当前位置:网站首页>The dynamic planning theory
The dynamic planning theory
2022-08-02 16:06:00 【A bigot is lovely】
General outline of algorithm:
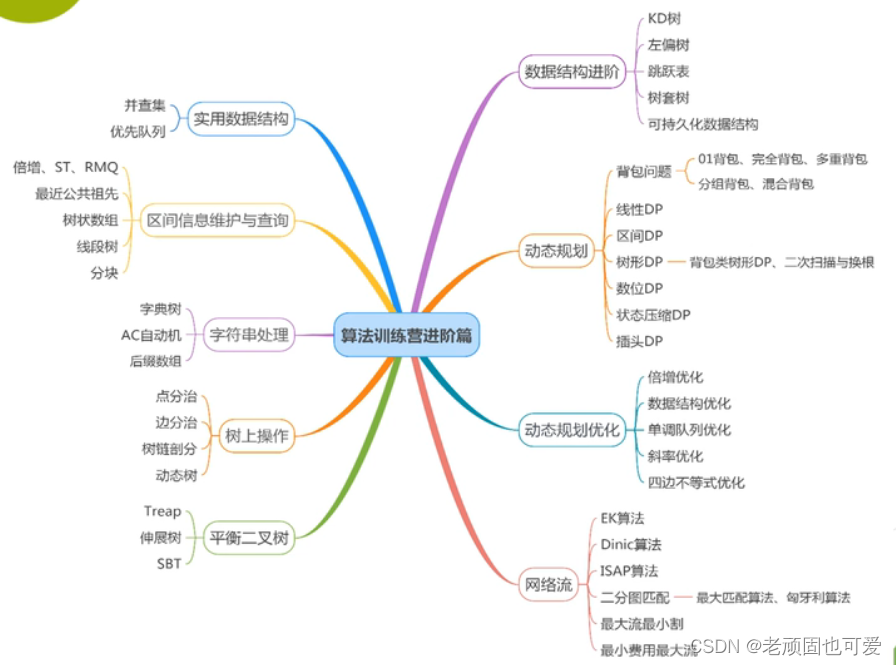

Dynamic Programming Theory
1、Which problems can use dynamic programming?
- 最优子结构
- 子问题重叠
- 无后效性
例子:
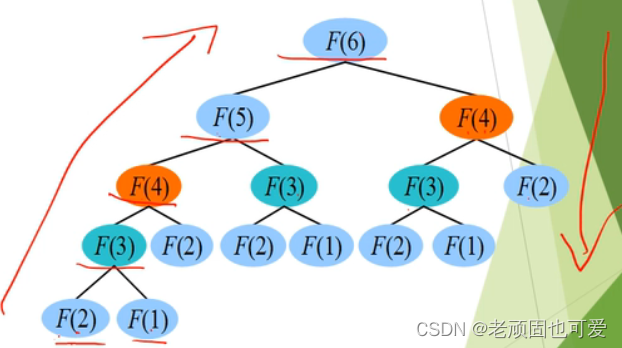
1.1 动态规划概念
Dynamic programming to the original problem is divided into several subproblems,The solution process of each subproblem constitutes a stage,Solve the previous stage and then solve the next stage.根据无后效性,The computation of the dynamic programming constitute a directed acyclic graph,The order of solving is a topological order of the directed acyclic graph.在有向无环图中,The status of the node corresponding to the problem,To the edge between the corresponding state transfer,The choice made when transferring is the decision.
动态规划的三个要素:
- 状态
- 阶段
- 决策
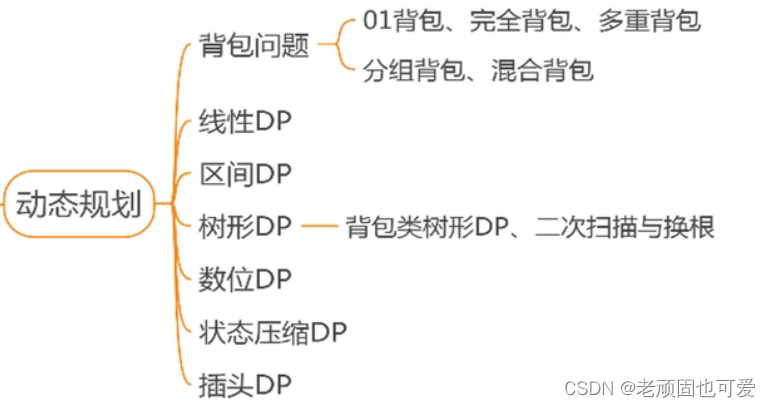
1.2 动态规划 模板分类
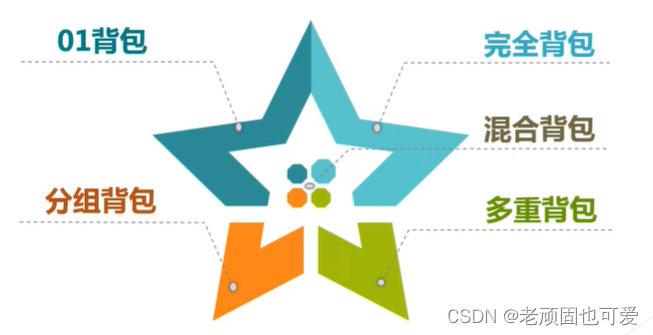
2、背包问题
One of the knapsack problem is a classic problem of dynamic programming.The knapsack problem refers to placing items in a knapsack that has volume or weight restrictions,item has volume、重量、价值等属性,Requires items to be placed while meeting backpack constraints,使背包中物品的价值之和最大.Depending on the item restrictions,背包问题可分为01背包、完全背包、多重背包、Group backpacks and hybrid backpacks, etc..
