当前位置:网站首页>Hardware Basics - diode Basics
Hardware Basics - diode Basics
2022-07-04 14:02:00 【ltqshs】
The most detailed diode foundation
Recently I saw a strange circuit symbol , Familiar with , But I can't remember what it is for . The advance and retreat of knowledge are vividly displayed in my mind . Just the following symbol , This is the symbol of a typical diode . But what can diodes do ? In fact, the sign says it clearly : Unidirectional conduction current .
This one-way conduction function , It lays a very important application foundation for diodes . It's like a one-way road in a city , Direct the current to the place you want . Although I hate one-way roads . But I like it in the circuit , Because we want to control everything in the circuit .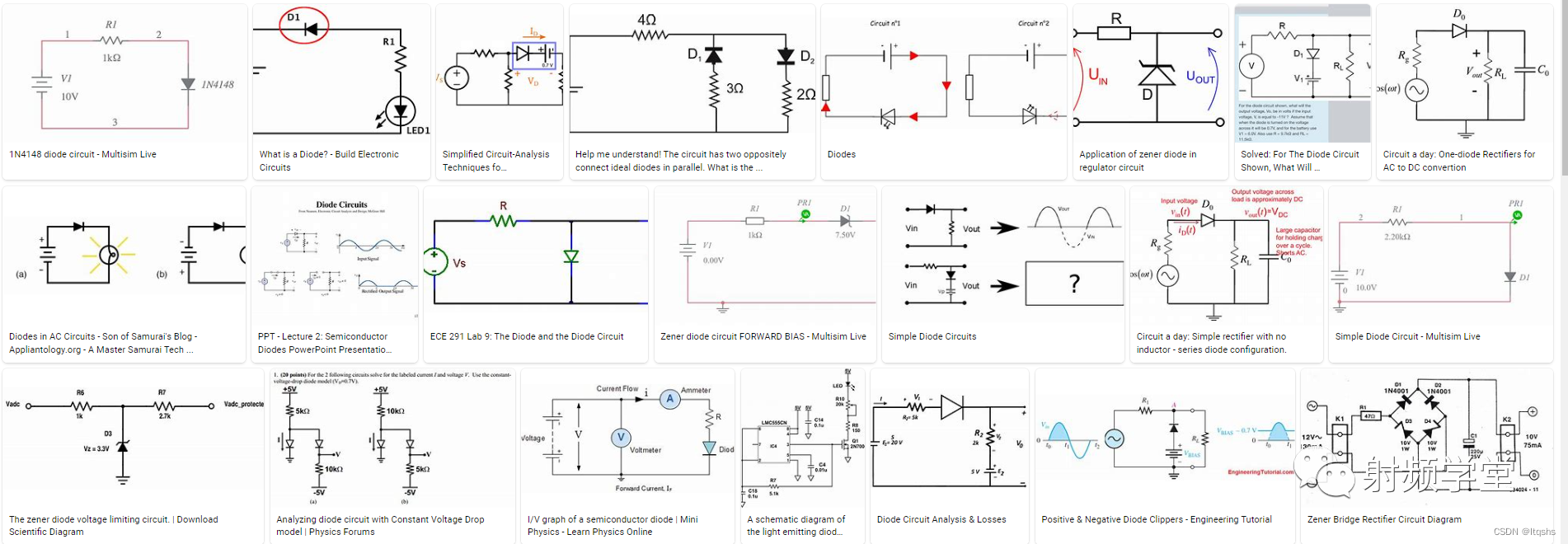
An ideal diode is like a one-way door , Only allow the current to flow in more than one direction , This direction of flow is called positive , And prevent the current from flowing in the other direction , This direction is reverse .
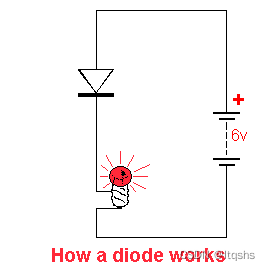
Types of diodes
According to the characteristics of diode , Diodes can be divided into several types .
