当前位置:网站首页>Image processing 8-cnn image classification
Image processing 8-cnn image classification
2022-07-03 08:17:00 【< Hunter>】
Image processing series
The image processing 1- Classical spatial domain enhancement —— Grayscale mapping
The image processing 2- Classical spatial domain enhancement —— Histogram equalization
The image processing 3- Classical spatial domain enhancement —— Spatial filtering
The image processing 4- Fourier transform of the image
The image processing 5- Image noise
The image processing 6- Otsu image threshold segmentation
The image processing 7- Image enhancement
One 、 Content
(1) utilize Pytorch Simple to build CNN The network realizes image classification , And test the classification effect ( For more steps, please refer to https://www.stefanfiott.com/machine-learning/cifar-10-classifier-using-cnn-in-pytorch/);
(2) Modify the network model , New training , And test the classification effect ;
(3) Write the experiment report .
Two 、 Easy to use CNN Network for image classification
1. Import package
Use the figure 2.1 Code import package .
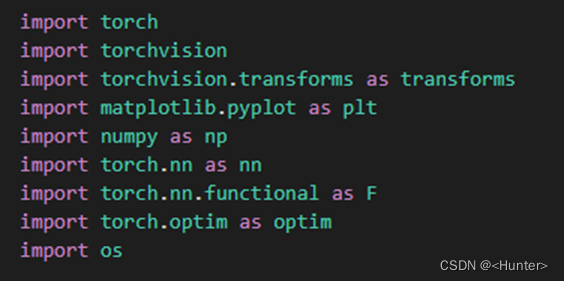
chart 2.1 Import package
2. Data download 、 Enhance and divide
Use the figure 2.2 Code for data download 、 Enhance and divide data sets .

chart 2.2 Data download 、 enhance 、 Divide
3. Neural network definition
Use the figure 2.3 The code defines a simple CNN neural network .

chart 2.3 The definition is simple CNN neural network
4. Define optimizer
Use the figure 2.4 Code definition optimizer .

chart 2.4 Define optimizer
5. Training and preserving Neural Networks
Use the figure 2.5 Code training definition model , And save , Output as shown in Figure 2.6.

chart 2.5 Neural network training and preservation

chart 2.6 Model training output
6. Testing neural networks
a. Accuracy rate
Use the figure 2.7 Code for , Calculate the accurate removal rate , Finally, the accuracy is 62.17%.

chart 2.7 Calculate the accuracy of the model
b. Calculate the classification accuracy of each category
Use the figure 2.8 The code calculates the accuracy of each category , The results are shown in the figure 2.9.

chart 2.8 Calculate the accuracy of each classification

chart 2.9 The accuracy of each classification
c. Draw the actual category and forecast classification curve
Use the figure 2.10 Code to draw , And output the size of each value , Pictured 2.11, The curve is as shown in the figure 2.12.
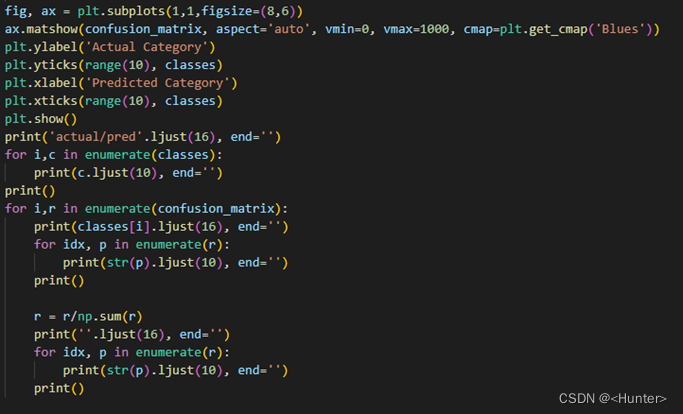
chart 2.11 Draw the actual category and forecast classification curve

