当前位置:网站首页>Simple and clear, the three paradigms of database design
Simple and clear, the three paradigms of database design
2022-08-04 06:04:00 【Live up to [email protected]】
Paradigm: Simply put, it is to standardize the design of database tables and some specifications that need to be met in order to optimize the way data is stored.
In relational databases these norms can be called paradigms.
First Normal Form
1. Each column attribute is a indivisible attribute value, ensuring the atomicity
of each column2. The attributes of the two columns are similar or similar or same, try to merge columns with the same attributes,Make sure not to generate redundant data.
Example:
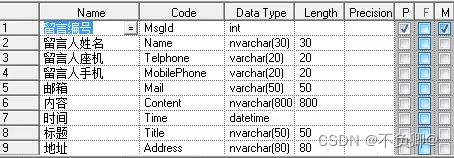
If the need is to split the address into provinces and cities,And according to its classification, then obviously the first table is not easy to meet the needs, and does not conform to the first normal form.
After splitting, example: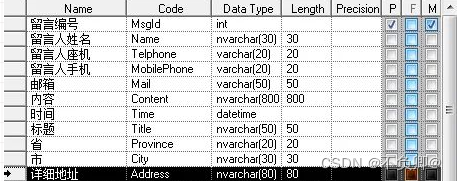
After splitting, it conforms to the first normal form.
Second Normal Form
Each row of data can only be associated with one of the columns, that is, a row of data does only one thing.
A table split should be split whenever duplication of data occurs in a data column.
Example: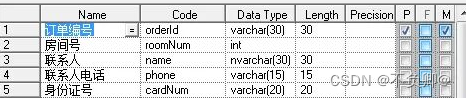
When a person books several rooms at the same time, multiple pieces of data will be generated for one order number, so that the sub-contacts are duplicated, which will cause data redundancy.We should take him apart.
