当前位置:网站首页>[rust notes] 11 practical features
[rust notes] 11 practical features
2022-07-03 08:36:00 【phial03】
11 - Practical features
| Special type | brief introduction |
|---|---|
Drop | Deconstruction function . When clearing the value Rust Automatic clearing code |
Sized | Mark the special type , For the type of size you can know at compile time ( Instead of dynamically sized types like slices ) |
Clone | For types that support clone values |
Copy | Mark the special type , For types that can be cloned simply by copying the values contained in memory byte by byte |
Deref And DerefMut | Special type of smart pointer type |
Default | Reasonable for “ The default value is ” The type of |
AsRef And AsMut | Convert the special type , Borrow some kind of reference |
Borrow And BorrowMut | Convert the special type , similar AsRef And AsMut, But the additional guarantee of consistent hashing 、 Order and equal |
From And Into | Convert the special type , Convert a value of one type to another |
ToOwned | Convert the special type , Convert references to all values |
11.1-Drop
When the owner of a value leaves ,Rust It will automatically clear (Drop) This value . Clearing values involves releasing related values 、 Heap space , And the system resources owned by this value .
Rust Standard special type
std::ops::Drop:trait Drop { fn drop(&mut self); }Clearance can occur under various conditions , Including variables out of scope 、 The value of the expression is
;Operators discard 、 When truncating a vector, delete its elements from the end , wait .Designed for custom types
Drop:- Structure and special design
struct Appellation { name: String, nicknames: Vec<String> } trait Drop { fn drop(&mut self); } impl Drop for Appellation { fn drop(&mut self) { print!("Dropping {}", self.name); if !self.nicknames.is_empty() { print!(" (AKA {})", self.nicknames.join(", ")); } println!(""); } }- Test code :
fn main() { let mut a = Appellation { name: "Zeus".to_string(), nicknames: vec!["cloud collector".to_string, "king of the gods".to_string()] }; println!("before assignment"); a.drop(); a = Appellation { // After the second assignment , The first assignment is cleared name: "Hera".to_string(), nicknames:vec![] }; println!("at end of block"); a.drop(); } // a Out of scope , The second assignment is cleared- Results output
before assignment Dropping Zeus (AKA cloud collector, king of the gods) at end of block Dropping HeraIf the value of the variable is transferred to another place , Causes the variable to be uninitialized when it is out of scope ,Rust The variable will not be cleared , Because this variable has no value to clear . here ,Rust Will use an invisible flag to track the status of variables , This flag indicates whether the value of the variable needs to be cleared :
let p; { let q = Appellation { name: "Cardamine hirsuta".to_string(), nicknames: vec!["shotweed".to_string(), "bittercress".to_string()] }; if complicated_condition() { p = q; } } // q The scope of ends here println!("Sproing!"); // p The scope of ends hereIf a type implements
DropSpecial type , Can no longer be achievedCopySpecial type .- If a type contains
CopySpecial type , Then a simple byte to byte assignment will produce an independent copy of the value . - Call the same... Multiple times in the same data
dropThe method is wrong .
- If a type contains
The standard front-end module contains a function to clear the value :
fn drop<T>(_x: T) { }- Receive the value of a parameter , Take ownership from the caller , Then do nothing .
- Rust When out of scope , eliminate
_xValue , Just like clearing the values of other variables .
11.2-Sized
Fixed size types (sized type): Its value has the same size in memory .
- Every
u64Occupy 8 Bytes . - Every
(f32, f32, f32)Tuple proportion 12 Bytes . - For enumeration types , Its value always takes up the space that can save its largest variation .
Vec<T>Have a variable size buffer allocated on the heap , howeverVecThe value itself contains a pointer to the buffer 、 Buffer capacity and its length . thereforeVec<T>It is also a fixed size type .
- Every
Non fixed size type (unsized type): The size of its value in memory is not fixed . Such as
strand[T]Type represents a collection of values of uncertain size , So they are non fixed size .- String slice type
str( Note that there is no&) It is non fixed size . Literal of a string"diminutive"and"big"It's right 19 and 3 bytestrReferences to slices . - Such as
[T]( Again, there is no&) Such array slice types are also non fixed size , Shared references&[u8]Can point to any size[u8]section .
- String slice type
The reference to the special target is also a non fixed size type .