chart 2.12 Plot the size of the actual category and the predicted classification value
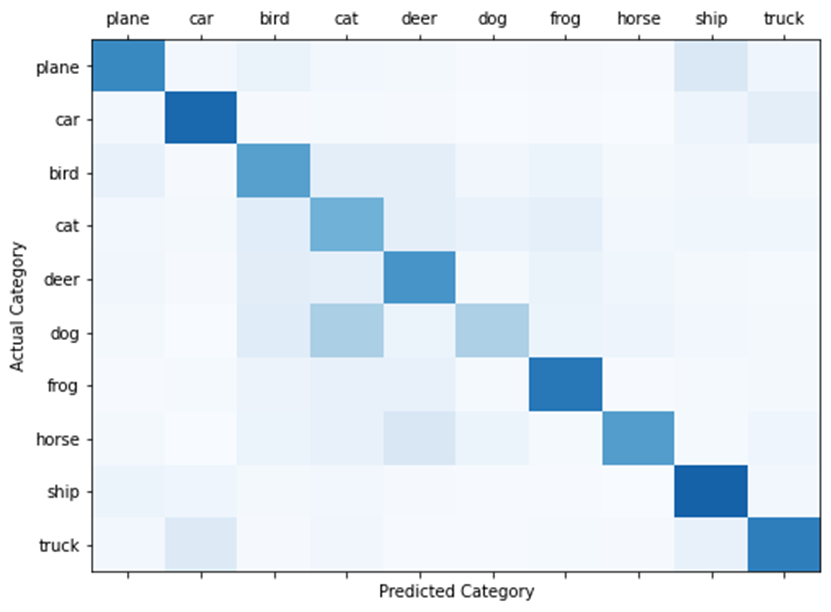
chart 2.13 Draw the curve of actual category and predicted classification value
3、 ... and 、Geogle Net Image classification
1. Import package
Use the figure 3.1 Code import package .
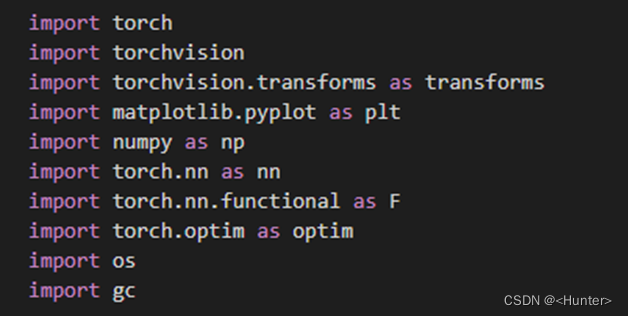
chart 3.1 Import package
2. Data import 、 Enhance and divide
Use the figure 3.2 Code for parameter definition , Data import 、 Enhance and divide .
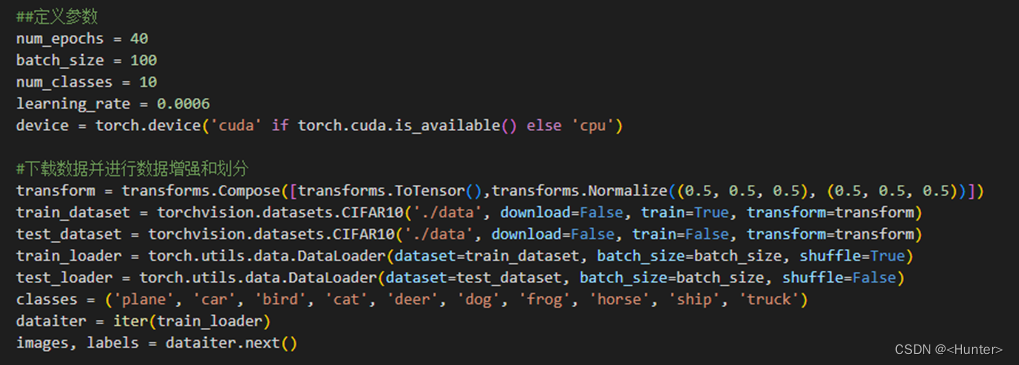
chart 3.2 Parameters are defined , Data import 、 Enhance and divide
3. Defining network
Use the figure 3.3 Code for network definition .
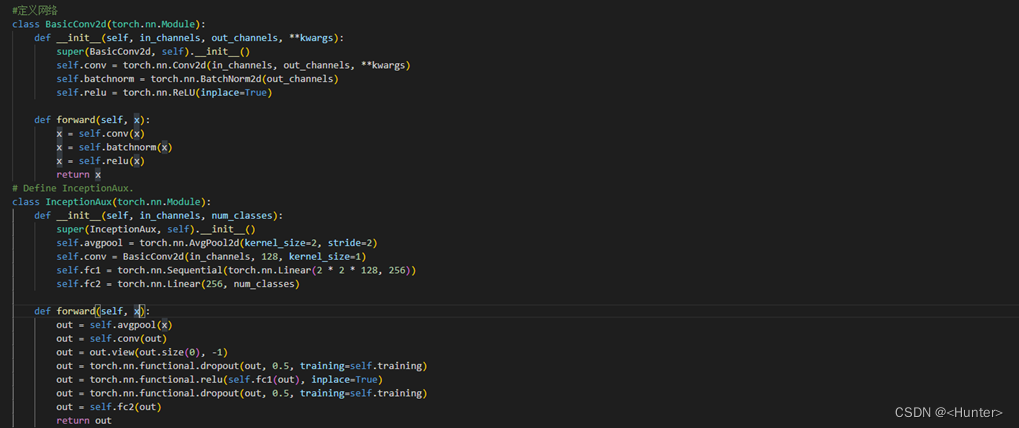

