当前位置:网站首页>How does ns3 solve cross reference issue
How does ns3 solve cross reference issue
2022-08-02 14:12:00 【Soonyang Zhang】
First part
The use of Ptr object may cause cross reference in ns3. How ns3 destroy the pointer in cross reference situation.
Code example, ns3_ptr_ref.cc
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "ns3/core-module.h"
#include "ns3/network-module.h"
#include "ns3/internet-module.h"
namespace ns3{
class BClass;
class AClass:public Application{
public:
~AClass(){
std::cout<<"A dtor"<<std::endl;
}
void Attach(Ptr<BClass> b);
protected:
void StartApplication() override {}
void StopApplication() override {}
virtual void DoDispose (void);
virtual void DoInitialize (void){}
private:
Ptr<BClass> b_;
};
class BClass:public Application{
public:
~BClass(){
std::cout<<"B dtor"<<std::endl;
}
void Attach(Ptr<AClass> a);
protected:
void StartApplication() override {}
void StopApplication() override {}
virtual void DoDispose (void);
virtual void DoInitialize (void){}
private:
Ptr<AClass> a_;
};
void AClass::DoDispose (void){
b_=0;
std::cout<<"A DoDispose "<<GetReferenceCount()<<" "<<GetNode()->GetReferenceCount()<<std::endl;
Application::DoDispose();
}
void AClass::Attach(Ptr<BClass> b){
b_=b;
}
void BClass::DoDispose (void){
a_=0;
std::cout<<"B DoDispose "<<GetReferenceCount()<<" "<<GetNode()->GetReferenceCount()<<std::endl;
Application::DoDispose();
}
void BClass::Attach(Ptr<AClass> a){
a_=a;
}
void cross_ref_test(){
Ptr<AClass> a=CreateObject<AClass>();
Ptr<BClass> b=CreateObject<BClass>();
a->Attach(b);
b->Attach(a);
}
void cross_ref_with_node(bool run=true){
Ptr<AClass> a=CreateObject<AClass>();
Ptr<BClass> b=CreateObject<BClass>();
a->Attach(b);
b->Attach(a);
Ptr<Node> h1=CreateObject<Node>();;
std::cout<<"node "<<h1->GetReferenceCount()<<std::endl;
h1->AddApplication(a);
h1->AddApplication(b);
std::cout<<"ref "<<a->GetReferenceCount()<<std::endl;
if(run){
Simulator::Run ();
Simulator::Destroy();
}
std::cout<<"ref "<<a->GetReferenceCount()<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"ref "<<b->GetReferenceCount()<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"node "<<h1->GetReferenceCount()<<std::endl;
}
void count_init_node_ref(bool run=true){
Ptr<Node> h1=CreateObject<Node>();;
std::cout<<"node "<<h1->GetReferenceCount()<<std::endl;
if(run){
Simulator::Run ();
Simulator::Destroy();
}
std::cout<<"node "<<h1->GetReferenceCount()<<std::endl;
}
}
using namespace ns3;
void print_usuage(){
std::cout<<"plese input the right command: "<<std::endl;
std::cout<<"./waf --run \"scratch/ns3_ptr_ref 0\""<<std::endl;
}
int main(int argc,const char *argv[]){
LogComponentEnable("NodeList",LOG_LEVEL_ALL);
LogComponentEnable("Node",LOG_LEVEL_ALL);
if(2==argc){
std::string command(argv[1]);
if(0==command.compare("0")){
cross_ref_test();
}else{
cross_ref_with_node();
}
}else{
print_usuage();
}
return 0;
}
cross_ref_test
Running the command: ./waf --run “scratch/ns3_ptr_ref 0”. The function cross_ref_test will be called.
In cross_ref_test, a will refer to b (a->Attach(b)) and b will refer to a (b->Attach(a)).
When program exits, both a and b will not be destoyed.
cross_ref_with_node
Running the command: ./waf --run "scratch/ns3_ptr_ref 1. The function cross_ref_with_node will be called.
a and b will be added in node object as application. The Dispose function in Node will be called when Simulator::Destroy() is called. Dispose will call DoDispose.
void Node::DoDispose (){
for (std::vector<Ptr<Application> >::iterator i = m_applications.begin ();
i != m_applications.end (); i++)
{
Ptr<Application> application = *i;
application->Dispose ();
*i = 0;
}
}
application->Dispose () will call DoDispose in Application. In object a, the reference to b is removed.
void AClass::DoDispose (void){
b_=0;
std::cout<<"A DoDispose"<<std::endl;
}
Both a and b will be destroyed.