Zener diode —— Zener diode is a kind of diode , It allows current to flow in the positive direction , It can also work in reverse breakdown but in breakdown state , Zener diodes have voltage stabilizing applications , Zener diode uses pn Knot in reverse offset mode , Give the zener effect .
Tunnel diode —— Tunnel diodes are used in microwave applications .
Schottky diode —— Schottky diode is a kind of metal - Semiconductor junction diode , Also called hot carrier diode 、 Low voltage diode or Schottky barrier diode . Schottky diodes are formed by the junction of semiconductors and metals . Schottky diode provides fast switching action and low forward voltage drop . As we know , stay PN Junction diode ,p The type and n Type connected together to form PN junction . In Schottky diodes , Use metals such as platinum or aluminum instead P Type semiconductor .
Light-emitting diode —— It is the most useful kind of diode , When the diode is connected with a forward bias , The current flowing through the junction produces light .
Variable capacitance diode —— This diode is also called VARICAP diode , Although the output of the variable capacitor can show general pn Junction diode , But because they are different types of diodes , This diode is approved to provide preferred capacitance variation .
photodiode —— The diode that generates current with a certain amount of light energy falls on it , In the forward bias current from p Transferred to the n Under the circumstances , When the reverse photocurrent flows in the opposite direction , There are two types of photodiodes, namely PN Photodiodes and PIN photodiode .
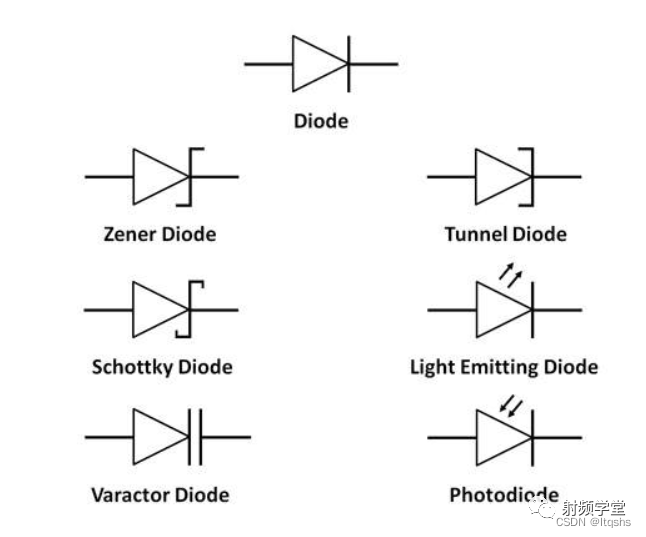
Diode construction
We know that there are two types of semiconductor materials : Intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors . In the intrinsic semiconductor , The electron number and hole concentration are equal at room temperature . In extrinsic semiconductors , Impurities are added to semiconductors to increase the number of electrons or holes . These impurities are pentavalent ( arsenic 、 antimony 、 phosphorus ) Or trivalent ( boron 、 indium 、 aluminum ).
Semiconductor diodes have two layers . The first floor is p type , The other is n Type semiconductor .
If we are in semiconductor ( Silicon and germanium ) Add trivalent impurities , Then more holes will appear and it is positively charged . Therefore, this type of layer is called p Type layer .
If we are in semiconductor ( Silicon or germanium ) Pentavalent impurity added to , Because there are too many electrons , A negative charge will be generated . Therefore, this type of layer is called n Type layer .
stay N Type area , Most charge carriers are electrons , A few charge carriers are holes . And in the P Type area , Most charge carriers are holes , Negative charge carriers are electrons . Due to concentration differences , Diffusion occurs in most charge carriers , They recombine with opposite charges . It produces positive or negative ions . They gathered near the intersection . This region is called the depletion region .
When the positive pole of the diode or p Connect the negative pole ,n Type or when the negative pole is connected to the positive pole of the battery , This diode is connected with reverse bias .
When the positive pole or p Type a terminal is connected to the positive pole of the battery ,n Type or when the negative pole is connected to the negative pole of the battery , This diode is connected to a forward bias .
