当前位置:网站首页>Map and set
Map and set
2022-06-11 18:28:00 【HHYX.】
map and set
Associative containers
STL Medium containers can generally be divided into two categories , One is to vector、list、deque And so on , Its characteristic is that its bottom layer is a data structure of linear sequence , What is stored inside is the element itself . There is also an associative container , It is also used to store data , But the difference from the sequential container is that it stores <key,value> Key value pairs of structure , It is more efficient than sequential containers in data retrieval .STL There are two kinds of relational containers with different structures in : Tree structure and hash structure . Here is a tree structure of relational containers :map and set. This container features a balanced search tree as its underlying structure . Let's take a look at his specific examples and applications .
set
set Template parameter list

from set You can see in the template definition ,set There are 3 Template parameters ,T Represents the data type of the element ,set It's a kind of key Structure of the search binary tree .Compare and STL The priority queue in is similar to , Is an imitative function used to control the sort basis of the binary tree .Alloc It is set A way of managing element space , Use STL Space configurator provided
set Construction


set Structure and others STL The container is similar to , Both support default constructs 、 Copy construction and assignment overloading . In the default constructor , It can be used to construct empty set You can also use an iterator interval to construct set.
set The iterator

set The iterator of is almost indistinguishable from that of other containers ,begin Used to return the address of the starting position element ,end Return the address after the last element , It also supports reverse iterators, etc .
set Capacity operation

empty It's for judgment set Is it empty
size Is to calculate set The number of elements in
set Add or delete check change


This is right set Add, delete, check and modify , Specifically, the following code demonstrates the specific use :
void TestSet()
{
set<int> st;
int arr[] = {
2,5,8,3,7,1,4,6 };
for (auto e : arr)
{
st.insert(e);
}
for (auto& s : st)
{
cout << s << " ";
}
cout << endl;
set<int>::iterator it = st.find(3);// lookup key value , Successfully returned iterator
if (it != st.end())// It is necessary to judge whether the boundary is crossed
{
st.erase(it);// Use iterators to delete values
}
st.erase(4);// Directly use the specified value to delete key value
for (auto& s : st)
{
cout << s << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}

Here you can pay attention to the following considerations for common functions :
insert

there insert Function when inserting a single element , The return value is pair type ,pair It's also a data structure , It contains two data , Form key value pairs , Use... Respectively when accessing first and second that will do . have access to make_pair To create pair.
here insert return pair An iterator location and a bool type
insert You can also use an iterator interval to insert or specify a location to insert .
erase
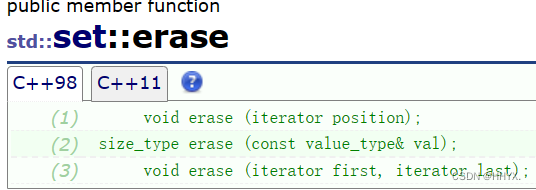
The deletion here can be done using the iterator location , You can also delete a specified value , You can also use an iterator interval to delete
find

stay set Find a specified val, If found, the iterator position is returned , If you don't find it, go back set Of end Iterator of position .
multiset
multiset and set Basically similar but set It has the function of de duplication , It cannot hold duplicate elements ,multiset As the name suggests, it can store repeated elements .
void TestSet()
{
set<int> st;
int arr[] = {
2,5,8,3,7,1,4,6,6,6,2,3 };
for (auto e : arr)
{
st.insert(e);
}
for (auto& s : st)
{
cout << s << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << st.count(2) << endl;
multiset<int> mst;
for (auto e : arr)
{
mst.insert(e);
}
for (auto& s : mst)
{
cout << s << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << mst.count(2) << endl;
}

matters needing attention
- set Is a container that stores elements in a certain order
- stay set in , Elemental value Also identify it (value Namely key, The type is T), And each value Must be unique .set Elements in cannot be modified in a container ( Elements always const), But you can insert or delete them from the container .
- In the internal ,set Elements in are always compared according to their internal objects ( Type comparison ) Sort according to the specified strict weak sorting criteria indicated .
- set Container by key Accessing a single element is usually faster than unordered_set Container slow , But they allow direct iteration of subsets according to order .
- set At the bottom is a binary search tree ( Red and black trees ) Realized .
- And map/multimap Different ,map/multimap Stored in is the real key value pair <key, value>,set Put only value, But what is actually stored at the bottom is by <value, value> The key value pairs of .
- set When you insert an element in , Just insert value that will do , There is no need to construct key value pairs .
- set The elements in cannot be repeated ( So you can use set Deduplication ).
- Use set Iterator traversal of set The elements in , You can get an ordered sequence
- set By default, elements in are compared by less than
- set Find an element in , The time complexity is :log2n
map
map Template parameters for

map Template parameters and set The main difference is that map yes <key,value> Key value pair structure , among key It's in a key value pair key type ,T It's in a key value pair value type .Compare Is the comparator type , The default is key To compare , But the comparison method can be modified by passing in a functor .Alloc It is to apply for the underlying space through the space configurator , No need for user delivery .
map Construction