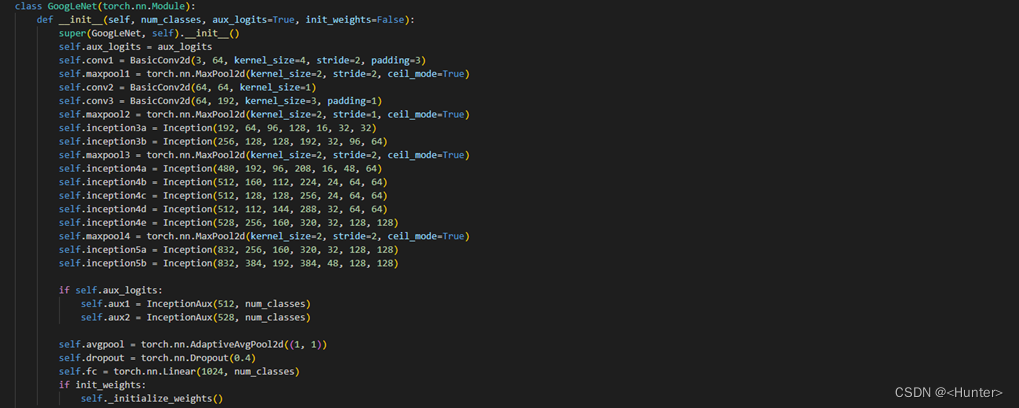
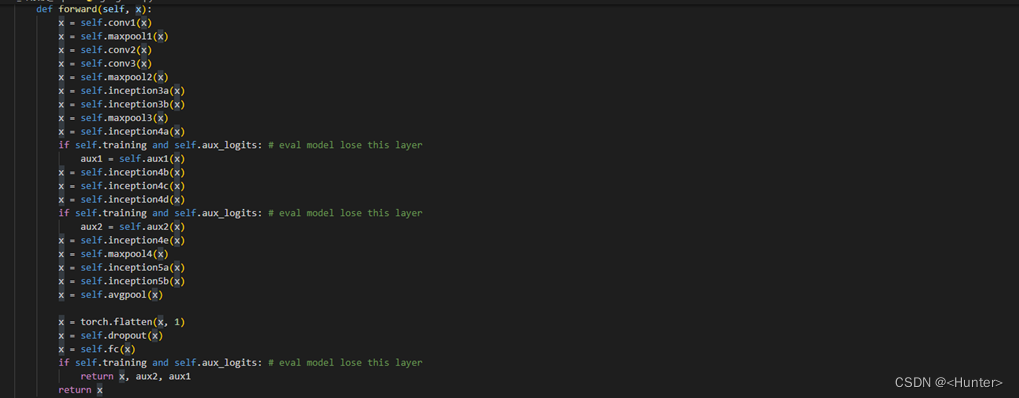

