当前位置:网站首页>Summary of spanner's paper
Summary of spanner's paper
2022-07-01 05:17:00 【Ethan97】
summary
Spanner It's developed by Google 、 Extensible 、 Many versions 、 Globally distributed 、 Synchronous replication database . It supports external consistency (external consistency) Of distributed transactions , adopt Paxos The agreement enables multiple database copies to reach a consensus .
Spanner With the help of one that can ensure that the clock error is within a certain range (bounded time uncertainty) Of TrueTime API, It realizes the external consistency of distributed transactions .
TrueTime
TrueTime API as follows .
TT.now() Time interval returned [earliest, latest] Contains the absolute time of the call .
TT.after(t) and TT.before(t) That's right. TT.now() Simple encapsulation . Because the absolute time of the call is [earliest, latest] Within the interval ,TT.after(t) Just go back latest Can guarantee a certain point in time t It's over ,TT.before(t) Just go back earliest Can guarantee a certain point in time t Haven't come yet. .
Timestamp management
Used to ensure that replica Enough new safe time
Spanner Central African leader replica You can also handle read requests .
only one replica New enough , To process read requests .
various replica Maintain a it The upper limit of timestamp that can read data :“ Safe time ”(safe time), Not from this replica Read above this “ Safe time ” The data of .“ Safe time ” Determined by the minimum of the following two :
- The last time Paxos write The timestamp ( Set to
t_paxos) - prepared The transaction with the state has the smallest timestamp ( There is currently no prepared transaction Time is set to infinity )
about Paxos write Time stamp , Take the most recent applied Of Paxos write Time stamp of ;
about prepared State of affairs , You need to extract the least timestamp from them . This is because these transactions are in prepared state , It is not known whether they will eventually be submitted , Therefore, the final result of the data under the timestamp cannot be determined . therefore “ Safe time ” Strictly less than prepared transactions Minimum timestamp in .
The above determination safe time The method has the following disadvantages :
- Even if one read And a prepared transaction No conflict ,safe time Will still be prepared transaction Get in the way . You can add a from key range To prepared transaction timestamp Mapping . When a read request arrives , It just needs to be based on key range Check the correspondence prepared transaction timestamp, To determine safe time;
- If not Paxos write when ,
t_paxosIt will also hinder safe time Progress of .Spanner Through leader-lease Disjoint of intervals Solve this problem . Every Paxos leader Maintain a timestamp threshold , Indicates that write operations above this threshold may occur . It maintains a from Paxos Serial number n To May be assigned to Paxos Serial number n+1 Minimum timestamp of MappingMinNextTS(n), When a copy apply The serial number is n Of log when , Can bet_paxosSet toMinNextTS(n) - 1,leader The default for each 8 Second advance MinNextTS().
to RW Transaction allocation timestamp
For both read and write transactions 2PL, They assign a timestamp after acquiring the lock . For a business , It is supposed to represent the Paxos write The timestamp of is t_paxos,Spanner Will t_paxos Assigned to this transaction .
Spanner Rely on the following monotonicity : In a Paxos group in ,Spanner The assigned timestamp is monotonically incremented . Even if leader change , This monotonicity also holds , This is through leader-lease Disjoint of intervals Guaranteed .
Spanner Ensure external consistency : If a transaction T2 stay T1 Start after submission , be T2 The timestamp of must be greater than T1 The timestamp , This is through commit-wait Ensure that the .
commit-wait
For transactions Ti,coordinator leader wait for Ti Submission timestamp of si Satisfy TT.after(si) after , Just let Ti Modification of client so .
The execution of a transaction
RW Business
When submitting client act
Before the transaction is committed , Writes that occur in transactions are cached in the client . When all reads of a transaction 、 After all the write operations are completed ( namely client Read out all the required data 、 All writes are cached ) Start 2PC,client Choose one first coordinator group, For each participant leader Send a commit message, With coordinator The identity of the 、 Cache write operations .