- 01背包:每种物品只有 1 1 1 个
- 完全背包:每种物品有无穷多个
- 分组背包:第 i i i 组有 C i C_i Ci 个物品
- 多重背包:每种物品有 C i C_i Ci 个
2.1 01背包
给定 n n n 种物品,每种物品都有重量 w i w_i wi ,和价值 v i v_i vi ,每种物品只有一个,背包容量为 W W W .求解在不超过背包容量的情况下,将哪些物品放入背包,使背包中的物品价值之和最大.每种物品只有一个,要么不放入(0),要么放入(1),因此称之为01背包.
- 确定状态. C [ i ] [ j ] C[i][j] C[i][j] 表示前 i i i 种物品放入容量为 j j j 的背包中获得的最大价值.
- 划分阶段.第 i i i 阶段处理第 i i i 种物品,第 i i i-1 阶段处理第 i i i 种物品.当处理第 i i i 种物品时,前 i − 1 i-1 i−1 Items have been processed,只需考虑第 i − 1 i-1 i−1 阶段向第 i i i stage transfer.
A two-dimensional array format01背包
c [ i ] [ j ] = { c [ i − 1 ] [ j ] , j < w [ i ] m a x { c [ i − 1 ] [ j ] , c [ i − 1 ] [ j − w [ i ] ] + v [ i ] } , j ⩾ w [ i ] c[i][j]=\left\{ \begin{aligned} c[i-1][j] & , &j<w[i] \\ max \{c[i-1][j],c[i-1][j-w[i]]+v[i]\} & ,& j \geqslant w[i] \end{aligned} \right. c[i][j]={ c[i−1][j]max{ c[i−1][j],c[i−1][j−w[i]]+v[i]},,j<w[i]j⩾w[i]
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=W;j++){
if(j<w[i]){
c[i][j]=c[i-1][j];
}else{
c[i][j]=max{
c[i-1][j],c[i-1][j-w[i]]+v[i]};
}
}
}
时间复杂度 O ( n W ) O(nW) O(nW),空间复杂度 O ( n W ) O(nW) O(nW)
根据最后的 c [ i ] [ j ] c[i][j] c[i][j]Reverse items put into backpack
- 初始时 i = n , j = W i=n, j=W i=n,j=W;
- 若 c [ i ] [ j ] > c [ i − 1 ] [ j ] c[i][j]>c[i-1][j] c[i][j]>c[i−1][j],则第 i i i 种物品被放入背包,令 x [ i ] = 1 x[i]=1 x[i]=1, j − = w [ i ] j-=w[i] j−=w[i];若 c [ i ] [ j ] ≤ c [ i − 1 ] [ j ] c[i][j] \leq c[i-1][j] c[i][j]≤c[i−1][j],则第 i i i Items are not put into the backpack,令 x [ i ] = 0 x[i]=0 x[i]=0
- i − − i-- i−−,转向第2步,直到 i = 0 i=0 i=0处理完毕
算法优化
求解第 i i i行的时候,只需要第 i − 1 i-1 i−1行的结果,There's no point in the previous results.求解 c [ i ] [ j ] c[i][j] c[i][j] 时,只需要上一行 j j j 列或上一行 j − w [ i ] j-w[i] j−w[i] 列的结果,可以进行空间优化,将二维数组转为一维数组.
- 状态表示: d p [ i ] dp[i] dp[i] 表示将物品放入容量为 j j j The maximum value that can be obtained from the backpack type of
- 状态转移方程: d p [ j ] = m a x { d p [ j ] , d p [ j − w [ i ] ] + v [ i ] } dp[j]=max\{ dp[j],dp[j-w[i]]+v[i] \} dp[j]=max{ dp[j],dp[j−w[i]]+v[i]}
但是注意一点,One-dimensional array to be pushed backwards,Avoid updating the updated data again.
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=W;j>=w[i];j--){
dp[j]=max(dp[j],dp[j-w[i]]+v[i])
}
}
2.2 完全背包
有 N N N 种物品和一个容量为 T T T 的背包,每种物品都就可以选择任意多个,第i种物品的价值为 P [ i ] P[i] P[i] ,体积为 V [ i ] V[i] V[i] ,求解:选哪些物品放入背包,Cocaine maximizes the value of these items,and the sum of the volumes does not exceed the backpack capacity.跟01背包一样,完全背包也是一个很经典的动态规划问题,不同的地方在于01背包问题中,每件物品最多选择一件,而在完全背包问题中,只要背包装得下,每件物品可以选择任意多件.从每件物品的角度来说,与之相关的策略已经不再是选或者不选了,而是有取0件、取1件、取2件…直到取⌊T/Vi⌋(向下取整)件.
