当前位置:网站首页>[C language - Advanced pointer] mining deeper knowledge of pointer
[C language - Advanced pointer] mining deeper knowledge of pointer
2022-06-11 08:57:00 【BaconZzz】
Preface
The knowledge of this article diverges from the elementary pointer , Mention more about the concept and basic usage of pointers , Too much dry goods ! Go get a glass of water !
List of articles
1. Character pointer
Mention a fallible usage :
int main()
{
const char* pstr = "hello bit.";// Here is to put a string into pstr Is it in the pointer variable ?
printf("%s\n", pstr);
return 0;
}
The operation of putting a string into a pointer is : Put the address of the first character of the string into the pointer
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char arr1[] = "bacon";
char arr2[] = "bacon";
const char* arr1 = "bacon";
const char* arr2 = "bacon";
if (p1 == p2)
printf("p1 and p2 are same\n");
else
printf("p1 and p2 are not same\n");
if (arr1 == arr2)
printf("arr1 and arr2 are same\n");
else
printf("arr1 and arr2 are not same\n");
return 0;
}
result :
p1 and p2 are same
arr1 and arr2 are not same
analysis :p1 and p2 All stored in RO Data , Two The same constant string is not stored repeatedly ;arr1 and arr2 be Create your own memory space in the stack area .abcdef Is a constant string ,const Prevent constant strings from being modified .
2. Pointer array
Reference to definitions and usage :
2.1 The definition of pointer array
Pointer array : An array of pointers
Basic form :
int* arr1[10];
type* Array name [n]
2.2 Pointer array usage
- One of the pointer array usages : Combination method !
Combine one-dimensional arrays at different positions into two-dimensional arrays
int main()
{
int arr1[] = {
1,2,3,4,5 };
int arr2[] = {
2,3,4,5,6 };
int arr3[] = {
3,4,5,6,7 };
int* parr[] = {
arr1,arr2,arr3 };
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
//printf("%d ", parr[i][j]);
printf("%d ", *(parr[i] + j));
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
3. Array pointer
Refer to definitions 、 Array name and usage :
3.1 Definition of array pointer
Array pointer : Pointer to array
To make a distinction
int *p1[10];// Pointer array
int (*p2)[10];// Array pointer
analysis : Here comes the question of priority ,[ ] Has a higher priority than *
p1 and [ ] combination , Ahead int* Is the type of array element
p2 and * combination , representative p2 It's a pointer , The object type pointed to is : The number of elements is 10 The shape array of
3.2 Array names
about
int arr[10];
There is such a saying :
arr As an array name , representative The address of the first element
&arr What you take out is The address of the entire array
Look at the difference
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {
0 };
printf("%p\n", arr);// First element address
printf("%p\n", &arr);// The entire array address
return 0;
}
result :
005CF86C
005CF86C
You can see that their addresses are the same .
But even if The values are the same , The meaning is different
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {
0 };
printf("%p\n", arr);// First element address
printf("%p\n", &arr);// The entire array address
printf("%p\n", arr+1);// First element +1 Address
printf("%p\n", &arr+1);// Entire array +1 Address
return 0;
}
result :
0318F61C
0318F61C
0318F620
0318F644
arr+1 Skip the 4 Bytes ( An element )
&arr+1 Skip the 40 Bytes ( Entire array )
This also confirms what I said above
3.3 Usage of array pointers
Look directly at the examples
void print(int(*p)[5], int row, int col)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
printf("%d ", *(*(p + i) + j));
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[3][5] = {
{
1,2,3,4,5},{
2,3,4,5,6},{
3,4,5,6,7} };
print(arr, 3, 5);
return 0;
}
analysis : I'm going to use a One dimensional array pointer To accept Array name of two-dimensional array ( The address on the first line ). amount to ,p Received the address of the first line ;p+1, The second line . and *(p+1) Is the array name of each row of one-dimensional array , It also indicates the address of the first element , Give it +1,*(p+1)+1, Equivalent to the second element of the second line
3.4 Distinguish between pointer array and array pointer
Careful analysis , To appreciate …
int arr[5];// Shape array
int *parr1[10];// An array of plastic pointers
int (*parr2)[10];// Point to Yes 5 An integer array of elements The pointer to
int (*parr3[10])[5];// Deposit 5 An array pointer to an integer array Array of
!!!
