当前位置:网站首页>[Paper Reading] TRO 2021: Fail-Safe Motion Planning for Online Verification of Autonomous Vehicles Using Conve
[Paper Reading] TRO 2021: Fail-Safe Motion Planning for Online Verification of Autonomous Vehicles Using Conve
2022-08-03 22:54:00 【Kin__Zhang】
参考与前言
Last edited time: August 3, 2022 10:04 AM
Status: Reading
Type: TRO
Year: 2021
论文链接:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9302873
1. Motivation
safe motion planningIt is important for automated driving,其中online verification To ensure no accident self-driving vehicles,But the existing methods of the following disadvantages:
- online verification并不高效,一般需要20HZOr higher frequency
- 在一些极端的情况下 All the time can't completely avoid collision
- In unsafe scene,Most methods are lack of supplyalternative motion plans
Related work
Due to the need of smart 所以总结了一下,感兴趣可看,Get a general idea of the unmanned vehicle planning related work
trajectory planning
discrete planning比较受欢迎,Mainly discretization search space、State and the input space, etc,motion primitivesMainly is to calculate in advance very fast track,然后通过search-based方案concatenaated到一起,This step is usuallyoffline的,So can be applied to more complex vehicle model,比如multibody modesl[19]
OS: Estimation is a form of record will track points,Or after building figurefreeThe global track points 搜素空间
- Sampling-based: RRT为主的,More suitable for high dimensional search space,But due to random sampling,Usually can't in timeoptimal motion
- Graph-search: 比如state lattices,同属discrete planning.To obtain a series of track,其goal states是预定义好的grid上的点,使用 lattice 结构表示.state latticesUsing the optimized to achievejerk-optimal.通常lattices能构建 To track,但是 due to grid, it lack optimality and completeness
虽然discrete planningIs relatively easy to implement and effective solution tomotion问题的,但是缺点也很明显:Also it is because the discrete,所以可能在safety-critical scenarios with small and convoluted solution spaces 无法求解;同样的原因 也会导致在fail to determine trajectories ending in small safe terminal sets
Therefore, continuousmodel predictive control通过minimizing cost function To generate the collisionless trajectory,Such as mixed integer optimization、sequential quadratic programs;For solving the problems are often convex,So to solve more difficult can't achieve the real time;The other is likely to causelocal minimal
Usually can put the non-convex problem into a convex,Such as linear vehicle dynamics,将motionDivided into horizontal and vertical;[47]-[51] Illustrates the method can be in the global convergence effectively solve the optimization problem under the condition of;But because the method on the transverse and longitudinal,May lead to can't feasible path in complex scenarios.我们通过focusing on simple evasive maneuvers and providing safe fallback solutions来解决这一问题 → 对应Section VI.
safety verification
In theorem proving, desired system properties are formulated using logical formulas,然后verificationSteps are mainlychecking the satisfiability of the logical formulas
If you've never enterinevitable collision states 则认为是安全的,ICS是一种状态:All vehicles themselves may track and collision,ICS reason over infinite time horizons,The random traffic scene 确定ICS是比较耗时的,Most of the work to improve the effect,Only consider other participants a path.
为补充ICS,controlled invariant sets 保证了persistent feasibility,According to the definition is based on other participants,如果在CISWithin each state are a collisionless trajectory,Shows the vehicle's safety.Because of obstacles in the future state of the unknown,计算CISIn a dynamic environment ischallenging
Set-based reachability analysis Through calculating allfeasible轨迹,Check whether there is a collision free path;But this method,Because of considering all possible states in the future,unsafe regions may grow rapidly. 导致的结果就是 Just planning the trajectory will be humanpotentially unsafe,leaving AV without a safe trajectory. 在本篇文章中,我们通过结合fail-safe planning来结合reachable sets在verficiationIn order to solve this problem
responsibility-sensible safety RSS 也是一种formal safety model
Contribution
Main contribution is demonstrated a verification technique 来保证车辆的安全性 Make up for a lack of the above mentioned below,The extracted from above:
- Related planning in transverse and longitudinal method points,May lead to can't feasible path in complex scenarios.本文通过focusing on simple evasive maneuvers and providing safe fallback solutions来解决这一问题 → 对应Section VI.