Forward offset
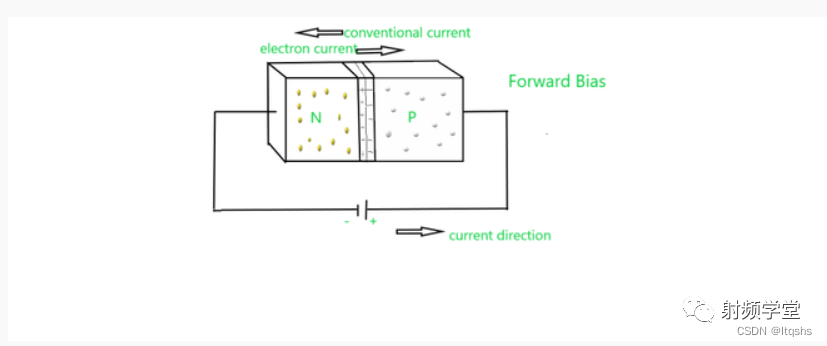
The bias semiconductor is connected to an external source . When p Type a semiconductor is connected to the positive terminal of the source or battery and the negative terminal is connected to n When it's type , This type of junction is said to be forward biased . In forward bias , The direction of the built-in electric field near the junction is opposite to that of the applied electric field . This means that the synthetic electric field is smaller than the built-in electric field . therefore , Low resistivity , Therefore, the depletion zone is thin . In Silicon , Voltage is 0.6 V when , The resistance in the depletion region is completely negligible .
Reverse bias
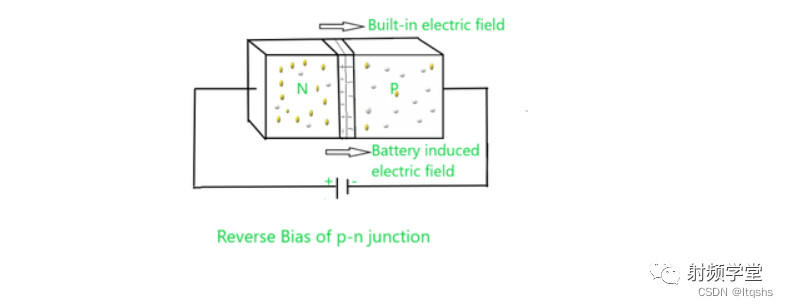
In reverse bias ,n Type A is connected to the positive pole of the battery ,p Type A is connected to the negative pole of the battery . under these circumstances , The applied electric field and the built-in electric field have the same direction , And the result of electric field is larger than that of built-in electric field , So as to produce greater resistance , Therefore, the depletion zone is thicker . If the applied voltage becomes larger , The depletion region becomes more resistive and thicker .
Unbiased diode
When no external source is applied to semiconductors , It is called unbiased diode . The electric field is built on p The type and n On the depletion layer between type a materials . This happens because of imbalance . Electrons and holes produced by doping . At room temperature , For silicon diodes ,0.7V Is the barrier potential .
The characteristics of the diode
diode IV curve
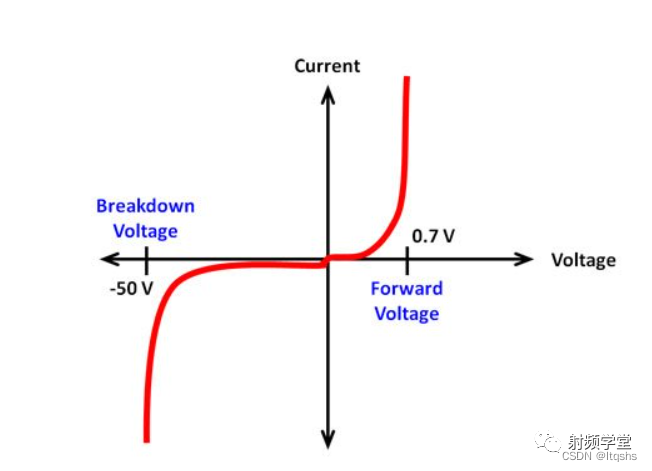
Please note that , For typical diodes ,y The current on the shaft is 0.7 How to flow through the diode under a forward voltage of V . The breakdown voltage is where the current begins to flow in the opposite direction , For a typical diode , This is a -50 Volt . All real diodes also have leakage current , The current will flow from the cathode to the anode without forward bias . Sometimes , You may need to understand other features , For example, diode resistance . For many circuits , This is not a real factor . However , For more sensitive circuits , One way to calculate diode resistance in forward bias mode is that you can use classic resistors = voltage / Current equation . under these circumstances , You can measure the diode voltage drop across the diode for different circuit modes , These circuit modes are related to the current through the diode .