- A feature target is a pointer to a value that implements a given feature . Such as
&str::io::WriteandBox<std::io::Write>All point to the implementationWritePointer to a value of a special type . - The reference target may be a file 、 A network socket , Or it does
WriteThe custom type of . - Because of the realization of
WriteThe type of is extensible , allWriteAs a type, it is considered to be non fixed size , That is, the size of its value is variable .
- A feature target is a pointer to a value that implements a given feature . Such as
The last field of the structure may be of non fixed size . here , The structure itself is also of non fixed size .
Rc<T>The reference count pointer is internally implemented as a pointer to a private typeRcBox<T>The pointer to , This type is used to save the typeTAnd its reference count .struct RcBox<T: Sized> { ref_count: usize, value: T, // }valueThe value of the field isT, Save itRc<T>Reference count of .Rc<T>Dereference is a pointer to this field .ref_countField saves the reference count .
Pointers to non fixed size values are fat pointers , Two words wide .
- Fat pointers contain both pointers to slices , It also includes the length of the slice .
- The special target also contains a pointer to the virtual table implemented by the method .
All fixed size types are implemented
std::marker::SizedSpecial type , This feature has no method or association type .- Rust This feature is automatically implemented for all types it applies .
- Developers cannot implement it by themselves .
Application scenarios : Bind type variables .
T: Sizedbinding , requirementTIt must be a type of known size at compile time .- This type is called marked type (marker trait), Some types can be marked as having characteristics of interest .
Most generic variables are by default Rust Limited to the use of
Sizedtype .struct S<T> {...}Will be Rust Understood as astruct S<T: Sized> {...}.- If the developer writes
struct S<T: ?Sized> {b: Box<T>}( Its meaning is “ Is not necessarilySized”), that Rust Will allow the use ofS<str>andS<Write>, Defined as fat pointer ; It's also allowed to useS<i32>andS<String>, Defined as a normal pointer .
I don't know whether to fix the size (questionably sized): Type variables have
?Sizedbinding , This makes this type possibleSized, Maybe not .
11.3-Clone
std::clone::CloneSpecial type : Applicable to types that can copy themselves .trait Clone: Sized { fn clone(&self) -> Self; fn clone_from(&mut self, source: &Self) { // take self It is amended as follows source A copy of . *self = source.clone() } }Rust Do not automatically clone values , Instead, it requires an explicit call to a method :
- Cloning a value usually involves creating a copy of everything the value has and allocating memory , therefore
cloneNo matter in time consumption or memory consumption , May be more expensive . - Such as clone
Vec<String>It's not just about copying vectors , Also copy all that it containsSringElements . Rc<T>andArc<T>Such a reference count pointer is an exception , Cloning them intelligently simply increments the corresponding reference count , Then return the new pointer .
- Cloning a value usually involves creating a copy of everything the value has and allocating memory , therefore
Yes
CloneExamples of special types : Many meaningful types of replication operations , It's all doneClone.- The original type
boolandi32; - Container type
String、Vec<T>andHashMap;
- The original type
nothing
CloneExamples of special types : Some types do not make sense to implement replication .std::sync::Mutex;std::fs::FileReplication fails when the operating system has no necessary resources . But it provides atry_cloneMethod , This method returns an error reportstd::io::Result<File>.
Cloning must be foolproof .
11.4-Copy
Assignment will transfer the value , Instead of copying values . Transferring values is more conducive to tracking the resources owned by variables .
A simple type that does not own any resources can be
Copytype , This type of assignment produces a copy of the value , Instead of transferring values and making the original variable uninitialized .If the type implements
std::marker::CopyMark the special type , So it's going to beCopytype .trait Copy: Clone { }It is also very simple to implement custom types :
impl Copy for MyType { }Realization
CopyThe type of must comply with the rules :- Rust Only allow types to be implemented when byte to byte deep replication meets the requirements
Copy. - Those who may have any resources , For example, the type of heap buffer or operating system hook , Can't achieve
Copy. - Any implementation
DropThe type of special type cannot beCopy. If a type requires special cleanup code , Then you must need special copy code , So it can't beCopytype .
- Rust Only allow types to be implemented when byte to byte deep replication meets the requirements
Special type derivation :
#[derive(Copy)]Let the type deriveCopy;#[derive(Clone, Copy)]Let types derive at the same timeCloneandCopy.
