After reading this article , You can go and get the following questions :
-----------
Previous post 「 Recursively reverses a part of a linked list 」 How to recursively reverse a part of a linked list , Some readers ask how to iteratively reverse the linked list , The problem that this article solves also needs to reverse the function of linked list , We may as well use the iterative method to solve .
This article is to solve 「K A set of reverse linked list 」, It's not difficult to understand. :

This problem is often seen in face sutras , and LeetCode The difficulty is Hard, Is it really that hard ?
The algorithm of basic data structure is not difficult , As long as the combination of characteristics a little bit disassembly analysis , Generally, there is no difficulty . Now let's take this problem apart .
One 、 To analyze problems
First , above Frame thinking of learning data structure Mentioned , Linked list is a data structure with recursive and iterative properties , If you think about it carefully, you can find that This problem is recursive .
What is recursive property ? Just look at the picture above , For example, we call the linked list reverseKGroup(head, 2), That is to 2 Nodes are a set of inverted linked lists :
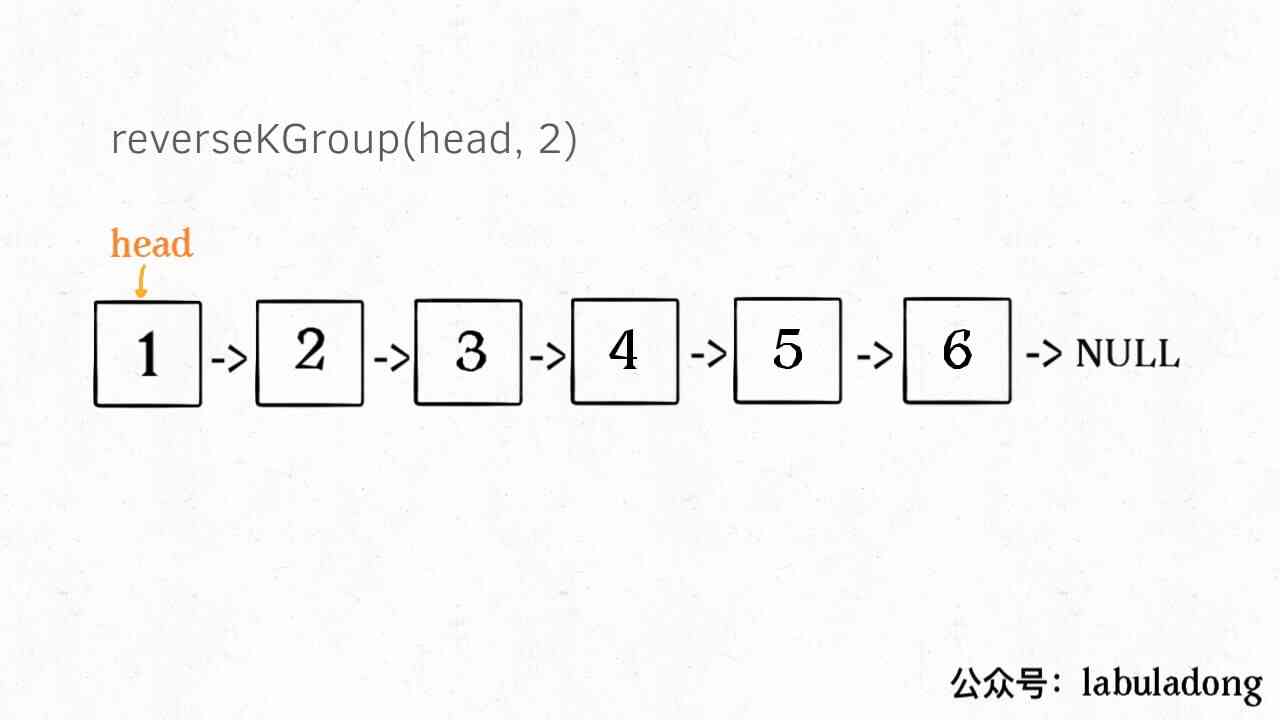
If I try to put the front 2 Nodes reversed , How to deal with the nodes at the back ? The following nodes are also a linked list , And the scale ( length ) It's smaller than the original list , This is called Sub problem .