最优化原理和无后效性
- 那这个问题可以不可以像01The knapsack problem is solved using dynamic programming.?来证明一下即可.首先,Prove the principle of optimization by contradiction:假设完全背包的解为 F ( n 1 , n 2 , . . . , n N ) F(n_1,n_2,...,n_N) F(n1,n2,...,nN)( n 1 n_1 n1, n 2 n_2 n2 分别代表第1、第2件物品的选取数量),完全背包的子问题为,将前i种物品放入容量为 t t t 的背包并取得最大价值,其对应的解为: F ( n 1 , n 2 , . . . , n i ) F(n_1,n_2,...,n_i) F(n1,n2,...,ni),Suppose the solution is not the optimal solution to the subproblem,即存在另一组解 F ( m 1 , m 2 , . . . , m i ) F(m_1,m_2,...,m_i) F(m1,m2,...,mi),使得 F ( m 1 , m 2 , . . . , m i ) F(m_1,m_2,...,m_i) F(m1,m2,...,mi) > F ( n 1 , n 2 , . . . , n i ) F(n_1,n_2,...,n_i) F(n1,n2,...,ni),那么 F ( m 1 , m 2 , . . . , m i , . . . , m N ) F(m_1,m_2,...,m_i,...,m_N) F(m1,m2,...,mi,...,mN) 必然大于 F ( n 1 , n 2 , . . . , n N ) F(n_1,n_2,...,n_N) F(n1,n2,...,nN),因此 F ( n 1 , n 2 , . . . , n N ) F(n_1,n_2,...,n_N) F(n1,n2,...,nN) 不是原问题的最优解,与原假设不符,所以 F ( n 1 , n 2 , . . . , n i ) F(n_1,n_2,...,n_i) F(n1,n2,...,ni)必然是子问题的最优解.
- 再来看看无后效性:对于子问题的任意解,will not affect the solution of subsequent subproblems.,也就是说,前 i i i 种物品如何选择,As long as the final remaining backpack space remains the same,It will not affect the selection of the following items..即满足无后效性.
- 因此,The complete knapsack problem can also be solved using dynamic programming.
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=w[i];j<=W;j++){
// 正向推
dp[j]=max(dp[j],dp[j-w[i]]+v[i])
}
}
2.3 多重背包
给定 n n n 种物品,每种物品都有重量 w i w_i wi 和价值 v i v_i vi ,第 i i i 种物品有 c i c_i ci 个.背包容量为 W W W ,求解在不超过背包容量的情况下如何放置物品,使背包中物品的价值之和最大.
The multiple knapsack problem can be transformed into01背包问题,Feasibility problems can also be solved by array optimization.
暴力拆分
Violent split refers to the i i i 种物品看作 c i c_i ci 种独立的物品,每种物品只有一个,转化为01背包问题
void multi_knapsack1(int n, int W){
// 容易TLE
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int k=1;k<=c[i];k++){
// 多一层循环
for(int j=W;j>=w[i];j--){
dp[j]=max(dp[j],dp[j-w[i]]+v[i])
}
}
}
}
时间复杂度为 O ( W ∑ i = 1 n c i ) O(W\sum^n_{i=1}{c_i}) O(W∑i=1nci) ,空间复杂度为 O ( W ) O(W) O(W)
二进制拆分
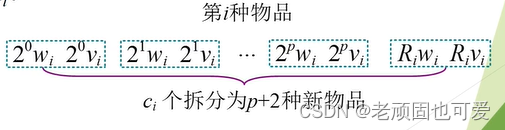
二进制拆分,将 c [ i ] c[i] c[i] Item split into several new species.There is a largest integer p p p ,使 2 0 + 2 1 + . . . 2 p ≤ c [ i ] 2^0+2^1+...2^p\leq c[i] 20+21+...2p≤c[i] .use the remainder R i R_i Ri 表示, R i = c [ i ] − ( 2 0 + 2 1 + . . . 2 p ) R_i=c[i]-(2^0+2^1+...2^p) Ri=c[i]−(20+21+...2p),将 c [ i ] c[i] c[i] 拆分成 p + 2 p+2 p+2 个数: 2 0 , 2 1 , . . . 2 p , R i 2^0, 2^1, ...2^p, R_i 20,21,...2p,Ri .
void multi_knapsack2(int n, int W){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(c[i]*w[i]>=W){
// To completely backpack
for(int j=w[i];j<=W;j++){
// 正向推
dp[j]=max(dp[j],dp[j-w[i]]+v[i])
}
}else{
for(int k=1;c[i]>0;k<<1){
int x=min(k,c[i]);
for(int j=W;j>=w[i]*x;j--){
// 转化01背包
dp[j]=max(dp[j],dp[j-w[i]*x]+x*v[i]);
}
c[i]-=x;
}
}
}
}
void multi_knapsack2(int n, int W){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(c[i]*w[i]>=W){
// To completely backpack
for(int j=w[i];j<=W;j++){
// 正向推
dp[j]=max(dp[j],dp[j-w[i]]+v[i])
}
}else{
for(int k=1;k<=c[i];k<<1){
for(int j=W;j>=w[i]*x;j--){
// 转化01背包
dp[j]=max(dp[j],dp[j-w[i]*x]+x*v[i]);
}
c[i]-=x;
}
if(c[i]>0){
for(int j=W;j>=w[i]*x;j--){
// 转化01背包
dp[j]=max(dp[j],dp[j-w[i]*x]+x*v[i]);
}
}
}
}
}
时间复杂度为 O ( W ∑ i = 1 n l o g c i ) O(W\sum^n_{i=1}{logc_i}) O(W∑i=1nlogci) ,空间复杂度为 O ( W ) O(W) O(W)
2.4 区间DP
区间DP属于线性DP的一种,Take the interval length asDP的阶段,Take the left and right endpoints of the interval as the dimension of the state.A state is usually by it contains and smaller range than it state transition.阶段(长度)、状态(左右端点)、The three decision-makers form a three-layer cycle in the order from outside to inside.
Whether can use dynamic programming?
最优子结构
分析第 i i i 个站点到第 j j j 个站点 ( i , i + 1 , . . . , j ) (i,i+1,...,j) (i,i+1,...,j) 的最优解(最少租金)问题,Check whether there is an optimal substructure property.