Diode equation
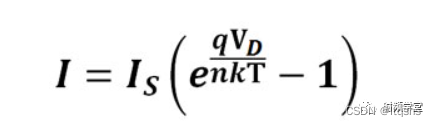
Is = Dark saturation current
q = Electron charge value
Vd = The voltage across the diode
n = Ideal factor , For ideal diodes ,n = 1, For actual diodes ,n = 1 To 2
k = Boltzmann constant ,1.38064852E-23 Joules / kelvin
T = temperature ( kelvin )
Common diode circuits
Rectifier diode
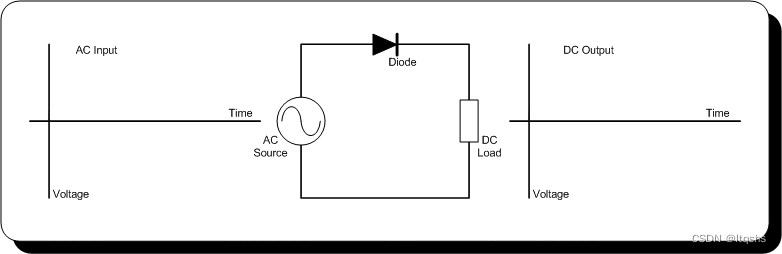
Half-wave rectifier
If we only want the upper half of a sinusoidal signal , You can add a diode directly into the circuit , Using the unidirectional conduction of diode , Filter out the bottom half of the signal . As shown in the figure below .
Full-wave rectifier
One disadvantage of half wave rectification is that half of the signal energy is consumed , Sometimes we need full wave rectification . At this time, the following diode circuit can be used . As shown in the figure below ( Animation is a little slow , Read it patiently )
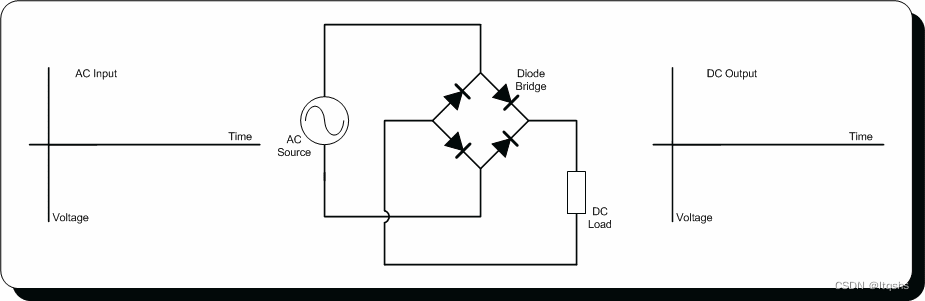
Flyback diode
This is sometimes called buffer diode 、 Freewheeling diode and suppression diode . Flyback diodes are a convenient way to use diodes to reduce sudden voltage spikes , This spike occurs when the current passing through the inductive load suddenly changes . As we discussed in our article on inductors , Whenever the inductor sees a change in the current flowing through it , It will produce a EMF Voltage spikes in an attempt to stabilize current changes .
In many circuits , This produces EMF Usually not needed , Sometimes it will damage other parts of the circuit . In order to eliminate damage , A diode can be placed , In order to appear EMF Voltage spikes encourage current to flow through the diode , Instead of flowing through other circuit components that may be damaged . A useful common circuit is the control of small fans or relay inductors . Usually , Most digital pins can provide less than 20 Milliampere current , Therefore, a current amplifier is needed . See the following example diode schematic .