How NodeListPriv::DoDispose is triggered?
Ptr<NodeListPriv> * NodeListPriv::DoGet (void){
static Ptr<NodeListPriv> ptr = 0;
if (ptr == 0)
{
ptr = CreateObject<NodeListPriv> ();
Config::RegisterRootNamespaceObject (ptr);
Simulator::ScheduleDestroy (&NodeListPriv::Delete);
}
return &ptr;
}
void NodeListPriv::Delete (void){
NS_LOG_FUNCTION_NOARGS ();
Config::UnregisterRootNamespaceObject (Get ());
(*DoGet ()) = 0;
}
Before NodeListPriv is destroyed in Delete, the Dispose function in NodeListPriv will be called first.
void
NodeListPriv::DoDispose (void)
{
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this);
for (std::vector<Ptr<Node> >::iterator i = m_nodes.begin ();
i != m_nodes.end (); i++)
{
Ptr<Node> node = *i;
node->Dispose ();
*i = 0;
}
m_nodes.erase (m_nodes.begin (), m_nodes.end ());
Object::DoDispose ();
}
class Object : public SimpleRefCount<Object, ObjectBase, ObjectDeleter>
void ObjectDeleter::Delete (Object *object){
object->DoDelete ();
}
Second part
During test, I found the Node object can be destroyed only after Simulator::Run () is called. After a node is created, its reference is 3. If run=false, h1 will not be destroyed.
void count_init_node_ref(bool run=true){
Ptr<Node> h1=CreateObject<Node>();
std::cout<<"node "<<h1->GetReferenceCount()<<std::endl;
if(run){
Simulator::Run ();
Simulator::Destroy();
}
std::cout<<"node "<<h1->GetReferenceCount()<<std::endl;
}
The number 3 is analyzed here:
Node::Node()
: m_id (0),
m_sid (0)
{
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this);
Construct ();
}
void Node::Construct (void){
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this);
m_id = NodeList::Add (this);
}
uint32_t NodeList::Add (Ptr<Node> node){