I have an idea : By priority , Remove Variable name / Array name , The rest is the type
!!!
int arr[5];
int [5] It's the type
int *parr1[10];
int *[10] It's the type
int (*parr2)[10];
int (*)[10] It's the type
int (*parr3[10])[5];
int (*)[5] It's the type
4. Shape parameter : Arrays and pointers
How arrays and pointers are passed ?
…
4.1 One dimensional array parameters
See examples
// One dimensional array as an argument , Use a one-dimensional array as a formal parameter to receive , That's all right.
void test1(int arr[])
{
}
// The essence of an array name is the address of the first element , Take a pointer to receive the first element address , That's all right.
void test1(int* parr)
{
}
// One dimensional array as an argument , But receive with a pointer array , wrong
void test2(int* arr[])
{
}
// One dimensional array as an argument , But with a two-level pointer
// The secondary pointer is used to store the address of the primary pointer variable , wrong
void test2(int** arr)
{
}
int main()
{
int arr1[10] = {
0 };
int* arr2[10] = {
0 };
test1(arr1);
test2(arr2);
return 0;
}
4.2 Two dimensional array parameters
See examples
Two dimensional array as argument , The design of formal parameters can only omit the first [ ] The number of
// wrong
void test(int arr[][])
{
}
// wrong
void test(int arr[3][])
{
}
// Yes
void test(int arr[][5])
{
}
//--------------------------------------------
Array name of two-dimensional array , It means the first line ( One dimensional array ) The address of
// You cannot simply receive with an integer pointer , wrong
void test(int* arr)
{
}
Two dimensional array as argument , But receive with an array of integer pointers , wrong
void test(int* arr[5])
{
}
Two dimensional array as argument , Receive array name with array pointer ( The address on the first line ),arr Can point to each line
That is, every element of a two-dimensional array , That's all right.
void test(int(*arr)[5])
{
}
Two dimensional array as argument , But with a two-level pointer
The secondary pointer is used to store the address of the primary pointer variable , wrong
void test(int** arr)
{
}
int main()
{
int arr[3][5] = {
0 };
test(arr);
return 0;
}
4.3 First level pointer parameter transfer
See examples :
- First level pointer parameter passing instance
void print(int* p, int sz)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%d ", *(p + i));
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
print(arr, sz);
return 0;
}
In time Converse thinking , Can make us go further
When the parameter part of a function is First level pointer , What parameters can a function take ?
void print(int* p)
{
}
int main()
{
int a = 0;
int* pa = &a;
int arr[10] = {
0 };
print(&a);
print(pa);
print(arr);
return 0;
}
When the parameter of the function is a secondary pointer , What parameters can be received ?
void print(int** p)
{
}
int main()
{
int a = 0;
int* pa = &a;
int** ppa = &pa;
print(ppa);
print(&pa);
return 0;
}
summary : As long as the arguments passed are essentially addresses / The address of the first level pointer variable , Is no problem
5. A function pointer
So let's see :
For functions , & Function name and Function name , All are the addresses of functions
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int main()
{
printf("%p\n", Add);
printf("%p\n", &Add);
return 0;
}
result :
00ED13B6
00ED13B6
5.1 Definition of function pointer
* Return type ( Pointer name )( parameter types , parameter types ,…)
int(*pf)(int, int)
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int main()
{
int (*pf)(int, int) = &Add;
//int ret = (*pf)(10, 20);
int ret = pf(10, 20);
printf("%d\n", ret);
return 0;
}
result :
30
5.2 Function pointer usage
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int calc(int(*pf)(int, int), int x, int y)
{
return pf(x, y);
}
int main()
{
int ret = calc(Add, 3, 5);
printf("%d\n", ret);
return 0;
}
!!!
