当前位置:网站首页>1. Introduction to generating countermeasures network
1. Introduction to generating countermeasures network
2022-06-30 20:23:00 【C--G】
GAN brief introduction (Generative Adversarial Nets)

Thief (Generator Network) Through random variables (Random Vector) Generate fake money (Fake Image) Deposit into bank (Discriminator Network), Banks use real money (Real Image)、 Fake money (Fake Image) Learn to judge the fake money of thieves , Cycle the above steps .
The thief wanted the bank to judge the fake money as real money , So fake money ( Tag value is true ) Leave it to the bank for judgment , Get feedback from the bank loss, This is used for update iterations , Optimize counterfeiting technology
The bank hopes to accurately judge the real and counterfeit money , So at the same time, the thief's fake money ( Tag value is false )、 And real money for training ( Tag value is true ) Training , This is used for update iterations
Loss function

import torch
from torch import autograd
import torch.nn as nn
import math
input = autograd.Variable(torch.tensor([
[1.9072, 1.1079, 1.4906],
[-0.6548, -0.0512, 0.7608],
[-0.0614, 0.6583, 0.1095]
]))
print(input)
print('-' * 100)
m = nn.Sigmoid()
print(m(input))
print('-' * 100)
target = torch.FloatTensor([
[0, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0]
])
print(target)
print('-' * 100)
r11 = 0 * math.log(0.8707) + (1 - 0) * math.log((1 - 0.8707))
r12 = 1 * math.log(0.7517) + (1 - 1) * math.log((1 - 0.7517))
r13 = 1 * math.log(0.8162) + (1 - 1) * math.log((1 - 0.8162))
r21 = 1 * math.log(0.3419) + (1 - 1) * math.log((1 - 0.3419))
r22 = 1 * math.log(0.4872) + (1 - 1) * math.log((1 - 0.4872))
r23 = 1 * math.log(0.6815) + (1 - 1) * math.log((1 - 0.6815))
r31 = 0 * math.log(0.4847) + (1 - 0) * math.log((1 - 0.4847))
r32 = 0 * math.log(0.6589) + (1 - 0) * math.log((1 - 0.6589))
r33 = 0 * math.log(0.5273) + (1 - 0) * math.log((1 - 0.5273))
r1 = -(r11 + r12 + r13) / 3
r2 = -(r21 + r22 + r23) / 3
r3 = -(r31 + r32 + r33) / 3
bceloss = (r1 + r2 + r3) / 3
print(bceloss)
print('-' * 100)
# torch need Sigmoid
loss = nn.BCELoss()
print(loss(m(input), target))
print('-' * 100)
# torch Unwanted Sigmoid
loss = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
print(loss(input, target))
print('-' * 100)

CycleGan
brief introduction
- Realization effect

- No pairing data is required


How to learn

generator Gab Make a fake horse from a real zebra , Fake horse passing Gba Generate fake zebras , False zebra and real zebra produce L2 Loss , Iterative optimizationOverall network architecture

PatchGAN

Entry test
- Source code address
https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix
- Data download
Open the file as text
Copy download link

- Trained parameter weights

https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/scripts/download_cyclegan_model.sh#L3
http://efrosgans.eecs.berkeley.edu/cyclegan/pretrained_models/
Will download okay horse2zebra.pth Files in pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix-master\checkpoints\horse2zebra_pretrained Next , And change the name to latest_net_G.pth
- Start the test
Test parameters
--dataroot datasets/horse2zebra/testA
--name horse2zebra.pth_pretrained
--model test --no_dropout
# Use cpu
--gpu_ids -1

stay pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix-master\results\horse2zebra_pretrained\test_latest Save the results under 
open index.html

visdom
CycleGan Use during training visdom As a visualization tool , Start before training visdom
pip install visdom
python -m visdom.server
stargan


