout << *rit << " "; rit++; } cout << endl; }The direction of traversal is opposite to that of the forward iterator , Pay attention to the grammatical form ,reverse_iterator、rbegin、rend
Although it is a reverse traversal , But still ++, No --
4. Range for
void test5() { //3. Range for Traverse string s1("hello csdn"); for (auto e:s1) { cout << e << " "; } cout << endl; }Create a variable e, according to s1 use auto Introduction e The type of , Ergodic time , automatically ++, Until I met '\0' end
Range for In the implementation of , Is actually replaced by an iterator
string Modification of
Now that you can traverse and access every character , The corresponding can also be used when accessing characters , Modify it
1. Subscript access modification
2. In access object at Function to modify
string Reference and reference
string Can be counted as a type , Parameters can be transferred
Here we directly transfer values and parameters , A formal parameter is a temporary copy of an argument
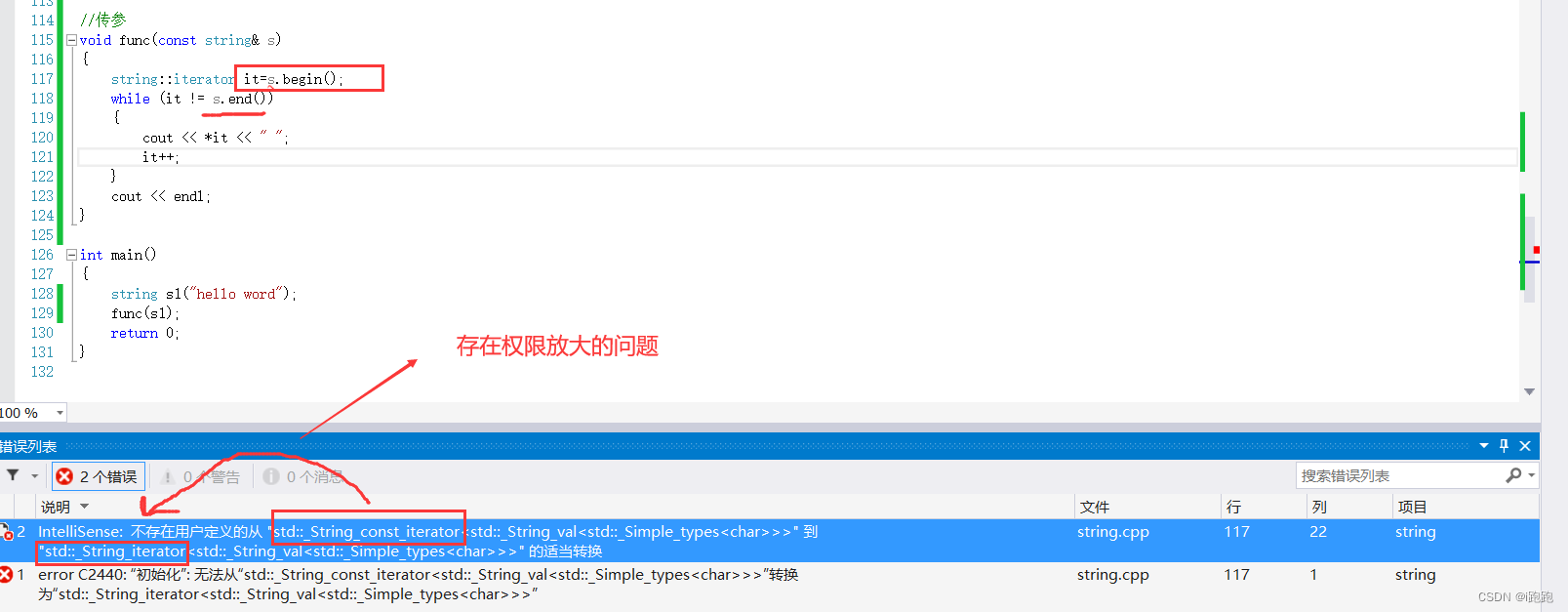
When the object is large , Consume large , therefore Formal parameter application reference passes parameter
Do not change the parameter content , Try to add const
add const Then you can't run through it , because begin and end There is a problem of permission amplification when returning