- 计算CISIn a dynamic environment ischallenging
- Because of considering all possible states in the future,unsafe regions may grow rapidly. 导致的结果就是 Just planning the trajectory will be humanpotentially unsafe,leaving AV without a safe trajectory
2. Method
First of all, defines the problem,及 相关sets,这一部分有点多,建议看原文,Mainly introduce the meaning of all variables, etc,定义了set Z R^1 Is the carpossible disturbances z,Motion differential equation for:
x ˙ ( t ) = f ( x ( t ) , u ( t ) , z ( t ) ) . \begin{equation*} \dot{x}(t) = f\left(x(t),u(t),z(t)\right). \tag{1} \end{equation*} x˙(t)=f(x(t),u(t),z(t)).(1)
使用 χ ( t h , x ( t 0 ) , u ( [ t 0 , t h ] ) ) \chi\left(t_{h}, x\left(t_{0}\right), u\left(\left[t_{0}, t_{h}\right]\right)\right) χ(th,x(t0),u([t0,th])) 来表示 The formula of solution,也就是满足motionThe trajectory under collection


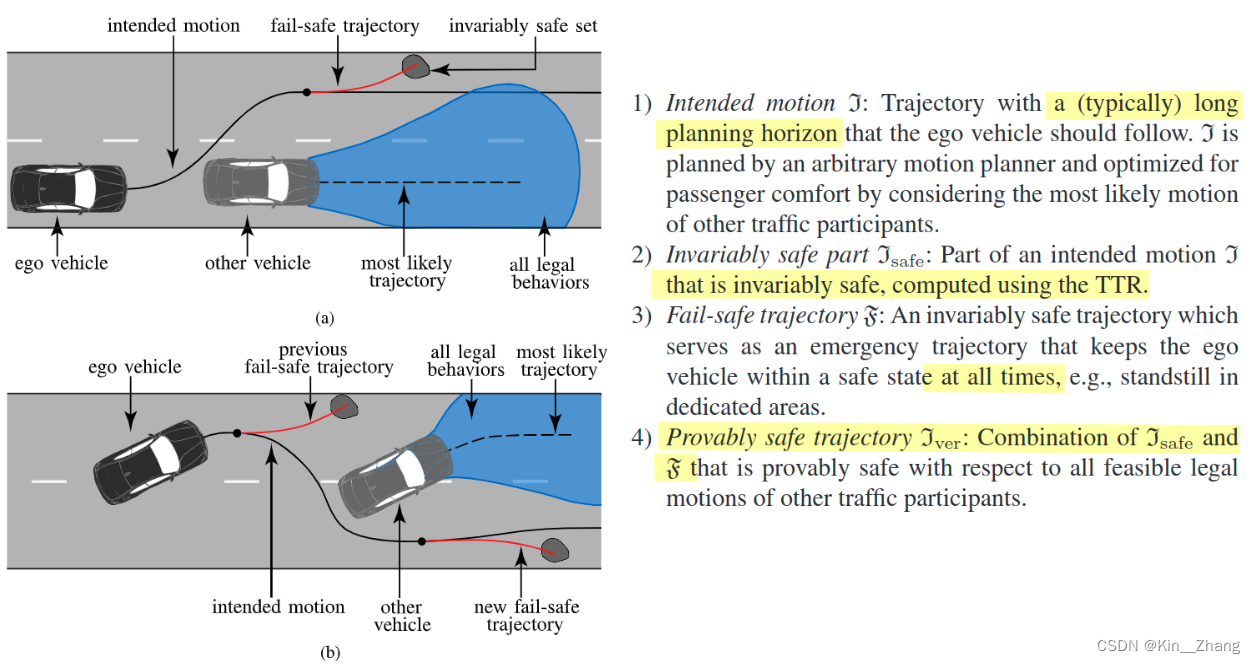
Mentioned before they work[68],为计算 S ( t ) \mathcal S(t) S(t),We follow the rules:
- Formal safe distances[79]:No matter how state of vehicle ahead Including the front vehicle brakes, and so on and so forth;Under this distance,We can always brake stop
- Evasive distances[80]:这个距离下 Even if the front vehicle brakes,We can also through the adjacent lanes to avoid collision
后面ab给我解释,Two formulas for a long time,First of all have a condition:
