当前位置:网站首页>C language character function
C language character function
2022-06-29 13:19:00 【Orange cat】
Character functions 《string.h》
String function without string length limit
1. strlen Calculate string length
strlen The parameters of the function
size_t strlen ( const char * str );
- strlne Is a calculated character
‘\0’The number of all previous characters , barring\0 - strlen The return value of the function is
unsigned inttype , Unsigned shaping - strlen The end of the string pointed to by the parameter of must contain
\0, String is based on\0As an end sign
strlen How to use
#include<string.h>
int main()
{
char arr[] = {
"abcde" };
int n = strlen(arr);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("%c ", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}
About strlen The return value of the function is size_t, That is to say uisigned int Examples
int main()
{
const char* n = "abcdef";
const char* x = "abx";
if (strlen(x) - strlen(n) > 0)
{
printf("x > n\n");
}
else
{
printf("n > x\n");
}
return 0;
}
- Answer key
In the example above ,n The number of strings of is 6,x The number of strings of is 3
3 - 6 = -3
The normal result is n > x
But I said before strlen The function returns size_t, It's unsigned
-3 If it is interpreted as an unsigned number , Then there is no sign bit
-3 Will be interpreted as a super large positive number , Will be greater than 0
result : x > n
2. strcpy String copy
strcpy The parameters of the function
char* strcpy(char * destination, const char * source );
- strcpy The source string of the string copy must be in
\0For the end sign - strcpy In the source string ‘\0’ Copy to target space
- The target space of the copy must be large enough , After copying, the string can be stored
- strcpy The copied string must be changeable , Cannot be a constant string
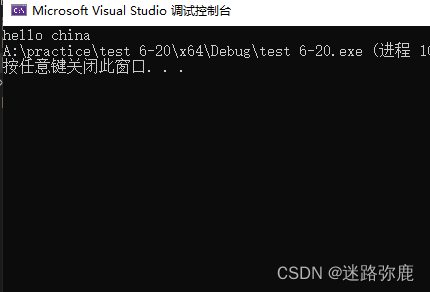
strcpy Use of functions
strcpy The first parameter in is a copy Target space , The second parameter is Copy content
int main()
{
char arr[20] = {
"################" };
char x[] = {
"hello china" };
strcpy(arr, x);
printf("%s", arr);
return 0;
}
3. strcat String append
strcat The parameters of the function
char * strcat ( char * destination, const char * source );
strcat String append , Is in the string A A string is appended B
- strcat The source string of must start with
\0For the end sign - strcat The space to be appended must be able to store the next appended string
- strcat The source string of must be changeable , Cannot be a constant string
strcat Use of functions
int main()
{
char arr[20] = {
"hello " };
char arr2[] = "china";
strcat(arr, arr2);
printf("%s\n", arr);
return 0;
}
- strcat Function appending will put arr2 Copy all strings of to arr1 in , Include
\0
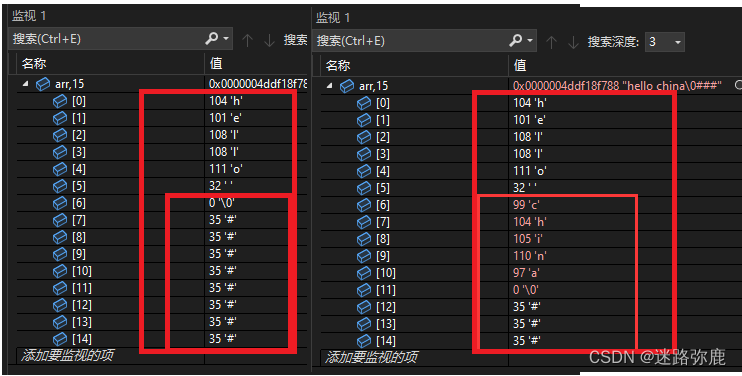
- arr2 When copying, it will put arr1 Inside
\0Cover , therefore strcat Functions cannotcharacter string A Additional character string A
4. strcmp String comparison
strcmp The parameters of the function
int strcmp ( const char * str1, const char * str2 );
strcmp The judgment standard of the function stipulates :
The first string is larger than the second string , Return greater than 0 The number of
The first string is equal to the second string , Then return to 0
The first string is less than the second string , Then return less than 0 The number ofstrcmp Is to compare the first character of each string , If equal ,
Then continue to compare the next pair of characters , Until the characters are not equal or the end null character is reached
strcmp Function USES
int main()
{
char arr[] = {
"abcdefg" };
char str[] = {
"abg" };
int ret = strcmp(arr, str);
if (ret > 0)
printf("arr > str");
else if (ret < 0)
printf("arr < str");
else
printf("arr == str");
return 0;
}
String function with string length limit
1. strncpy String copy
strncpy The parameters of the function
char * strncpy ( char * destination, const char * source, size_t num );
strncpyandstrcpyFunctions are used in the same way , Just one more parametersize_t num- The extra parameter is to limit the length of the string copy , Increased security
- If the length of the source string is less than num, After copying the source string , Add... After the target
\0, until num individual
strncpy Use of functions
int main()
{
char arr[25] = {
"hello worle!" };
char arr2[] = {
"For a better tomorrow!########" };
strncpy(arr, arr2, 22);
printf("%s\n", arr);
return 0;
}
2. strncat String append
strncat Function parameter
char * strncat ( char * destination, const char * source, size_t num );
- and strcat Functions use similar methods and rules , Just one more parameter
size_t num - num This parameter represents the number of strings that need to be appended
strncat Function USES
int main()
{
char arr[20] = "hello ";
char* str = "world! For a better tomorrow!";
strncat(arr, str, 6);
printf("%s\n", arr);
return 0;
}
3. strncmp String comparison
strncmp Function parameter
int strncmp ( const char * str1, const char * str2, size_t num );
- Rules and strcmp ditto
- The extra parameter is used to compare the number of strings
strncmp Function USES
Compare 3 The size of the first string
int main()
{
char arr[] = {
"abgefg" };
char str[] = {
"abgaaaa" };
int ret = strncmp(arr, str,3);
if (ret > 0)
printf("arr > str");
else if (ret < 0)
printf("arr < str");
else
printf("arr == str");
return 0;
}

