当前位置:网站首页>Broadcast and multicast (tcp/ip details volume 1/2)
Broadcast and multicast (tcp/ip details volume 1/2)
2022-06-12 15:21:00 【QQ851301776】
One 、 brief introduction
Three IP Address : Unicast address 、 Broadcast address and multicast address .
Broadcast and multicast only apply to U D P, They are very important for applications that need to send messages to multiple recipients at the same time .T C P It's a connection oriented protocol , It means running on two hosts ( from I P Address determination ) Two processes within ( Determined by the port number ) There is a connection between .
Consider a shared channel network with multiple hosts such as Ethernet . Each Ethernet frame contains the Ethernet address of the source host and the destination host (4 8 b i t). Usually Each Ethernet frame is only sent to a single destination host , The destination address indicates a single receiving interface , So it's called unicast ( u n i c a s t ). In this way , The communication between any two hosts will not interfere with other hosts in the network ( Except for the cases that may cause contention for the shared channel ).
However , Sometimes a host sends frames to all other hosts on the network , This is radio . adopt A R P and R A R P You can see the process . multicast (multicast) Between unicast and broadcast : The frame is only transmitted to multiple hosts belonging to the multicast group .
In order to understand radio and multicast , It is necessary to understand the filtering process of frames transmitted from the channel by the host . chart 1 2 - 1 Explain the process .

First , The network card views the frames transmitted by the channel , Determine whether to receive the frame , If you receive it and then send it to the device driver . Usually, the network card only receives those destination addresses Physical address of network card or Broadcast address Frame of . in addition , Most interfaces are Set to mixed mode , This mode can receive a copy of each frame . As an example , t c p d u m p Use this mode .
at present , Most network cards are configured to receive a destination address of Multicast address or Some subnet multicast addresses Frame of . For Ethernet , When the lowest bit of the highest byte in the address is set to 1 Indicates that the address is a multicast address , It can be expressed in hexadecimal as 0 1 : 0 0 : 0 0 : 0 0 : 0 0 : 0 0( Ethernet broadcast address ff : ff : ff : ff : ff : ff It can be regarded as a special case of Ethernet multicast address ).
If the network card receives a frame , This frame will be sent to the device driver ( If Frame check and error , The network card will discard the frame ). The device driver will perform additional frame filtering . First , The protocol to be used must be specified in the frame type ( I P、A R P wait ). secondly , Perform multicast filtering to detect whether the host belongs to the multicast group described by the multicast address . The device driver then transmits the data frame to the next layer , such as , When the frame type is specified as I P The data tell the time , Just send it to I P layer .I P according to I P The source address and destination address in the address are more filtered and detected . If normal , Send the datagram to the next layer ( Such as T C P or U D P).
Every time U D P Received by I P The datagram sent , According to the destination port number , Sometimes active port number is used for datagram filtering . If no process currently uses the destination port number , Just discard the datagram and create a I C M P Unreachable message (T C P Make similar filtering according to its port number ). If U D P There are tests and errors in data reports , Will be discarded . The problem with using broadcast is that it increases the processing load of hosts that are not interested in broadcast data . Take one and use U D P Broadcast application as an example . If there is 5 0 Host computer , But only 2 0 Participate in the app , Every time 2 0 One of the hosts sent U D P When broadcasting data , rest 3 0 A host has to process these broadcast datagrams . Until U D P layer , received U D P Broadcast datagram will be discarded . this 3 0 Hosts discarded U D P Broadcast datagram because these hosts do not use the destination port .
The emergence of multicast reduces the processing load of hosts that are not interested in applications . Use multicast , The host can join one or more multicast groups . such , The network card will know which multicast group the host belongs to , Then only those multicast frames of the multicast group where the host is located are received .
Two 、 radio broadcast

Introduce 7 A special I P Address , Pictured 3 - 9 Shown . In this picture , 0 Indicates that all bits are 0;- 1 Indicates that all bits are 1;n e t i d、s u b n e t i d and h o s t i d They are not all 0 Or all 1 The corresponding field of . If the subnet number column is empty, it means that the address is not divided into subnets .