The meaning of function pointers : The principle is the same as that of an ordinary pointer , Functions can be called through pointers , in other words , You can use functions as arguments
!!!
6. Function pointer array
6.1 Definition of function pointer array
Define a Deposit 10 An array of function pointers , Every The return type of the function pointed to by the function pointer is int, No parameter
int(*parr[10])()
- How to understand ?
parr The first and [ ] combination , Let's take it off parr[10] , You get the type of the array : int(*)() - A function pointer
6.2 Usage of function pointer array
One of the usages : Transfer table
================= Transfer table ===============
void menu()
{
printf("***************************\n");
printf("****1.Add******2.Sub*****\n");
printf("****3.Mul******4.Div******\n");
printf("**********0.exit***********\n");
printf("***************************\n");
}
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int Sub(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}
int Mul(int x, int y)
{
return x * y;
}
int Div(int x, int y)
{
return x / y;
}
int main()
{
int input = 0;
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
int ret = 0;
int (*pfarr[])(int, int) = {
Add,Sub,Mul,Div };
do
{
menu();
printf(" Please select :");
scanf("%d", &input);
if (input == 0)
{
printf(" Exit calculator ......\n");
break;
}
else if (input >= 1 && input <= 4)
{
printf(" Please enter two operands :");
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
ret = pfarr[input-1](x, y);// adopt input To access specific functions
printf("%d\n", ret);
}
else
{
printf(" Wrong choice \n");
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
Function pointer array saves redundant code here , If you don't believe me, let's take a look at the common implementation :
int main()
{
int input = 0;
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
do
{
menu();
printf(" Please select :");
scanf("%d", &input);
switch (input)
{
case 1:
printf(" Please enter two operands :");
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
printf("%d\n", Add(x, y));
break;
case 2:
printf(" Please enter two operands :");
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
printf("%d\n", Sub(x, y));
break;
case 3:
printf(" Please enter two operands :");
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
printf("%d\n", Mul(x, y));
break;
case 4:
printf(" Please enter two operands :");
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
printf("%d\n", Div(x, y));
break;
case 0:
printf(" sign out ...\n");
break;
default:
printf(" Please select correctly !\n");
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
7. A pointer to an array of function pointers
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int main()
{
int(*pf)(int, int) = Add;// A function pointer
int(*parr[1])(int, int) = {
pf };// Function pointer array
int(*(*pparr)[1])(int, int) = &parr;// A pointer to an array of function pointers
return 0;
}
I've got a pattern :
- balabala The pointer : Combine pointer variables with * Cover up —— bala (*p) bala
- balabal Array : Let the array name and [ ] Get together —— bala arr[10] bala
8. Callback function
The callback function is a Functions called through function pointers . If you put a pointer to a function ( Address ) Pass as argument to another function , When this pointer is used to call the function it points to , Let's just say this is a callback function . The callback function is not called directly by the function's implementer , It's called by another party when a particular event or condition occurs , Used to respond to the event or condition .
- Not called by the implementer
- Called by a function pointer
Library function qsort Use , The knowledge of callback function is used
also qosrt Design logic of , There are many places worth learning
thus , Let's study qsort !
8.1 qsort
To study a function , It is not necessary to study the function first Use scenarios 、 Return type 、 Parameters Well !
- Use scenarios : Maybe I didn't know until I studied it ?
- Return type :void, They just make an order
- Parameters : This needs a good look !
8.1.1 qsort Parameters of
qsort The parameters are as follows :
void qsort
(
void *base,// The starting position of the data to be sorted
size_t num, // Element number
size_t width,// The size of each element ( Company : byte )
int (__cdecl//C Language function calling convention , Don't go into it
*compare )//“ Comparison function ” The pointer to
(const void *elem1, const void *elem2 )
);
Now let's analyze why it is designed like this :
- Why start position 、 Element number 、 Element size … So many parameters , No trouble ?
