当前位置:网站首页>C Expert Programming Chapter 5 Thinking about Linking 5.1 Libraries, Linking and Loading
C Expert Programming Chapter 5 Thinking about Linking 5.1 Libraries, Linking and Loading
2022-08-04 04:45:00 【weixin_Guest time】
Linker basics: The compiler creates an output file that contains relocatable objects.These objects are the data and machine instructions corresponding to the source program.
The linker is at that stage of the compilation process
The complex form of linking in SRV4 systems.
C preprocessor ---> (stage p) front end (syntax and semantic analysis) ---> (stage o) back end (code generator) --->
(stage c)Optimizer---->(Phase 2) Assembler---->(Phase a) Linker-Loader
Most compilers are not a single monolithic program.They usually consist of as many as six or seven smaller programs called by a control program called a "compiler driver".These separate programs that are easily separated from the compiler include the preprocessor, the syntactic and semantic checker, the code generator, the assembler, and the optimizer., the linker, and of course a driver program that calls all of these programs and passes the correct options to each program.The optimizer can add almost all the stages above.Current SPARC performs most of the optimizations at the intermediate presentation layer between the front-end and back-end of the compiler.
Separate programs are easier to design and maintain.
The rules governing the preprocessing process are unique to the preprocessing phase and have little in common with the rest of the C language.
The C preprocessor is often (but not always) a standalone program.If the code generator (aka "backend") is written
as a separate program, it is likely to be shared by other languages.The tradeoff for this design approach is that running several smaller programs
takes longer than running one large program (because of the overhead of the initialization process and passing information between stages).
The -# option looks at the individual stages of the compilation process.The -V option provides version information.
Pass option information to the various stages by giving the compiler driver a special -W option (meaning to pass this option to which stage).
"W" followed by a character (prompting that stage), a comma, and then the specific option.
Any option passed by the compiler driver to the linker must be prefixed with -W1 before the specific option to tell the compiler driver that this option is intended to be passed to the linker.
cc -W1, -m main.c > main.linker.map
Pass the -m option to the linker-loader, asking it to generate a linker image.
The object file cannot be executed directly, it first needs to be loaded into the linker.Linking confirms that the main function is the initial entry point (where program execution begins), binds symbolic references to memory addresses, lumps all object files together, and adds library files to produce an executable file.
PC's linking mechanisms are vastly different from those of larger systems.The linker of a PC generally provides only a few basic I/O services, a program called the BIOS.They exist in fixed locations in memory and are not part of every executable.If the PC program or program suite requires more advanced services, it can be provided through library functions, but the compiler must link the library functions into each executable file.