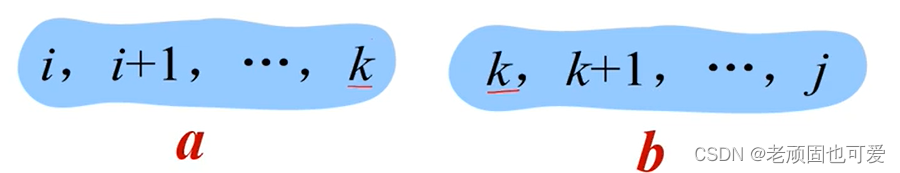
- 确定状态. d p [ i ] [ j ] dp[i][j] dp[i][j] 表 示第 i i i 个站点到第 j j j Minimum rent for sites.
- 划分阶段.区间长度.
- 决策选择.The original problem and the relationship between the subproblems.
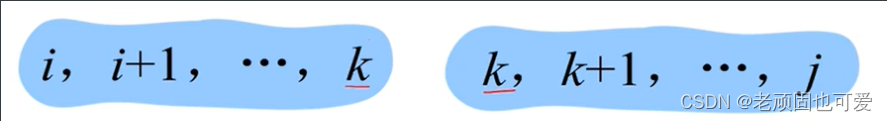
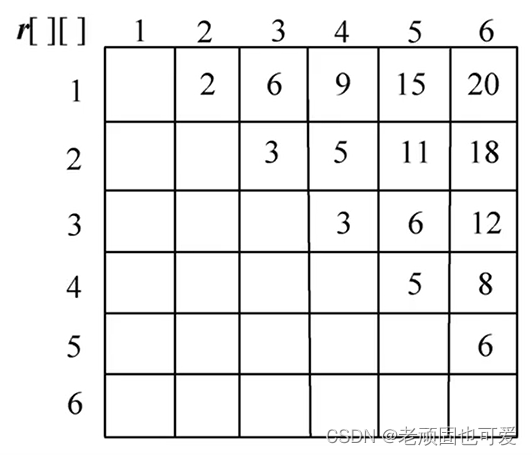
状态转移方程:$dp[i][j]= min{dp[i][k]+ dp[k][j],dp[i][j]} $
- 边界条件. i < j , d p [ i ] [ j ] = r [ i ] [ j ] i<j, dp[i][j]=r[i][j] i<j,dp[i][j]=r[i][j]
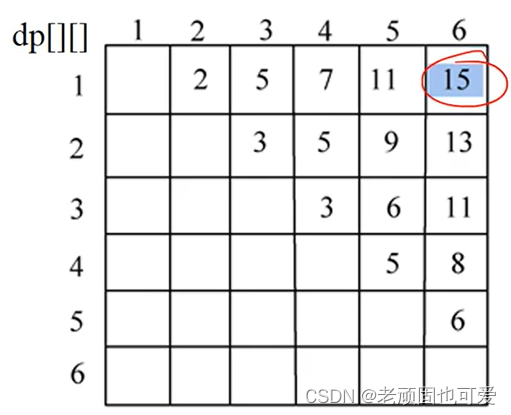
- 求解目标. d p [ i ] [ n ] dp[i][n] dp[i][n]
例题-Yangtze River Yacht Club
题目描述(P1359/T1624):Yangtze River Yacht Club在长江上设置了n个游艇出租站,Tourists can be in the taxi stand rented a yacht,Return the yacht at any of the yacht rental stations downstream.游艇出租站i到游艇出租站j之间的租金为r(i, j).Request now from the yacht rental station1到游艇出租站nMinimum rent required.
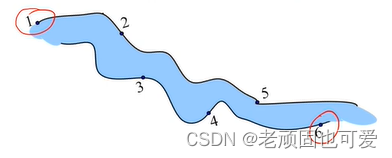
问题分析:
When it comes to rent the yacht from one station to another station,There may be many stops in the middle,Different stop strategies have different rents.If the exhaustive all stop strategy,例如一共有10个站点, When seeking sub-problems4stop strategy,子问题有:(1,2,3,4)、(2,3,4,5)、(3,4,5,6)、(4,5,6,7)、(5,6,7,8)、(6,7,8,9)、(7,8,9,10).If we continue to solve the subproblem,You will find that there is a large number of overlapping subproblems,其算法的时间复杂度为 2 n 2^n 2n ,The method of violent exhaustion is not advisable.