Such a parameter , Can make qsort A more general , Whatever your type , We can all line up
- void* ?
void* , No pointer of exact type , Therefore You can pass different types of pointers to him , For the sake of generality
however , Because there is no exact type , unable Quoting and +- Integers ( I don't know how much space to visit , I don't know how many bytes to skip )
- num?width?
Think , Only know the data to be sorted The starting position , You can find every element ?
The starting position + Element number + Element size —> Find each element accurately
- Comparison function ?
Still the same , In the service of generality , qsort Users of , root According to the data you want to sort , Self implementation of a comparison function
int It can be used > Compare , String ? The structure ? Therefore, it is more appropriate to implement it on your own according to your needs
- requirement :e1>e2 Return to one >0 Number of numbers ,e1=e2 return 0,e1<e2 Return to one <0 Number of numbers
wow ! The position of the pointer in my heart rises in a straight line , miao !
Analysis of the qsort Parameters of , Try again :
8.2 qsort Use & qsort The callback function in
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
int cmp(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return *(int*)e1 - *(int*)e2;
}
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {
9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1 };
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
qsort(arr, sz, sizeof(arr[0]), cmp);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}
result :
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- cmp The implementation of is not certain , therefore , We can achieve it according to our own ideas , To compare different data
yo ? there cmp? yo ?qsort Called cmp?
cmp Is a pointer
qosrt During the sorting process cmp The pointer The comparison function pointed to —— It is not called by the implementer !
This is no different from the definition of callback function ! adopt qsort , We not only learned The magic of the pointer , Also learned Callback function
qsort summary :
- utilize void* The pointer Features that can receive various pointers , Improve versatility
- Take some functions as parameters , Through function pointers , Transfer functions flexibly , Further improve commonality
8.3 take qsort The long way , repair bubble Short
- We have learned the basic bubble sorting :
void BubbleSort(int arr[], int sz)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int flag = 1;
for (i = 0; i < sz - 1; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < sz - 1 - i; j++)
{
if (arr[i] > arr[i + 1])
{
int tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[i + 1];
arr[i + 1] = tmp;
flag = 0;
}
}
if(1 == flag)
break;
}
}
however , Has absorbed qsort After the essence , We will not be satisfied with this :
Only integer type can be arranged , This bubble is too stupid !
Imitate qsort Parameter design of , Let's see if we can also make Benben popular
- Improved bubble sorting
int cmp_int(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return *(int*)e1 - *(int*)e2;
}
void Swap(char* buf1, char* buf2, int width)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < width; i++)// Swap the bytes of each element according to the type
{
char tmp = *buf1;
*buf1 = *buf2;
*buf2 = tmp;
buf1++;
buf2++;
}
}
void BubbleSort(void* base, int sz, int width, int(*cmp)(const void*, const void*))
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz - 1; i++)
{
int flag = 1;// If it's sorted out
for (j = 0; j < sz - 1 - i; j++)
{
//base yes void*: You can't +- Integers ;
// If cast to int* Maybe it's too much to skip , Unable to achieve the desired effect
if (cmp((char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width) > 0
{
// In exchange for
// Here's a message width In the past , Swap bytes directly , Don't worry about the type
// Why swap bytes ? If you swap variables , Temporary variables are hard to create ( I don't know what kind of )
Swap((char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width, width);
flag = 0;
}
}
if (flag == 1)
{
break;
}
}
}int main()
{
int arr[10] = {
9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1 };
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
//qsort(arr, sz, sizeof(arr[0]), cmp);
BubbleSort(arr, sz, sizeof(arr[0]), cmp_int);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}
result :
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Absorbed the essence Bubblesort , Already much smarter !
