当前位置:网站首页>Chapter 3 stack, queue and array
Chapter 3 stack, queue and array
2022-07-28 14:56:00 【Three waters of ndream】
Chapter one The introduction
Chapter two The linear table
The third chapter Stack 、 Queues and arrays
Chapter four strand
The fifth chapter Trees and binary trees
Chapter six chart
Chapter vii. lookup
Chapter viii. Sort
03 Stack 、 Queues and arrays
3.1 Definition of stack
Stack (stack) It is a linear table that only allows insertion or deletion at one end (LIFO)
Important terms : To the top of the stack 、 At the bottom of the stack 、 Empty stack
3.2 The basic operation of the stack
InitStack(&S): Initialization stack . Construct an empty stack S, Allocate memory space
DestroyStack(&S): Destroy the stack . Destroy and release the stack S Memory space occupied
Push(&S, x): Into the stack . Ruozhan S under , Will x Add to make it the top of the new stack
Pop(&S, &x): Out of the stack . Ruozhan S Non empty , Then pop up the top element of the stack , And use x return
GetTop(S, &x): Read top of stack elements . Ruozhan S Non empty , Then use x Back to top of stack element
StackEmpty(S): Judge a stack S Is it empty . If it is empty , Then return to true, Otherwise return to false

3.3 Implementation of sequential stack

Definition of sequential stack
#define MaxSize 10 // Define the maximum number of elements in the stack typedef struct { ElemType data[MaxSize]; // Static arrays hold the elements in the stack int top; /// Top pointer of stack } SqStack; int main() { SqStack S; // Declare a sequential stack …… }Stack in operation
#define MaxSize 10 // Define the maximum number of elements in the stack typedef struct { ElemType data[MaxSize]; // Static arrays hold the elements in the stack int top; /// Top pointer of stack } SqStack; // Put new elements on the stack bool Push(SqStack &S, ElemType x) { if (S.top == MaxSize() - 1) return false; S.top = S.top + 1; S.data[S.top] = x; return true; }The stack,
#define MaxSize 10 // Define the maximum number of elements in the stack typedef struct { ElemType data[MaxSize]; // Static arrays hold the elements in the stack int top; /// Top pointer of stack } SqStack; // The stack, bool Pop(SqStack &S, ElemType &x) { if (S.top == -1) return false; x = S.data[S.top]; S.top = S.top - 1; return true; }Shared stack
Using shared stack can improve the utilization of space
#define MaxSize 10 // Define the maximum number of elements in the stack typedef struct { ElemType data[MaxSize]; // Static arrays hold the elements in the stack int top0; // 0 No. stack top pointer int top1; // 1 No. stack top pointer } SqStack; // Initialization stack void InitStack(ShStack &S) { S.top0 = -1; S.top1 = MaxSize(); }