Divide the table into three parts . The first two entries in the table are special source addresses , The middle term is a special loopback address , The last four items are broad Broadcast address .
The first two items in the table , The network number is 0, If the host uses B O O T P The protocol determines the native I P Address can only appear as the source address during initialization .
1. Limited broadcasting
The restricted broadcast address is 2 5 5 . 2 5 5 . 2 5 5 . 2 5 5. The address Used during host configuration I P Destination address of datagram , here , The host may not yet know the netmask of its network , Even its I P I don't know the address .
In any case , Routers do not forward datagrams whose destination address is a restricted broadcast address , Such datagrams only appear in the local network .
An unsolved problem is : If a host has multiple interfaces , When a process sends a datagram to the broadcast address of the network , For broadcasting , Whether datagrams should be sent to each connected interface ? If not , Applications that want to broadcast to all interfaces of the host must determine all interfaces in the host that support broadcasting , Then send a datagram copy to each interface . majority B S D The system will 2 5 5 . 2 5 5 . 2 5 5 . 2 5 5 It is regarded as the broadcast address of the first interface after configuration , And it does not provide the function of transmitting datagrams to the interface with broadcasting capability . however , r o u t e d( see 1 0 . 3 section ) and r w h o d(B S Dr w h o Client's server ) Is to send... To each interface U D P Two applications of datagram . Both applications use a similar startup process to determine all interfaces in the host , And know which interfaces have broadcast capability . meanwhile , Take the broadcast address pointing to the network corresponding to that interface as the destination address of the datagram sent to the interface .
Host Requirements RFC There is no further reference to whether a multi interface host should send a restricted broadcast to all its interfaces .
2. Broadcast to the Internet
The broadcast address pointing to the network is the host number of all 1 The address of .A Class webcast address is n e t i d . 2 5 5 . 2 5 5 . 2 5 5, among netid by A The network number of the class .
A router must forward broadcasts to the network , But it also has to have a choice not to forward .
3. Broadcast to subnet
The broadcast address to the subnet is the host number of all 1 And the address with a specific subnet number . As a direct broadcast address of the subnet I P The address needs to know the mask of the subnet . for example , If the router receives a message to 1 2 8 . 1 . 2 . 2 5 5 Datagram , When B Class network 1 2 8 . 1 The subnet mask of is 2 5 5 . 2 5 5 . 2 5 5 . 0 when , This address is the broadcast address pointing to the subnet ; But if the mask of the subnet is 2 5 5 . 2 5 5 . 2 5 4 . 0, This address is not a broadcast address pointing to a subnet .
4. Broadcast to all subnets
Broadcast also needs to know the subnet mask of the destination network , So as to distinguish it from the broadcast address pointing to the network . The subnet number and host number of the broadcast address pointing to all subnets are all 1. for example , If the destination subnet mask is 2 5 5 . 2 5 5 . 2 5 5 . 0, that I P Address 1 2 8 . 1 . 2 5 5 . 2 5 5 Is a broadcast address to all subnets . However , If the network is not divided into subnets , This is a broadcast to the Internet .
3、 ... and 、 multicast
Points to all subnets I P Multicast provides two types of services :
- Send data to multiple destination addresses . There are many applications that send information to multiple recipients : For example, interactive conference system and distributing mail or news to multiple recipients . If multicast is not used , At present, most of these applications use T C P To complete ( A separate data copy is sent to each destination address ). However , Even with multicast , Some applications may continue to use T C P To ensure its reliability .
- The client's request to the server . for example , The diskless workstation needs to determine to start the boot server . at present , This service is provided through broadcasting ( Just like No 1 6 Chapter B O O T P), However, using multicast can reduce the burden of hosts that do not provide this service .
1. Multicast group address