算法实现:
- 阶段(区间长度)
- 状态(区间起点和终点)
- 决策(状态转移方程)
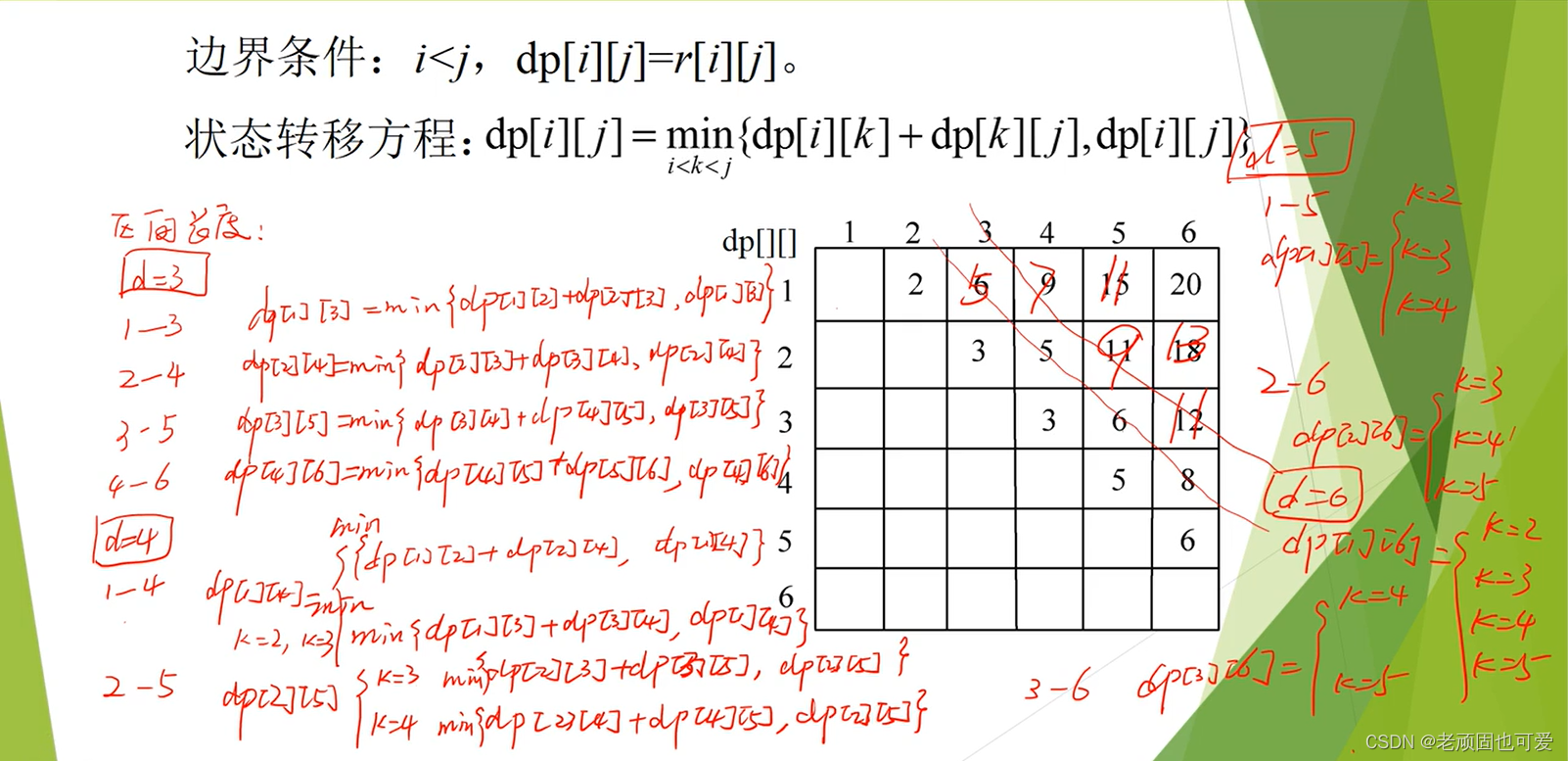
void rent(){
for(int d=3;d<=n;d++){
// 区间长度d
for(int i=1;i<=n-d+1;i++){
// state starting pointi,终点j
int j=i+d-1;
for(int k=i+1;k<j;k++){
// 枚举决策点k
if(dp[i][j]>dp[i][k]+dp[k][j])
dp[i][j]=dp[i][k]+dp[k][j];
}
}
}
}
延伸思考:
The optimal value obtained above is only the first1个站点到第nMinimum rent between sites,Don't know what dock which sites,If you want to know where to stop,怎么办?
- 状态转移方程:$dp[i][j]= min{dp[i][k]+ dp[k][j],dp[i][j]} $;
- 用辅助数组 s [ i ] [ j ] s[i][j] s[i][j] record each sub-question ( i . . . j ) (i...j) (i...j) 的最优决策 k k k (停靠站点).
void rent(){
for(int d=3;d<=n;d++){
// 区间长度d
for(int i=1;i<=n-d+1;i++){
// state starting pointi,终点j
int j=i+d-1;
for(int k=i+1;k<j;k++){
// 枚举决策点k
if(dp[i][j]>dp[i][k]+dp[k][j]){
dp[i][j]=dp[i][k]+dp[k][j];
s[i][j]=k;
}
}
}
}
}
2.5 树形DP
A dynamic programming implemented on a tree structure is called a treeDP.Dynamic programming is a multi-order decision problem,The tree structure has obvious hierarchy,Just corresponds to the multiple stages of dynamic programming.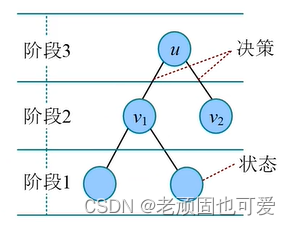
树形DP一般自底向上,Sort the subtree from small to large asDP的“阶段”,Take the node number asDPfirst dimension of state,represents the subtree rooted at this node.树形DPGenerally adopting depth-first traversal,Solve each subtree recursively,回溯时从子节点向上进行状态转移.After all subtrees of the current node have been solved,才可以求解当前结点.
例题-周年派对
题目描述(POJ2342/HDU1520):Ural University will be held80Anniversary party.University staff, director of the relationship as a to the principal for the root of the tree.In order to let everyone have a good time,The principal does not want the staff and his immediate supervisor to be present.The Personnel Office has assessed the happiness of each employee,Your task is to list a invited staff list,Maximize the sum of the joy of participating staff.
输入:Staff number from1到N.输入的第一行包含 数字N (1≤N≤6000).后面的NEach row in the row contains the happiness of the corresponding staff member.Joy is a-128到127整数.之后的N-1The row is the tree describing the supervisor relationship.Each row has the following format: L K,表示第Kstaff is the firstLdirect supervisor of staff.Enter to include 0 0 end of line.