3.4 The realization of chain stack

A single linked list that can only be inserted and deleted at the head node can be regarded as a chain stack
Definition
typedef struct Linknode { ElemType data; struct Linknode *next; } *LiStack;
3.5 Definition of queue
queue (Queue) Is only allowed to insert at one end , Linear table deleted at the other end (FIFO)
Important terms : Team head 、 A party 、 Empty queue
3.5 Basic operations of queues
InitQueue(&Q): Initialize queue . Construct an empty queue
DestroyQueue(&Q): Destroy queue . Destroy and release the queue Q Memory space occupied
EnQueue(&Q, x): The team . If queue Q under , take x Join in , Make it a new tail
DeQueue(&Q, &x): Out of the team . If queue Q Non empty , Delete team leader element , And use x return
GetHead(Q, &x): Read the team leader element . If queue Q Non empty , Then assign the team head element to x
QueueEmpty(Q): Determines if the queue is empty . Empty return true, Otherwise return to false
3.6 Sequential implementation of queues
Definition 、 initialization 、 Sentenced to empty 、 The team 、 Out of the team
#define MaxSize 10
typedef struct {
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int front, rear;
} SqQueue;
// Initialize queue
void InitQueue(SqQueue &Q) {
Q.rear = Q.front = 0;
}
// Determines if the queue is empty
bool QueueEmpty(SqQueue Q) {
if (Q.rear == Q.front) return true;
else return false;
}
// The team
bool EnQueue(SqQueue &Q, ElemType x) {
// A space is sacrificed here to judge whether the team is full / Team space
if ((Q.rear + 1) % MaxSize == Q.front) return false;
Q.data[Q.rear] = x;
Q.rear = (Q.rear + 1) % MaxSize;
return false;
}
// Out of the team ( Delete a team head element , And use x return )
bool DeQueue(SqQueue &Q, ElemType &x) {
if (Q.rear == Q.front) return false;
x = Q.data[Q.front];
Q.front = (Q.front + 1) % MaxSize;
return true;
}
// Get the value of the team head element , use x return
bool GetHead(SqQueue Q, ElemType &x) {
if (Q.rear == Q.front) return false;
x = Q.data[Q.front];
return true;
}
int main()
{
SqQueue Q;
……
}
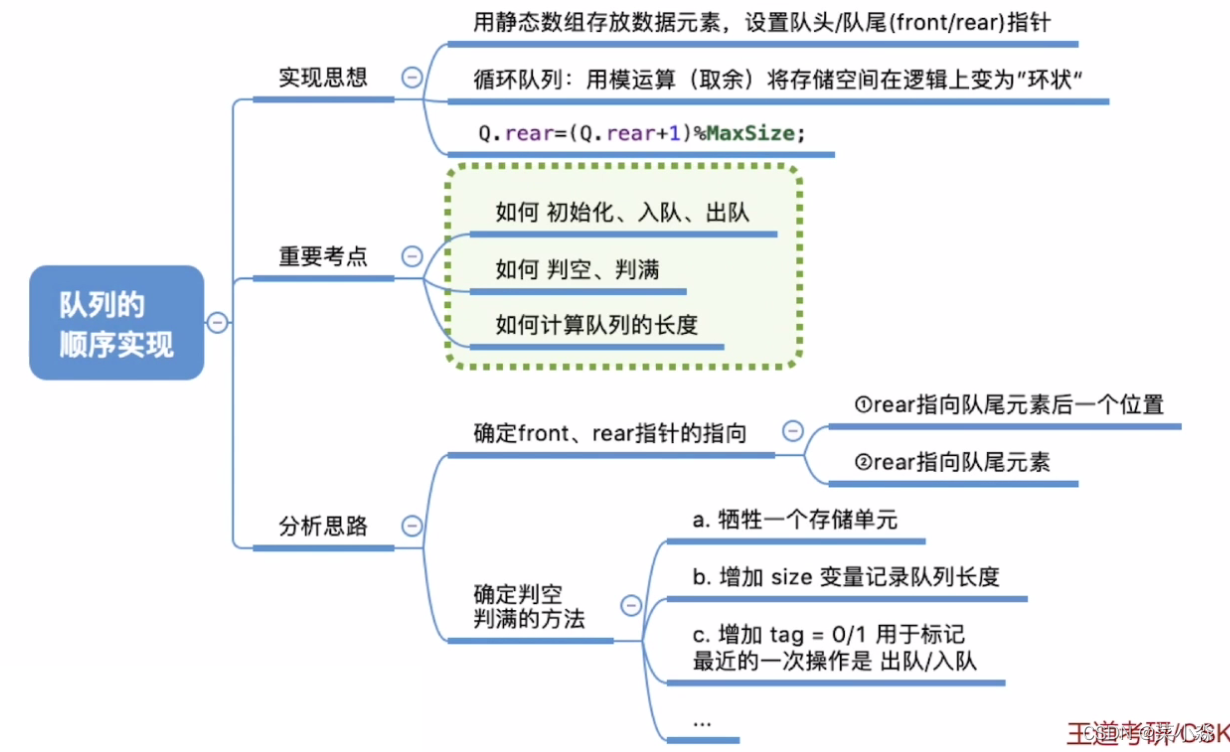
Determine whether a queue is empty / Three methods of full
- Sacrifice a space , Judge by taking mold
- Add a size attribute , Used to record the elements in the queue
- Add a tag, Used to store 0 and 1. Every time the delete operation succeeds , Du Ling tag=0; Every time the insert operation succeeds , Du Ling tag=1. Only delete , Can lead to the team empty , Only insert operation , Can lead to a full team .
3.7 Chained implementation of queues
typedef struct LinkNode {
ElemType data;
struct LinkNode *next;
} LinkNode;
tyepdef struct {
LinkNode *front, *rear;
} LinkQueue;
// Initialize queue ( Leading node )
void InitQueue(LinkQueue &Q) {
Q.front = Q.rear = (LinkNode*)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
Q.front -> next = null;
}
// Initialize queue ( No leading node )
void InitQueue(LinkQueue &Q) {
Q.front = null;
Q.rear = null;
}
// Determines if the queue is empty ( Leading node )
bool IsEmpyt(LinkQueue Q) {
if (Q.front == Q.rear) return true;
else return false;
}
// Determines if the queue is empty ( No leading node )
bool IsEmpyt(LinkQueue Q) {
if (Q.front == null) return true;
else return false;
}
// New elements in the team ( Leading node )
void EnQueue(LinkQueue &Q, ElemType x) {