The multicast group address includes 111 0 The highest 4 bit And multicast group number . They can usually be expressed as dotted decimal numbers , Range from 2 2 4 . 0 . 0 . 0 To 2 3 9 . 2 5 5 . 2 5 5 . 2 5 5.
A set of hosts that can receive address data sent to a specific multicast group is called a host group (host group). A host group can span multiple networks . Members of the host group can join or leave the host group at any time . There is no limit on the number of hosts in the host group , At the same time, hosts that do not belong to a host group can send information to the group .
Some multicast group addresses are I A N A Identified as a well-known address . They are also referred to as permanent host groups , This sum T C P And U D P The familiar ports in are similar . Again , These well-known multicast addresses are in R F C In the latest allocation figures . Note that the groups represented by these multicast addresses are permanent groups , And their members are not permanent .
for example ,2 2 4 . 0 . 0 . 1 representative “ All system groups in the subnet ”,2 2 4 . 0 . 0 . 2 representative “ All router groups in this subnet ”. Multicast address 2 2 4 . 0 . 1 . 1 Used as network time protocol N T P,2 2 4 . 0 . 0 . 9 Used as a R I P - 2 ,2 2 4 . 0 . 1 . 2 use do S G I The company's d o g f i g h t application .
2. Multicast group address to Ethernet address translation
I A N A Have an Ethernet address block , That's high 24 bit by 0 0 : 0 0 : 5 e( Hexadecimal representation ), This means that the address block has an address range from 0 0 : 0 0 : 5 e : 0 0 : 0 0 : 0 0 To 0 0 : 0 0 : 5 e : ff : ff : ff.I A N A Assign half of them as multicast addresses . To specify a multicast address , The first byte of any Ethernet address must be 0 1, It means with I P The Ethernet address range corresponding to multicast is from 0 1 : 0 0 : 5 e : 0 0 : 0 0 : 0 0 To 0 1 : 0 0 : 5 e : 7 f : ff : ff.
Here to C S M A / C D Or token network uses I n t e r n e t Standard bit order , In the same order as the bits that appear in memory . This is also the order adopted by most programmers and system administrators . I E E E The document adopts this bit transmission order .Assigned Numbers RFC The differences between these representations are given .
This kind of address assignment will make the Ethernet multicast address 2 3 b i t And I P The multicast group number corresponds to , By placing the low bit in the multicast group number 2 3 b i t Mapped to the low order in the Ethernet address 2 3 b i t Realization , This process is shown in the figure 1 2 - 3 Shown . Due to the highest multicast group number 5 bit Ignored in the mapping process , Therefore, the multicast group corresponding to each Ethernet multicast address is not unique . 3 2 Different multicast group numbers are mapped to an Ethernet address . for example , Multicast address 2 2 4 . 1 2 8 . 6 4 . 3 2( Hexadecimal e 0 . 8 0 . 4 0 . 2 0) and 2 2 4 . 0 . 6 4 . 3 2( Hexadecimal e 0 . 0 0 . 4 0 . 2 0) Both map to the same Ethernet address 0 1 : 0 0 : 5 e : 0 0 : 4 0 : 2 0.
Since address mapping is not unique , Then the device driver or I P layer ( See the picture 1 2 - 1) The datagram must be filtered . Because the network card may receive multicast data frames that the host does not want to receive . in addition , If the network card does not provide enough multicast data frame filtering function , The device driver must receive all multicast data frames , And then filter them .