输出:Output the maximum sum value of the happiness of the participating staff.
输入样例:
7
1
1
1
1
1
1
1 3
2 3
6 4
7 4
4 5
3 5
0 0
输出样例:
5
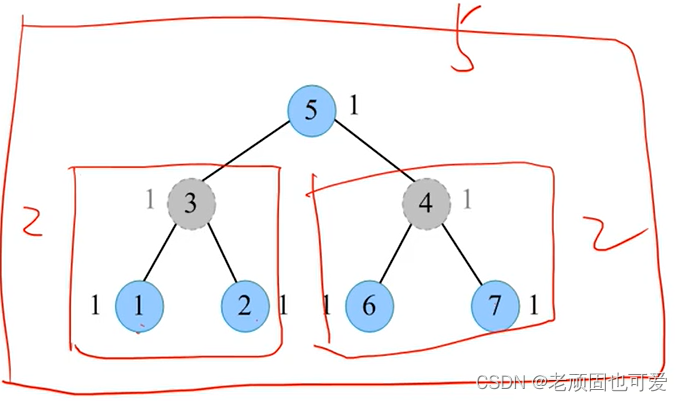
- 确定状态: d p [ u ] [ 0 ] dp[u][0] dp[u][0] 表示不选择节点 u u u 时,在以节点 u u u The joy of participating employees in the rooted subtree is the highest and the;
d p [ u ] [ 1 ] dp[u][1] dp[u][1] Indicates the selection node u u u 时,在以节点 u u u The joy of participating employees in the rooted subtree is the highest and the. - 划分阶段:The order of subtrees from smallest to largest
- 决策选择:
- If the current node is not selected u u u ,则它的所有子节点 v v v Can choose or not choose,取最大值即可. d p [ u ] [ 0 ] + = m a x ( d p [ v ] [ 0 ] , d p [ v ] [ 1 ] ) dp[u][0]+=max(dp[v][0], dp[v][1]) dp[u][0]+=max(dp[v][0],dp[v][1])
- If you choose the current node u u u,则它的所有子节点 v v v None are optional. d p [ u ] [ 1 ] + = d p [ v ] [ 0 ] dp[u][1 ]+=dp[v][0] dp[u][1]+=dp[v][0]
- 边界条件: d p [ u ] [ 0 ] = 0 , d p [ u ] [ 1 ] = v a l [ u ] dp[u][0]=0, dp[u][1 ]=val[u] dp[u][0]=0,dp[u][1]=val[u]
- 求解目标: m a x ( d p [ r o o t ] [ 0 ] , d p [ r o o t ] [ 1 ] ) max(dp[root][0], dp[root][1]) max(dp[root][0],dp[root][1]), r o o t root root 为树根.
void dfs(int u){
dp[u][0]=0;
dp[u][1]=val[u];
for(int i=0;i<E[u].size();i++){
int v=E[u][i];
dfs(v);
dp[u][0]+=max(dp[v][1],dp[v][0]);
dp[u][1]+=dp[v][0];
}
}
例题2-workers petition
题目描述(UVA12186):The company has a strict hierarchy,除了大老板,Each employee has only ten
老板(直接上司).An employee who is not the boss of another employee is called a worker,The rest of the employees and the boss is called the boss.要求加薪时,Workers should petition their bosses.if at leastT%Direct reports to submit a petition,The boss will have pressure,Submit a petition to your boss.Each boss can submit at most one petition to his own boss. The boss only counts the number of petitions of his direct reports to calculate the stress percentage.When a petition is submitted to the big boss of the company,Wages will increase for all.Please find out the minimum number of workers that must submit a petition in order for the big boss to receive the petition.
输入:输入包含几个测试用例.Each test case consists of two lines,第1行包含两个整数 n n n 和 T T T (1≤n≤ 1 0 5 10^5 105,1≤T≤100), n n n Indicates the number of employees in the company(Excluding company boss), T T T Is the parameters described above.The number of each employee is1~n,Big boss number is0;第2row contains a list of integers,列表中的位置 i i i (从1开始) 为整数 b b b (0≤b;≤i-l),表示员工ithe number of the immediate supervisor.In the last test case contains two behind0.
输出:对每个测试用例,Single output to make big boss receive petitions and must submit the fewest number of workers.
输入样例:
3 100
0 0 0
3 50
0 0 0
14 60
0 0 1 1 2 2 2 5 7 5 7 5 7 5
0 0
输出样例:
3
2
5
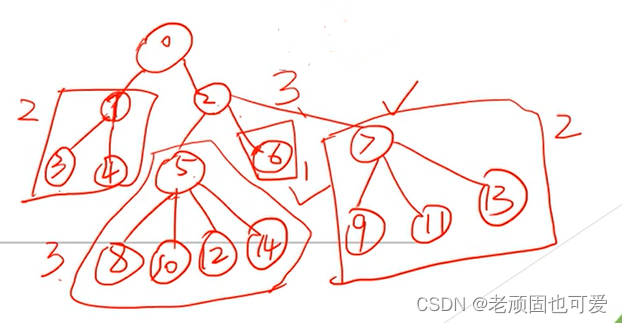
Subject to solve the petitions the fewest number of workers.solve with nodes u u u Minimum number of workers to submit petitions in the rooted subtree, u u u The lower the number of workers in the subtree that submit the petition, the better,所以可以将 u u u The child nodes are sorted non-decreasingly by the number of workers who submitted the petition,选择前 c c c Child node to the petitions add up the number of workers.