To solve the problem of making permissions the same , Then the iterator type should be const, The changes are as follows :

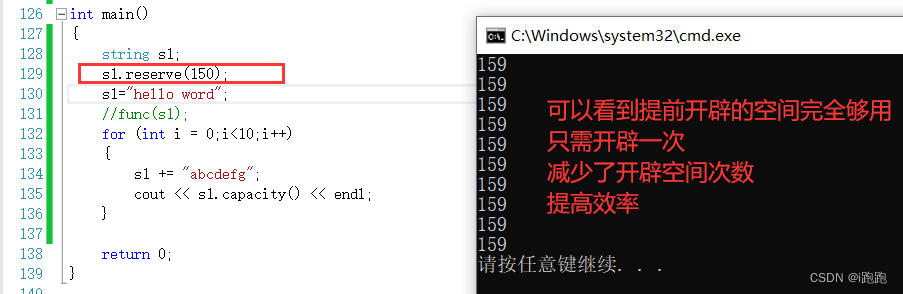
string The capacity of the object
string Type supports viewing the size and capacity of objects
Capacity
Call the object's capacity() function , You can view the capacity
But each dynamic development will increase the consumption , Is there any way to reduce the number of open space ?
reserve
Just change the size of the space , Yes size No impact
resize

string End insert of object
Insert characters push_back
Usage is as follows :
Insert string append
Two ways of using : Insert the string directly 、 Insert string Class object
direct +=
Support for characters and strings , Is the most widely used
边栏推荐
- Canvas infinite scan JS special effect code
- A group of skeletons flying canvas animation JS special effect
- Customize the toolbars of the kindeditor editor. Items removes unnecessary toolbars or retains some toolbars
- Canvas pipe animation JS special effect
- Fais ce que tu veux.
- 机械臂速成小指南(三):机械臂的机械结构
- Stack Title: exclusive time of function
- 【本周六活动】.NET Day in China
- Rising bubble canvas breaking animation JS special effect
- cuda runtime error (801) : Raw out
猜你喜欢

Rising bubble canvas breaking animation JS special effect

Fais ce que tu veux.

Spark提交参数--files的使用

Flink cluster construction and enterprise level yarn cluster construction
What you must know about distributed systems -cap

26. delete duplicates of ordered array
Thread pool execution process

283. move zero
Canvas pipe animation JS special effect

【资源分享】2022年环境工程与生物技术国际会议(CoEEB 2022)
随机推荐
【资源分享】2022年环境工程与生物技术国际会议(CoEEB 2022)
What characteristics should a good design website have?
Learn to use PHP to implement unlimited comments and unlimited to secondary comments solutions
[resource sharing] 2022 International Conference on Environmental Engineering and Biotechnology (coeeb 2022)
Pycharm shortcut keys
What is the knowledge map? What does it do
SF Technology Smart logistics Campus Technology Challenge (June 19, 2022) [AK]
2022年智能机器人与系统国际研讨会(ISoIRS 2022)
A method to solve the self-adaptive width and height of the internal picture of rich text label in wechat applet
The nodejs service global timeout callback failed to get process Domain problem
Differences among cookies, session, localstorage and sessionstorage
Spark submission parameter -- use of files
Niuke-top101-bm28
cuda runtime error (801) : Raw out
Charles packet capturing tool tutorial
[Qianfan 618 countdown!] IAAs operation and maintenance special preferential activities
[IEEE publication] 2022 International Conference on service robots (iwosr 2022)
Distributed transaction principle and solution
[energy reports] International Conference on energy and environmental engineering in 2022 (cfeee 2022)
Quick completion guide for mechanical arm (II): application of mechanical arm