当前位置:网站首页>Naive Bayes classification of scikit learn
Naive Bayes classification of scikit learn
2022-06-12 03:27:00 【Watermelon】
This tutorial will show you how to use Python Of Scikit-learn Package construction and evaluation of naive Bayesian classifiers .
Suppose you are a product manager , You want to classify customer comments into positive and negative categories . Or as a loan Manager , You want to determine which loan applicants are safe or risky ? As a healthcare Analyst , You want to predict which patients may have diabetes . All examples have comments on 、 The same problem of classifying loan applicants and patients .
Naive Bayes is the most direct 、 The fastest classification algorithm , For large amounts of data . Naive Bayesian classifier has been successfully used in various applications , For example, spam filtering 、 Text classification 、 Emotion analysis and recommendation system . It uses Bayesian probability theorem to predict unknown classes .
In this tutorial , You will learn all of the following :
- Classification workflow
- What is a naive Bayesian classifier ?
- How naive Bayesian classifiers work ?
- Scikit-learn Classifier construction in
- Zero probability problem
- Its advantages and disadvantages
1 Classification workflow
Whenever classification is performed , The first step is to understand the problem and identify potential features and labels . Features are those features or attributes that affect the results of the tag . for example , In the case of loan allocation , The bank manager determines the client's occupation 、 income 、 Age 、 place 、 Previous loan history 、 Transaction history and credit score . These features are called features that help the model classify customers .
Classification has two stages , Learning phase and evaluation phase . In the learning phase , The classifier trains its model on a given data set , In the evaluation phase , It tests the performance of the classifier . Performance is evaluated based on various parameters , For example, accuracy 、 error 、 Precision and recall .

2 What is a naive Bayesian classifier ?
Naive Bayes is a statistical classification technique based on Bayes theorem . It is one of the simplest supervised learning algorithms . Naive Bayes classifier is a fast classifier 、 Accurate and reliable algorithms . Naive Bayes classifier has high accuracy and speed in large data sets .
Naive Bayesian classifiers assume that the effect of a particular feature in a class is independent of other features . for example , Whether the loan applicant is desirable depends on him / Her income 、 Previous loan and transaction history 、 Age and position . Even if these features are interdependent , These characteristics are still considered independently . This assumption simplifies the calculation , That is why it is considered “ simple ” Of . This assumption is called class conditional independence .

- P(h): hypothesis h The probability of being true ( No matter what the data is ). This is called h The prior probability of .
- P(D): Probability of data ( Whatever the assumptions ). This is called a priori probability .
- P(h|D): Given data D Assumptions h Probability . This is called a posteriori probability .
- P(D|h): hypothesis h It's true , data D Probability . This is called a posteriori probability .
3 How naive Bayesian classifiers work ?
This section covers a lot of knowledge about linear algebra and probability , Readers who have high requirements for theoretical research can refer to more professional books , Readers who only care about how to apply can skip this section . I only care about application , therefore , Let's skip this section . Leave a title just for structural integrity . Ha ha ha ~~~ I hope the math teacher will forgive me ~~~
4 Scikit-learn Classifier construction in
4.1 Naive Bayes classifier
1) Define datasets
In this example , You can use a virtual dataset with three columns : The weather 、 Temperature and whether to go out to play . The first two are characteristics ( The weather 、 temperature ), The other is the label .

2) Coding features
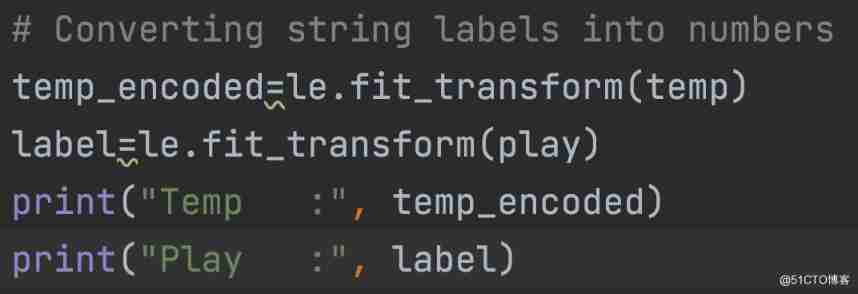
First , You need to convert these string labels to numbers . for example :'Overcast', 'Rainy', 'Sunny' as 0, 1, 2. This is called tag encoding . Scikit-learn Provides LabelEncoder library , Used to encode labels , Its value is 0 To 1 Between , Less than the number of discrete classes .


