当前位置:网站首页>【学习笔记之菜Dog学C】动态内存管理
【学习笔记之菜Dog学C】动态内存管理
2022-08-04 02:06:00 【姜君竹】
一、为什么存在动态内存管理
内存分为三个区,栈区、堆区和静态区(也被叫做数据段)。栈区用来存放局部变量、函数形参等临时变量;堆区用来进行动态内存开辟;静态区用来存放全局变量、静态变量等。
形如int val = 20;、char arr[10] = {0};的内存开辟方式是在栈空间上开辟的, 它空间开辟大小是固定的,并且在申明数组的时候,必须指定数组的长度,它所需要的内存在编译时分配。
但是有时我们需要的空间大小在程序运行的时候才能知道,那数组的编译时开辟空间的方式就不能满足了,这时候就只能试试动态存开辟了。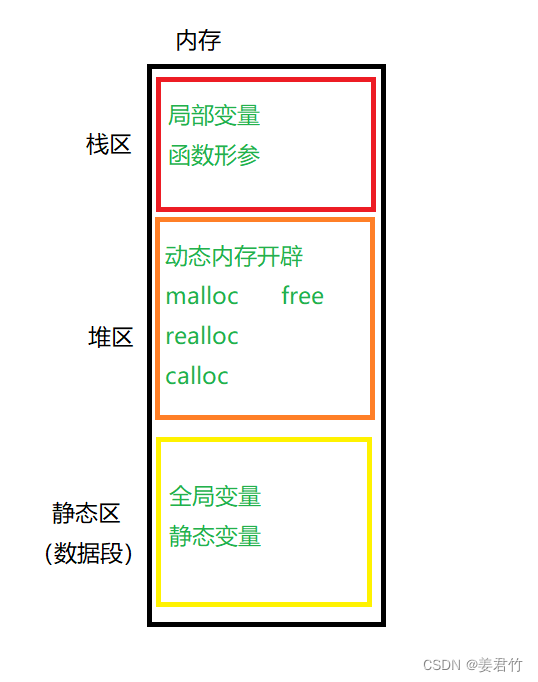
二、动态内存介绍
1、malloc函数和free函数
- malloc函数介绍
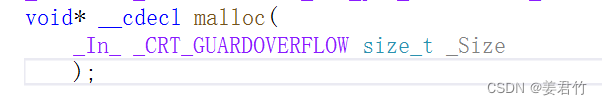
这个函数向内存申请一块连续可用的空间,并返回指向这块空间的指针;
如果开辟成功,则返回一个指向开辟好空间的指针;
如果开辟失败,则返回一个NULL指针,因此malloc的返回值一定要做检查;
返回值的类型是 void* ,所以malloc函数并不知道开辟空间的类型,具体在使用的时候使用者自己来决定;
如果参数size为0,malloc的行为是标准是未定义的,取决于编译器。
- free函数介绍

C语言提供了另外一个函数free,专门是用来做动态内存的释放和回收的;
如果参数 ptr 指向的空间不是动态开辟的,那free函数的行为是未定义的;
如果参数 ptr 是NULL指针,则函数什么事都不做。
- 代码实例
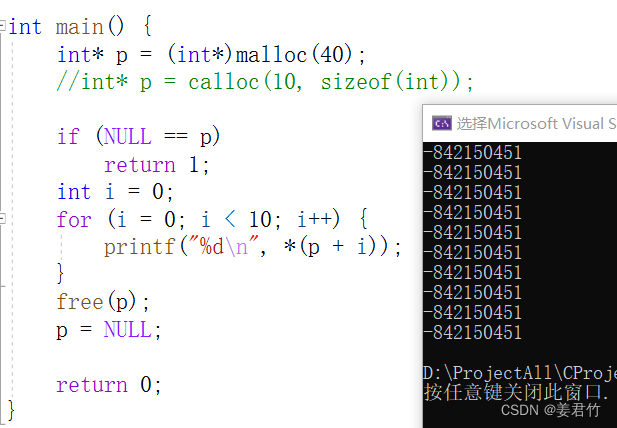
int main() {
//假设开辟10个整型空间 - 10* sizeof(int)
//动态内存开辟空间
int* p = (int*)malloc(10 * sizeof(int));//void*
//使用这些空间的时候
if (NULL == p) {
//printf + strerror
perror("main");//main:xxxxxxxxxxxxx
return 0;
}
//使用
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
*(p + i) = i;
printf("%d\n", *(p + i));
}
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
printf("%d ", p[i]);//p[i] --> *(p + i)
}
//回收空间
free(p);
p = NULL;//手动把p置为NULL,防止访问越界在,造成野指针
return 0;
}
malloc基本上和free是成对出现的。
2、calloc函数
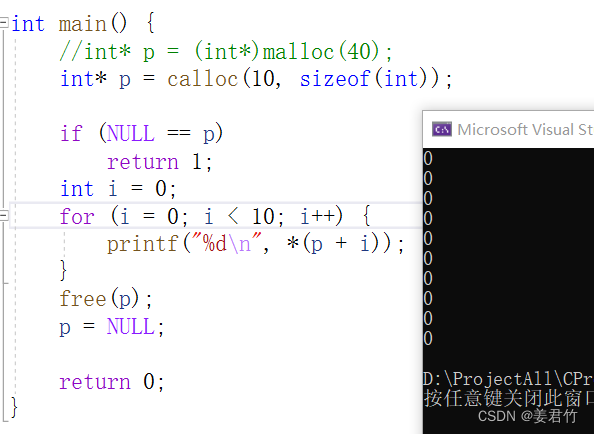
- calloc函数介绍