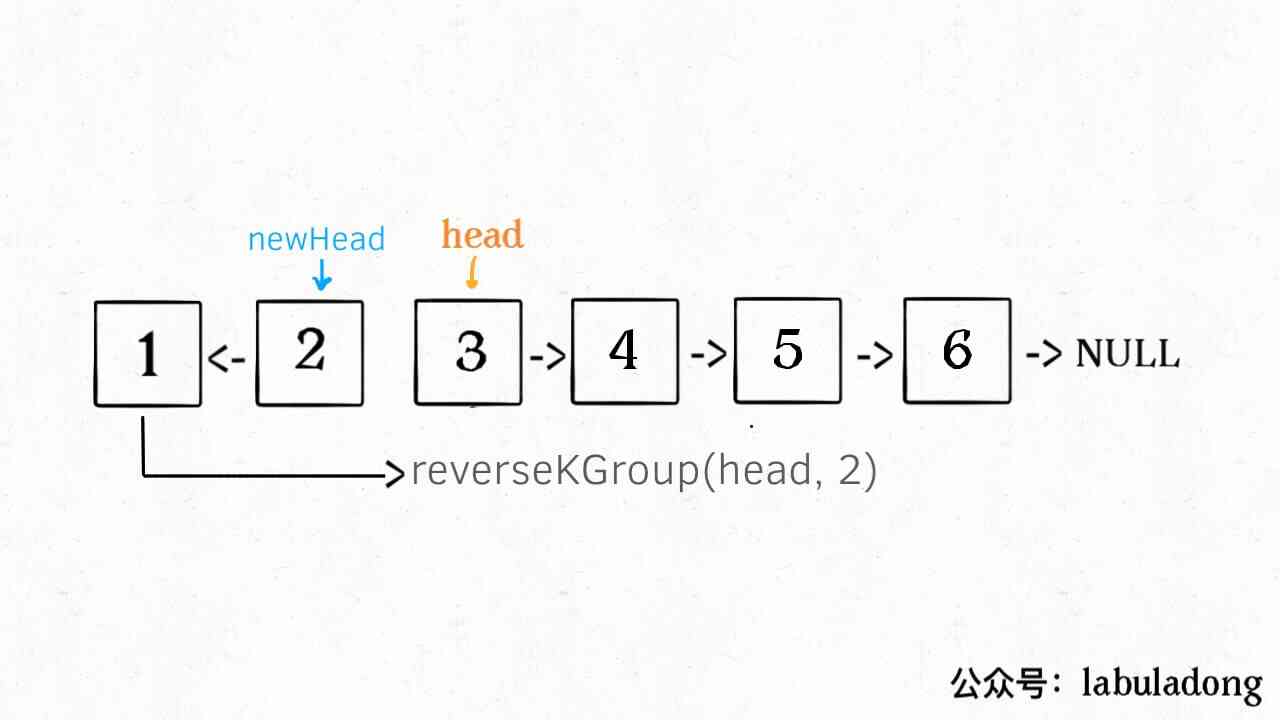
We can call... Directly recursively reverseKGroup(cur, 2), Because the structure of the subproblem and the original problem are exactly the same , This is the so-called recursive property .
Found the recursive property , We can get the general algorithm flow :
1、 First reverse to head At the beginning k Elements .