Again , You can also be right temp and play Column .

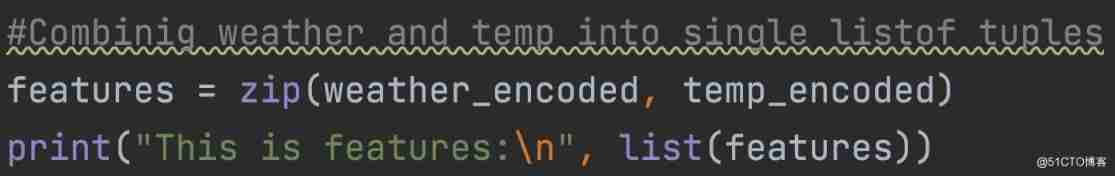
Now take these two features ( Weather and temperature ) Combined in one variable ( Tuple list ) in .

3) Generate models
In the following steps, a naive Bayesian classifier is used to generate the model :
- Create a naive Bayesian classifier
- Fit the data set to the classifier
- Execution forecast


here ,1 Indicates that players can “ hang out ”.
4.2 Naive Bayes with multiple labels
up to now , You have learned about naive Bayesian classification using binary tags . Now you will learn about multi class classification in naive Bayes . This is called multinomial naive Bayes classification . for example , If you want to know about the technology 、 entertainment 、 Classify political or sports news articles .
In the model building part , You can use wine datasets , This is a very famous multi class classification problem . “ This data set is the result of chemical analysis of wines grown in the same region of Italy but from three different varieties .”
Data set containing 13 Features ( alcohol 、 Malic acid 、 ash content 、alcalinity_of_ash、 magnesium 、 Total phenol 、 Flavonoids 、 Non flavonoid phenols 、 procyanidins 、 Color intensity 、 tonal 、od280/od315_of_diluted_wines、 Proline ) And the type of wine . The data has 3 Wine growing Class_0、Class_1 and Class_3. ad locum , You can build a model to classify the types of wines .
The dataset is in scikit-learn Available in Library .
1) Load data
Let's start with scikit-learn The data set is loaded with wine Data sets .

