当前位置:网站首页>2022 northeast four provinces match VP record / supplementary questions
2022 northeast four provinces match VP record / supplementary questions
2022-07-03 11:27:00 【HeartFireY】
VP situation
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| await a vacancy or job opening | AC | AC(-6) | AC | AC | Supplementary questions | Supplementary questions | – | AC(-2) | – | AC | AC | – |
A.Encryption
– await a vacancy or job opening –
B.Capital Progra
Topic analysis
It is required to select a connected block on a given graph , Make the distance sum between the connected block and other points minimum .
Consider greedy choices , We can expand the graph , Then start from the leaf node and follow the inverse B F S BFS BFS Delete points in sequence , End of deletion n − k n-k n−k Up to . This process can be realized by topological sorting , set up d i s [ i ] dis[i] dis[i] Indicates the number of sides of the subtree ( Border rights and interests ), Update the maximum value in the sorting process .
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
vector<int> g[N];
int deg[N], dis[N];
inline void solve(){
int n, k; cin >> n >> k;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
int u, v; cin >> u >> v;
g[u].emplace_back(v);
g[v].emplace_back(u);
deg[u]++, deg[v]++;
}
if(n == k){
cout << 0 << endl; return; }
queue<int> q;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) if(deg[i] == 1) dis[i] = 1, q.emplace(i);
int cnt = 0, ans = -1;
while(q.size()){
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
if(++cnt > n - k) break;
ans = max(ans, dis[u]);
for(auto v : g[u]){
dis[v] = max(dis[v], dis[u] + 1);
if(--deg[v] == 1) q.emplace(v);
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
signed main(){
solve();
return 0;
}
C.SegmentTree
Topic analysis
Require a given coverage [ 1 , m ] [1,m] [1,m] Find on the segment tree of the interval q q q Paths ( Self construction ), Maximize the number of covered points .
The first thing is for sure , When q ≥ m q \ge m q≥m when , We can choose m m m Leaf nodes A D D ADD ADD operation , Thus, the whole segment tree is covered .
consider q ≤ m q \le m q≤m when , How to select leaf nodes to maximize the number of coverage points .
The following figure shows that the coverage interval is [ 1 , 12 ] [1,12] [1,12] The line segment tree , We can find the law of greedy selection :
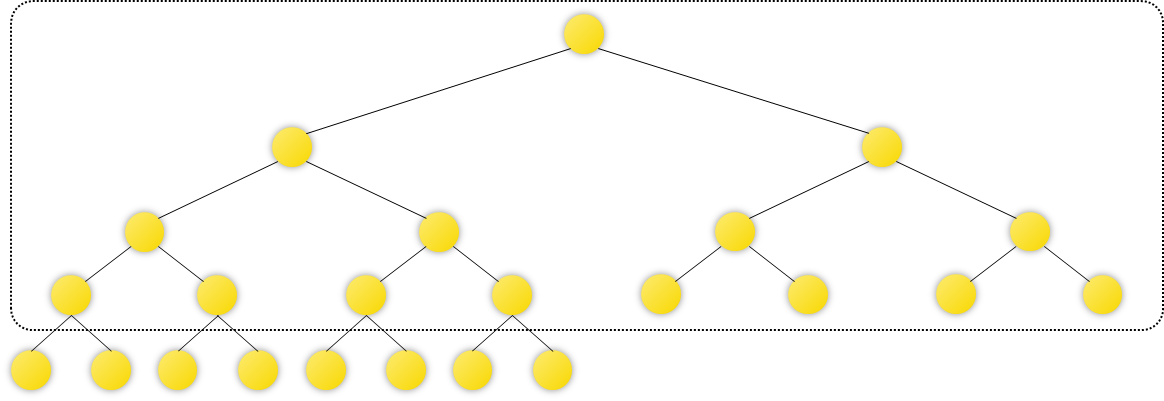
- For the first floor ( common 1 1 1 Nodes ), When the operands p ≥ 1 p \geq 1 p≥1 Can cover all , Otherwise, at most q q q Nodes ( namely 0 0 0 Nodes );
- For the second layer ( common 2 2 2 Nodes ), When the operands p ≥ 2 p \ge 2 p≥2 Can cover all , Otherwise, at most q q q Nodes ;
- For the third layer ( common 4 4 4 Nodes ), When the operands p ≥ 4 p \ge 4 p≥4 Can cover all , Otherwise, at most q q q Nodes ;
- For the third layer ( common 8 8 8 Nodes ), When the operands p ≥ 8 p \ge 8 p≥8 Can cover all , Otherwise, at most q q q Nodes ;
Note: You can ask for a r g _ m a x i ( 2 i ≤ m ) arg\_max_i\ (2^i \leq m) arg_maxi (2i≤m) Find the depth of the last complete layer
The last layer may be incomplete , Therefore, it needs to be discussed : Currently, the last floor has 12 − 8 = 4 12 - 8 = 4 12−8=4 Kezi tree :
- q ≤ 4 q \leq 4 q≤4, At most q q q The trees were selected 1 1 1 Nodes ( Ensure that the root node is selected greedily );
- 4 ≤ q ≤ 8 4 \le q \leq 8 4≤q≤8, All subtrees are selected 1 1 1 Nodes ;
- Otherwise, select all .