LinkNode *s = (LinkNode *) malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
s -> data = x;
s -> next = null;
Q.rear -> next = s;
Q.rear = s;
}
// New elements in the team ( No leading node )
void EnQueue(LinkQueue &Q, ElemType x) {
LinkNode *s = (LinkNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
s -> data = x;
s -> next = null;
if (Q.front == null) {
Q.front = s;
Q.rear = s;
} else {
Q.rear -> next = s;
Q.rear = s;
}
}
// Team leader element out of the team ( Leading node )
bool DeQueue(LinkQueue &Q, ElemType &x) {
if (Q.front == Q.rear) return false; // Air force
LinkNode *p = Q.front -> next;
x = p -> data; // With variable x Return to team leader element
Q.front -> next = p -> next; // Modify the header node next The pointer
if (Q.rear == p) // This is the last node out of the team
Q.rear = Q.front; // modify rear The pointer
free(p); // Release node space
return true;
}
// Team leader element out of the team ( No leading node )
bool DeQueue(LinkQueue &Q, ElemType &x) {
if (Q.front == null) return false; // Air force
LinkNode *p = Q.front; // p Point to the node out of the team
x = p -> data; // With variable x Return to team leader element
Q.front = p -> next; // modify front The pointer
if (Q.rear == p) {
// This is the last node out of the team
Q.front = null;
Q.rear = null;
}
free(p); // Release node space
return true;
}
void testLinkQueue() {
LinkQueue Q;
InitQueue(Q);
……
}
3.8 deque
deque : It is only allowed to insert... From both ends 、 Linear table deleted at both ends
Input restricted double ended queue : It is only allowed to insert... From one end 、 Linear table deleted at both ends
Output the first double ended queue : It is only allowed to insert... From both ends 、 Delete one end of the linear table
3.9 The application of the stack —— Parentheses matching
The last left parenthesis is matched first (LIFO)
Each occurrence of a right parenthesis consumes an left parenthesis ( Out of the stack )
Put it on the stack when you encounter the left bracket , If you encounter the right parenthesis, you will get out of the stack
#define MaxSize 10
typedef struct {
char data[MaxSize];
int top;
} SqStack;
// Initialization stack
void InitStack(SqStack &S) {
}
// Judge whether the stack is empty
bool StackEmpty(SqStack S) {
}
// Put new elements on the stack
bool Push(SqStack &S, char x) {
}
// Stack top element out of stack , use x return
bool Pop(SqStack &S, char &x) {
}
bool bracketCheck(char str[], int length) {
SqStack S;
InitStack(S);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i ++) {
if (str[i] == '(' || str[i] == '[' || str[i] == '{') {
Push(S, str[i]);
} else {
if (StackEmpty(S))
return false;
char topElem;
Pop(S, topElem);
if (str[i] == ')' && topElem != '(') return false;
else if (str[i] == ']' && topElem != '[') return false;
else if (str[i] == '}' && topElem != '{') return false;
}
}
return StackEmpty(S);
}
3. 10 The application of the stack —— Arithmetic expression
Prefix expression : Operator before two operands
Infix expression : Operator is in the middle of two operands
Postfix expression : Operator after two operands
computing method : Scanning from left to right , Every operator encountered , Let the last two operands in front of the operator perform the corresponding operation , The combination is an operand