( ∣ a s,max,b ∣ < ∣ a s,max ∣ ) ∧ ( v b ∗ < v ego ) ∧ ( v e g o ∣ a s , m a x ∣ < v b ∗ ∣ a s , m a x , b ∣ ) , \begin{align*} & \left(|a_{\text{s,max,b}}| < |a_{\text{s,max}}| \right)\wedge \left(v^*_b < v_\text{ego} \right)\wedge\left(\frac{v_{\mathrm{ego}}}{|a_{\mathrm{s,max}}|} < \frac{v_b^*}{|a_{\mathrm{s,max,b}}|}\right), \tag{2} \end{align*} (∣as,max,b∣<∣as,max∣)∧(vb∗<vego)∧(∣as,max∣vego<∣as,max,b∣vb∗),(2)
如果满足这个条件,So safe distance as:
Δ s a f e , 1 ( v e g o , b ) : = ( v b − ∣ a s,max,b ∣ δ b r a k e − v ego ) 2 − 2 ( ∣ a s,max,b ∣ − ∣ a s,max ∣ ) + v ego δ b r a k e − v b δ b r a k e + 1 2 ∣ a s,max,b ∣ δ b r a k e 2 \begin{align*} \Delta _{\mathrm{safe,1}}(v_{\mathrm{ego}},b):=&\frac{(v_b-|a_{\text{s,max,b}}|\delta _{\mathrm{brake}}-v_\text{ego})^2}{-2(|a_{\text{s,max,b}}|-|a_{\text{s,max}}|)}+v_\text{ego}\delta _{\mathrm{brake}}-v_b\delta _{\mathrm{brake}}+\frac{1}{2}|a_{\text{s,max,b}}|\delta _{\mathrm{brake}}^2\end{align*} Δsafe,1(vego,b):=−2(∣as,max,b∣−∣as,max∣)(vb−∣as,max,b∣δbrake−vego)2+vegoδbrake−vbδbrake+21∣as,max,b∣δbrake2
The front is a whole 即 ( v − 0 ) 2 2 a \frac{(v-0)^2}{2a} 2a(v−0)2;Is followed by another whole In the reaction time on relative distance 即 0 + v t + 1 2 a t 2 0+vt+\frac{1}{2}at^2 0+vt+21at2
Otherwise the safety distance for the: The maximum rate of acceleration to everyone to0的时候,Plus a car since the reaction time
Δ s a f e , 2 ( v e g o , b ) : = v b 2 − 2 ∣ a s,max,b ∣ − v ego 2 − 2 ∣ a s,max ∣ + v ego δ b r a k e . \Delta _{\mathrm{safe,2}}(v_{\mathrm{ego}},b):=\frac{v_b^2}{-2|a_{\text{s,max,b}}|}-\frac{v_\text{ego}^2}{-2|a_{\text{s,max}}|} + v_\text{ego}\delta _{\mathrm{brake}}. Δsafe,2(vego,b):=−2∣as,max,b∣vb2−−2∣as,max∣vego2+vegoδbrake.