chart 3.3 Network definition
4. Training network
Use the figure 3.4 Code for network training , Output as shown in Figure 3.5.
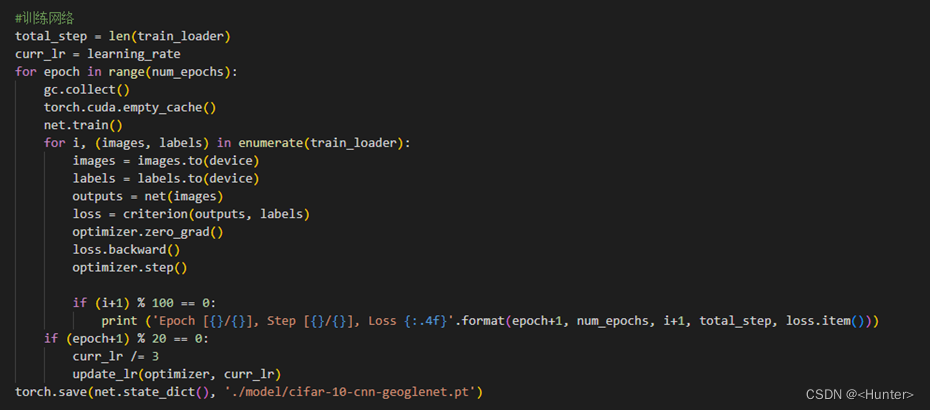
chart 3.4 Network training