- What is the star
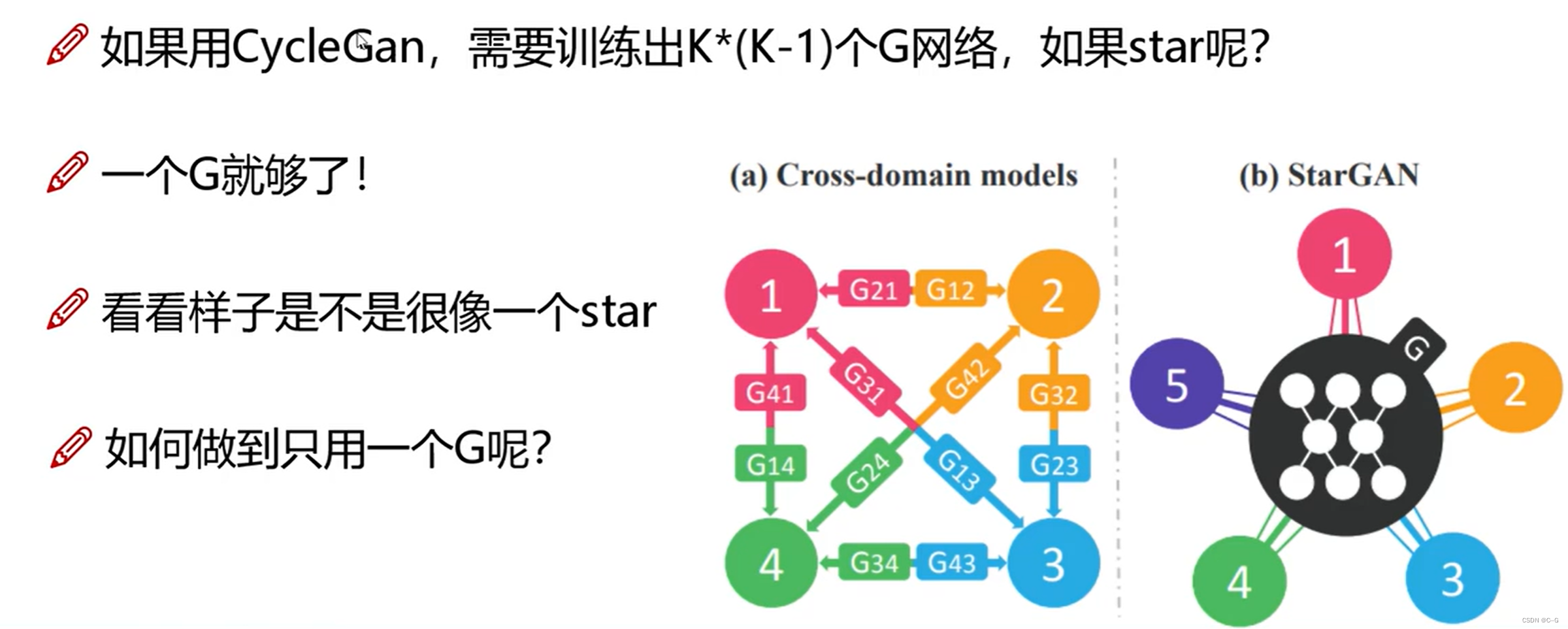
- The basic idea

- Overall process


Input picture and coding features , Get fake photos through the generator , Then the fake photos are generated to get the real photos , And compare with the original drawing , Narrow the gap between the real photos and the original pictures
stargan Use coding instead of style , Not very characteristic , Not involved in the calculation
- Expand : Sound transformer

stargan-v2


- Overall network architecture

- Encoder training (Style reconstruction)

- Diversified training (Style diversification)