4. strstr Find another string in a string
strstr Function parameter
char * strstr ( const char *str1, const char * str2);
- effect : stay A Find whether the string contains B character string
If A Contained in the B , Then return to B stay A The address that first appears in .
Otherwise return null pointer ! - If you find , The return is the address of the string , So we need to use pointer variables to receive
strstr Function USES
int main()
{
char arr[] = {
"abcdefg" };
char str[] = {
"cde" };
char* ret = strstr(arr, str);
if (ret == NULL)
printf(" Can't find \n");
else
printf("%s\n", ret);
return 0;
}

5. strtok Cut string
strtok Function parameter
char * strtok ( char * str, const char * sep );
The first parameter is a string , It contains 0 One or more characters
The second parameter is the split string , Scan the string of the first parameter , Encountered any one of the split strings
Just mark that character as ‘\0’ , Then return the address before splitting the string , And save its position in the stringstrtok The first parameter of the function's second lookup is NULL , The function will start at the same position in the string that is saved , Find next tag
If there are no more split characters in the string , Then return to NULL The pointer .strtok Function changes the string being manipulated , So it's using strtok The string cut by the function is usually a temporary copy and can be modified

strtok Function USES
This method is troublesome , And the code repetition is high
int main()
{
char* arr = {
"[email protected]" };
const char* n = "@.";
char str[30];
strcpy(str, arr);
char* tmp = NULL;
tmp = strtok(str, n);
printf("%s\n", tmp);
tmp = strtok(NULL, n);
printf("%s\n", tmp);
tmp = strtok(NULL, n);
printf("%s\n", tmp);
return 0;
}
Simplified edition
It can be used for The cycle is cleverly achieved , The results are the same
int main()
{
char* arr = {
"[email protected]" };
const char* n = "@.";
char str[30];
char* tmp = NULL;
strcpy(str,arr);
for (tmp = strtok(str, n); tmp != NULL; tmp = strtok(NULL,n))
{
printf("%s\n", tmp);
}
return 0;
}

6. strerror Parse error code
strerror Function parameter
char * strerror ( int errnum );
- When using library functions , When calling a library function fails , Will set the error code
- C The language has a global variable called
errno, Whenever an error occurs when calling a library function , Will put the error code inerrnoin - strerror Will translate the error code into the corresponding error message
- Use must include header file
<errno.h>
srerror Use
All returned are corresponding error messages
int main()
{
printf("%s\n", strerror(0));
printf("%s\n", strerror(1));
printf("%s\n", strerror(2));
printf("%s\n", strerror(3));
printf("%s\n", strerror(4));
printf("%s\n", strerror(5));
return 0;
}