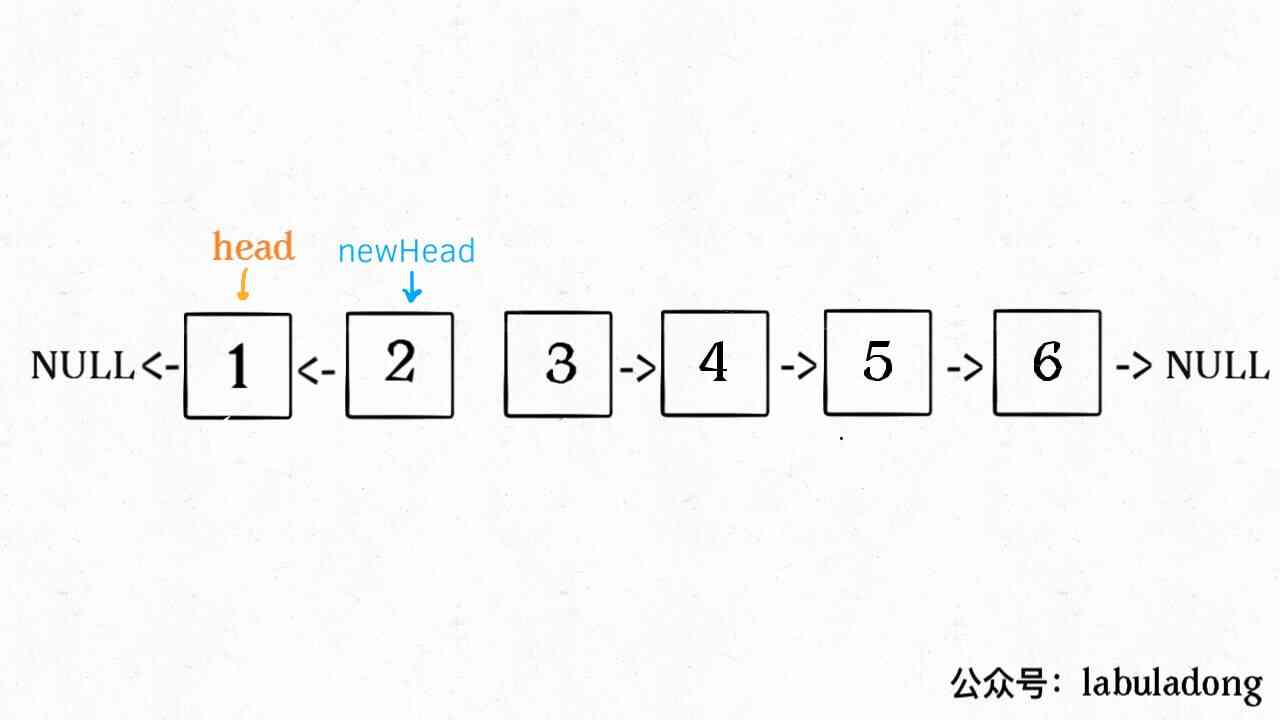
2、 Will be the first k + 1 Elements as head Recursively call reverseKGroup function .
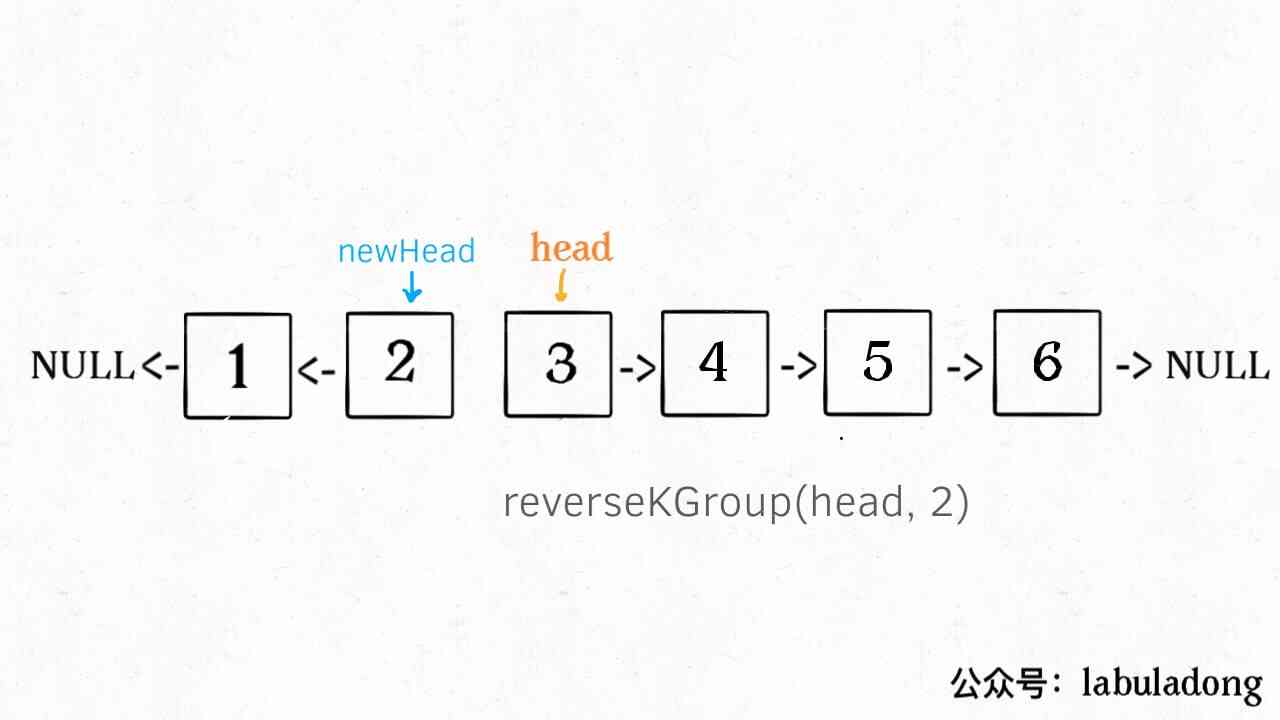
3、 Connect the results of these two processes .