11.5-Deref And DerefMut
std::ops::DerefAndstd::ops::DerefMutThe special type can modify the dereference operator*and.Behavior on custom types .Box<T>andRc<T>Such a pointer type implements these two special types . If there is aBox<Complex>Type valueb, that*bThe quote isbPoint toComplexValue , andb.reIt refers to the actual number of parts .- Context assignment , And borrowing modifiable references from reference targets , Then you can use
DerefMut( Variable dereference ) Special type . DerefOnly get read-only permission .
Definition of special type :
trait Deref { type Target: ?Sized; fn deref(&self) -> &Self::Target; } trait DerefMut: Deref { fn deref_mut(&mut self) -> &mut Self::Target; }derefandderef_mutMethod reception&SelfQuote and return&Self::Targetquote .TargetyesSelfcontain 、 Owned or referenced resources . aboutBox<Complex>Come on ,TargetThe type ofComplex.DerefMutyesDerefAn extension of : If you can dereference and modify resources , Then you can borrow a shared reference to it .- The references returned by these two methods have the same as
&selfThe same long life span , thereforeselfIt will always be borrowed during the life of the returned reference .
Dereference forced transformation (deref coercion): One type is “ mandatory ” Show another type of behavior . Such as the implementation
DerefMutYou can realize the type conversion of modifiable references .- about
Rc<String>Valuer, If you want to call itString::find, Then you can simply writer.find('?'). here&Rc<String>Be coerced into&String, becauseRc<T>RealizedDeref<Target=T>. - Can be in
StringUseSplit_atOther methods , Even ifSplit_atyesStrSlice type method , becauseStringRealizedDeref<Target=str>. here&StringForced transition to&str. - If byte vector
v, Pass it an expected byte slice&[u8]Function of , Then you can put&vAs a parameter , becauseVec<T>RealizedDeref<Target=[T]>. - Rust Will not try to dereference forced transformation to meet the type variable binding .
- about
11.6-Default
All types with default values are implemented
std::default::DefaultSpecial type :trait Default { fn default() -> Self; }StringYesDefaultThe implementation of is as follows :impl Default for String { fn default() -> String { String::new() } }DefaultIt can represent a large number of parameter sets ( Most parameters usually do not need to be changed ) The default value generated by the structure of .If type
TRealizedDefault, Then the standard library will automatically beRc<T>、Arc<T>、Box<T>、Cell<T>、RefCell<T>、Cow<T>、Mutex<T>andRwLock<T>RealizationDefault.- If all element types of tuple type are implemented
Default, And the tuple type also implementsDefault, Then this tuple will hold the default value of each element by default . - If all fields of the structure are implemented
Default, You can use#[derive(Default)]Automatically implement for the structureDefault. - whatever
Option<T>The default values of areNone.
- If all element types of tuple type are implemented
11.7-AsRef And AsMut
If a type implements AsRef<T>, Then you can borrow one from it &T. namely AsRef Is a shared reference , Again AsMut That is, modifiable references .
trait AsRef<T: ?Sized> {
fn as_ref(&self) -> &T;
}
trait AsMut<T: ?Sized> {
fn as_mut(&mut self) -> &mut T;
}
11.8-Borrow And BorrowMut
If a type implements
Borrow<T>, So it'sborrowMethods can effectively borrow one from themselves&T. differAsRef: Only when&TWhen it has the same hash and comparison characteristics as the value it borrows , A type can be implementedBorrow<T>.trait Borrow<Borrowed: ?Sized> { fn borrow(&self) -> &Borrowed; }Application scenarios :
- It is often used to deal with keys in hash tables or trees .
- Handle values that will be hashed or compared for other reasons .
StringRealizedAsRef<str>、AsRef<u8>andAsRef<Path>, But these three target types usually have different hash values . Only&strSlicing ensures correspondence OfStringHave the same hash result , thereforeStringonlyBorrow<str>.
11.9-From And Into
std::convert::Fromandstd::convert::IntoSpecial type represents type conversion , That is, consume a type of value , Then return another type of value .AsRefandAsMutA special type is a reference borrowed from one type to another ;FromandIntoIs to take ownership of their parameters , Conversion type , Then return the ownership of the result to the caller .