The specific use :
Normally strerror Put in errno,errno The error code is stored in the
int main()
{
FILE* pFile;
pFile = fopen("test.txt", "r");// open test.txt, Open the file as read
if (pFile == NULL) // Open failure is a null pointer
printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));
// Error codes are automatically saved in errno Among variables
return 0;
}

perror Parse error code , Print information
perror Function parameter
void perror(const char* str);
- perror The header file for is <stdio.h>
- perror and strerror The effect is the same , however strerror No printing
- perror Is to convert the error code into error information , In print
int main()
{
//1. When opening a file fails , return NULL
FILE* pd = fopen("test.txt", "r");
if (pd == NULL)
{
perror(" error message ");
return 1;
}
// 2. Reading documents
// .....
//3. Close file
fclose(pd);
pd = NULL;
return 0;
}
Character manipulation functions
| Function name | Returns true if the parameter meets the following conditions ( Not 0 The number of ) |
|---|---|
| iscntrl | Any control character |
| isspace | Blank character : Space ‘ ’, Change the page ‘\f’, Line break ’\n’, enter ‘\r’, tabs ’\t’ Or vertical tabs ’\v’ |
| isdigit | Decimal number 0~9 |
| sxdigit | Hexadecimal number , Include all decimal digits , Lowercase letters a ~ f, Capital A ~ F |
| islower | Lowercase letters a~z |
| isupper | Capital A~Z |
| isalpha | Letter a ~ z Or uppercase characters A - Z |
| salnum | Letters or numbers ,az,AZ,0~9 |
| ispunct | Punctuation , Any graphic character that is not a number or letter ( Printable ) |
| isgraph | Any graphic character |
| isprint | Any printable character , Including graphic characters and white space characters |
- The header file of the above function :<ctype.h>
Function usage demonstration :
1. isdigit Determine whether it is a numeric character
int main()
{
char ch = '#';
int ret = isdigit(ch);
printf("%d\n", ret);
return 0;
}

- The following example shows , If it's a numeric character , Returns yes or no 0 The number of
- Not numeric characters , Return to digital 0
#include<ctype.h>
int main()
{
char ch = '3';
int ret = isdigit(ch);
printf("%d\n", ret);
return 0;
}
answer :

2. islower Determine whether it is a lowercase character
- islower If the lower case character is judged, the returned value is Not 0 , Not return 0
#include<ctype.h>
int main()
{
char ch = 'a';
int ret = islower(ch);
printf("%d\n",ret);
return 0;
}
answer :

- The above is just a few examples , The rest of the usage is similar
Character conversion letter
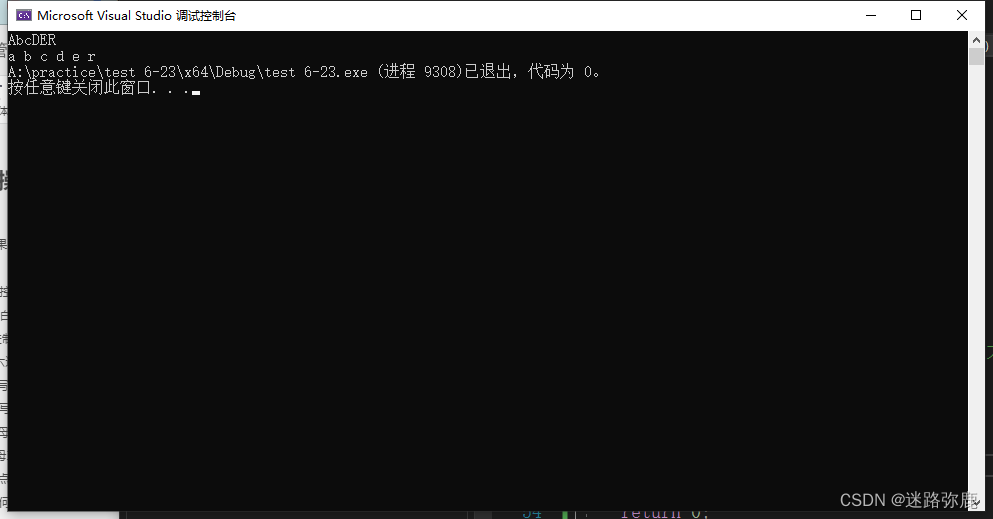
tolower Character to lowercase
#include<ctype.h>
int main()
{
char arr[20] = {
0 };
scanf("%s", &arr);
int i = 0;
while (arr[i] != '\0')
{
if (isupper(arr[i])) // Decide if it's a capital letter
{
arr[i] = tolower(arr[i]);
}
printf("%c ", arr[i]);
i++;
}
return 0;
}
toupper Capitalize characters
int main()
{
char arr[20] = {
0 };
scanf("%s", &arr);
int i = 0;
while (arr[i] != '\0')
{
if (islower(arr[i])) // Determine if it's lowercase
{
arr[i] = toupper(arr[i]); // Convert to uppercase characters
}
printf("%c ", arr[i]);
i++;
}
return 0;
}