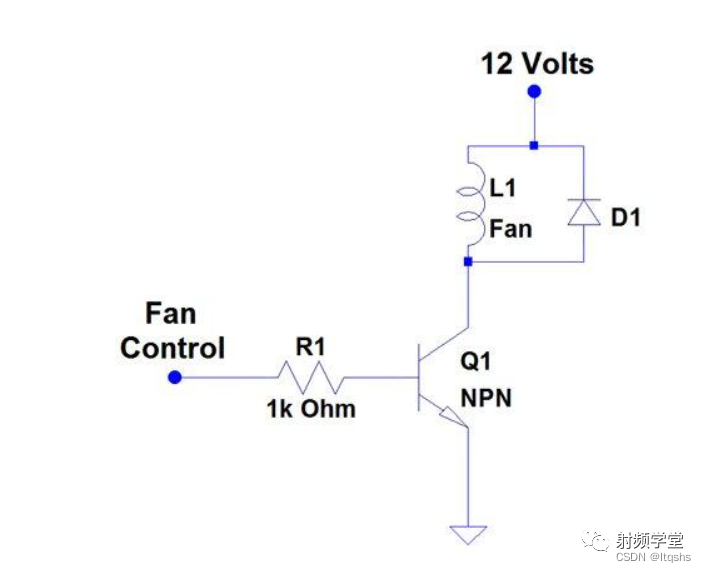
NPN Transistors work well here , Because digital pins can provide 10 Milliampere current to open NPN The transistor , And the transistor can handle the current of about Ampere required by the fan or relay inductor . Whenever the transistor is turned off , The inductor will see the current drop sharply and produce a peak of back EMF .
If there is no diode , The spike will flow through the transistor , Usually it will be damaged . By connecting the diode in parallel with the inductor ,EMF The voltage spike turns on the diode , And allow the current to flow through the diode and return to the inductor and dissipate . This current flowing back to the inductor is the source of the name of this diode .
Zener diode
Zener diodes are designed to operate in breakdown voltage mode . One way to take advantage of this is to use a zener regulator . We only need a resistor and a properly selected Zener , It can provide us with the required voltage output . An example zener diode circuit can be seen below .
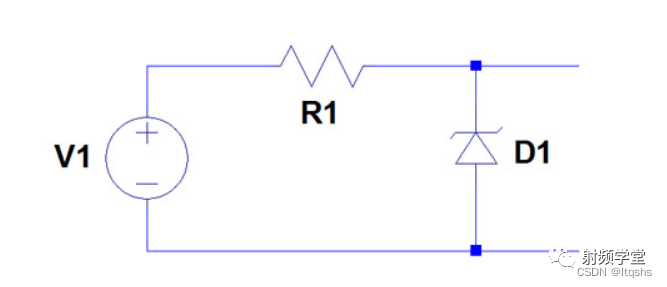
The zener diode will reduce the input voltage to the breakdown voltage of the diode in the circuit for output . To do this , It must allow current to flow through the diode , This will dissipate as heat , But only when the input voltage is higher than the breakdown voltage . The required output voltage will determine the zener diode , Because you will choose the diode according to its breakdown voltage to match the output voltage . You have to get a diode that can handle the power that must be dissipated .
Blocking diode
This use of diode is only the name for the case that diode is used to guide current to flow in only one direction .
A good example is solar panels and battery charger circuits . When the sun comes out and the solar panel generates electricity , Their voltage is usually higher than the battery the circuit is charging , Therefore, the current will flow from the battery board to the battery .