// The definitions of these two types are symmetrical trait Into<T>: Sized { fn into(self) -> T; } trait From<T>: Sized { fn from(T) -> Self; }Each type in the standard library
TIt's all doneFrom<T>andInto<T>Special type .Use
IntoYou can make it more flexible to receive parameters :use std::net::Ipv4Addr; fn ping<A>(address: A) -> std::io::Result<bool> where A: Into<Ipv4Addr> { let ipv4_address = address.into(); ... }pingFunction can receiveIpv4AddrAs a parameter , You can also receiveu32or[u8; 4]Array of .u32and[u8; 4]Arrays of have been implementedInto<Ipv4Addr>Special type .Call the above feature :
println!("{:?}", ping(Ipv4Addr::new(23, 21, 68, 141))); // Pass in Ipv4Addr println!("{:?}", ping([66, 146, 219, 98])); // Pass in [u8; 4] println!("{:?}", ping(0xd076eb94_u32)); // Pass in u32
FromonlyFrom<[u8; 4]>andFrom<u32>:let addr1 = Ipv4Addr::from([66, 146, 219, 98]); let addr2 = Ipv4Addr::from(0xd076eb94_u32);In the process of conversion, the resources of the original value can be used to build the converted value .
let text = "Beautiful Soup".to_string(); let bytes: Vec<u8> = text.into();
11.10-ToOwned
CloneAchieved the cloning of the reference target ;ToOwnedThen it realizes the cloning of referencing itself . It can convert references to values of all types :trait ToOwned { type Owned: Borrow<Self>; fn to_owned(&self) -> Self::Owned; // It can be returned and borrowed as &Self Any type of }It can be downloaded from
Vec<T>Borrow a&[T], therefore[T]Can achieveToOwned<Owned=Vec<T>>.strRealizedToOwned<Owned=String>;PathRealizedToOwned<Owned=PathBuf>;
11.11-Borrow And ToOwned example
Whether a function should receive parameters by reference or by value , In some cases, it is more appropriate to decide whether to borrow or acquire ownership when the program is running . In response to this problem ,
std::borrow::CowIt can realize write time cloning (clone on write):enum Cow<'a, B: ?Sized + 'a> where B: ToOwned { Borrowed(&'a B), Owned(<B as ToOwned>::Owned), }Cow<B>You can borrow rightBA shared reference to ;- You can also have a value , Then borrow such a reference .
CowUse of : Returns statically allocated string constants or computed strings .Convert an error enumeration into a message : Most variants can be handled with fixed size strings , But some also need to include additional data in the message . I can return one
Cow<'static, str>:use std::path::PathBuf; use std::borrow::Cow; fn describe(error: &Error) -> Cow<'static, str> { match *error { Error::OutOfMemory => "out of memory".into(), Error::StackOverflow => "stack overflow".into(), Error::MachineOnFire => "machine on fire".into(), Error::Unfathomable => "machine bewildered".into(), Error::FileNotFound(ref path) => { format!("file not found: {}", path.display()).into() } } }describeIf the caller of does not need to modify the return value , You can putCowThink of it as a&str:println!("Disaster has struck: {}", describe(&error));When you need a caller of all types , It can also be easily obtained :
let mut log: Vec<String> = Vec::new(); ... log.push(describe(&error).into_owned());CowYou can putdescirbeAnd its caller can postpone memory allocation until necessary .