chart 3.5 Training output
5. Calculation accuracy
Use the figure 3.6 Code calculation accuracy , Accuracy of 80.43%.
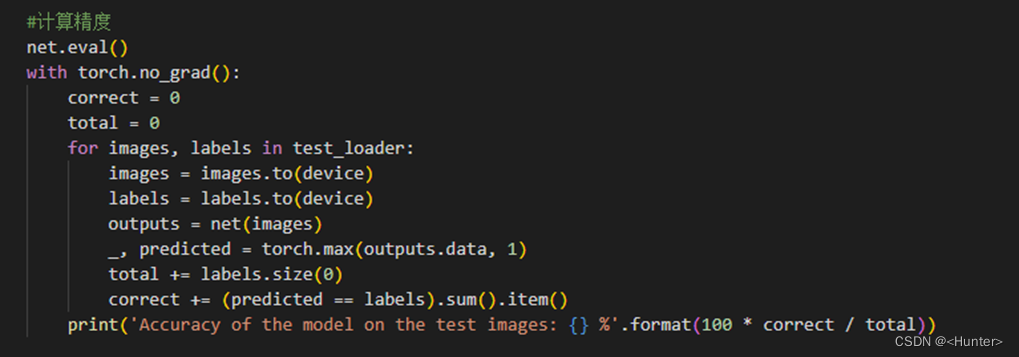
chart 3.6 Calculation accuracy
Four 、 summary
Use pytorch, Built a simple CNN The Internet and Geogle Net The Internet , Yes Cifar10 Image classification , The corresponding model verification parameters are calculated .
5、 ... and 、 Source code
1. Simple CNN Source code
'''
Simple CNN Image classification
'''
import torch
import torchvision
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
import os
# Download data, enhance and divide data
transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(),transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])
trainset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10('./data', train=True,download=True, transform=transform)
trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=4,num_workers=4,shuffle=True)
testset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10('./data', train=False,download=True, transform=transform)
testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testset, batch_size=4,num_workers=4,shuffle=False)
classes = ('plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck')
dataiter = iter(trainloader)
images, labels = dataiter.next()
# Define network structure
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 5)
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))
x = x.view(-1, 16 * 5 * 5)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
net = Net()
# Define optimizer
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9)
# Training network
model_directory_path = './model、'
model_path = model_directory_path + 'cifar-10-cnn-model-oralcnn.pt'
if not os.path.exists(model_directory_path):
os.makedirs(model_directory_path)
if os.path.isfile(model_path):
# load trained model parameters from disk
net.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path))
print('Loaded model parameters from disk.')
else:
for epoch in range(10): # loop over the dataset multiple times
running_loss = 0.0
for i, data in enumerate(trainloader, 0):
# get the inputs
inputs, labels = data
# zero the parameter gradients
optimizer.zero_grad()
# forward + backward + optimize
outputs = net(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# print statistics
running_loss += loss.item()
if i % 2000 == 1999: # print every 2000 mini-batches
print('[%d, %5d] loss: %.3f' %
(epoch + 1, i + 1, running_loss / 2000))
running_loss = 0.0
print('Finished Training.')
torch.save(net.state_dict(), model_path)
print('Saved model parameters to disk.')
# Network testing
dataiter = iter(testloader)
images, labels = dataiter.next()
outputs = net(images)
sm = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
sm_outputs = sm(outputs)
probs, index = torch.max(sm_outputs, dim=1)
total_correct = 0
total_images = 0
confusion_matrix = np.zeros([10,10], int)
with torch.no_grad():
for data in testloader:
images, labels = data
outputs = net(images)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total_images += labels.size(0)
total_correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
for i, l in enumerate(labels):
confusion_matrix[l.item(), predicted[i].item()] += 1
model_accuracy = total_correct / total_images * 100
print('Model accuracy on {0} test images: {1:.2f}%'.format(total_images, model_accuracy))
print('{0:10s} - {1}'.format('Category','Accuracy'))
for i, r in enumerate(confusion_matrix):
print('{0:10s} - {1:.1f}'.format(classes[i], r[i]/np.sum(r)*100))
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1,figsize=(8,6))
ax.matshow(confusion_matrix, aspect='auto', vmin=0, vmax=1000, cmap=plt.get_cmap('Blues'))
plt.ylabel('Actual Category')
plt.yticks(range(10), classes)
plt.xlabel('Predicted Category')
plt.xticks(range(10), classes)
plt.show()
print('actual/pred'.ljust(16), end='')
for i,c in enumerate(classes):
print(c.ljust(10), end='')
print()
for i,r in enumerate(confusion_matrix):
print(classes[i].ljust(16), end='')
for idx, p in enumerate(r):
print(str(p).ljust(10), end='')
print()
r = r/np.sum(r)
print(''.ljust(16), end='')
for idx, p in enumerate(r):
print(str(p).ljust(10), end='')
print()2.Geogle Net
'''
geoglenet Image classification
'''
import torch
import torchvision
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
import os
import gc
## Defining parameters
num_epochs = 40
batch_size = 100
num_classes = 10
learning_rate = 0.0006
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
# Download data, enhance and divide data
transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(),transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])
train_dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10('./data', download=False, train=True, transform=transform)
test_dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10('./data', download=False, train=False, transform=transform)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=test_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
classes = ('plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck')
dataiter = iter(train_loader)
images, labels = dataiter.next()
# Defining network
class BasicConv2d(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs):
super(BasicConv2d, self).__init__()
self.conv = torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, **kwargs)
self.batchnorm = torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.relu = torch.nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.batchnorm(x)
x = self.relu(x)
return x
# Define InceptionAux.
class InceptionAux(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, num_classes):
super(InceptionAux, self).__init__()
self.avgpool = torch.nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.conv = BasicConv2d(in_channels, 128, kernel_size=1)
self.fc1 = torch.nn.Sequential(torch.nn.Linear(2 * 2 * 128, 256))