函数的功能是为num个大小为size的元素开辟一块空间,并且把空间的每个字节初始化为0;
与函数malloc的区别只在于calloc会在返回地址之前把申请的空间的每个字节初始化为全0。
- 代码实例
int main() {
int* p = calloc(10, sizeof(int));
if (NULL == p)
return 1;
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
printf("%d\n", *(p + i));
}
free(p);
p = NULL;
return 0;
}
3、realloc函数
- realloc函数介绍

ptr 是要调整的内存地址;
size 调整之后新大小;
返回值为调整之后的内存起始位置;
这个函数调整原内存空间大小的基础上,还会将原来内存中的数据移动到 新 的空间;
realloc在调整内存空间的是存在两种情况:
情况1:原有空间之后有足够大的空间
情况2:原有空间之后没有足够大的空间
情况一: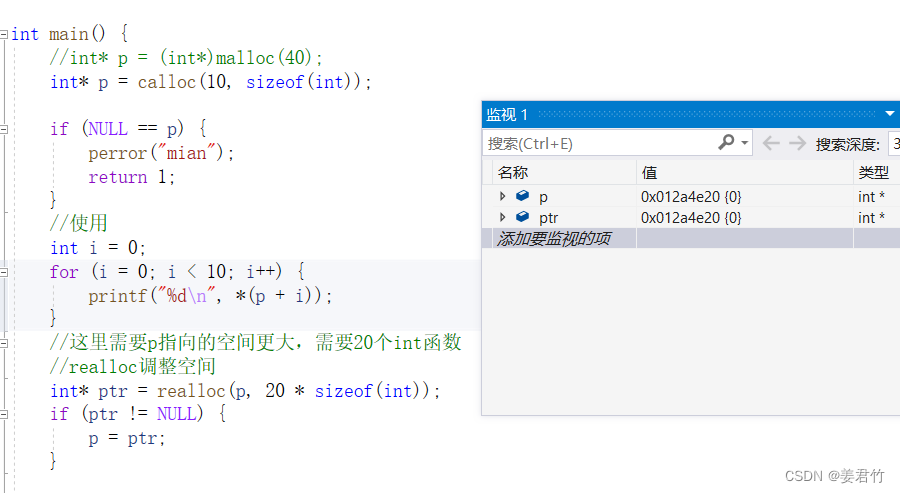
情况二: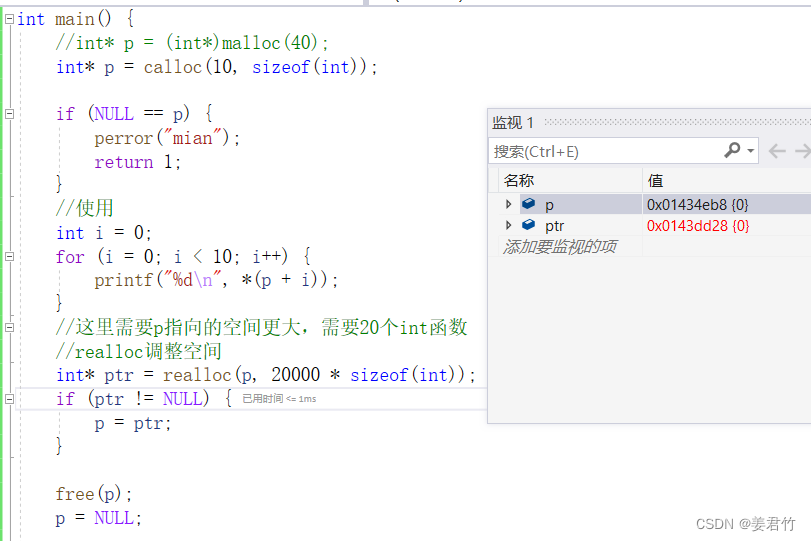
- 代码实例
int main() {
int* p = calloc(10, sizeof(int));
if (NULL == p) {
perror("mian");
return 1;
}
//使用
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
printf("%d\n", *(p + i));
}
//这里需要p指向的空间更大,需要20个int函数
//realloc调整空间
int* ptr = realloc(p, 20 * sizeof(int));
if (ptr != NULL) {
p = ptr;
}
free(p);
p = NULL;
return 0;
}
三、常见动态内存错误
- 对NULL指针进行解引用操作
void test()
{
int* p = (int*)malloc(INT_MAX / 4);
*p = 20;//如果p的值是NULL,就会有问题
free(p);
}
- 对动态开辟的空间越界访问
void test()
{
int i = 0;
int* p = (int*)malloc(10 * sizeof(int));
if (NULL == p)
{
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
for (i = 0; i <= 10; i++)
{
*(p + i) = i;//当i是10的时候越界访问
}
free(p);
}
- 对非动态开辟的内存使用free释放
void test()
{
int a = 10;
int* p = &a;
free(p);//ok?
}
- 使用free释放一块动态开辟内存的一部分
void test()
{
int* p = (int*)malloc(100);
p++;
free(p);//p不再指向动态内存的起始位置
}
- 对同一块动态内存多次释放
void test()
{
int* p = (int*)malloc(100);
free(p);
free(p);//重复释放
}
- 动态开辟内存忘记释放,导致内存泄露
void test()
{
int* p = (int*)malloc(100);
if (NULL != p)
{
*p = 20;
}
}
int main()
{
test();
while (1);
}
边栏推荐
- Summary of GNSS Articles
- 大佬们,读取mysql300万单表要很长时间,有什么参数可以优惠,或者有什么办法可以快点
- LDO investigation
- Flutter3.0线程——四步教你如何全方位了解(事件队列)
- Slipper - virtual point, shortest path
- 在Activity中获取另一个XML文件的控件
- appium软件自动化测试框架
- The browser
- JS 从零教你手写节流throttle
- Continuing to invest in product research and development, Dingdong Maicai wins in supply chain investment
猜你喜欢