Not coordinator Participant leader act
A non coordinator Participant leader Received from client Of commit message after , It chooses one prepared timestamp Time stamp ( This timestamp must be greater than all timestamps it has previously allocated ), stay Paxos in log One prepared record, And then tell coordinator Its prepared timestamp.
coordinator act
determine commit timestamp
coordinator Listen to all leader Of prepared timestamp after ,commit timestamp The following submittals must be met :
- Greater than or equal to all received prepared timestamp;
- Greater than all coordinator leader Previously assigned timestamp;
- Greater than coordinator received commit message At the time of the TT.now().latest.
determine commit timestamp after , stay Paxos in log One commit record.( Or because we didn't receive any from the participants prepared timestamp and timeout)
commit-wait
According to the foregoing commit-wait The rules , stay coordinator applies commit record Before ,coordinator Need to wait TT.after(S) by true. stay commit-wait after ,coordinator take commit timestamp issue client And other participants leader. All the participants leader The transaction result log To Paxos in , then apply commit record.
RO Business
When RO The keys required for the transaction are all in the same Paxos group when ,client take RO The transaction request is sent to this Paxos group Of leader. Definition LastTs() For the sake of Paxos group Timestamp of the last committed write operation , For just one Paxos group Of RO Business , When there is no prepared transaction when , Assign read timestamps to transactions s_read = lastTS() To meet external consistency (external consistency).
If RO The transaction requires multiple Paxos group There are many choices .
- With everyone Paxos group leader negotiation , According to their LastTS() Determine the read timestamp ;
- No negotiation , Directly determine the read timestamp
s_read = TT.now().latest.
LastTS() The shortcomings of :
When a transaction has just been committed , One that does not conflict with it RO The transaction still needs to determine the read timestamp as LastTS(). Can enhance LastTS(), Add one key ranges To commit timestamp Mapping , When one RO When the transaction arrives , Just according to key Take out the corresponding key ranges Of LastTS().
Schema-change
Spanner Medium schema-change Execute as a transaction . In its prepare phase Assign a future timestamp to the transaction t. For dependency schema Read and write operations , If their timestamp is t Before , Then they can be executed smoothly ; If they are time stamped t after , They need to be blocked until schema-change complete .
wound wait Prevent deadlock
RW Read operations in transactions wound-wait To avoid deadlock .
Here's an introduction to wait-die and wound-wait.
wait-die
This is a non preemptive deadlock prevention strategy . When a transaction Tn Request a currently Tk When you occupy data , Only Tn The timestamp Less than Tk Time stamp of ,Tn Can wait , otherwise Tn Death (die).
wound-wait
This is a preemptive deadlock prevention strategy . It and wait-die contrary , When Tn Request one to be Tk When you occupy data , Only Tn The timestamp Greater than Tk Time stamp of ,Tn Can wait , otherwise Tk Death (Tk is wounded by Tn).
Summary
Either way , Only transactions with older timestamps will be killed .
summary
Because a transaction involves different key May belong to different key range, And then belong to different Paxos group. When multiple transactions are executed , Maybe the modification of a new transaction is overwritten by the modification of an old transaction , This leads to external inconsistencies , So we need to provide additional means to sort transactions .
Spanner With the help of TrueTime API, By sorting the timestamp size of transactions , External consistency is achieved .
边栏推荐
- Intelligent operation and maintenance: visual management system based on BIM Technology
- tar命令
- Sqlplus connects using the instance name
- FileInputStream
- 【暑期每日一題】洛穀 P1568 賽跑
- Pico neo3 handle grabs objects
- LeetCode522-最长特殊序列II-哈希表-字符串-双指针
- AcWing 886. Finding combinatorial number II (pretreatment factorial)
- Distributed transactions - Solutions
- 【暑期每日一题】洛谷 P5886 Hello, 2020!
猜你喜欢
![[RootersCTF2019]babyWeb](/img/b4/aa8f8e107a9dacbace72d4717b1834.png)
[RootersCTF2019]babyWeb