self.fc2 = torch.nn.Linear(256, num_classes)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.avgpool(x)
out = self.conv(out)
out = out.view(out.size(0), -1)
out = torch.nn.functional.dropout(out, 0.5, training=self.training)
out = torch.nn.functional.relu(self.fc1(out), inplace=True)
out = torch.nn.functional.dropout(out, 0.5, training=self.training)
out = self.fc2(out)
return out
class Inception(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, ch1x1, ch3x3red, ch3x3, ch5x5red, ch5x5, pool_proj):
super(Inception, self).__init__()
self.branch1 = BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch1x1, kernel_size=1)
self.branch2 = torch.nn.Sequential(BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch3x3red, kernel_size=1),
BasicConv2d(ch3x3red, ch3x3, kernel_size=3, padding=1))
self.branch3 = torch.nn.Sequential(BasicConv2d(in_channels, ch5x5red, kernel_size=1),
BasicConv2d(ch5x5red, ch5x5, kernel_size=5, padding=2))
self.branch4 = torch.nn.Sequential(torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
BasicConv2d(in_channels, pool_proj, kernel_size=1))
def forward(self, x):
branch1 = self.branch1(x)
branch2 = self.branch2(x)
branch3 = self.branch3(x)
branch4 = self.branch4(x)
outputs = [branch1, branch2, branch3, branch4]
return torch.cat(outputs, 1)
# Define GooLeNet.
class GoogLeNet(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes, aux_logits=True, init_weights=False):
super(GoogLeNet, self).__init__()
self.aux_logits = aux_logits
self.conv1 = BasicConv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=4, stride=2, padding=3)
self.maxpool1 = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.conv2 = BasicConv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=1)
self.conv3 = BasicConv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
self.maxpool2 = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=1, ceil_mode=True)
self.inception3a = Inception(192, 64, 96, 128, 16, 32, 32)
self.inception3b = Inception(256, 128, 128, 192, 32, 96, 64)
self.maxpool3 = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.inception4a = Inception(480, 192, 96, 208, 16, 48, 64)
self.inception4b = Inception(512, 160, 112, 224, 24, 64, 64)
self.inception4c = Inception(512, 128, 128, 256, 24, 64, 64)
self.inception4d = Inception(512, 112, 144, 288, 32, 64, 64)
self.inception4e = Inception(528, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128)
self.maxpool4 = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, ceil_mode=True)
self.inception5a = Inception(832, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128)
self.inception5b = Inception(832, 384, 192, 384, 48, 128, 128)
if self.aux_logits:
self.aux1 = InceptionAux(512, num_classes)
self.aux2 = InceptionAux(528, num_classes)
self.avgpool = torch.nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.dropout = torch.nn.Dropout(0.4)
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(1024, num_classes)
if init_weights:
self._initialize_weights()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.maxpool1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
x = self.maxpool2(x)
x = self.inception3a(x)
x = self.inception3b(x)
x = self.maxpool3(x)
x = self.inception4a(x)
if self.training and self.aux_logits: # eval model lose this layer
aux1 = self.aux1(x)
x = self.inception4b(x)
x = self.inception4c(x)
x = self.inception4d(x)
if self.training and self.aux_logits: # eval model lose this layer
aux2 = self.aux2(x)
x = self.inception4e(x)
x = self.maxpool4(x)
x = self.inception5a(x)
x = self.inception5b(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.fc(x)
if self.training and self.aux_logits: # eval model lose this layer
return x, aux2, aux1
return x
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, torch.nn.Conv2d):
torch.nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if m.bias is not None:
torch.nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, torch.nn.Linear):
torch.nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
torch.nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
net = GoogLeNet(10, False, True).to(device)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.001, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-08, weight_decay=0)
def update_lr(optimizer, lr):
for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
param_group['lr'] = lr
# Training network
total_step = len(train_loader)
curr_lr = learning_rate
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
gc.collect()
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
net.train()
for i, (images, labels) in enumerate(train_loader):
images = images.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
outputs = net(images)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if (i+1) % 100 == 0:
print ('Epoch [{}/{}], Step [{}/{}], Loss {:.4f}'.format(epoch+1, num_epochs, i+1, total_step, loss.item()))
if (epoch+1) % 20 == 0:
curr_lr /= 3
update_lr(optimizer, curr_lr)
torch.save(net.state_dict(), './model/cifar-10-cnn-geoglenet.pt')
# Calculation accuracy
net.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
correct = 0
total = 0
for images, labels in test_loader:
images = images.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
outputs = net(images)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total += labels.size(0)
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
print('Accuracy of the model on the test images: {} %'.format(100 * correct / total))边栏推荐
- Delete the last character of the string in golang
- swagger文档配置
- Unity2019_ Natural ambient light_ Sky box
- VMware virtual machine configuration static IP
- Luaframwrok handles resource updates
- P1596 [USACO10OCT]Lake Counting S
- Pycharm remote ssh pyenv error: pydev debugger: warning: trying to add breakpoint to file that does
- Minimap plug-in
- [set theory] order relation (the relation between elements of partial order set | comparable | strictly less than | covering | Haas diagram)
- UE4 plug in development
猜你喜欢