LAN cards tend to have two types of processing : One is that the network card implements multicast filtering according to the hash value of the multicast address , This means that unwanted multicast data will still be received ; The other is that the network card only receives a fixed number of multicast addresses , This means that when the host wants to receive multicast addresses other than those previously supported by the network card , The network card must be set to “ Multicast hybrid (multicast promiscuous)” Pattern . therefore , Both types of network cards still need the device driver to check whether the received frame is really what the host needs .
Even if the network card realizes perfect multicast filtering ( be based on 48 bit The hardware address of ), As a result of D class I P Address to 48 bit The mapping of hardware addresses is not one-to-one , The filtration process is still necessary . Despite the imperfections of address mapping and the need for hardware filtering , Multicast is still better than broadcasting .
Multicast over a single physical network is simple . The multicast process will aim to I P The address is specified as a multicast address , The device driver converts it to the corresponding Ethernet address , Then send the data out . These receiving processes must notify their I P layer , The datagrams they want to receive sent to a given multicast address , And the device driver must be able to receive these multicast frames . This process is “ Join a multicast group ”( Use “ Receiving process ” The reason for the plural form is that for a certain multicast information , There are multiple recipients on the same host or multiple hosts , That's why we should use multicast first ). When a host receives a multicast datagram , It must send a copy to each process belonging to that multicast group . This is similar to the unicast received by a single process U D P The data report U D P Different . Use multicast , There may be multiple processes belonging to the same multicast group on a host .
When multicast is extended beyond a single physical network, multicast data needs to be forwarded through the router , Complexity increases . A protocol is needed to let the multicast router know any host belonging to the multicast group in the network . This agreement is I n t e r n e t Group management protocol (I G M P)
Four 、 unicast 、 radio broadcast 、 Multicast advantages and disadvantages
unicast : Communication between network nodes is like a conversation between people . If one person speaks to another , So in terms of network technology, it's “ unicast ”, At this point, information is received and transmitted only between the two nodes . Unicast has been widely used in the network , Most of the data on the network is transmitted in the form of unicast , It's just that ordinary network users don't know . for example , You're on email 、 While browsing the web , Must work with mail server 、Web Server establishes connection , In this case, unicast data transmission mode is used . But usually it uses “ Point to point communication ”(Point to Point) Instead of “ unicast ”, because “ unicast ” Generally speaking, it is related to “ multicast ” and “ radio broadcast ” Use... Correspondingly .
The advantages of unicast :
- The server responds to the client's request in time
- The server sends impassable data for each customer's impassable request , Easy to realize personalized service .
The disadvantages of unicast :
- The server sends a data stream for each client , Server traffic = Number of clients × Client traffic ; When the number of customers is large 、 In streaming media applications with large traffic per client, the server is overwhelmed .
- The existing network bandwidth is a pyramid structure , The inter city and inter provincial backbone bandwidth is only equal to the sum of the bandwidth of all users 5%. If all unicast protocols are used , The network backbone will be overwhelmed . current P2P The application has often blocked the trunk . And expand the trunk 20 Times is almost impossible .
multicast :“ multicast ” It can also be called “ Multicast ”, There are not many applications of network technology , Online video conference 、 Online video on demand is particularly suitable for multicasting . Because if you do unicast , Node-by-node transmission , How many target nodes are there , How many times will there be transfers , This approach is obviously highly inefficient , Is not desirable ; If the target is not distinguished 、 Broadcast mode for all transmissions , Although the data can be transmitted at one time , But obviously, it can not achieve the purpose of distinguishing specific data receiving objects . Adopt multicast mode , The data of all target nodes can be transmitted at once , You can also achieve the goal of passing data only to specific objects . IP Network multicast is generally through multicast IP Address to achieve . multicast IP The address is D class IP Address , namely 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 Between IP Address .Windows 2000 Medium DHCP The manager supports multicast IP Automatic address assignment .
Advantages of multicast :
- Clients that need the same data stream join the same group and share a data stream , Save the load of the server . Have the advantages of broadcasting .
- Because the multicast protocol copies and forwards the data stream according to the needs of the recipient , Therefore, the total service bandwidth of the server is not limited by the bandwidth of the customer's access end .IP The agreement allows for 2 Billion 6 More than ten million multicast , So its services can be very rich .
- This protocol is the same as unicast protocol, which allows you to Internet Broadband network transmission .
The disadvantages of multicast :
- Compared with unicast protocol, there is no error correction mechanism , It is difficult to make up for packet loss and error , However, some fault tolerance mechanisms and QOS To make up for .
- Although the current networks support multicast transmission , But in customer certification 、QOS And other aspects need to be improved , These shortcomings have mature solutions in theory , It just needs to be gradually popularized and applied to the existing network .
radio broadcast :“ radio broadcast ” It is widely used in the network , If the client passes DHCP Automatically get IP The process of address is realized by broadcasting . But compared with unicast and multicast , Broadcasting takes up almost all the bandwidth of the network in the subnet . Take a meeting for example , Only one person can speak at the meeting , Imagine if everyone spoke with a microphone at the same time , There will be a mess in the meeting place . Because of the working principle of the hub, it is impossible to filter broadcast storms , General switches do not have this function , But now some network switches ( As omnidirectional QS Series switches ) It also has the function of filtering broadcast storms , The router itself has the function of isolating broadcast storms . Broadcast storms cannot be completely eliminated , But it can only spread in the same subnet , Just like the sound of the horn can only be transmitted in the same field , Therefore, in the large and medium-sized LAN composed of hundreds or even thousands of computers , Generally, subnets are divided , It's like separating a hall into many small halls with walls , In order to isolate the broadcast storm . stay IP In the network , For broadcast address IP Address “255.255.255.255” To express , This IP The address represents all in the same subnet IP Address .
The advantages of broadcasting :
- Network devices are simple , Simple maintenance , The cost of the net is low
- Because the server doesn't have to send data to each client separately , So the server traffic load is very low .
The disadvantages of broadcasting :
- Unable to provide personalized service in time according to the requirements and time of each customer .
- The bandwidth that the network allows the server to provide data is limited , The maximum bandwidth of the client = Total service bandwidth . For example, cable TV client line support 100 Channels ( If we use digital compression technology , In theory, it can provide 500 Channels ), Even if the service provider has more financial resources to allocate more transmitting devices 、 Change to fiber backbone , You can't go beyond that limit . In other words, it is impossible to provide more diversity to many customers 、 More personalized service .
- Broadcast prohibition is allowed in Internet Broadband network transmission .
边栏推荐
- Classification of annotations
- 3D reconstruction system | L3 incremental motion recovery structure (incremental SFM)
- Alibaba, Tencent and pinduoduo set an example, and the new logic of industrial Internet is gradually emerging
- Some useful websites
- Leetcode daily question - fair candy bar exchange
- Pta: self test -3 array element cyclic right shift problem (20 points)
- TF learning notes in ROS
- What is reflection-- The soul of frame design
- Introduction to microservices
- Tcp/ip three handshakes and four waves (interview questions)
猜你喜欢