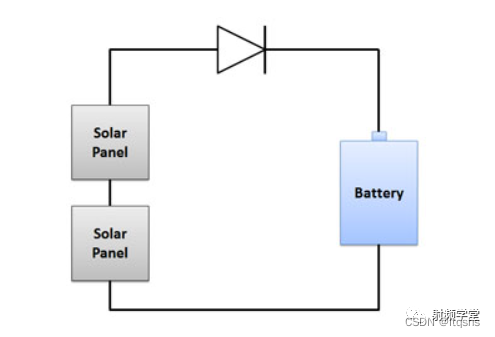
However , At night , There is no sunlight on the solar panel , So they don't generate electricity . At this time, the battery will be at a higher voltage and there will be no blocking diode , Current will flow from the battery to the panel , Waste energy . When placing a diode between the solar panel and the battery , It will allow current to flow from the panel to the battery , However, current is not allowed to flow from the battery to the battery board . therefore , it “ prevent ” The current flows in an unwanted way .
Another useful place is the battery in the circuit . At any time, someone may install the battery upside down , Or plug the DC power supply upside down , A good way to protect circuits is to use blocking diodes .
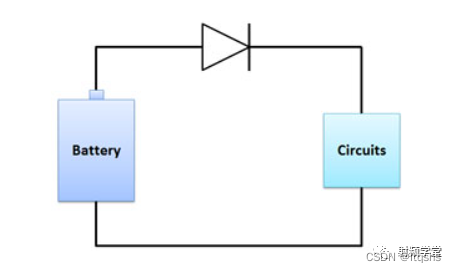
The diode ensures that only the correct voltage polarity allows current to flow into the circuit , Protect them from negative voltage .
Clamp diode
Clamp diode is just a method of using capacitors and diodes to control the DC level of the signal . In the following example circuit , Capacitors and diodes produce a DC offset on the input AC signal .
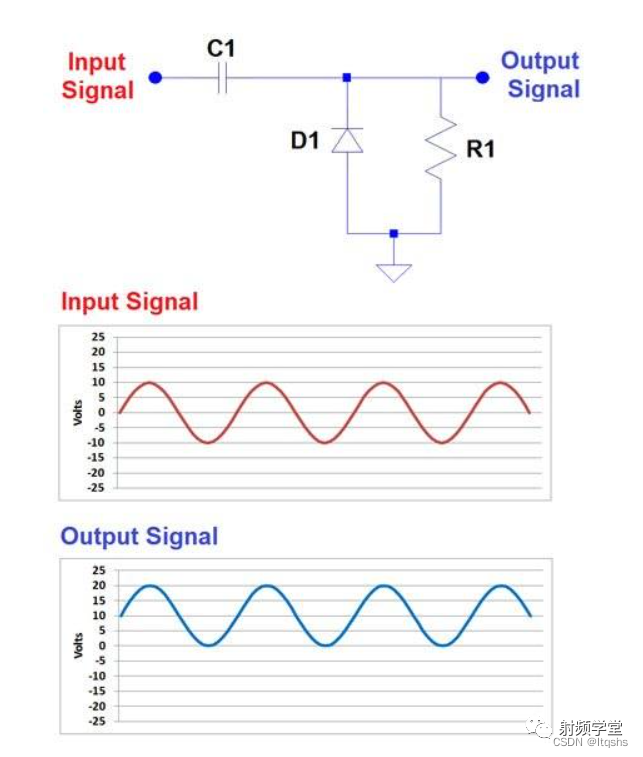
If we want to move in the other direction DC The offset , Then we just need to reverse the direction of the diode , As shown below .