In MS-DOS, there is no way to deduce which of the programs the library is commonly used for, and thus install it only once on the PC.
UNIX systems used to be the same.When the program is linked, a copy of each library function that needs to be used is added to the executable.
In recent years, a more modern and superior method called dynamic linking has been adopted.
Dynamic linking allows the system to provide a huge set of function libraries that can provide many useful services.However, the program will look for them at runtime, rather than having the binary code of these libraries as part of its own executable.
If a copy of the library is a physical part of the executable, then we call it static linking: if the executable just contains the filename, it allows the loader to find what the program needs at runtimefunction library, then we call it dynamic linking.
The canonical names for the three phases that the collection module prepares to execute are link-editing, loading, and runtime linking.Statically linked modules are link-edited and loaded to run.Dynamically linked modules are link-edited, loaded, and linked at runtime to run.During program execution, before the main() function is called, the runtime loader loads the shared data object into the process's address space.The runtime loader does not resolve external functions until they are actually called.Therefore, the function library is linked, and if it is not actually called, it will not bring additional overhead.
Even in static linking, the entire libc.a file is not loaded into the executable, only the required functions are loaded.
边栏推荐
- Tensors - Application Cases
- 7.LVS负载均衡群集之原理叙述
- Deep learning -- CNN clothing image classification, for example, discussed how to evaluate neural network model
- 八年软件测试工程师带你了解-测试岗进阶之路
- docker安装mysql与宿主机相差8小时的问题。
- 【技巧】借助Sentinel实现请求的优先处理
- go module的介绍与应用
- 将xml标签转换为txt(voc格式转换为yolo方便进行训练)
- 信息学奥赛一本通 1312:【例3.4】昆虫繁殖
- 【Ryerson情感说话/歌唱视听数据集(RAVDESS) 】
猜你喜欢
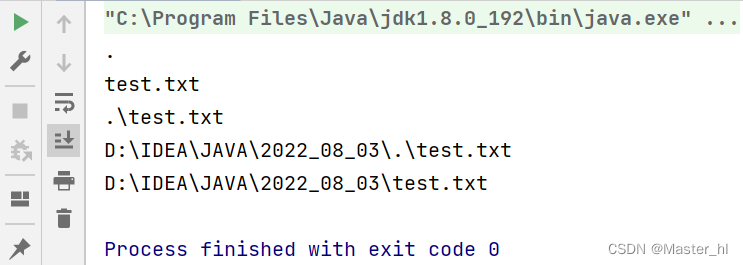
Simple operation of the file system
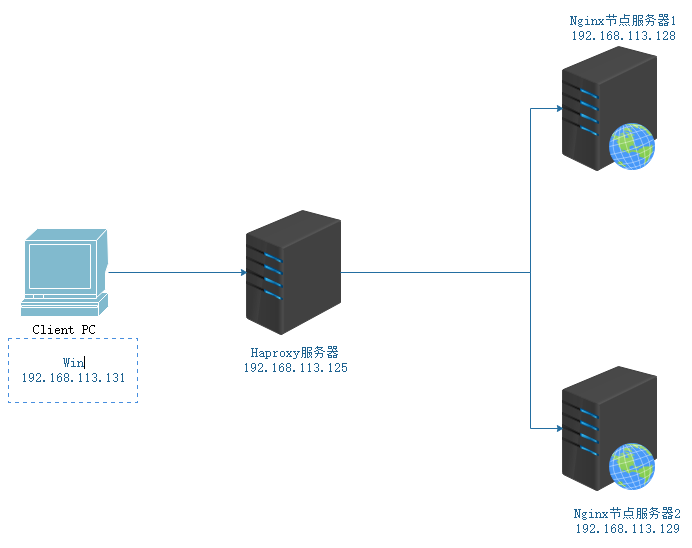
8. Haproxy builds a web cluster
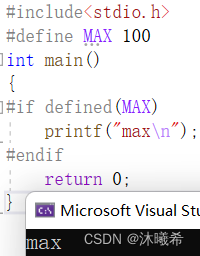
【C语言进阶】程序环境和预处理
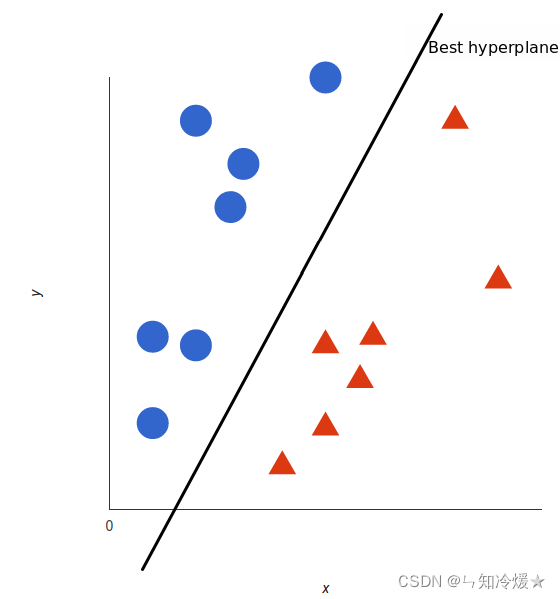
SVM介绍以及实战
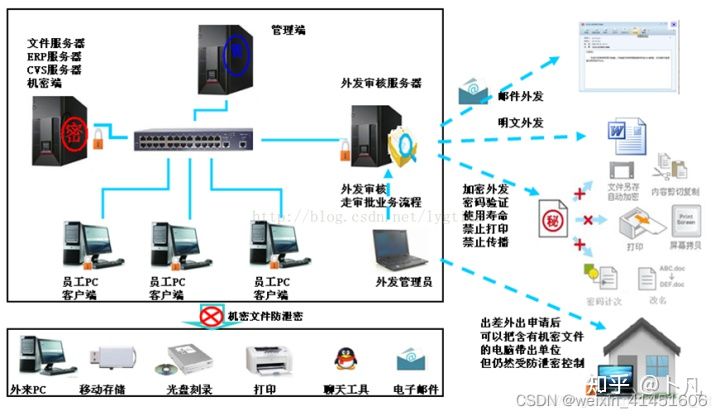
烧录场景下开发如何进行源代码保密工作
A Preliminary Study of RSS Subscription to WeChat Official Account-feed43
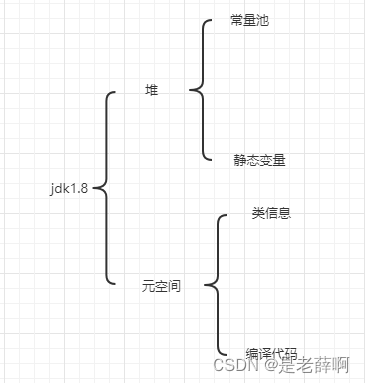
Take care of JVM performance optimization (own note version)
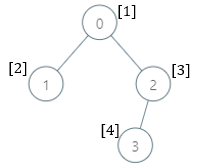
2003. 每棵子树内缺失的最小基因值 DFS

Eight guiding principles to help businesses achieve digital transformation success
如何简化现代电子采购的自动化?
随机推荐
2023年PMP考试会用新版教材吗?回复来了!
C专家编程 第4章 令人震惊的事实:数组和指针并不相同 4.1 数组并非指针
Turn: Management is the love of possibility, and managers must have the courage to break into the unknown
软件测试如何系统规划学习呢?
Eight guiding principles to help businesses achieve digital transformation success
Mobile payment online and offline payment scenarios
【21 Days Learning Challenge】Direct Insertion Sort
某母婴小程序加密参数解密
类如何只能静态分配和只能动态分配
el-Select 选择器 底部固定
商城系统APP如何开发 都有哪些步骤
PHP高级开发案例(1):使用MYSQL语句跨表查询无法导出全部记录的解决方案
C专家编程 第5章 对链接的思考 5.4 警惕Interpositioning
How to keep the source code confidential in the development under the burning scenario
深度学习环境配置
使用Patroni回调脚本绑定VIP的坑
The Shell function
系统设计.秒杀系统
docker安装mysql与宿主机相差8小时的问题。
8. Haproxy builds a web cluster