See 《Rust Programming 》( Jim - Brandy 、 Jason, - By orendov , Translated by lisongfeng ) Chapter 13
Original address
边栏推荐
- 详解sizeof、strlen、指针和数组等组合题
- Unity editor expansion - window, sub window, menu, right-click menu (context menu)
- Base64和Base64URL
- 图像处理8-CNN图像分类
- Cesium for unreal quick start - simple scenario configuration
- [concurrent programming] working mechanism and type of thread pool
- Unity Editor Extension - event handling
- Cesium service deployment, and import and display local 3dfiles data
- Golang 中string和int类型相互转换
- Unity interactive water ripple post-treatment
猜你喜欢
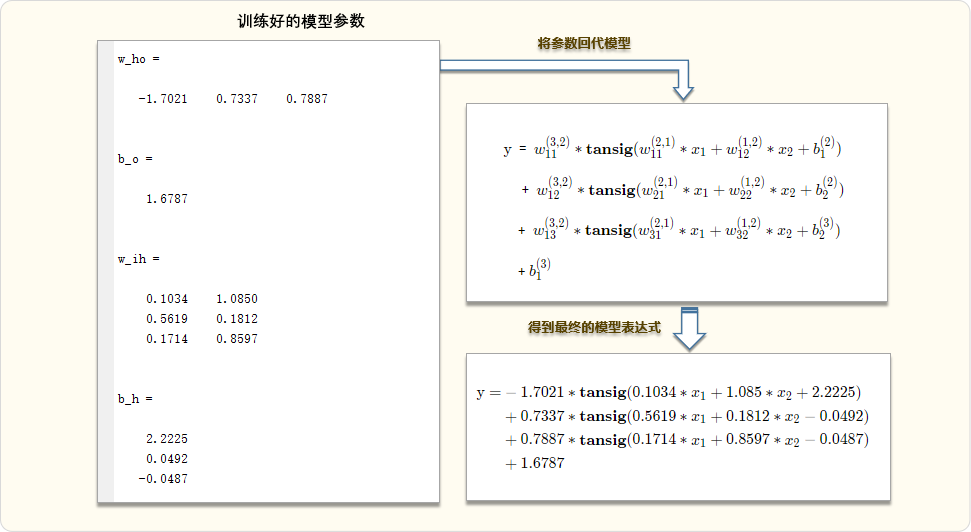
Simple demo of solving BP neural network by gradient descent method
![P1596 [USACO10OCT]Lake Counting S](/img/a7/07a84c93ee476788d9443c0add808b.png)
P1596 [USACO10OCT]Lake Counting S
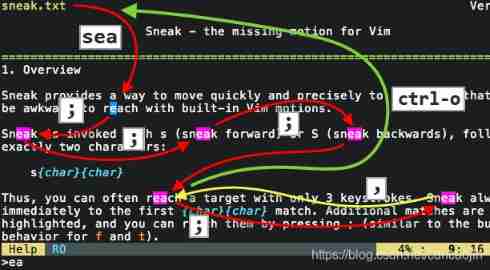
VIM learning notes from introduction to silk skating
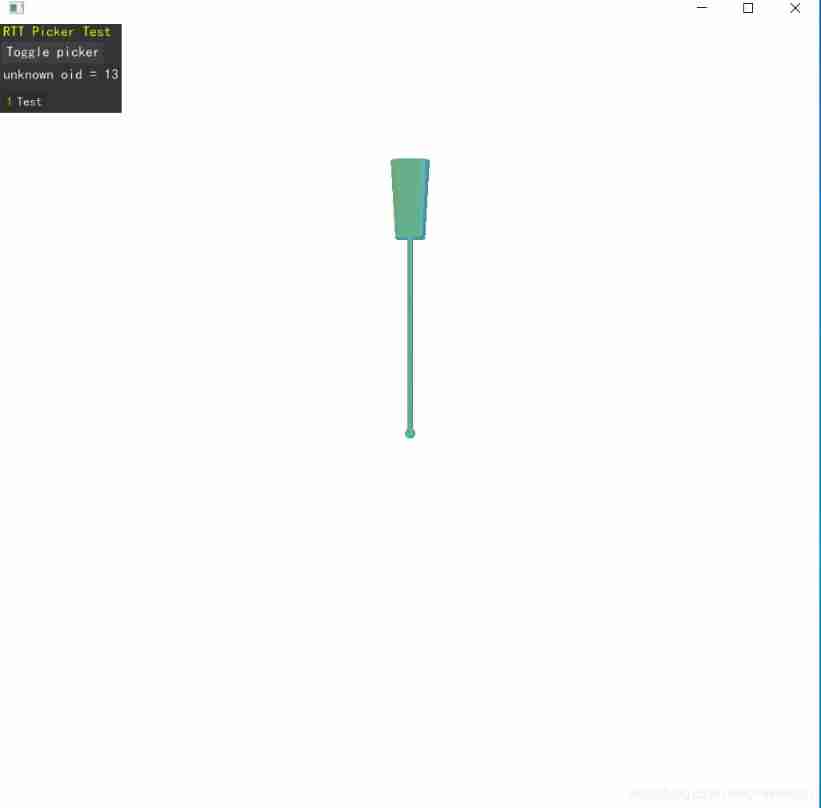
Osgearth target selection

Redis data structure
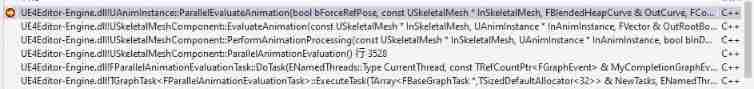
UE4 source code reading_ Bone model and animation system_ Animation process
![P1596 [USACO10OCT]Lake Counting S](/img/a7/07a84c93ee476788d9443c0add808b.png)