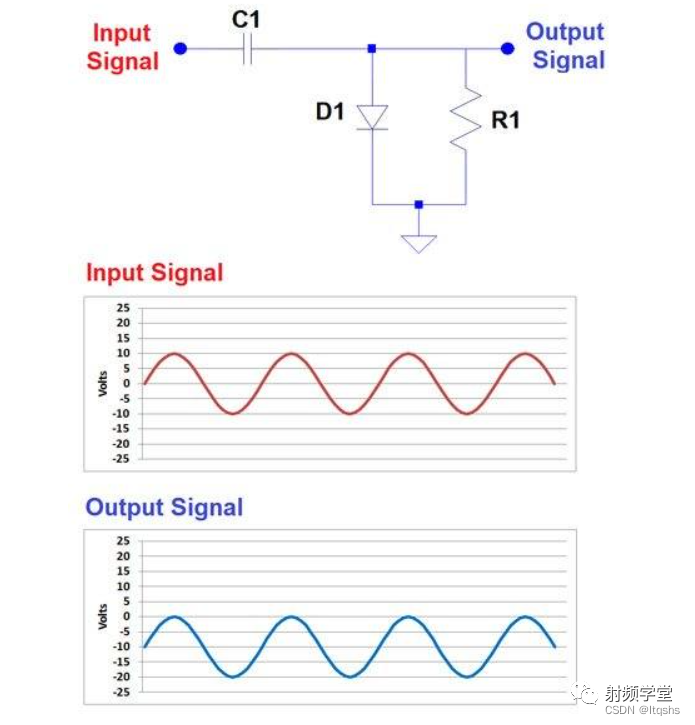
If you place a voltage source between the diode and the ground , You can go further , In this way, you can add more DC bias in the desired direction .
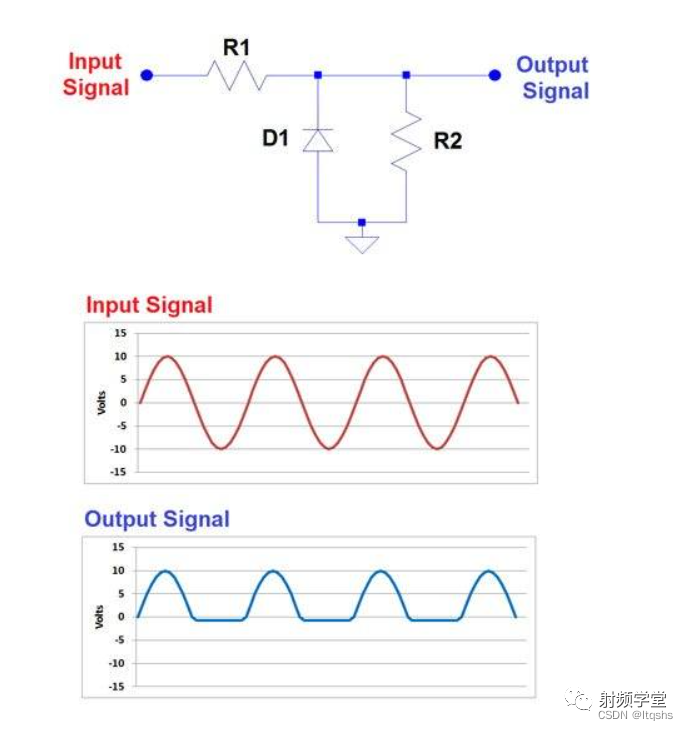
CLIPPING DIODE
The opposite of clamping is clipping . ad locum , You can use series resistors and diodes to intercept unwanted parts of the input signal . For positive limiting , The arrangement of the diode makes it turn on when the signal is higher than the forward voltage , Therefore, the diode conducts current , Limit the upper limit voltage to 0.7 Lie about . An example can be seen below .R2 Just an example resistor , Not required .
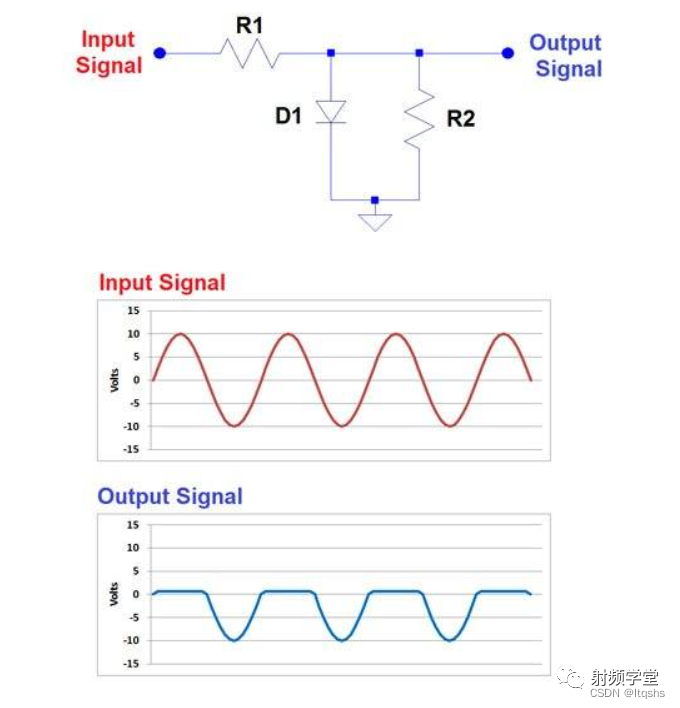
In the example above , Please note how the maximum up voltage is limited to 0.7 Volt , This is the forward voltage of the diode .