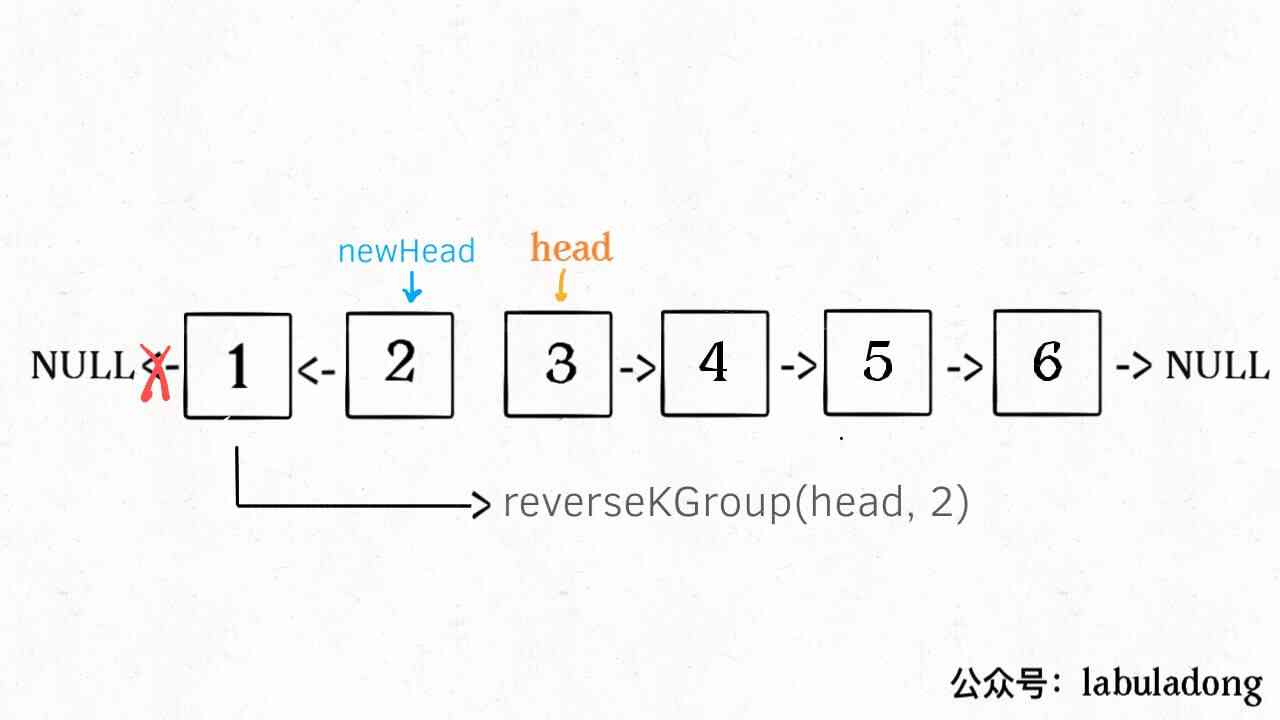
The whole idea is like this , The last thing to note is , Recursive functions have a base case, What's the problem ?