The structure and set similar , I won't go into that .
map The iterator

map The iterator of is also related to set similar , However, it should be noted that when the iterator prints data, it also needs to specify the output in addition to knowing the reference pair Of first still second Parameters . The following code will be used to demonstrate
map Capacity operation

map Add, delete, check and modify


Let's test with a piece of code map Add, delete, check and modify functions of :
void Testmap()
{
map<string, string> dict;
pair<string, string> kv1("left", " On the left ");
dict.insert(kv1);
dict.insert(pair<string, string>("right", " On the right "));
dict.insert(make_pair("down", " Down "));
map<string, string>::iterator it = dict.begin();
while (it != dict.end())
{
cout << (*it).first << ":" << (*it).second << endl;
it++;
}
cout << endl;
dict.erase("down");
it = dict.find("right");
dict.erase(it);
it = dict.begin();
while (it != dict.end())
{
cout << (*it).first << ":" << (*it).second << endl;
it++;
}
}

there insert The type of insertion is pair Type data is also called key value pairs , There are three ways to insert : Define a pair Type and insert , Insert using anonymous objects , Use make_pair Define objects for insertion , Recommended make_pair This method will automatically derive template parameter types , It is convenient to use .
there erase Delete method and set similar , But here are two parameters ,erase If the value is used to delete, it is in the form of key Value as the basis .
find Functions are also basically and set similar , Return to found key Value iterator .
here map And set There is a big difference between map have access to [] Make element access 

and set Different ,map There are two values, of which key Value cannot be modified , Because the modification will cause problems in the sorting of the whole structure , Will lead to disorder , however value Values can be modified . According to the picture above , there [] The overloading of the operator is by entering a key Value to its corresponding value Value for modification , The specific test code is as follows :
void Testmap()
{
map<string, int> Countmap;
string arr[] = {
" Apple "," Apple "," Banana "," Apple "," Banana "," Apple "," Cherry " };
for (auto& str : arr)
{
Countmap[str]++;
}
for (auto& e : Countmap)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}

matters needing attention
- map The elements in are key value pairs
- map Medium key Is the only one. , And can't modify
- The default value is less than key Compare
- map If you use an iterator to traverse the elements in , You can get an ordered sequence
- map The bottom layer is the balanced search tree ( Red and black trees ), Search efficiency is relatively high log2N
- Support [] The operator ,operator[] Actually insert and find .
multimap

multimap and map The difference is equivalent to set and multiset The difference between ,multimap It is also used to store duplicates key value
void Testmultimap()
{
map<string, string> dict;
dict.insert(make_pair("left", " On the left "));
dict.insert(make_pair("left", " The remaining "));
dict.insert(make_pair("down", " Down "));
dict.insert(make_pair("up", " Up "));
for (auto& e : dict)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
multimap<string, string> mdict;
mdict.insert(make_pair("left", " On the left "));
mdict.insert(make_pair("left", " The remaining "));
mdict.insert(make_pair("down", " Down "));
mdict.insert(make_pair("up", " Up "));
for (auto& e : mdict)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
}

matters needing attention
multimap The interface in can refer to map, The functions are similar .
Be careful :
- multimap Medium key It can be repeated .
- multimap The elements in the default will be key Compare by less than
- multimap There are no overloads in operator[] operation ( Students can think about why ?).
- When used with map Contains the same header file :
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
DC-DC自举电容(BOOT)几个问题
* Jetpack 笔记 LifeCycle ViewModel 与LiveData的了解
论高可用架构
全志科技T3开发板(4核ARM Cortex-A7)——视频开发案例
ACL 2022: is it no longer difficult to evaluate word polysemy? A new benchmark "dibimt"
论工作流选型
The HashSet collection stores student objects and traverses
Oracle高级数据库复习
高性能架构设计
IEDA 底层菜单菜单简介
力扣34在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
Function and principle of key in V-for
5 minutes to understand the red, blue and purple in the attack and defense drill
Ctfhub SQL Boolean blind annotation
[golang] leetcode - 292 Nim games (Mathematics)
map和set
牛客刷题——求最小公倍数
SISO decoder for a general (n,n-1) SPC code(补充章节3)
力扣31 下一个排列
力扣刷题——根据二叉树创建字符串






![[C语言]对一个数组的元素排序后平移元素](/img/5b/3e74fc40787d94f6d0ab93332140ba.png)