2) Explore data
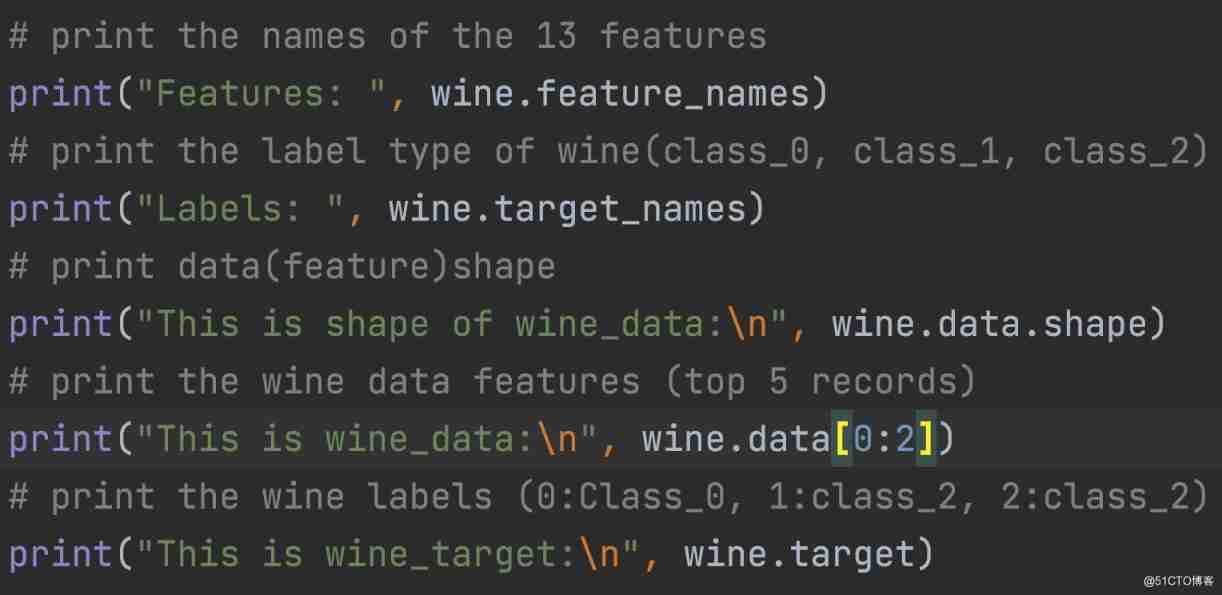
You can print target and feature names , To make sure you have the right data set , As shown below :
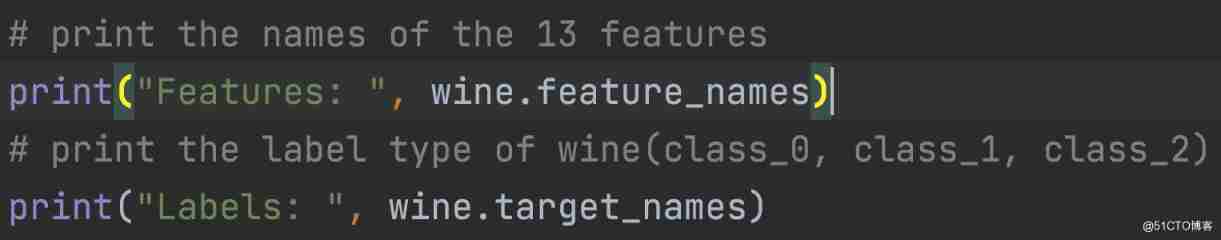

A little exploration of your data is never wrong , So you know what you're dealing with . ad locum , You can see that the first five rows of the dataset are printed , And the target variables for the entire dataset .

3) Split data
First , You divide columns into dependent and independent variables ( Or features and labels ). Then these variables are divided into training set and test set .

4) Generate models
After break up , You will generate a random forest model on the training set , And predict the characteristics of the test set .

5) Evaluation model
After the model is generated , Check accuracy using actual and predicted values .
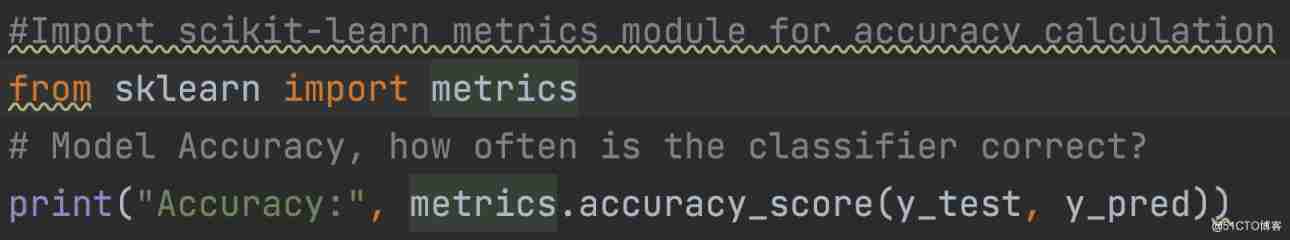