- cycle loss

The code analysis
- Source download
https://github.com/clovaai/stargan-v2 - Import the necessary packages
conda create -n stargan-v2 python=3.6.7
conda activate stargan-v2
conda install -y pytorch=1.4.0 torchvision=0.5.0 cudatoolkit=10.0 -c pytorch
conda install x264=='1!152.20180717' ffmpeg=4.0.2 -c conda-forge
pip install opencv-python==4.1.2.30 ffmpeg-python==0.2.0 scikit-image==0.16.2
pip install pillow==7.0.0 scipy==1.2.1 tqdm==4.43.0 munch==2.5.0
- generator
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, img_size=256, style_dim=64, max_conv_dim=512, w_hpf=1):
super().__init__()
dim_in = 2**14 // img_size
self.img_size = img_size
self.from_rgb = nn.Conv2d(3, dim_in, 3, 1, 1)
self.encode = nn.ModuleList()
self.decode = nn.ModuleList()
self.to_rgb = nn.Sequential(
nn.InstanceNorm2d(dim_in, affine=True),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.Conv2d(dim_in, 3, 1, 1, 0))
# down/up-sampling blocks
repeat_num = int(np.log2(img_size)) - 4
if w_hpf > 0:
repeat_num += 1
for _ in range(repeat_num):
dim_out = min(dim_in*2, max_conv_dim)
self.encode.append(
ResBlk(dim_in, dim_out, normalize=True, downsample=True))
self.decode.insert(
0, AdainResBlk(dim_out, dim_in, style_dim,
w_hpf=w_hpf, upsample=True)) # stack-like
dim_in = dim_out
# bottleneck blocks
for _ in range(2):
self.encode.append(
ResBlk(dim_out, dim_out, normalize=True))
self.decode.insert(
0, AdainResBlk(dim_out, dim_out, style_dim, w_hpf=w_hpf))
if w_hpf > 0:
device = torch.device(
'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
self.hpf = HighPass(w_hpf, device)
def forward(self, x, s, masks=None):
x = self.from_rgb(x)
cache = {
}
for block in self.encode:
if (masks is not None) and (x.size(2) in [32, 64, 128]):
cache[x.size(2)] = x
x = block(x)
for block in self.decode:
x = block(x, s)
if (masks is not None) and (x.size(2) in [32, 64, 128]):
mask = masks[0] if x.size(2) in [32] else masks[1]
mask = F.interpolate(mask, size=x.size(2), mode='bilinear')
x = x + self.hpf(mask * cache[x.size(2)])
return self.to_rgb(x)

Normalized layer , At present, there are mainly these methods ,Batch Normalization(2015 year )、Layer Normalization(2016 year )、Instance Normalization(2017 year )、Group Normalization(2018 year )、Switchable Normalization(2018 year );
Will input the image shape Write it down as [N, C, H, W], The main difference between these methods is ,
- batchNorm Is in batch On , Yes NHW Normalization , Yes, small batchsize The result is bad ;
- layerNorm In the direction of the passage , Yes CHW normalization , Mainly for RNN The effect is obvious ;
- instanceNorm On the image pixels , Yes HW Normalization , Used in stylized migration ;
- GroupNorm take channel grouping , And then do normalization ;
- SwitchableNorm Yes, it will BN、LN、IN combination , Give weight to , Let the network learn the normalization layer by itself .

- Style feature code
class MappingNetwork(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, latent_dim=16, style_dim=64, num_domains=2):
super().__init__()
layers = []
layers += [nn.Linear(latent_dim, 512)]
layers += [nn.ReLU()]
for _ in range(3):
layers += [nn.Linear(512, 512)]
layers += [nn.ReLU()]
self.shared = nn.Sequential(*layers)
self.unshared = nn.ModuleList()
for _ in range(num_domains):
self.unshared += [nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(512, 512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(512, 512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(512, 512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(512, style_dim))]
def forward(self, z, y):
h = self.shared(z)
out = []
for layer in self.unshared:
out += [layer(h)]
out = torch.stack(out, dim=1) # (batch, num_domains, style_dim)
idx = torch.LongTensor(range(y.size(0))).to(y.device)
s = out[idx, y] # (batch, style_dim)
return s

- Judging device
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, img_size=256, num_domains=2, max_conv_dim=512):
super().__init__()
dim_in = 2**14 // img_size
blocks = []
blocks += [nn.Conv2d(3, dim_in, 3, 1, 1)]
repeat_num = int(np.log2(img_size)) - 2
for _ in range(repeat_num):
dim_out = min(dim_in*2, max_conv_dim)
blocks += [ResBlk(dim_in, dim_out, downsample=True)]
dim_in = dim_out
blocks += [nn.LeakyReLU(0.2)]
blocks += [nn.Conv2d(dim_out, dim_out, 4, 1, 0)]
blocks += [nn.LeakyReLU(0.2)]
blocks += [nn.Conv2d(dim_out, num_domains, 1, 1, 0)]
self.main = nn.Sequential(*blocks)
def forward(self, x, y):
out = self.main(x)
out = out.view(out.size(0), -1) # (batch, num_domains)
idx = torch.LongTensor(range(y.size(0))).to(y.device)
out = out[idx, y] # (batch)
return out