It's a question , If the final element is not enough k individual , Keep it the same . This is it. base case, It'll be reflected in the code later .
Two 、 Code implementation
First , We want to achieve one reverse Function reverses the elements within an interval . Before that, let's simplify , Given the chain header node , How to reverse the entire list ?
// Reverse to a Is the linked list of the head node
ListNode reverse(ListNode a) {
ListNode pre, cur, nxt;
pre = null; cur = a; nxt = a;
while (cur != null) {
nxt = cur.next;
// Reverse node by node
cur.next = pre;
// Update pointer position
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
}
// Returns the inverted head node
return pre;
}
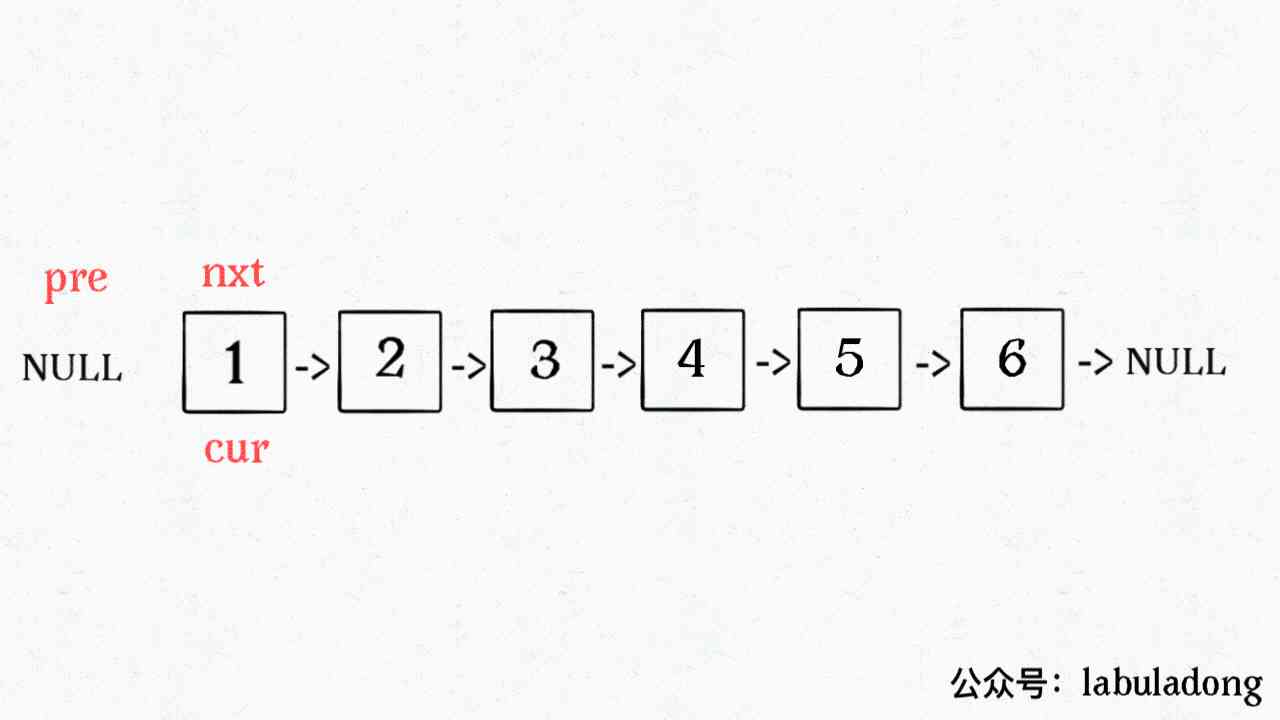
This time, we use the idea of iteration to achieve , It should be easy to understand with animation .
「 Reverse to a Is the linked list of the head node 」 In fact, that is 「 reverse a To null The node between 」, So if you're allowed to 「 reverse a To b The node between 」, Will you ?
