当前位置:网站首页>Delphi time to timestamp
Delphi time to timestamp
2022-06-29 02:53:00 【Listest】
The code is as follows
function Gettimestamp(dateTimeStr:String): string;
var
unix_time:int64;
begin
unix_time:=Datetimetounix( IncHour( strToDateTime(dateTimeStr),-8) ); // reduce 8 Hours
Result := inttostr(unix_time);
end;
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
Concise words tell about technical people who must master basic IT knowledge and skills. Part 1

sql训练01

Pvcreate ASM disk causes abnormal recovery of ASM disk group - sparing separation

EMC、EMI、EMS的关系

How does kubernetes store business data persistently? (10)

EMC、EMI、EMS的關系
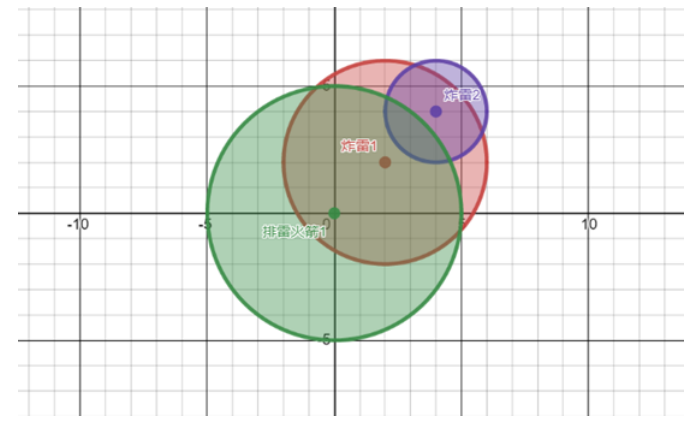
蓝桥杯2022初赛——扫雷

Double click events and click events

Handling method of occasional error reporting on overseas equipment
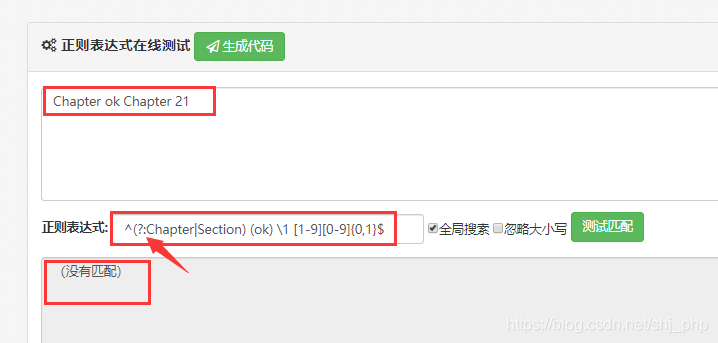
正则表达式(?:pattern)
随机推荐
Overview of PMP project management
Redis master-slave replication
Use photoshop2022 to create a wonderful gradient effect for pictures
Exec function of PHP
微信小程序自定义组件
Double click events and click events
PHP system function
PAT甲级 A1057 Stack
How to add the live video function to the website built by your own live video software (build a live video website)
Pvcreate ASM disk causes abnormal recovery of ASM disk group - sparing separation
今日直播|Apache Pulsar x KubeSphere 在线 Meetup 火热来袭
Tortoise does not display a green Icon
[线性代数] 1.2 全排列和对换
PWN新手入门Level0
【无标题】
Solve the problem that the cursor flashes after clicking a point when measuring the distance in Allegro
认证培训|StreamNative Certification 培训第2期
99 multiplication table
priority_ Understanding of queue
Only in the past four years, Microsoft finally gave it up!