Then choose according to the above greedy ideas .
Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
void solve(){
int m, q; cin >> m >> q;
int ret = 1, sum = 0;
for(ret = 1; ret < m; ret <<= 1) sum += std::min(ret, q);
int sub = m - (ret >> 1);
if(sub >= q) cout << sum + q << endl;
else if((ret >> 1) >= q) cout << sum + sub << endl;
else cout << sum + sub + min(sub, (q - (ret >> 1))) << endl;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int _=1;
cin>>_;
while(_--){
solve();
}
}
D.Game
Topic analysis
Given n n n Rubble , Take turns picking stones , Inoperable input . Choose at least one pile at a time 1 1 1 individual , The remaining stones can be allocated to other piles . Each round of the game is given a query , Ask for an answer [ l , r ] [l,r] [l,r] The game result of the interval .
whole 0 0 0 When , If you start, you'll lose , Then consider the state that can reach this state : have only 1 1 1 Rubble -> The first step is to win .
Continue to summarize , Two piles 1 1 1 A stone , At this time, the first hand will be defeated , Promote this status , Find any A , B A,B A,B Satisfy A ≠ B A \neq B A=B, All are the first to win .
Extension : Found that when m m m Rubble , m m m In an odd number of , If you start, you'll lose , Then you can guess that there are only even numbers of stones , The first hand may win .
Then continue to guess : set up f ( x ) f(x) f(x) Representation number x x x In the interval [ l , r ] [l,r] [l,r] Number of occurrences of . If you start first, you will lose, and only if ∀ x , f ( x ) ≡ 0 ( m o d 2 ) ∀x, f(x) ≡ 0 (mod 2) ∀x,f(x)≡0(mod2).
See the official explanation for the specific proof …
Then find out whether the occurrence times of interval numbers are all even , Just ask team Mo offline .
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int a[N], BLCOK_SIZE = 0;
struct node{
int l, r, id;
const bool operator<(const node &x) const {
int d1 = l / BLCOK_SIZE, d2 = x.l / BLCOK_SIZE;
return d1 < d2 || (d1 == d2 && r < x.r);
}
}ask[N];
int ans[N], cnt[N], nowAns = 0;
inline void op(int x){
cnt[a[x]]++;
cnt[a[x]] & 1 ? nowAns++ : nowAns--;
}
inline void solve(){
int n = 0, q = 0; cin >> n >> q;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
BLCOK_SIZE = int(ceil(pow(n, 0.5)));
for(int i = 1; i <= q; i++){
cin >> ask[i].l >> ask[i].r, ask[i].id = i;
}
sort(ask + 1, ask + 1 + q);
for(int i = 1, l = 1, r = 0; i <= q; i++){
auto q = ask[i];
while(l > q.l) op(--l);
while(r < q.r) op(++r);
while(l < q.l) op(l++);
while(r > q.r) op(r--);
ans[q.id] = nowAns;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= q; i++){
if(ans[i]) cout << "Alice\n";
else cout << "Bob\n";
}
}
signed main(){
solve();
return 0;
}
E.Plus
Topic analysis
Beat the watch to find the rules , Can be found when n ≥ 3 n \geq 3 n≥3 when , Yes and no 1 1 1 Group answers meet , by 2 , 3 2, 3 2,3.
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
inline void solve(){
int n = 0; cin >> n;
if(n >= 3) cout << "1" << endl << "2 3" << endl;
else cout << "0\n" << endl;
}
signed main(){
solve();
return 0;
}
F.Tree Path
See blog alone :
Topic analysis
Given a tree , contain n n n Nodes and k k k Strip weight path , Operation support is required :
- Delete the smallest weighted path
- For a given node x x x, Output all without x x x The minimum value in the weighted path of
Two ways of thinking , The whole dichotomy needs to be supplemented , See :[P3250 HNOI2016] The Internet + [NECPC2022] F.Tree Path Tree analysis + Segment tree maintenance heap _HeartFireY The blog of -CSDN Blog
Code - Tree analysis + The difference in the tree + The whole score is two points.