2.2 Safe& Evasive Distance Set
safe distance set
Points horizontal longitudinal safety distance,The longitudinal distance in[81,82] This paper has a detailed consideration and prove:
S 1 ( t ) = { ( s , d , v ) T ∈ X ∣ ∀ ( s b , d b ) T ∈ O b , c l s ( t ) : s ≤ s b − Δ s a f e , 2 ( v , b ) } \mathcal{S}^{1}(t)=\left\{(s, d, v)^{T} \in \mathcal{X} \mid \forall\left(s_{b}, d_{b}\right)^{T} \in \mathcal{O}_{b, \mathrm{cls}}(t): s \leq s_{b}-\Delta_{\mathrm{safe}, 2}(v, b)\right\} S1(t)={ (s,d,v)T∈X∣∀(sb,db)T∈Ob,cls(t):s≤sb−Δsafe,2(v,b)}
And here mainly explain the horizontalevasive distance [Translated into escape feeling Escape distance is not so good So with the original],首先引入 d e v a d_{\mathrm{eva}} deva As vehicle lane changing completely the transverse distance,aFor lateral acceleration
t e v a : = 2 d e v a a d , m a x + δ s t e e r (5) t_{\mathrm{eva}}:= \sqrt{\frac{2d_{\mathrm{eva}}}{a_{\mathrm{d,max}}}} + \delta _{\mathrm{steer}}\tag{5} teva:=ad,max2deva+δsteer(5)
At the same time considering the vehicles ahead in the distance for a set period of time(纵)
Δ s b : = v b t b − 1 2 ∣ a s , m a x , b ∣ t b 2 t b : = min ( t e v a , v b ∣ a s , m a x , b ∣ ) . (6) \begin{split} \Delta s_b &:= v_bt_b-\frac{1}{2}|a_{\mathrm{s,max,b}}|t_b^2\\ t_b&:= \min (t_{\mathrm{eva}},\frac{v_b}{|a_{\mathrm{s,max,b}}|}). \end{split} \tag{6} Δsbtb:=vbtb−21∣as,max,b∣tb2:=min(teva,∣as,max,b∣vb).(6)
evasive distance set
定义如下,证明在[80]
S 2 ( t ) = { ( s , d , v ) T ∈ X ∣ ∀ ( s b , d b ) T ∈ O b , c l s ( t ) : s ≤ s b − Δ eva t ( v , b ) } \mathcal{S}^{2}(t)=\left\{(s, d, v)^{T} \in \mathcal{X} \mid \forall\left(s_{b}, d_{b}\right)^{T} \in \mathcal{O}_{b, \mathrm{cls}}(t): s \leq s_{b}-\Delta_{\text {eva }}^{t}(v, b)\right\} S2(t)={ (s,d,v)T∈X∣∀(sb,db)T∈Ob,cls(t):s≤sb−Δeva t(v,b)}
Underapproximation of S
The first twoset取并集,得到S
2.3 生成fail-safe Trajectories
纵向 Longitudinal Motion
首先是 Longitudinal motion formula said: x lon = ( s , v , a , j ) T x_{\text {lon }}=(s, v, a, j)^{T} xlon =(s,v,a,j)T,纵向距离、速度、加速度、jerk;We use the acceleration asinput,Described vehicle longitudinal motion aslinear time-invariant system
d 4 d t 4 s ( t ) = u l o n ( t ) . \begin{equation*} \frac{d^4}{dt^4}s(t)=u_{\mathrm{lon}}(t). \tag{8} \end{equation*} dt4d4s(t)=ulon(t).(8)