- If you don't believe me, let's let him arrange a structure data :
struct stu
{
char name[20];
int id;
};
int cmp_stu_by_name(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return strcmp(((struct stu*)e1)->name, ((struct stu*)e2)->name);
}
int cmp_stu_by_id(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return ((struct stu*)e1)->id - ((struct stu*)e2)->id;
}
void Swap(char* buf1, char* buf2, int width)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < width; i++)
{
char tmp = *buf1;
*buf1 = *buf2;
*buf2 = tmp;
buf1++;
buf2++;
}
}
void BubbleSort(void* base, int sz, int width, int(*cmp)(const void*, const void*))
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz - 1; i++)
{
int flag = 1;// If it's sorted out
for (j = 0; j < sz - 1 - i; j++)
{
if (cmp((char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width) > 0)//base yes void*: You can't +- Integers ; If cast to int* Maybe it's too much to skip , Unable to achieve the desired effect
{
// In exchange for
// Here's a message width In the past , Swap bytes directly , Don't worry about the type
// Why swap bytes ? If you swap variables , Temporary variables are hard to create ( I don't know what kind of )
Swap((char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width, width);
flag = 0;
}
}
if (flag == 1)
{
break;
}
}
}
void test()
{
struct stu s[] = {
{
"zhangsan",110},{
"lisi",120},{
"wangwu",911} };
int sz = sizeof(s) / sizeof(s[0]);
BubbleSort(s, sz, sizeof(s[0]), cmp_stu_by_name);
BubbleSort(s, sz, sizeof(s[0]), cmp_stu_by_id);
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
Debugging found ,s The array starts with name In ascending order , And then to id In ascending order
* Complex pointer types
- Judge :
By priority , hold Variable name / Array name Remove , The rest is the type
- Definition
From the most basic pointer / Array start , Layers of Dolls
Strange and interesting ?
Can you try to analyze what these two sentences mean ?
1.
(*(void (*)())0)();
2.
void (*signal(int , void(*)(int)))(int);
analysis 1:
- hold 0 Force type to : No arguments , The return type is void Pointer to the function of
- Quoting This strange function pointer
- Call the function pointed to by this function pointer
: hold 0 This value , Convert to pointer , And then I'll explain the quotation , Find the function at this address and call it
analysis 2:
- First, according to priority :signal Is the function name
- signal In the parentheses after is the type , So this code is a function declaration
- In our classic way : hold signal(int, void(*)(int)) move aside
- be left over void(*)(int) What else could it be ? It is the return type of the function
: Declare a function signal, The return type of the function is void(*)(int), Parameter is int and void(*)(int)
9. Summary of known pointer usage
The usage here , It's going to increase
I hope you will share the good usage freely , Common progress ; I hope you can point out the clumsy points , And help me optimize , thank
9.1 Normal pointer
- The pointer can be used to find data 、 Address …
- void* Can improve commonality
9.2 Pointer array
- You can put different memory regions Data combination together ( It feels like a list ?)
9.3 Array pointer
- A one-dimensional array pointer receives a two-dimensional array name
9.4 A function pointer
- Can achieve Function arguments , Improve versatility
- Callback function
9.5 Function pointer array
- Transfer table
unfinished ……
Limited author , There must be something wrong 、 What needs to be improved , I hope you will point out that
This is Bacon's blog, Make progress with you !