// await a vacancy or job opening
Code - Tree analysis + Segment tree maintenance complement
// see :https://blog.csdn.net/yanweiqi1754989931/article/details/125575597
G.Hot Water Pipe
Topic analysis
Given a paragraph by n n n Hot water pipe composed of segments , Every paragraph has 1 1 1 Volume per unit , this n n n Section of water pipe starts from 1 1 1 To n n n Number from left to right , Water flows from left to right . Each section of water pipe in the initial state i i i There will be a temperature a i a_i ai, The temperature will drop every minute 1 1 1, When the temperature drops T m i n T_{min} Tmin Will be immediately heated to T m a x T_{max} Tmax. When the first n n n After running out of water in the section of water pipe , Water will flow from left to right . Now ask you to use water after a period of time , The average temperature of the water taken .
Use a double ended queue to simulate the process of water inflow and outflow , If the water consumption is greater than the total water consumption, we can discuss it separately .
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int a[N];
struct node{
int vol, tem, t;
};
deque<node> q;
inline void solve(){
int n, m, tmin, tmax; cin >> n >> m >> tmin >> tmax;
auto calc = [&](int st, int time, int tem){
time -= st;
if(time < tem - tmin + 1) return tem - time;
(time -= (tem - tmin + 1)) %= (tmax - tmin + 1);
return tmax - time;
};
for(int i = 1, num = 0; i <= n; i++) cin >> num, q.emplace_front(node{
1, num, 0});
int time_cnt = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
int t, k; cin >> t >> k;
time_cnt += t;
int ans = 0, kk = k;
while(kk && q.size()){
node now = q.front(); q.pop_front();
int nvol = now.vol, ntm = now.tem, nst = now.t;
if(nvol > kk) q.emplace_front(node{
nvol - kk, ntm, nst}), nvol = kk;
kk -= nvol;
ans += nvol * calc(nst, time_cnt, ntm);
}
if(kk) ans += kk * tmax;
cout << ans << endl;
if(i != m) q.emplace_back(node{
k - kk, tmax, time_cnt});
}
}
signed main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0);
solve();
return 0;
}
I.Generator
Topic analysis
Given in the initial state n n n, Each time will be n n n Turn into [ 1 , n ] [1, n] [1,n] A number in , After a limited number of operations, it will become 1 1 1. Change into 1 1 1 Expected number of operations .
set up d p [ n ] dp[n] dp[n] Indicates that the current number is n n n, expect d p [ n ] dp[n] dp[n] The second change is 1 1 1. Then there is the transfer equation :
d p [ n ] = d p [ 1 ] n + d p [ 2 ] n + ⋯ + d p [ n ] n + 1 dp[n] = \frac{dp[1]}{n} + \frac{dp[2]}{n} + \dots + \frac{dp[n]}{n} + 1 dp[n]=ndp[1]+ndp[2]+⋯+ndp[n]+1
How to understand ? Current number n n n Can be directed to [ 1 , n ] [1,n] [1,n] Transfer any number in , The transition probabilities are 1 n \frac{1}{n} n1, Transfer and occupy one step , So we need to + 1 +1 +1.
among , because d p [ 1 ] dp[1] dp[1] Indicates that the current number is 1 1 1, It can no longer be transferred , At this time, the operation has been terminated . So the expectation is 0 0 0 namely d p [ 1 ] = 0 dp[1] = 0 dp[1]=0
transposition , You can get :
n d p [ n ] = ∑ i = 1 n d p [ i ] + n ndp[n] = \sum_{i = 1}^{n} dp[i] + n \\ ndp[n]=i=1∑ndp[i]+n
Using the dislocation subtraction method, we can get d p [ n ] − d p [ n − 1 ] = 1 n − 1 dp[n] - dp[n - 1] = \frac{1}{n - 1} dp[n]−dp[n−1]=n−11, Then you can get d p [ 2 ] = 2 dp[2] = 2 dp[2]=2, Then the summation is :
1 + 1 2 + 1 3 + ⋯ + 1 n 1 + \frac{1}{2} + \frac{1}{3} + \dots + \frac{1}{n} 1+21+31+⋯+n1
Sum harmonic series : 1 + 1 2 + 1 3 + ⋯ + 1 n = ln ( n ) + γ 1 + \frac{1}{2} + \frac{1}{3} + \dots + \frac{1}{n} = \ln(n) + \gamma 1+21+31+⋯+n1=ln(n)+γ, among γ \gamma γ Is Euler constant . Then for larger data, the approximate value can be obtained by using this formula .