3.11 The application of stack in recursion
Features of function calls : The last called function is executed first and ends (LIFO)
When a function is called , You need to use a stack to store :
- Call return address
- Actual parameters
- local variable
When called recursively , The function call stack can be called “ Recursive work stack ”
Every time you enter a layer of recursion , Press the information required for recursive calls into the top of the stack ;
Every exit layer recursion , The corresponding message pops up from the top of the stack
3.12 Application of queues
Sequence traversal of trees
Breadth first traversal of graphs
The first come, first serve strategy of the operating system (FCFS)
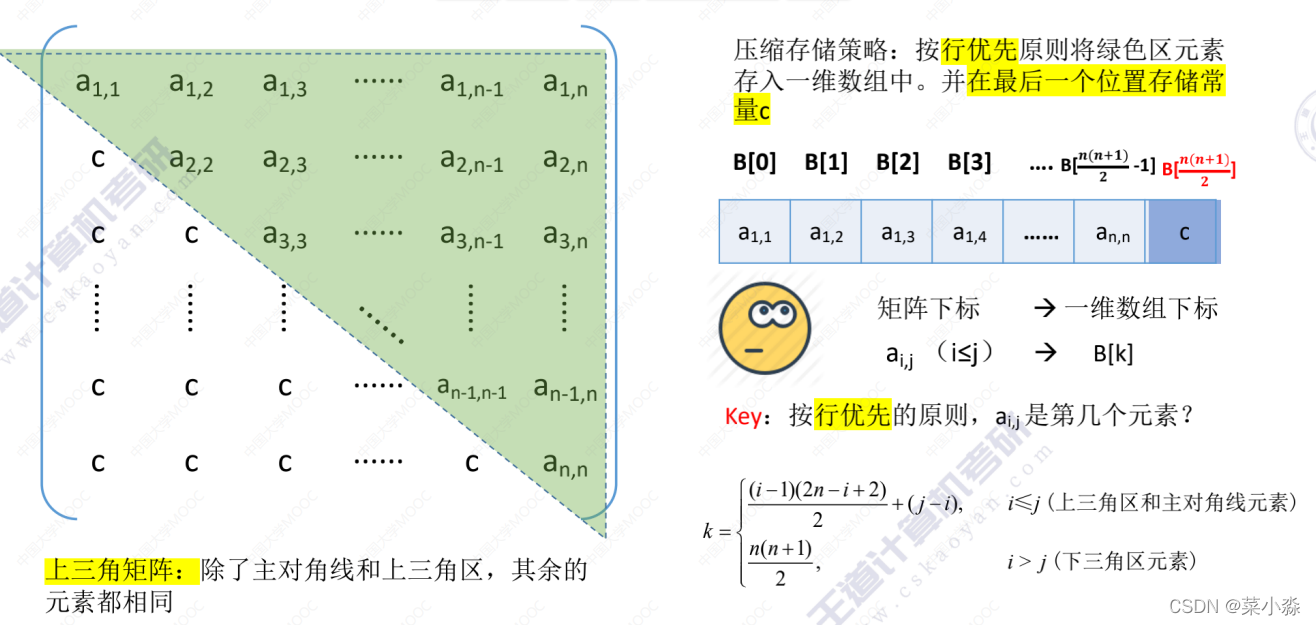
3.13 Compressed storage of special matrices