边栏推荐
- 标准化编写知识
- 1721. exchange nodes in the linked list
- Mazhiqiang: research progress and application of speech recognition technology -- RTC dev Meetup
- 19. delete the penultimate node of the linked list
- Why is the string class final decorated
- 面試題 02.02. 返回倒數第 k 個節點
- Award winning survey | how Apache pulsar lived in 2022, you the final say
- C语言打印菱形
- EN 45545-2:2020 T11烟毒性检测
- 83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素
猜你喜欢

【Image Processing】空间域图像增强

Android interview transcript (carefully sorted out)
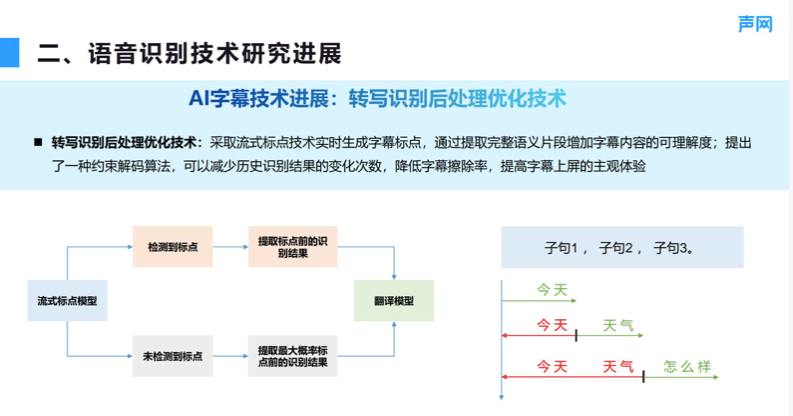
马志强:语音识别技术研究进展和应用落地分享丨RTC Dev Meetup

Matlab learning 8- linear and nonlinear sharpening filtering and nonlinear smoothing filtering of image processing

Vagrant mounting pit

Mazhiqiang: research progress and application of speech recognition technology -- RTC dev Meetup

File system check of the root filesystem failed

AS 3744.1标准中提及ISO8191测试,两者测试一样吗?
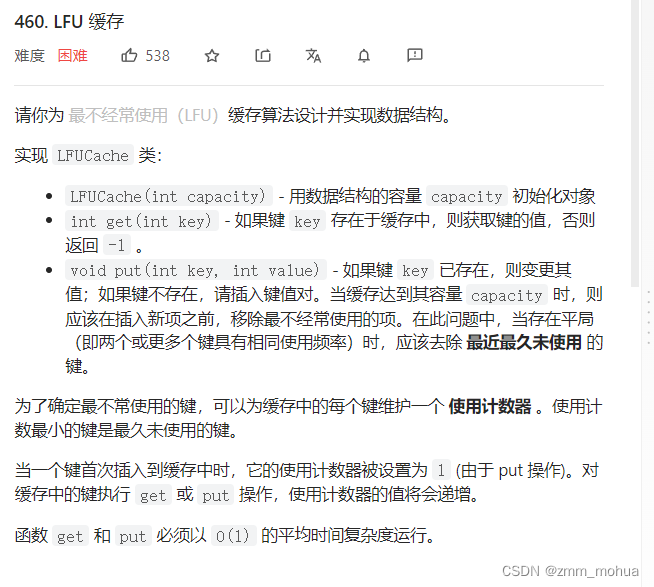
leetcode - 460. LFU cache

Standardized compilation knowledge
随机推荐
C language printing heart
(1) AAC opening - lifecycle, livedata, ViewModel and source code analysis skills of core component principles (Reprint)
Sword finger offer 62 The last remaining number in the circle
Are the test methods of CMVSS TSD No. 302 and 49 CFR 571.302 the same
TextView文本大小自动适配与TextView边距的去除
窗帘做EN 1101易燃性测试过程是怎么样的?
Flutter开发日志——路由管理
PVC 塑料片BS 476-6 火焰传播性能测定
File system check of the root filesystem failed
Codeworks round 680 div2
Create a nodejs based background service using express+mysql
完整的ES6面试题
206. reverse linked list
BS 7176软垫家具阻燃防火测试
Why is the string class final decorated
PVC plastic sheets BS 476-6 determination of flame propagation properties
Port occupancy problem, 10000 ports
EN 45545-2:2020 T11烟毒性检测
SAP abap 数据类型与数据对象
Sword finger offer 18 Delete the node of the linked list