stargan-vc2
http://www.kecl.ntt.co.jp/people/kaneko.takuhiro/projects/stargan-vc2/index.html
- Sound transformer
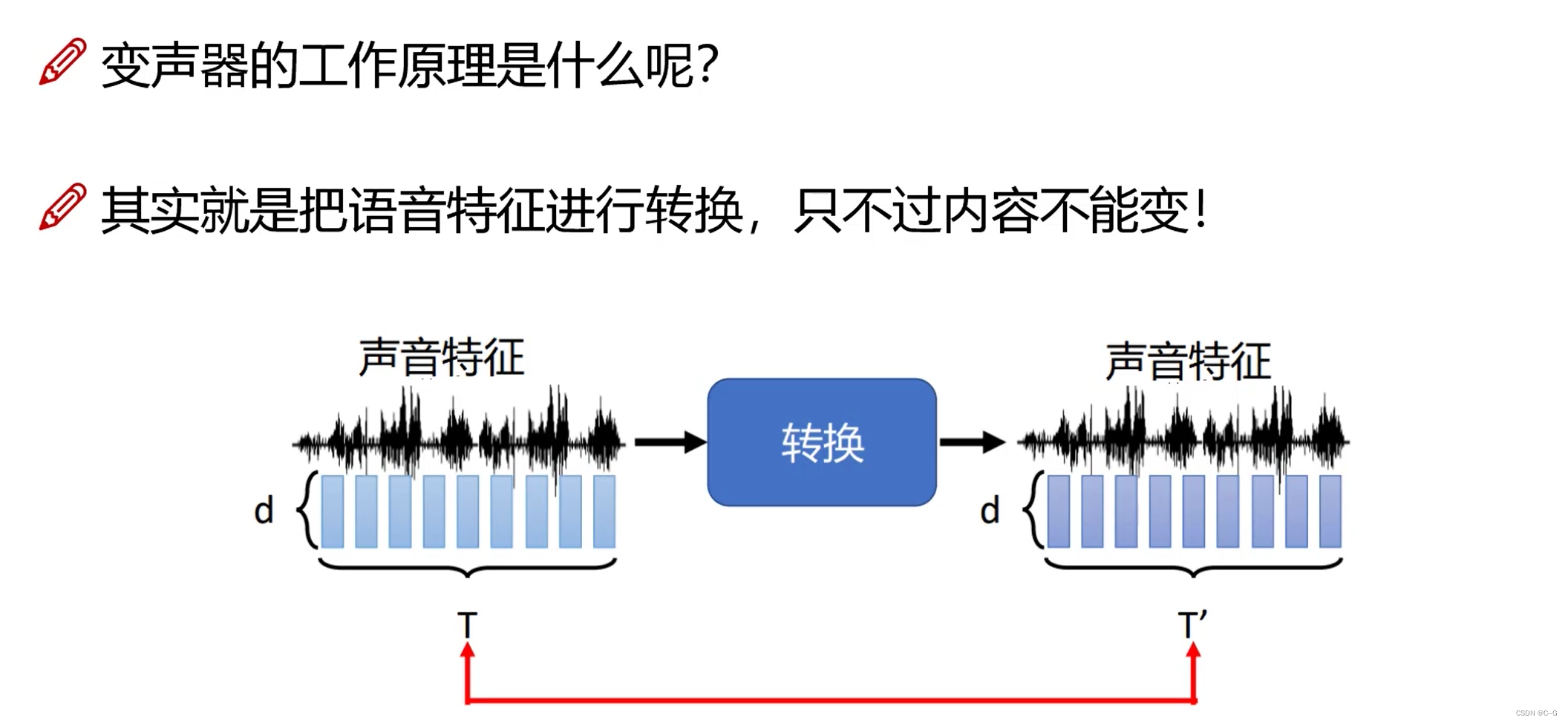

input data

Preprocessing

Feature summary

MFCC

generator

The components contained in linguistic data

Instance Normalization and Adaptive Instance Normalization

Instance Normalization

The content encoder only needs content , No linguistic features are required , So use Instance Normalization Normalize each feature map , Average the sound characteristics , Remove language featuresAdaIn