Just change the function signature , And put the code above null Change to b that will do :
/** Reverse the interval [a, b) The elements of , Attention is left closed, right open */
ListNode reverse(ListNode a, ListNode b) {
ListNode pre, cur, nxt;
pre = null; cur = a; nxt = a;
// while Just change the termination conditions
while (cur != b) {
nxt = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = nxt;
}
// Returns the inverted head node
return pre;
}
PS: I've seriously written about 100 Multiple original articles , Hand brush 200 Daoli is the subject , All published in labuladong A copy of the algorithm , Continuous updating . Recommended collection , Write the title in the order of my article , Master all kinds of algorithm set, then put into the sea of questions, like fish .
Now we iteratively implement the function of reversing part of the linked list , Next, I'll write it according to the previous logic reverseKGroup Function :
ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null) return null;
// Section [a, b) contain k Elements to be reversed
ListNode a, b;
a = b = head;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
// Insufficient k individual , There is no need to reverse ,base case
if (b == null) return head;
b = b.next;
}
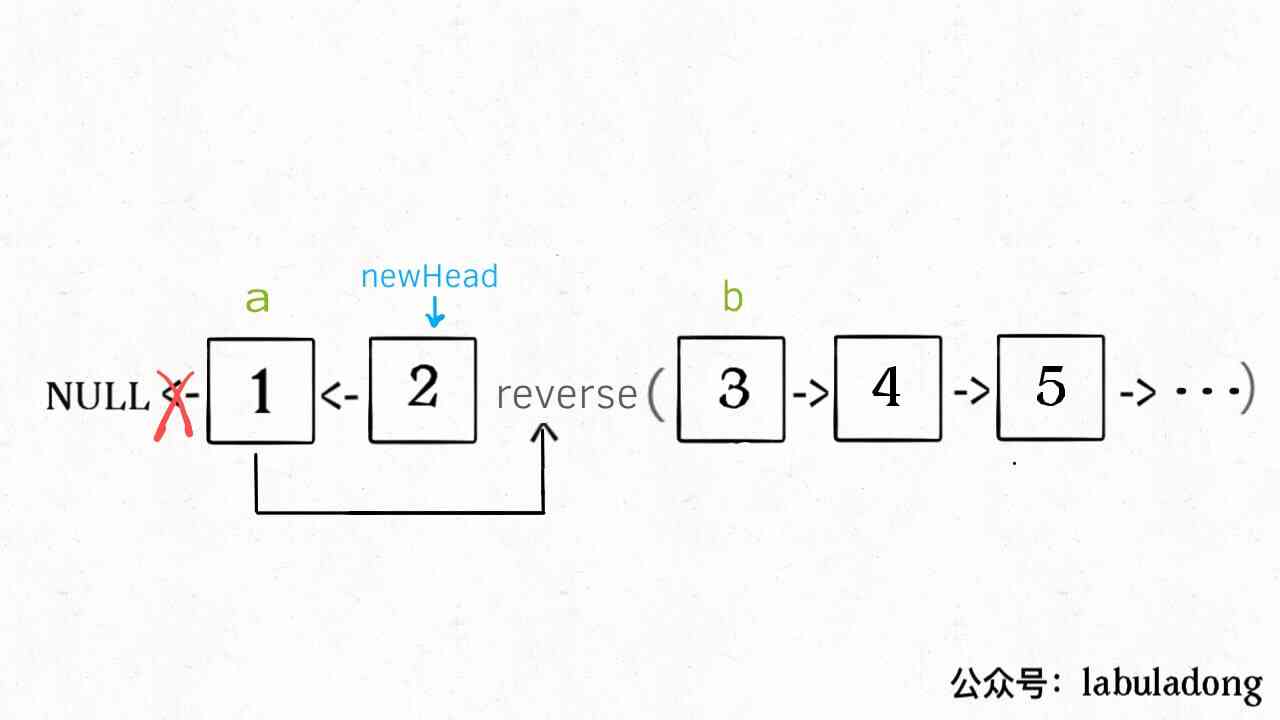
// Before reversal k Elements
ListNode newHead = reverse(a, b);
// Recursively reverses subsequent linked lists and joins them
a.next = reverseKGroup(b, k);
return newHead;
}