Lock free concurrency of JUC (leguan lock)

LevelDB源码分析之memtable

Spanner 论文小结
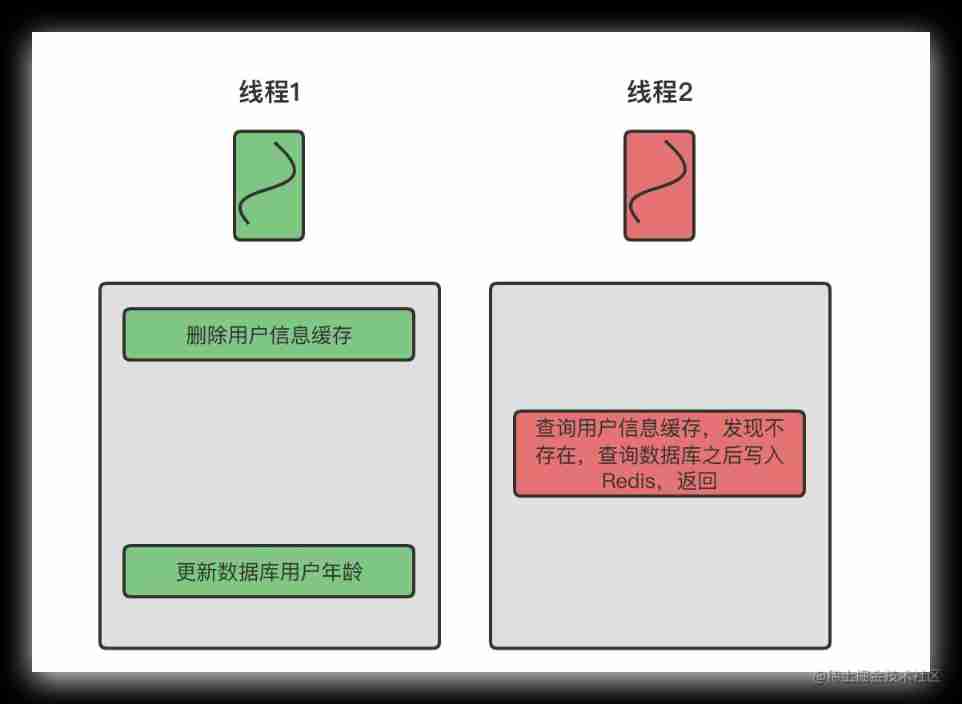
Data consistency between redis and database

And search: the suspects (find the number of people related to the nth person)

LevelDB源码分析之LRU Cache
eBPF Cilium实战(2) - 底层网络可观测性

实战:redux的基本使用

CockroachDB: The Resilient Geo-Distributed SQL Database 论文阅读笔记
随机推荐
STM32 expansion board digital tube display
Design and application of immutable classes
Simple read / write verification of qdatastream
【暑期每日一题】洛谷 P5740【深基7.例9】最厉害的学生
担心侵权?必备无版权素材网站分享,不用担心视频剪辑缺素材
3D建模與處理軟件簡介 劉利剛 中國科技大學
Global and Chinese markets for soft ferrite cores 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Leetcode522- longest special sequence ii- hash table - String - double pointer
AcWing 887. Finding combinatorial number III (Lucas theorem)
Flutter can refresh data every time the interface comes in
[data recovery in North Asia] a data recovery case of raid crash caused by hard disk drop during data synchronization of hot spare disk of RAID5 disk array
Rainbond结合NeuVector实践容器安全管理
Global and Chinese market of 3D design and modeling software 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Pytoch (III) -- function optimization
LeetCode1497-检查数组对是否可以被 k 整除-数组-哈希表-计数
Global and Chinese market of solder wire 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Receiving package install and uninstall events
Mathematical knowledge: finding the number of divisors
Implementation of distributed lock
Tcp/ip explanation (version 2) notes / 3 link layer / 3.2 Ethernet and IEEE 802 lan/man standards