In Normalization removes linguistic features ,AdaIn Through additional FC Layers give language featuresPixelShuffle
Up sampling and down sampling : They are all old ways ,stride=2 Let's take a sample , Deconvolution to upsample
**PixelShuffle Layer is also known as sub-pixel convolution layer , It's a paper Real-Time Single Image and Video Super-Resolution Using an Efficient Sub-Pixel Convolutional Neural Network A convolution layer with up sampling function for super-resolution reconstruction is introduced in . This article ESPCN This paper introduces the function of this layer ,sub-pixel convolution layer With stride = 1 r stride=\frac{1}{r}stride= r1 (r rr by SR The magnification of upscaling factor) To extract feature map, Although it is called convolution , But it doesn't use any parameters that need to be learned , Its principle is very simple , Is to enter feature map Pixel reorganization , In other words, although the sub-pixel convolution layer is called convolution , But I didn't do any multiplication and addition , It's just another way to extract features :
**

The last layer shown above is the sub-pixel convolution layer , It is to format the input as ( b a t c h , r 2 C , H , W ) (batch,r^2C, H, W)(batch,r 2C,H,W) Of feature map The pixels in the same channel are extracted as output feature map A small piece of , Traverse the entire input feature map You can get the final output image . On the whole , It's like using 1r\frac{1}{r}r1 The step size is the same as convolution , This results in not convoluting the whole pixel , It's convolution of subpixels , Therefore, it is called sub-pixel convolution layer , The final output format is ( b a t c h , 1 , r H , r W ) (batch,1, rH,rW)(batch,1,rH,rW).
therefore , In a word ,PixelShuffle What the layer does is input feature map Pixel reorganization outputs high-resolution images feature map, Is an up sampling method , The specific expression is 
among r Is the upper sampling magnification ( Above picture r = 3)
- Judging device

Image super-resolution reconstruction (SPGAN)
- Network architecture

- The basic idea
Basic GAN Network thinking , The generator uses PixelShuffle Achieve super-resolution reconstruction , At the same time, in order to improve the detail effect , introduce vgg19, Put the false and true graphs generated by the generator into vgg19 Model extraction features , And extract the last layer of characteristic graph to calculate the loss , Add this loss to the generator loss
- Tools
Image completion
The paper :Globally and Locally Consistent Image Completion
Network architecture

Fully convolutional network , Do not limit the size of the input picture
Dilated Conv Cavity convolution Increase the receptive field replace pooling
Local Discriminator Local discriminant network Collect local information