Then add the constraint,a Before and after vehicle distance of longitudinal,b The size of the vehicle itself 速度、加速度和jerk
s m i n ( t ) ≤ x l o n ( 0 ) ( t ) ≤ s m a x ( t ) v m i n ≤ x l o n ( 1 ) ( t ) ≤ v m a x a m i n ≤ x l o n ( 2 ) ( t ) ≤ a m a x j m i n ≤ x l o n ( 3 ) ( t ) ≤ j m a x \begin{align*} s_{\mathrm{min}}(t) \leq &x_{\mathrm{lon}}^{(0)}(t) \leq s_{\mathrm{max}}(t)\\ v_{\mathrm{min}}\leq &x_{\mathrm{lon}}^{(1)}(t) \leq v_{\mathrm{max}}\\ a_{\mathrm{min}}\leq &x_{\mathrm{lon}}^{(2)}(t) \leq a_{\mathrm{max}}\\ j_{\mathrm{min}}\leq &x_{\mathrm{lon}}^{(3)}(t) \leq j_{\mathrm{max}} \tag{10} \end{align*} smin(t)≤vmin≤amin≤jmin≤xlon(0)(t)≤smax(t)xlon(1)(t)≤vmaxxlon(2)(t)≤amaxxlon(3)(t)≤jmax(10)
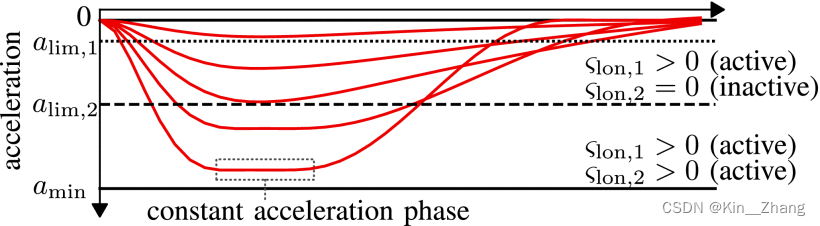
We have demonstrated the brakes,但是因为是>0的加速度,So here we introduce twodeceleration limits a min < a lim , 2 < a lim , 1 < 0 a_{\min }<a_{\lim , 2}<a_{\lim , 1}<0 amin<alim,2<alim,1<0,其中 ς l o n , 1 , ς l o n , 2 ≥ 0 \varsigma _{\mathrm{lon},1},\varsigma _{\mathrm{lon},2}\geq0 ςlon,1,ςlon,2≥0 是slack variables Relaxation constraint (JG: Optimization of smalltrick 可以加速 更容易求解)
x l o n ( 2 ) ( t ) ≥ a l i m , 1 − ς l o n , 1 x l o n ( 2 ) ( t ) ≥ a l i m , 2 − ς l o n , 2 . \begin{align*} x_{\mathrm{lon}}^{(2)}(t)&\geq a_{\mathrm{lim},1} - \varsigma _{\mathrm{lon},1}\\ x_{\mathrm{lon}}^{(2)}(t)&\geq a_{\mathrm{lim},2} - \varsigma _{\mathrm{lon},2}. \tag{11} \end{align*} xlon(2)(t)xlon(2)(t)≥alim,1−ςlon,1≥alim,2−ςlon,2.(11)
纵向的cost
J l o n ( x ( t ) , u ( t ) ) = w a x l o n ( 2 ) ( t ) 2 + w j x l o n ( 3 ) ( t ) 2 + w ς 1 ς l o n , 1 + w ς 2 ς l o n , 2 2 . \begin{align*} J_{\mathrm{lon}}\left(x(t),u(t)\right) =&\,w_ax_{\mathrm{lon}}^{(2)}(t)^2+w_jx_{\mathrm{lon}}^{(3)}(t)^2+w_{\varsigma _1}\varsigma _{\mathrm{lon},1}+w_{\varsigma _2}\varsigma _{\mathrm{lon},2}^2. \tag{12} \end{align*} Jlon(x(t),u(t))=waxlon(2)(t)2+wjxlon(3)(t)2+wς1ςlon,1+wς2ςlon,22.(12)
横向 Lateral Motion
同理 Lateral movement said: x lat = ( d , θ , κ , κ ˙ ) T x_{\text {lat }}=(d, \theta, \kappa, \dot{\kappa})^{T} xlat =(d,θ,κ,κ˙)T,沿frenetCoordinates of the horizontal distance from the reference line、orientation、曲率、Since the car curvature change
Lateral motion description for the following13公式,其中 u l a t ( t ) = κ ¨ ( t ) u_{\mathrm{lat}}(t)=\ddot \kappa(t) ulat(t)=κ¨(t) 来源于 time-invariant linear