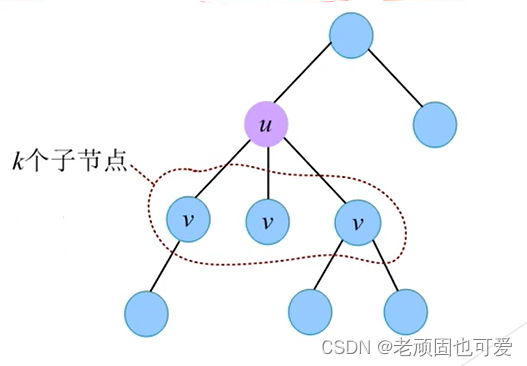
- 确定状态. d p [ u ] dp[u] dp[u] 表示让 u u u petition to superior,The minimum number of workers required to submit a petition.
- 划分阶段.The order of subtrees from smallest to largest.
- 决策选择.对于 u u u 的子节点 v v v ,将 $ dp[v]$ 按照非递减排序,选择前 c c c cumulative,$c=\lceil k \times T% \rceil $ , d p [ u ] + = s u m ( d p [ v ] ) dp[u]+=sum(dp[v]) dp[u]+=sum(dp[v]).
- 边界条件.叶子结点, d p [ u ] = 1 dp[u]=1 dp[u]=1
- 求解目标. d p [ 0 ] dp[0] dp[0]
int dfs(int u){
if(E[u].size()==0) return 1;
int k=E[u].size();
vector<int> d;
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
d.push_back(dfs(E[u][i]));
}
sort(d.begin(),d.end());
int c=(k*T-1)/100+1,ans=0;//c=ceil(k*T/100.0)
for(int i=0;i<c;i++){
ans+=d[i];
}
return ans;
}
- 时间复杂度:Depth-first traversal each node,执行次数为 O ( n ) O(n) O(n),Sort each node's child nodes with the most optimal values O ( n l o g n ) O(nlogn) O(nlogn),总时间复杂度为 O ( n l o g n ) O(nlogn) O(nlogn).
- 空间复杂度:The space complexity is the depth of the recursion tree O ( l o g n ) O(logn) O(logn).
3、 动态规划优化
Dynamic programming optimization can be carried out from three aspects:状态总数、Number of decisions per state and time required for each state transition.
- 减少状态总数.Including revision status(状态压缩、倍增优化)、选择适当的DP方向(双向DP)等.
- Reduce the number of state decisions.Monotonic Queue Optimization Using Optimal Decision Monotonicity、斜率优化、四边不等式优化、Pruning optimization, etc..
- Reduce the time required for the state transition.Can adopt pretreatment、Appropriate calculation methods and data structure optimization, etc..

A monotonic queue is a special kind of queue,Can operate on both ends of the queue,and always maintain the monotonicity of the queue.There are two kinds of monotonous queue monotonicity:The value of the element strictly monotone(递减或递增),Element subscripts are strictly monotonic(递减或递增).Monotonic queues can only be queued from the end of the queue,But you can go out from the back of the team or from the front of the team.
When the state transition is the following two cases,考虑优化.
- The state transition equation is of the form d p [ i ] = m i n { d p [ j ] + f [ j ] } dp[i]=min\{dp[j]+f[j]\} dp[i]=min{ dp[j]+f[j]}, 0 ≤ j < i 0≤j<i 0≤j<i.在这种情况下,Lower the same, i i i 增加1时, j j j The upper bound of also increases1,Decision candidate set only expand、不缩小,Use only one variable to maintain the most value.用一个变量 v a l val val 维护 ( 0 , i ) (0, i) (0,i) 区间中 d p [ j ] + f [ j ] dp[j]+f[j] dp[j]+f[j] 的最小值即可.
- The state transition equation is of the form d p [ i ] = m i n { d p [ j ] + f [ j ] } dp[i]=min\{dp[j]+f[j]\} dp[i]=min{ dp[j]+f[j]}, i − a ≤ j ≤ i − b i-a≤j≤i-b i−a≤j≤i−b.在这种情况下, i i i 增加1时, j j j 的上界、Nether increases at the same time1,When a new decision is added to the candidate set,need to be outdated(The previous one was out of range)decision to remove from the candidate set.例如,当前 j j j 的范围为[2,4],当 i i i 增加 1 时, j j j 的范围变为 [3,5] ,此时 2已过时(不属于[3,5]区间).When the value range of the decision is on the upper、When the lower bounds change monotonically,Each decision inserts or deletes at most one time in the candidate set,Can use a monotonous queue maintenance [i-a, i-b] 区间 d p [ j ] + f [ j ] dp[j]+f[j] dp[j]+f[j] 的最小值.
例题-滑动窗口
题目描述(POJ2823): 有n (n≤106) 个元素的数组,以及一个大小为k的滑动窗口,Move the sliding window from the leftmost to the rightmost of the array,can only be seen in this windowk个数字,The sliding window moves one position to the right at a time,Please determine the maximum and minimum values of the sliding window at each position.下面是一个例子, 数组是[1 3 -1 -3 5 3 6 7],k是3.