Compressed storage of symmetric matrix
if n Any element of a square matrix of order ai,j There are ai,j=aj,i, Then the matrix is called a symmetric matrix
Ordinary storage :n*n Two dimensional array
Compressed storage policy : Store only the main diagonal + Lower triangle ( Or the main diagonal + Upper triangle )
Store each element into a one-dimensional array according to the principle of row priority
How to use ?
It can realize a from matrix subscript to one-dimensional array subscript ” mapping “ function

Compressed storage of triangular matrix


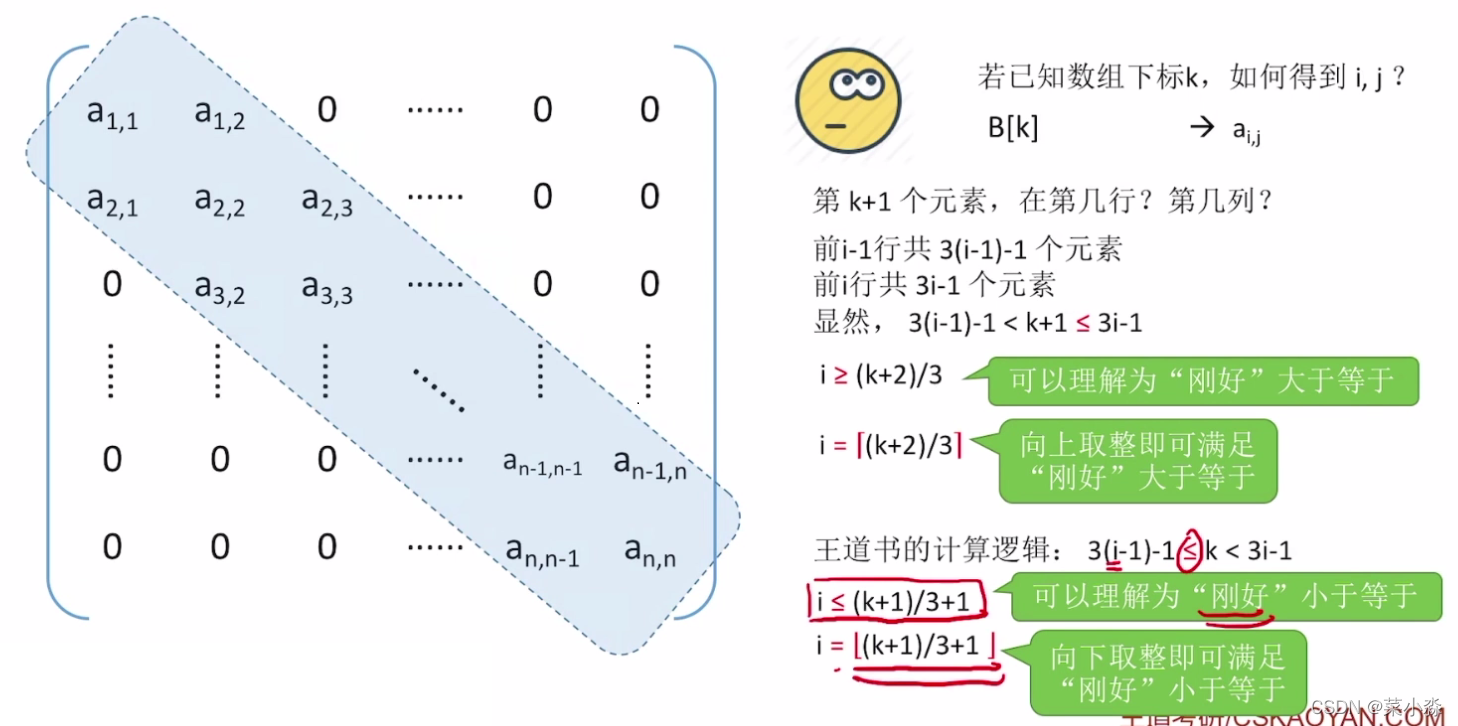

- Compressed storage of sparse matrix



边栏推荐
- 8、 C scope rules
- How to reduce the resolution of only 3D camera but not UI camera
- QT hex, decimal, qbytearray, qstring data conversion
- 使用Weka与Excel进行简单的数据分析
- Downloading PIP package is too slow
- Create a table under swiftui with table
- SwiftUI 布局 —— 尺寸( 下 )
- MITK create module
- Second class exercise
- 14、 ROS meta function package
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
How does core data save data in SQLite
7、 Detailed explanation of C language function definition
Summarize the knowledge points of the ten JVM modules. If you don't believe it, you still don't understand it
Installing MySQL on Linux
14、 ROS meta function package
多线程顺序运行有几种方法?
22、 TF coordinate transformation (II): static coordinate transformation
How to reduce the resolution of only 3D camera but not UI camera
Crawler: from entry to imprisonment (II) -- Web collector
ScottPlot入门教程:获取和显示鼠标处的数值
Redis-持久化
15、 Launch file label of ROS (I)
实时切换 Core Data 的云同步状态
17、 Solutions to duplicate names of ROS function packages and nodes
How long can we "eat" the dividends of domestic databases?
10、 Timestamp
Getting started with scottplot tutorial: getting and displaying values at the mouse
How to use the C language library function getchar ()
Install biological sequence de redundancy software CD hit
Error reason for converting string to long type: to convert to long type, it must be int, double, float type [easy to understand]