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (node);
return NodeListPriv::Get ()->Add (node);
}
uint32_t NodeListPriv::Add (Ptr<Node> node) {
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << node);
uint32_t index = m_nodes.size ();
m_nodes.push_back (node);
Simulator::ScheduleWithContext (index, TimeStep (0), &Node::Initialize, node);
return index;
}
When count_init_node_ref(false), the events in simulator will not traggier. The node object here Simulator::ScheduleWithContext (index, TimeStep (0), &Node::Initialize, node) will not derefered.
Reference:
[1] HOWTO resolve circular references in ns-3 memory disposal
[2] NS3 Node聚合对象说明
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
Unity-PlayMaker
STM32LL library - USART interrupt to receive variable length information
Detailed introduction to the hierarchical method of binary tree creation
数学工具-desmos 图形曲线
Codeforces Round #605 (Div. 3)
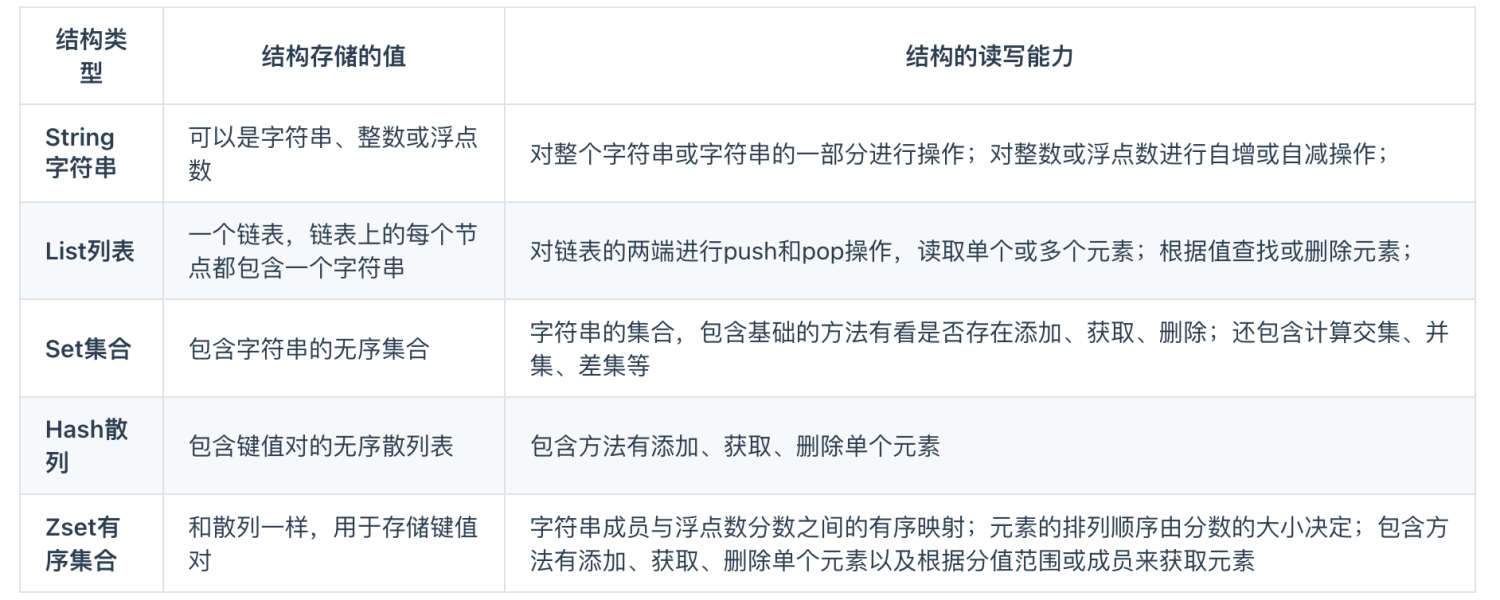
Redis common interview questions
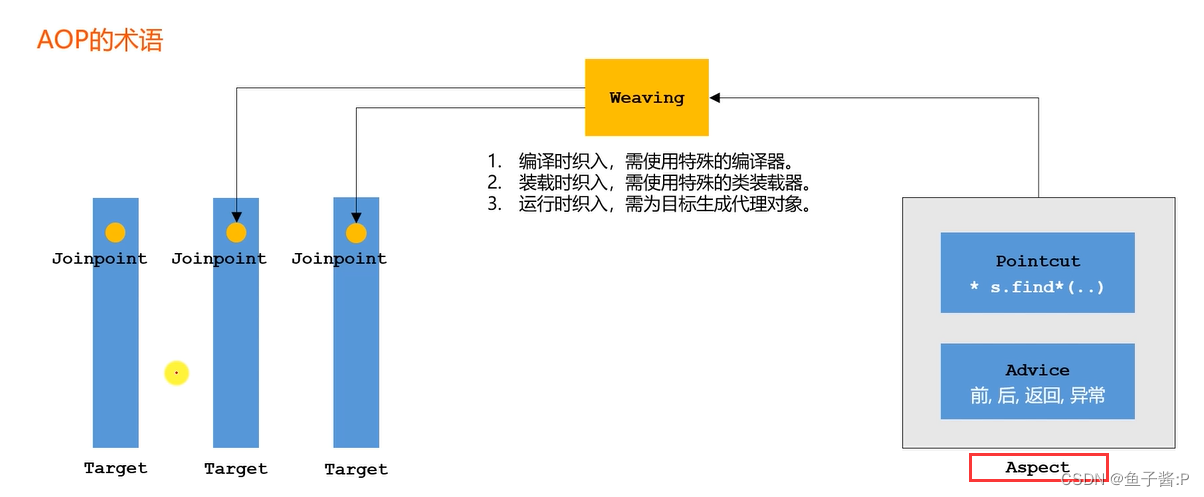
6. Unified logging
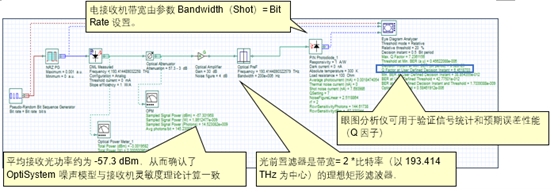
Optisystem应用:光电检测器灵敏度建模
EastWave应用:光场与石墨烯和特异介质相互作用的研究

第二十七章:时间复杂度与优化
随机推荐
质数相关问题-小记
Qt | 播放音频文件 QMediaplayer
Redis常见面试题
JCMsuite应用:四分之一波片
What are IPV4 and IPV6?
Qt | 实现一个简单的可以转动的仪表盘
二叉排序树与 set、map
Doubled and sparse tables
二叉树的遍历:递归法/ 迭代法/ 统一迭代法(强QAQ)
第三十章:普通树的存储和遍历
远程连接Ubuntu中的Mysql
关于混淆的问题
Based on the least squares linear regression equation coefficient estimation
队列与栈
使用1D-1D EPE的光波导布局设计工具
3. User upload avatar
shader入门精要1
shader入门精要3
Introduction to C language function parameter passing mode
Open the door to electricity "Circuit" (3): Talk about different resistance and conductance