P1596 [USACO10OCT]Lake Counting S
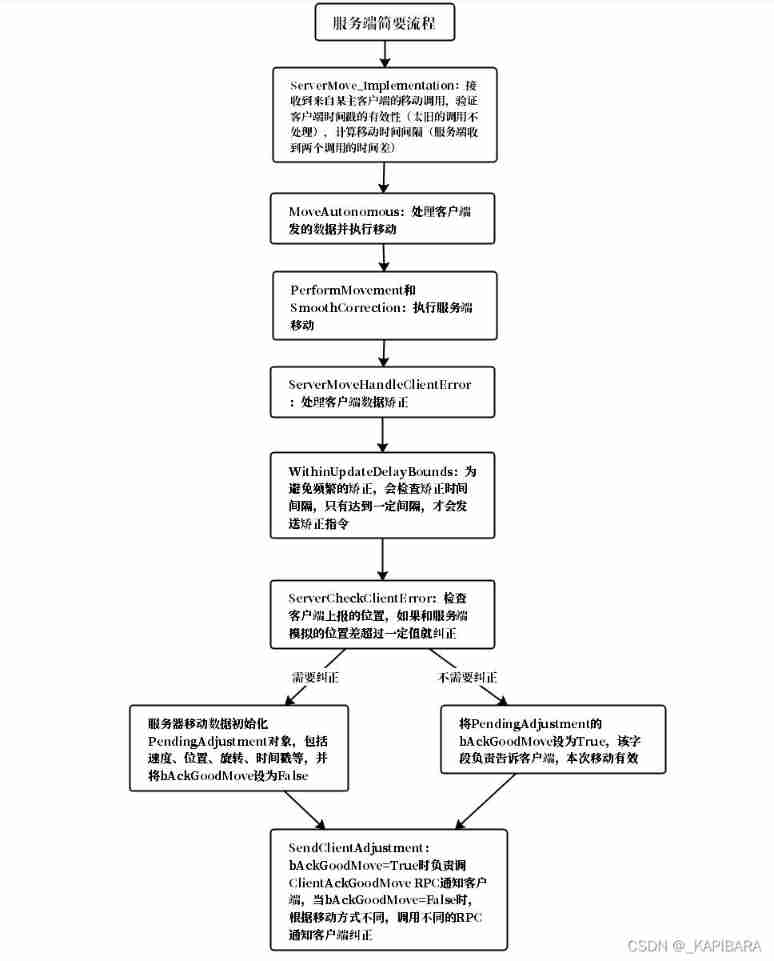
UE4 source code reading_ Mobile synchronization

MXone Pro自适应2.0影视模板西瓜视频主题苹果cmsV10模板
Campus lost and found platform based on SSM, source code, database script, project import and operation video tutorial, Thesis Writing Tutorial
随机推荐
Talking about: is the HashSet set ordered or disordered /hashset set unique, why can we store elements with the same content
Introduction to Base64 coding
【更新中】微信小程序学习笔记_3
Clion toolchains are not configured configure disable profile problem solving
Explain sizeof, strlen, pointer, array and other combination questions in detail
animation
C#课程设计之学生教务管理系统
UE4 source code reading_ Mobile synchronization
LinkedList set
Go resolve ID card
Golang 字符串分割,替换和截取
UE4 source code reading_ Bone model and animation system_ Animation compression
Jupyter remote server configuration and server startup
Thymeleaf 404 reports an error: there was unexpected error (type=not found, status=404)
简易入手《SOM神经网络》的本质与原理
producer consumer problem
【Rust笔记】06-包和模块
2021-10-19
UE4 source code reading_ Bone model and animation system_ Animation process
MXone Pro自适应2.0影视模板西瓜视频主题苹果cmsV10模板