Code
Note: Euler constant is used Python Punch the watch until 1 e 8 1e8 1e8 that will do . The tabulation procedure is as follows :
import numpy as np
n = 100000000
logn_val = np.log(n)
sum = 0
for i in range(1, n + 1):
sum += (1 / i)
print(sum - logn_val)
AC Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
const long double C = 0.5772156599001868;
inline void solve(){
int n = 0; cin >> n, n--;
if(n >= 20000000) cout << log(n) + 1 + C << endl;
else{
long double ans = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) ans += 1.0 / (1.0 * i);
cout << ans << endl;
}
}
signed main(){
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(12);
solve();
return 0;
}
K.Maze
Topic analysis
Given n × n n \times n n×n Maze of size , It is required to go from the upper left corner to the lower right corner , Do not pass through obstacles during , And cannot walk continuously in the same direction for more than m m m Step .
Consider using d i s [ x ] [ y ] [ f a c e ] [ s t e p ] dis[x][y][face][step] dis[x][y][face][step] Indicates that the current is ( x , y ) (x, y) (x,y) Point oriented f a c e face face The direction has been walking continuously s t e p step step The maximum distance of step . Then we can get the transfer equation :
d i s [ x ′ ] [ y ′ ] [ f a c e ′ ] [ s t e p ′ ] = d i s [ x ] [ y ] [ f a c e ] [ s t e p ] + 1 , s . t . s t e p ′ = ( s t e p + 1 ) i f ( f a c e ′ = f a c e ) e l s e ( 1 ) dis[x'][y'][face'][step'] = dis[x][y][face][step] + 1, s.t.step' = (step + 1) if (face' = face)else(1) dis[x′][y′][face′][step′]=dis[x][y][face][step]+1,s.t.step′=(step+1)if(face′=face)else(1)
So directly B F S BFS BFS Search .
Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define mod 998244353
using namespace std;
const int dx[] = {
0 ,0, 1, -1};
const int dy[] = {
1, -1, 0 ,0};
const int INF = 1e9;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
char g[110][110];
int dis[110][110][4][110], n, m;
struct node{
int x, y, face, step; };
inline int bfs(){
memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof(dis));
queue<node> q;
q.emplace(node{
1, 1, 0, 0});
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) dis[1][1][i][0] = 0;
while(!q.empty()){
node now = q.front(); q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
if(now.face != i || now.step <= m){
int nx = now.x + dx[i], ny = now.y + dy[i], nxstep = now.step + 1;
if(now.face != i) nxstep = 1;
if(g[nx][ny] == '*' || nx > n || ny > n || nxstep > m || dis[nx][ny][i][nxstep] < INF) continue;
dis[nx][ny][i][nxstep] = dis[now.x][now.y][now.face][now.step] + 1;
if(nx == n && ny == n) return dis[nx][ny][i][nxstep];
q.emplace(node{
nx, ny, i, nxstep});
//cout << "#DEBUG " << nx << ' ' << ny << ' ' << i << ' ' << nxstep << endl;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
inline void solve(){
cin >> n >> m; getchar();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
cin >> g[i][j];
}
}
cout << bfs() << endl;
}
signed main(){
int t = 1; cin >> t;
for(int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) g[0][i] = '*';
for(int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) g[i][0] = '*';
while(t--) solve();
return 0;
}
L.Polygon
Topic analysis
Given n n n Line segments and the length of each line segment , It is required to judge whether it can form a polygon .
Consider the conditions of polygon formation . Just ask for the sum of the side lengths and then check one by one .