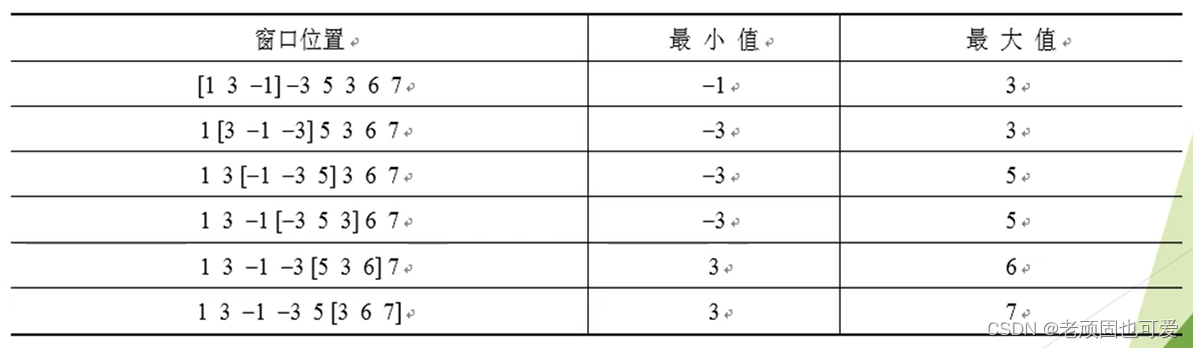
输入:第1行包含整数n和k,Indicates the number of elements and the length of the sliding window;第2行包含n个整数.
输出:第1Lines output the minimum value in each window separately from left to right,第2row output max.
- M i n [ i ] = m i n { a j } Min[i]=min\{a_j\} Min[i]=min{ aj}, i − k + 1 ≤ j ≤ i i-k+1≤j≤i i−k+1≤j≤i.
- M a x [ i ] = m a x { a j } Max[i]=max\{a_j\} Max[i]=max{ aj}, i − k + 1 ≤ j ≤ i i-k+1≤j≤i i−k+1≤j≤i.
如果对每个 i i i,枚举 [ i − k + 1 , i ] [i-k+1, i] [i−k+1,i]中 k k k Minimum or maximum number of,总时间复杂度为 O ( n − k + 1 ) k O(n-k+1)k O(n−k+1)k,时间复杂度为 O ( n k ) O(nk) O(nk).
单调队列优化:
当 i i i增加1时,jThe upper and lower bounds of1,省略 j j j,It can be maintained with a monotonic queue.本题求解 M i n [ i ] Min[i] Min[i]When using monotone increasing element(队头最小),求解 M a x [ i ] Max[i] Max[i]element-wise monotonically decreasing(队头最大).注意:What is stored in the queue is the subscript,队头最小(最大)Refers to the team head element subscript corresponds to the minimum(最大).
求解 M i n [ i ] Min[i] Min[i]的步骤如下.
- Monotonically increasing queue,The head element is always the smallest.
- If the element to be enqueued is less than or equal to the element at the end of the queue,then the tail element is dequeued,Until the element to be enqueued is greater than the element at the end of the queue,或队列为空,Then the subscript of the element to be enqueued is enqueued from the end of the queue.
- If the subscript of the head element is less than i − k + 1 i-k+1 i−k+1,then the head element is out of date(不在窗口内),Queue head element subscript dequeue.
求解 M a x [ i ] Max[i] Max[i] 的步骤如下.
- 单调递减的队列,The head element is always the largest.
- If the element to be enqueued is greater than or equal to the element at the end of the queue,then the tail element is dequeued,until the element to be enqueued is less than the element at the end of the queue,或队列为空,Then the subscript of the element to be enqueued is enqueued from the end of the queue.
- If the subscript of the head element is less than i-k+1,then the head element is out of date(不在窗口内),Queue head element subscript dequeue.
Element is out of date to the subscript,So what is stored in the queue is the subscript,Get the most value when simply visit team head element subscript in the sequence of the corresponding element can get the answer.Each element subscript is enqueued at most、出队一次,总时间复杂度为 O ( n ) O(n) O(n) ,The average time is O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1).

#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#define MAXN 1000010
using namespace std;
int a[MAXN],Min[MAXN],Max[MAXN],Q[MAXN],n,k;
void get_min(){
int st=0,ed=0;
Q[ed++]=1;
Min[1]=a[1];
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
while(st<ed&&a[i]<a[Q[ed-1]])//删除队尾元素
ed--; //插入队尾元素
Q[ed++]=i;
while(st<ed&&Q[st]<i-k+1)//Delete the team first obsolete element
st++;
Min[i]=a[Q[st]];
}
}
void get_max(){
int st=0,ed=0;
Q[ed++]=1;
Max[1]=a[1];
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
while(st<ed&&(a[i]>a[Q[ed-1]]))
ed--;
Q[ed++]=i;
while(st<ed&&Q[st]<i-k+1)
st++;
Max[i]=a[Q[st]];
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&k);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
get_min();
get_max();
for(int i=k;i<n;i++)
printf("%d ",Min[i]);
printf("%d\n",Min[n]);
for(int i=k;i<n;i++)
printf("%d ",Max[i]);
printf("%d\n",Max[n]);
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
The use of a semaphore/interprocess communication 】 【 Shared memory
couldn't find 'libflutter.so' --flutter
锥形相位掩模的Talbot图像
win10无法识别蓝牙麦克风
Unity-存档与读档
VirtualLab Fusion中的可视化设置
HCIE学习记录——数据封装与常用协议(TCP/UDP)
线性结构,顺序结构
优先级表和Ascll表
LITESTAR 4D应用:室内植物照明模拟
C#实现简单的计算器
Qt | 读取文件内容并删除文件 QFile
MySQL协议长什么样子
消息队列的技术选型
shader入门精要1
implement tcp copa on ns3
Unity插件-NGUI
5款最好用的免费3D建模软件(附下载链接)
udp transparent proxy
CDH (computational Diffie-Hellman) problem and its differences with discrete logarithm and DDH problems