Simple crawler framework: parsing 51job page position information

解决log4j2漏洞遭到挖矿、僵尸进程病毒攻击

Change according to the situation, the road to promotion in the second half of 2022

ROS中tf学习笔记
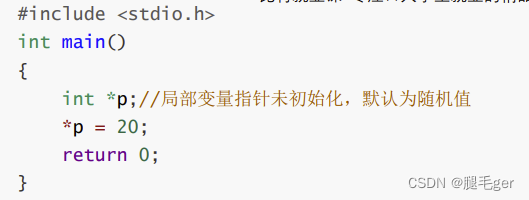
Wild pointer understanding

Function related matters

Pointer related concepts

应势而变,2022年下半场的升级之路

粒子滤波学习记录

Ngork implements intranet penetration -- free
随机推荐
Function related matters
Increase the maximum number of MySQL connections
广播和多播(TCP/IP详解卷1/2)
Codeforces Round 797 (Div. 3,CF1690)全题解
Qiming Zhixian shares the application scheme of 2.8-inch handheld central control screen
Jetpack architecture component learning (3) -- activity results API usage
Rust tip - running the tensorrt model through FFI programming
vim的安装以及常用命令
odom坐标系的理解
C main function
Conversion between sparse array and array and file reading and writing
Method reference instance method reference
Servlet知识详解(2)
Introduction to Eureka
[game server design cases] insights
Idea pull branch code
Dart typedef的理解
Error 1105: message:\“raft entry is too large
Error 1105: message:\“raft entry is too large
Swap numbers, XOR, operator correlation