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int a[N], sum = 0;
void solve(){
int n = 0; cin >> n; sum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i], sum += a[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(sum - a[i] <= a[i]){
cout << "NO\n";
return;
}
}
cout << "YES\n";
}
signed main(){
int t = 0; cin >> t;
while(t--) solve();
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- 如何清理v$rman_backup_job_details视图 报错ORA-02030
- Function details of CorelDRAW graphics suite 2022
- ASP.NET-酒店管理系统
- Processes and threads
- Driver development based on I2C protocol
- asyncio 警告 DeprecationWarning: There is no current event loop
- Matlab extracts numerical data from irregular txt files (simple and practical)
- MATLAB extrait les données numériques d'un fichier txt irrégulier (simple et pratique)
- 活动预告 | 直播行业“内卷”,以产品力拉动新的数据增长点
- CorelDRAW Graphics Suite 2022新版功能详情介绍
猜你喜欢
00后抛弃互联网: 毕业不想进大厂,要去搞最潮Web3
C language AES encryption and decryption
如何清理v$rman_backup_job_details视图 报错ORA-02030

Summary of interview questions (2) IO model, set, NiO principle, cache penetration, breakdown avalanche

有赞CTO崔玉松:有赞Jarvis核心目标是使产品变得更加聪明和可靠
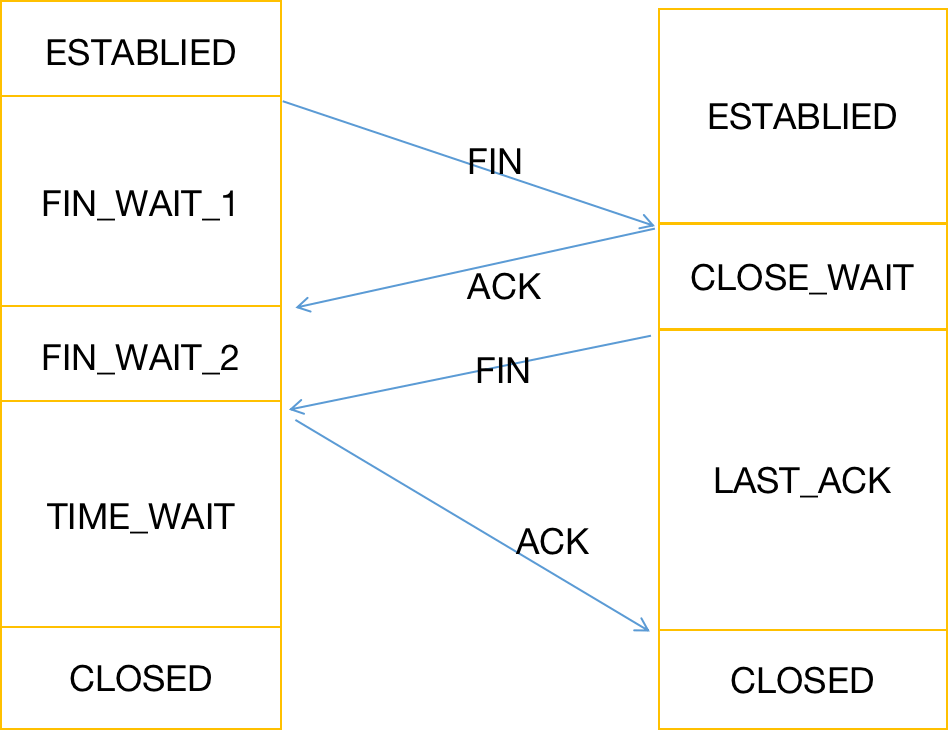
PHP server interacts with redis with a large number of close_ Wait analysis

面試題總結(2) IO模型,集合,NIO 原理,緩存穿透,擊穿雪崩
Google Earth engine (GEE) - ghsl global population grid dataset 250 meter resolution
Use typora to draw flow chart, sequence diagram, sequence diagram, Gantt chart, etc. for detailed explanation

Abandon the Internet after 00: don't want to enter a big factory after graduation, but go to the most fashionable Web3
随机推荐
Bi skills - permission axis
Cuiyusong, CTO of youzan: the core goal of Jarvis is to make products smarter and more reliable
PHP server interacts with redis with a large number of close_ Wait analysis
Gut | 香港中文大学于君组揭示吸烟改变肠道菌群并促进结直肠癌(不要吸烟)
How to clean up v$rman_ backup_ job_ Details view reports error ora-02030
线性表的双链表
Function details of CorelDRAW graphics suite 2022
AIDL
如何成为一名高级数字 IC 设计工程师(1-3)Verilog 编码语法篇:Verilog 行为级、寄存器传输级、门级(抽象级别)
如何将数字字符串转换为整数
Double linked list of linear list
[vtk] source code interpretation of vtkpolydatatoimagestencil
Reading notes: heart like Bodhi, Cao Dewang
读书笔记:《心若菩提》 曹德旺
Programmers' entrepreneurial trap: taking private jobs
软件测试周刊(第78期):你对未来越有信心,你对现在越有耐心。
MATLAB extrait les données numériques d'un fichier txt irrégulier (simple et pratique)
Key switch: press FN when pressing F1-F12
【obs】封装obs实现采集的基础流程
Google Earth engine (GEE) - ghsl global population grid dataset 250 meter resolution