Base64 and base64url

数据库应用技术课程设计之商城管理系统

Haproxy+kept cluster setup 02

Puhua PLM empowers the whole scene product lifecycle management and helps the enterprise digital transformation of the main line of products

A tunnel to all ports of the server
![[set theory] order relation (the relation between elements of partial order set | comparable | strictly less than | covering | Haas diagram)](/img/df/a034032e203e7935dafaf8a71cb6c8.jpg)
[set theory] order relation (the relation between elements of partial order set | comparable | strictly less than | covering | Haas diagram)

MAE
Xlua task list youyou
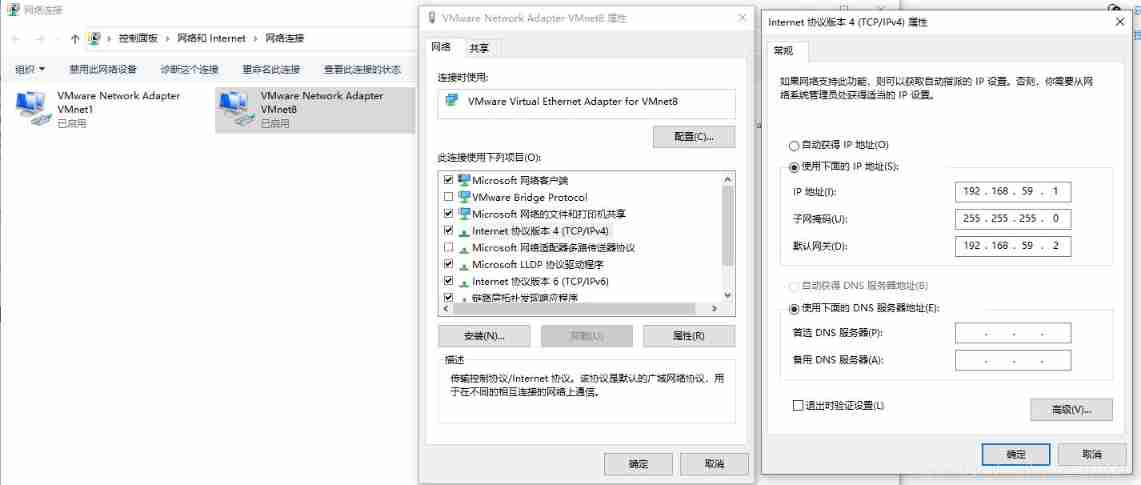
VMware virtual machine configuration static IP
C#课程设计之员工信息管理系统
随机推荐
Mutual call between Lua and C #
Golang 字符串分割,替换和截取
Redis的数据结构
tslib库的移植
Demonstration of plug-in use of ventuz basic series
swagger文档配置
Wechat applet taro learning record
What is BFC?
ArrayList
haproxy+keepalived搭建01
idea取消引用顯示效果
Student educational administration management system of C # curriculum design
Basic operation and process control
Clip Related Script
[cocos creator] Click the button to switch the interface
the installer has encountered an unexpected error installing this package
Unity2019_ Lighting system
Editor Extensions
JS regular case-
[untitled]