边栏推荐
- The former security director of Uber faced fraud allegations and concealed the data leakage event
- qt json
- 23、 1-bit data storage (delay line / core /dram/sram/ tape / disk / optical disc /flash SSD)
- @Table爆红
- C # realize the hierarchical traversal of binary tree
- AcWing第57场周赛
- 基于51单片机控制的BUCK开关电源Proteus仿真
- Memorized Function
- Problem solving: modulenotfounderror: no module named 'pip‘
- C binary tree structure definition and node value addition
猜你喜欢

Definition of C # clue binary tree

YOLO系列梳理(九)初尝新鲜出炉的YOLOv6

Viewing splitchunks code segmentation from MPX resource construction optimization

Interesting talk on network protocol (II) transport layer
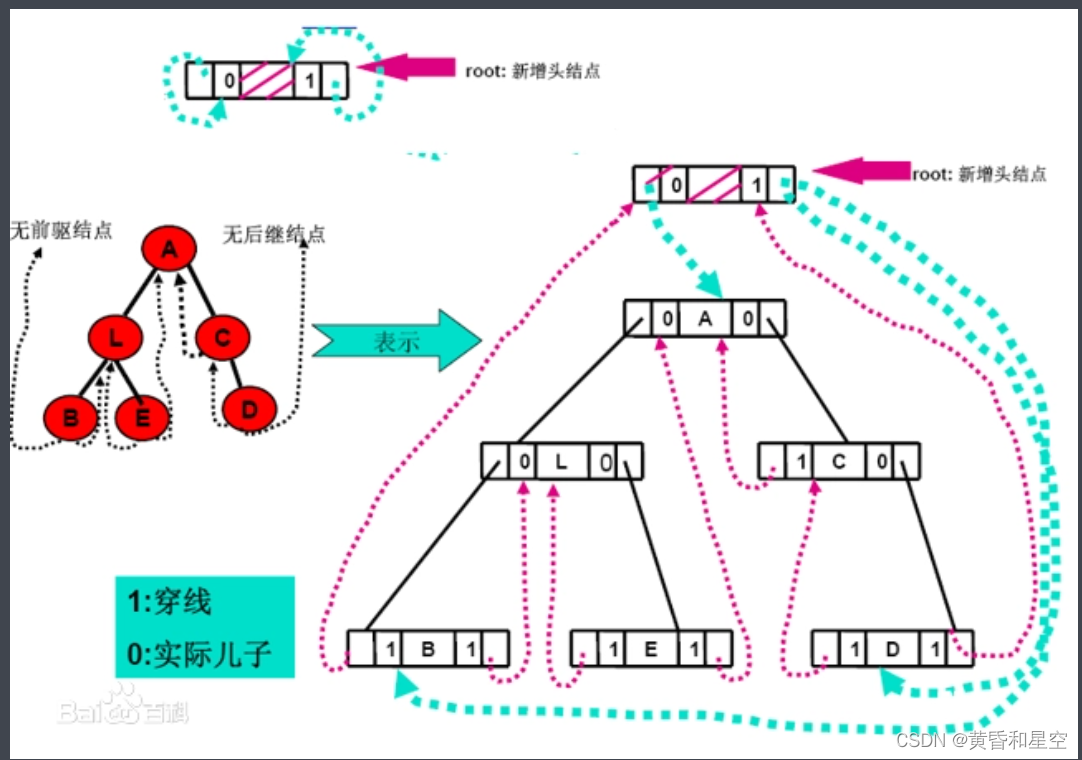
C # clue binary tree through middle order traversal

三维模型下载与动画控制

leetcode 第 299场周赛
Adjacency matrix and adjacency table structure of C # realization graph

C语言内存函数

QQ group was stolen, a large-scale social death scene caught off guard
随机推荐
Beifu controls the third-party servo to follow CSV mode -- Taking Huichuan servo as an example
Deep understanding of volatile keyword
C语言内存函数
QT signal and slot
商品搜索引擎—推荐系统设计
Clickhouse database uses JDBC to store milliseconds and nanoseconds
【云驻共创】工业智慧“大脑”,老厂焕新的加速秘籍
Simple introduction to matlab
Schiederwerk power supply maintenance smps12/50 pfc3800 analysis
hutool工具类的学习(持续更新)
Interesting talk on network protocol (II) transport layer
Acwing 234 abandoning testing
qt 自定义控件 :取值范围
C#实现二叉树的层次遍历
YOLO系列梳理(九)初尝新鲜出炉的YOLOv6
[intelligent QBD risk assessment tool] Shanghai daoning brings you leanqbd introduction, trial and tutorial
CVPR2022 | A ConvNet for the 2020s & 如何设计神经网络总结
Schiederwerk Power Supply repair smps12 / 50 pfc3800 Analysis
Another "provincial capital university", coming!
PyGame accurately detects image collision