Explain it. for A few lines of code after the loop , Be careful reverse The function is an inverse interval [a, b), So the situation is like this :
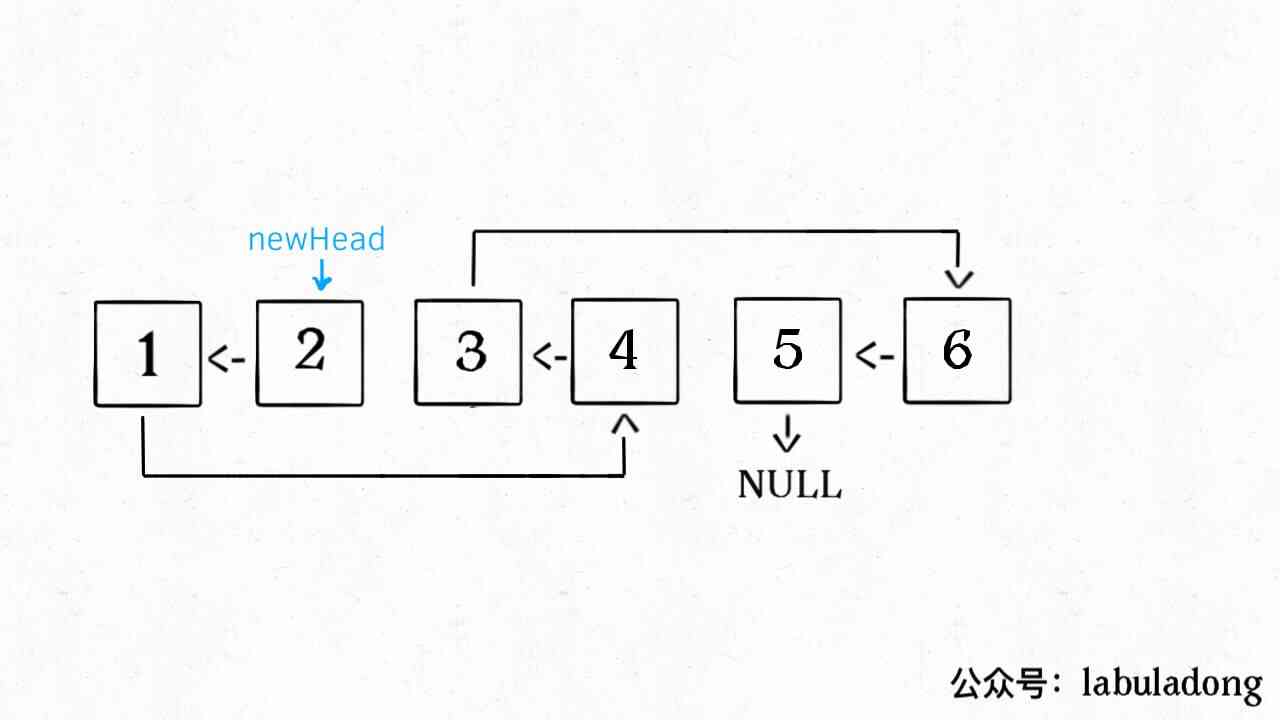
The recursive part is not expanded , This is the result of the recursion of the entire function , It's completely in line with the meaning of the question :
3、 ... and 、 Finally, say two words
In terms of the amount of reading , The basic data structure related algorithm articles are not many people , I'd like to say that it's going to suffer .
People like to look at dynamic planning issues , Maybe because interviews are very common , But I understand it personally , A lot of algorithmic ideas are derived from data structure . One of the famous names of our official account. ,「 Frame thinking of learning data structure 」 Just mentioned , What moving rules 、 to flash back 、 Divide and conquer algorithm , It's all tree traversal , The structure of tree is not a multi cross linked list ? You can deal with basic data structures , Solving general algorithmic problems should not be too laborious .
So how to decompose the problem 、 What about recursion ? This can only be practiced more , Maybe we can write a special article to discuss , This is the end of this article , Hopefully that helped !
_____________
my Online e-books Yes 100 Original articles , Hands with brushes 200 Daoli is the subject , Recommended collection ! Corresponding GitHub Algorithm Repository We've got it 70k star, Welcome to mark star !