Global Discriminator Global discriminant network Collect global information

Image generation network

The final synthetic network

MSE Loss

By generating the image and the original MSE Loss , Avoid over relying on the feature judgment of the discriminatorCalculate the loss step by step
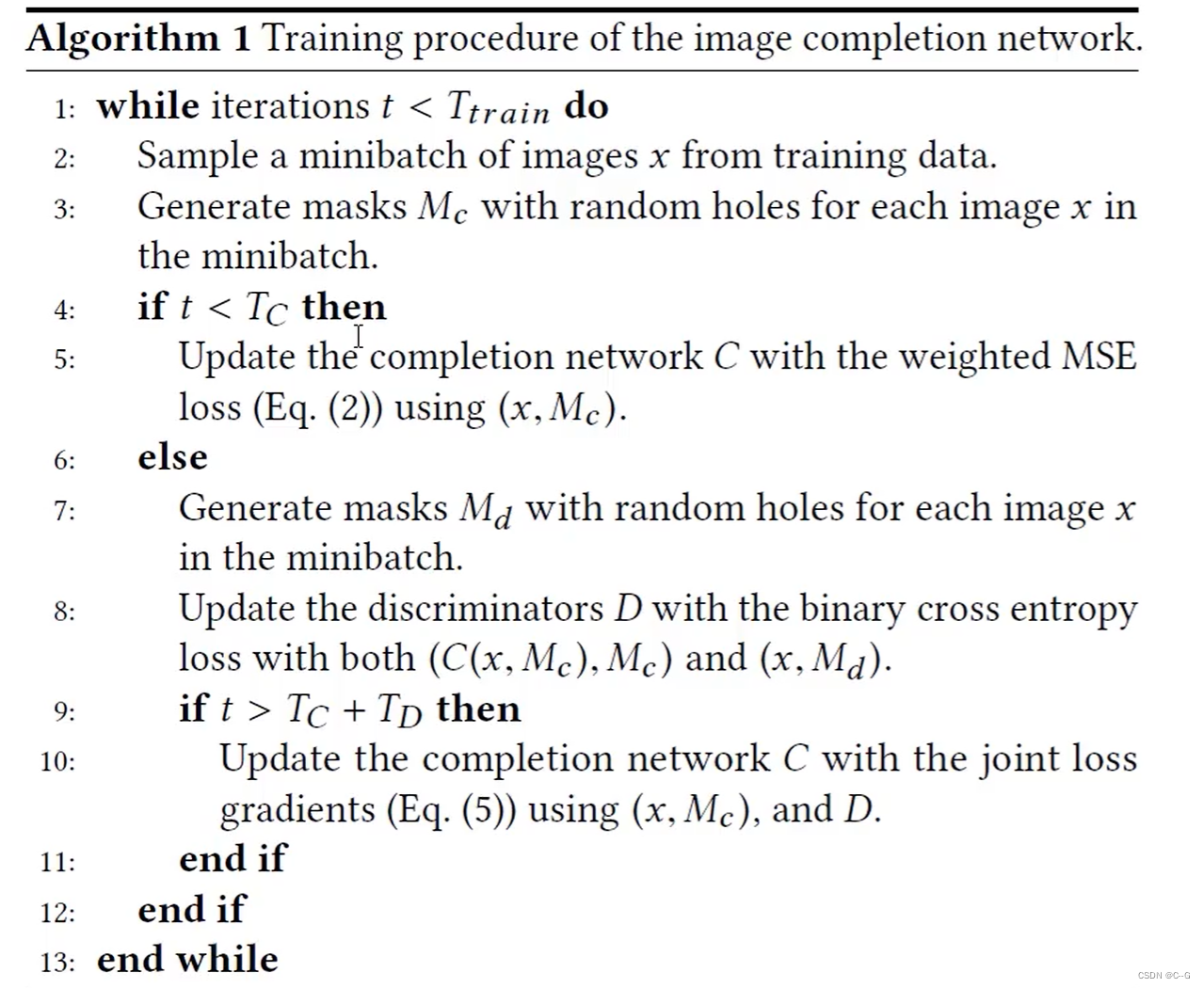
front Tc Calculation only in the next iteration MSE Loss , When t Greater than TC Less than Tc+Td Calculate the discriminator loss , When t Greater than Tc+Td Hourly calculation MSE And discriminator loss
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

GeoServer安装
Source code analysis of redis ziplist compressed list

Why should offline stores do new retail?

25:第三章:开发通行证服务:8:【注册/登录】接口:接收并校验“手机号和验证码”参数;(重点需要知道【利用redis来暂存数据,获取数据的】的应用场景)(使用到了【@Valid注解】参数校验)

Detailed explanation of specific methods and steps for TCP communication between s7-1500 PLCs (picture and text)

GeoServer installation
![Jerry's touch key recognition process [chapter]](/img/ec/25d2d6fd26571e4fb642129a4eee1b.png)
Jerry's touch key recognition process [chapter]

昨晚 Spark Summit 重要功能发布全在这里(附超清视频)

Data intelligence - dtcc2022! China database technology conference is about to open

NLP paper lead reading | what about the degradation of text generation model? Simctg tells you the answer
随机推荐
Openfire在使用MySQL数据库后的中文乱码问题解决
maya房子建模
Primary school, session 3 - afternoon: Web_ sessionlfi
Tensorflow2.4实现RepVGG
Meeting, onemeeting, OK!
[ICLR 2021] semi supervised object detection: unbiased teacher for semi supervised object detection
How unity pulls one of multiple components
PM这样汇报工作,老板心甘情愿给你加薪
Maya House Modeling
GeoServer installation
CV+Deep Learning——网络架构Pytorch复现系列——basenets(BackBones)(一)
静态类使用@Resource注解注入
Transport layer uses sliding window to realize flow control
Build your own website (20)
25: Chapter 3: developing pass service: 8: [registration / login] interface: receiving and verifying "mobile number and verification code" parameters; (it is important to know the application scenario
Jenkins can't pull the latest jar package
Heartbeat 与DRBD 配置过程
文件包含&条件竞争
CADD课程学习(2)-- 靶点晶体结构信息
Exness: the final value of US GDP unexpectedly accelerated to shrink by 1.6%