Example: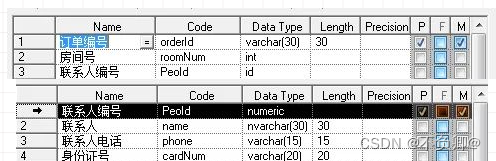
After splitting, it conforms to the second normal form.
Third Normal Form
Data cannot have transitive relationship, that is, each attribute has a direct relationship with the primary key rather than an indirect relationship.
Such a relationship between attributes like: a–>b–>c does not conform to the third normal form.
Such as Student table (student number, name, age, gender, institution, institution address, institution phone number)
In such a table structure, the above relationship exists.Student ID –> Institution --> (Institution address, institution phone number)
Such a table structure should be disassembled, as follows.
(Student ID, Name, Age, Gender, School) – (School, School Address, School Phone)
版权声明
本文为[Live up to [email protected]]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/216/202208040525327395.html
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
IvNWJVPMLt
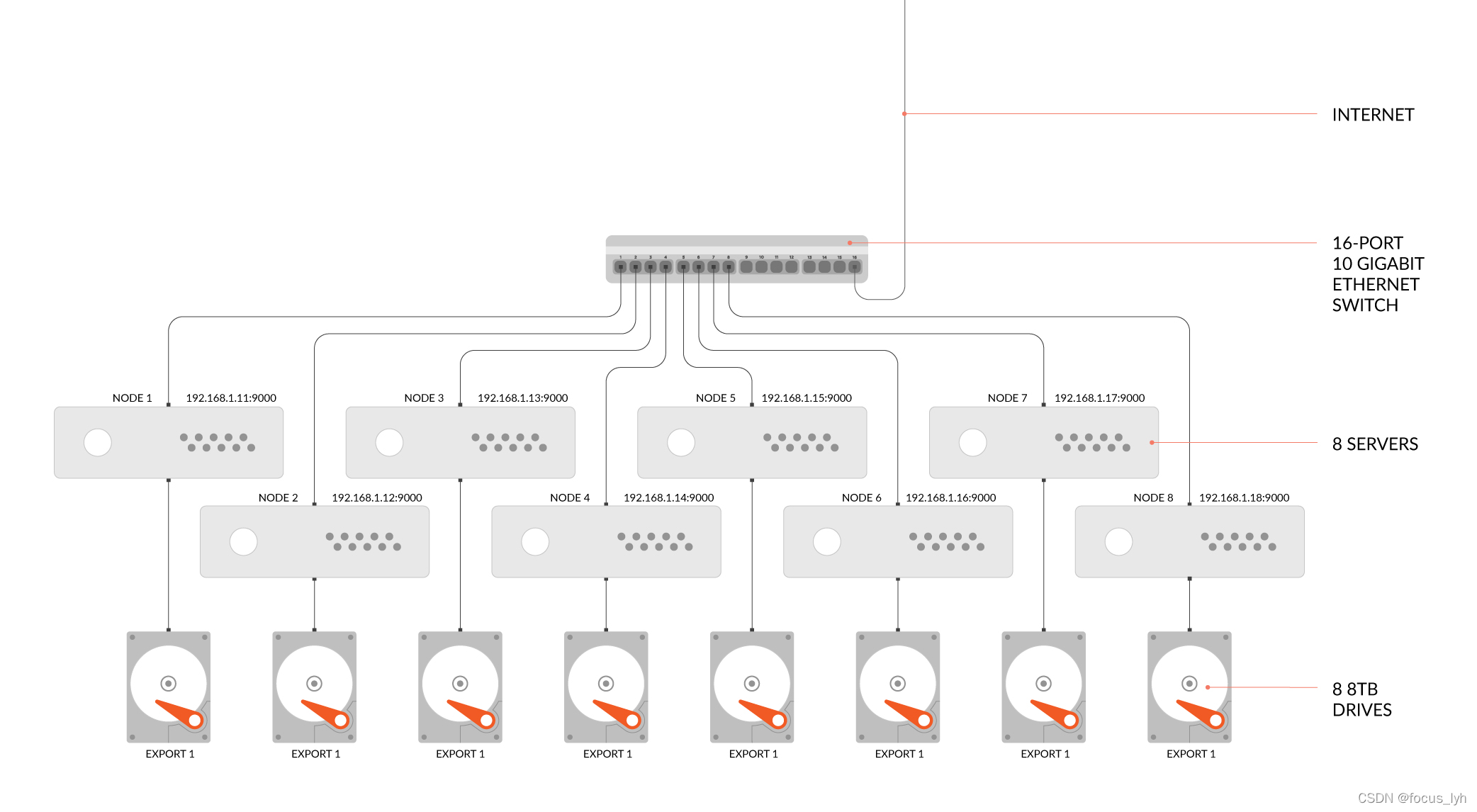
Kubernetes集群安装
原型对象及原型链的理解
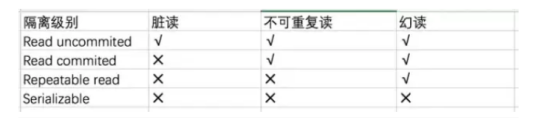
MySQL事务详解(事务隔离级别、实现、MVCC、幻读问题)
自动化运维工具Ansible(6)Jinja2模板
Jupyter Notebook安装库;ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘plotly‘解决方案。
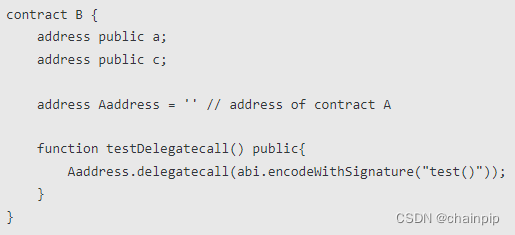
智能合约安全——delegatecall (1)
彻底搞懂箱形图分析
字典特征提取,文本特征提取。
【深度学习21天学习挑战赛】3、使用自制数据集——卷积神经网络(CNN)天气识别
关系型数据库-MySQL:体系结构
关系型数据库-MySQL:错误日志(log_error)
Kubernetes基础入门(完整版)
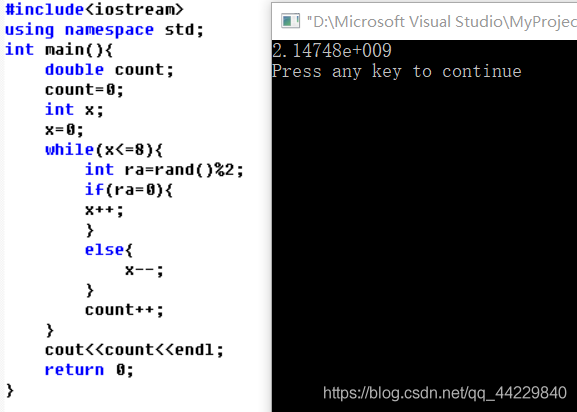
Shell(3)条件控制语句
win云服务器搭建个人博客失败记录(wordpress,wamp)
剑指 Offer 2022/7/2
(十)树的基础部分(一)
flink-sql查询配置与性能优化参数详解
自动化运维工具Ansible(1)基础
lmxcms1.4