5 Zero probability problem
Suppose there are no tuples of risky loans in the data set , under these circumstances , The posterior probability is zero , The model cannot predict . This problem is called zero probability , Because the occurrence of a specific class is zero .
The solution to this problem is Laplace correction (Laplacian correction) Or Laplace transform (Laplace Transformation). Laplace correction is one of the smoothing techniques . ad locum , You can assume that the data set is large enough , Adding a row to each class does not affect the estimated probability . This will overcome the problem of zero probability .
for example : Suppose that for risky loans , It's in the database 1000 Training tuples . In this database , The income is listed as 0 Tuples represent low income ,990 Tuples represent middle income ,10 Tuples represent high income . Without Laplace correction , The probability of these events is 0、0.990( come from 990/1000) and 0.010( come from 10/1000)
Now? , Apply Laplace correction to a given data set . Let's pay for each income - Add value to 1 Tuples . The probability of these events :

6 advantage
- It's not just a simple method , And it is a fast and accurate prediction method .
- The computational cost of naive Bayes is very low .
- It can effectively handle large data sets .
- Compared with continuous variables , It performs well in the case of discrete response variables .
- It can be used for multi class prediction problems .
- It also performs well in the case of text analysis problems .
- When the independence assumption holds , Naive Bayesian classifier and other models ( Like logical regression ) Better than .
7 shortcoming
- The assumption of independent characteristics . In practice , It is almost impossible for the model to obtain a set of completely independent predictive variables .
- If there is no training tuple for a specific class , This will result in a posteriori probability of zero . under these circumstances , The model cannot predict . This problem is called zero probability / Frequency problem .
8 Conclusion
In this tutorial , You learned about the naive Bayesian algorithm 、 How it works 、 Naive Bayes hypothesis 、 problem 、 Realization 、 pros and cons . In the process , You also learned scikit-learn Modeling and evaluation of binary and multinomial classes in .
Naive Bayes is the most direct and effective algorithm . Although machine learning has made great progress in the past few years , But it has proved its value . It has been successfully deployed in many applications ranging from text analysis to recommendation engines .
边栏推荐
- 2022 communication industry ultimate Exhibition Guide
- Infinite loop judgment method;
- oralce 处理列转行的三种方式 最后生成表格样式数据
- 3769 moving stones (simulated)
- Evolution and practice of Unicom real-time computing platform
- 2020-12-06
- GeForce GTX 2050/2080/3090/A6000自动安装nvidia显卡驱动
- Steamvr--- grab objects
- Geforce GTX 2050/2080/3090/a6000 auto install NVIDIA graphics driver
- 技术经济与企业管理 复习 第四章
猜你喜欢

Demand and business model innovation - demand 6- stakeholder analysis and hard sampling

2020-12-06

Domestic mobile phones are snubbing low-end consumers, and Nokia provides them with high-quality products

微信小程序项目实例——我有一支画笔(画画)

ics-07
central limit theorem

Convert py file to EXE file
![Leetcode 6[finding rules] Z-transform the leetcode path of heroding](/img/c0/aca2eb185ce4b423df9ee171ee91e1.jpg)
Leetcode 6[finding rules] Z-transform the leetcode path of heroding

Inverted string - two solutions

C language array
随机推荐
Computer configuration suggestions for learning modeling
Go syntax variable
Evolution and practice of Unicom real-time computing platform
Using SSH public key to transfer files
[point cloud compression] variable image compression with a scale hyperprior
tcp 三次握手与四次挥手
云原生概述
Hacker + marathon =? Hacker marathon?
Go 语法 变量
2020-12-06
Final summary of addition, deletion, modification and query - 2.1 (single table - addition, deletion, modification and query)
微服务概念及介绍
Sequence list and linked list - primary level
Domestic mobile phones are snubbing low-end consumers, and Nokia provides them with high-quality products
Demand and business model innovation - demand 9- prototype
MySQL的check约束数字问题
C language array
Eight fallacies of distributed computing
【mysql】mysql安装
Yu Xia looks at win system kernel -- debugging