mpf5_定价Bond_yield curve_Spot coupon_duration_有效利率_连续复利_远期_Vasicek短期_CIR模型Derivatives_Tridiagonal_ppf

实例035:设置输出颜色
5. Scrapy middleware & distributed crawler
Zabbix设置邮件告警+企业微信告警

持续投入商品研发,叮咚买菜赢在了供应链投入上
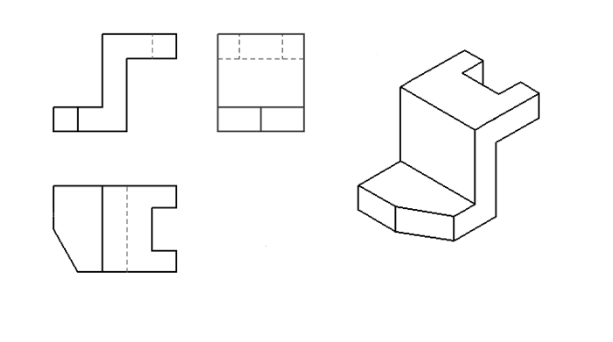
工程制图复习题(带答案)

Continuing to invest in product research and development, Dingdong Maicai wins in supply chain investment
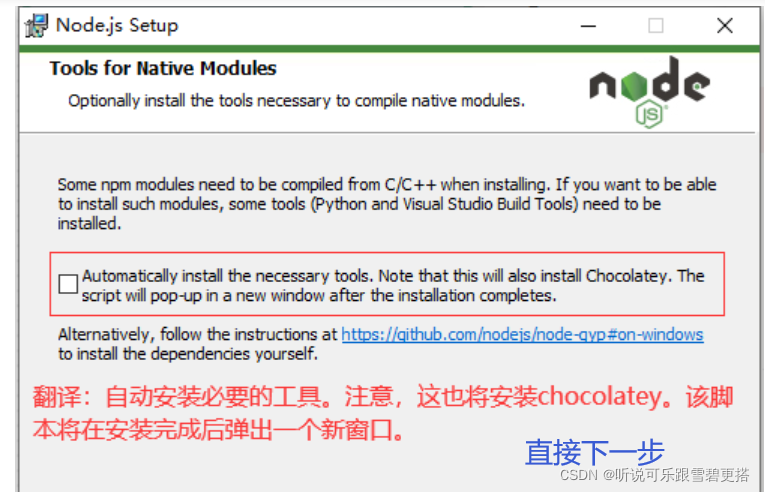
nodejs installation and environment configuration
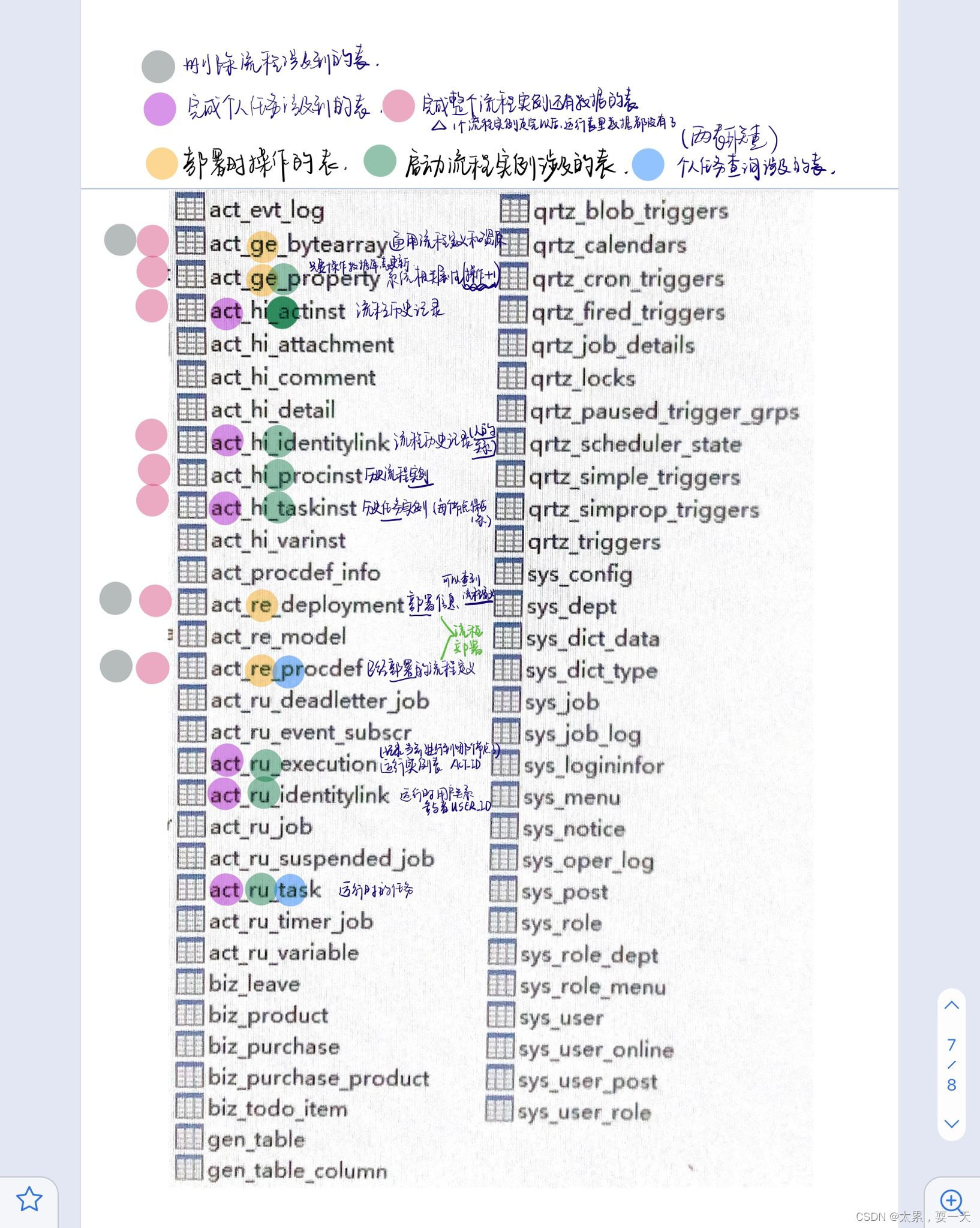
activiti流程执行过程中,数据库表的使用关系

织梦内核电动伸缩门卷闸门门业公司网站模板 带手机版【站长亲测】
随机推荐
STM32-遥感数据处理
The browser
Multithreading JUC Learning Chapter 1 Steps to Create Multithreading
JS 保姆级贴心,从零教你手写实现一个防抖debounce方法
Continuing to invest in product research and development, Dingdong Maicai wins in supply chain investment
实例036:算素数
Promise solves blocking synchronization and turns asynchronous into synchronous
C program compilation and predefined detailed explanation
织梦响应式酒店民宿住宿类网站织梦模板(自适应手机端)
内网穿透-应用
2022 China Computing Power Conference released the excellent results of "Innovation Pioneer"
安全至上:落地DevSecOps最佳实践你不得不知道的工具
C程序编译和预定义详解
Security First: Tools You Need to Know to Implement DevSecOps Best Practices
nodejs+express realizes the access to the database mysql and displays the data on the page
Example 041: Methods and variables of a class
yum 仅下载包
阿里云国际版基于快照与镜像功能迁移云服务器数据
idea中diagram使用
持续投入商品研发,叮咚买菜赢在了供应链投入上