If negative clipping is required , You can simply flip the diode . under these circumstances , As long as the signal input is negative and exceeds the forward voltage , The diode will turn on and conduct current , Limit the negative signal to -0.7 Volt . Here is an example . Again , Unwanted R2. Notice how the negative part of the signal is clipped -0.7 v .
Reference material
https://byjus.com/physics/photodiodes-applications/
https://www.circuitbasics.com/what-is-a-diode/
https://byjus.com/physics/diodes/
https://www.fluke.com/en-us/learn/blog/electrical/what-is-a-diode
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/what-is-a-diode-definition-working-types-applications/
https://www.electronicsdesignhq.com/diodes/
disclaimer : This article is authorized by the author , Reprinted from “ RF school ” official account , The copyright belongs to the original author . Reprinted for reference only , It does not mean that this number agrees with its view , This number is also incorrect for its content 、 written words 、 Pictures bear any liability for infringement .
Reference article :《 The most detailed diode foundation 》
边栏推荐
- Unittest框架之断言
- 程序员转方向
- 软件测试之测试评估
- 2022 Shandong Province safety officer C certificate examination question bank and online simulation examination
- IDEA快捷键大全
- ViewBinding和DataBinding的理解和区别
- Openharmony application development how to create dayu200 previewer
- golang fmt.printf()(转)
- 美国土安全部长:国内暴力极端主义是目前美面临的最大恐怖主义威胁之一
- The Secretary of Homeland Security warned immigrants "not to embark on a dangerous journey"
猜你喜欢
基于STM32+华为云IOT设计的酒驾监控系统
Use the default route as the route to the Internet
sharding key type not supported
Understanding and difference between viewbinding and databinding
MySQL 5 installation and modification free

Flet tutorial 03 basic introduction to filledbutton (tutorial includes source code) (tutorial includes source code)

MySQL5免安装修改

德明利深交所上市:市值31亿 为李虎与田华夫妻档
unity不识别rider的其中一种解决方法
Huahao Zhongtian rushes to the scientific and Technological Innovation Board: the annual loss is 280million, and it is proposed to raise 1.5 billion. Beida pharmaceutical is a shareholder
随机推荐
做事的真正意义和目的,真正想得到什么
C array supplement
Openharmony application development how to create dayu200 previewer
吃透Chisel语言.10.Chisel项目构建、运行和测试(二)——Chisel中生成Verilog代码&Chisel开发流程
Gorm 读写分离(转)
逆向调试入门-PE结构-资源表07/07
程序员转方向
2022G3锅炉水处理考试题模拟考试题库及模拟考试
go语言中的文件创建,写入,读取,删除(转)
Ruichengxin micro sprint technology innovation board: annual revenue of 367million, proposed to raise 1.3 billion, Datang Telecom is a shareholder
苹果5G芯片研发失败:继续依赖高通,还要担心被起诉?
Unittest框架之断言
js中的变量提升和函数提升
学习项目是自己找的,成长机会是自己创造的
. Net delay queue
程序员的焦虑
2022年起重机械指挥考试模拟100题模拟考试平台操作
Lick the dog until the last one has nothing (state machine)
Unittest中的TestSuite和TestRunner
Applet live + e-commerce, if you want to be a new retail e-commerce, use it!