x ˙ l a t = ( 0 v ( t ) 0 0 0 0 v ( t ) 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 ) x l a t ( t ) + ( 0 0 0 1 ) u l a t ( t ) + ( − v ( t ) 0 0 0 ) z l a t ( t ) . \begin{align*} \dot{x}_{\mathrm{lat}} =& \begin{pmatrix}0&v(t)&0&0\\ 0&0&v(t)&0\\ 0&0&0&1 \\ 0&0&0&0 \\ \end{pmatrix}x_{\mathrm{lat}}(t) + \begin{pmatrix}0\\ 0\\ 0\\ 1 \end{pmatrix}u_{\mathrm{lat}}(t)\\ &+ \begin{pmatrix}-v(t)\\ 0\\ 0\\ 0 \end{pmatrix}z_{\mathrm{lat}}(t). \tag{13} \end{align*} x˙lat=⎝⎛0000v(t)0000v(t)000010⎠⎞xlat(t)+⎝⎛0001⎠⎞ulat(t)+⎝⎛−v(t)000⎠⎞zlat(t).(13)
对于collision free The vehicle as three round,Each circle distance from a reference line can be expressed in the following formula
d i = d + i − 1 2 ℓ sin ( θ − θ Γ ) ≈ d + i − 1 2 ℓ ( θ − θ Γ ) . \begin{equation*} d_i = d + \frac{i-1}{2}\ell \sin (\theta -\theta _\Gamma)\approx d+\frac{i-1}{2}\ell (\theta -\theta _\Gamma). \tag{14} \end{equation*} di=d+2i−1ℓsin(θ−θΓ)≈d+2i−1ℓ(θ−θΓ).(14)
Combined with a series of vertical and similar constraints,就不在此赘述了
横向的cost function:
J l a t ( x ( t ) , u ( t ) ) = w d x l a t ( 0 ) ( t ) 2 + w θ ( x l a t ( 1 ) ( t ) − θ Γ ( t ) ) 2 + w κ x l a t ( 2 ) ( t ) 2 + w κ ˙ x l a t ( 3 ) ( t ) 2 . \begin{equation*} \begin{split} J_{\mathrm{lat}}\left(x(t),u(t)\right) =&\,w_d x_{\mathrm{lat}}^{(0)}(t)^2+w_\theta \left(x_{\mathrm{lat}}^{(1)}(t)-\theta _\Gamma (t)\right)^2\\ &+w_\kappa x_{\mathrm{lat}}^{(2)}(t)^2+w_{\dot{\kappa }}x_{\mathrm{lat}}^{(3)}(t)^2. \end{split} \tag{18} \end{equation*} Jlat(x(t),u(t))=wdxlat(0)(t)2+wθ(xlat(1)(t)−θΓ(t))2+wκxlat(2)(t)2+wκ˙xlat(3)(t)2.(18)
生成Fail-Safe
首先是根据TTR生成初始状态,Calculated by the initial state to the next againfail-safe轨迹
下列公式中 Δ c o r \Delta_{cor} ΔcorFor vehicles to the rear axle center distance correction term, s m i n ≤ s ≤ s m a x s_{min}\leq s \leq s_{max} smin≤s≤smax
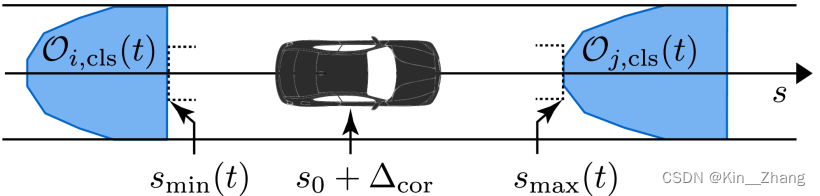
s m i n ( t ) = sup { s − Δ c o r ∣ ∀ b ∈ B f o l : s − Δ c o r < s 0 ∧ ( s , d ) T ∈ O b , c l s ( t ) } . \begin{equation*} \begin{split} s_{\mathrm{min}}(t) = \sup \left\lbrace s-\Delta _{\mathrm{cor}}\,|\,\forall b \in \mathcal {B}_{\mathrm{fol}}: s-\Delta _{\mathrm{cor}}< s_0\right.\\ \left.\wedge (s,d)^T\in \mathcal {O}_{b,\mathrm{cls}}(t)\right\rbrace . \end{split} \tag{20} \end{equation*} smin(t)=sup{ s−Δcor∣∀b∈Bfol:s−Δcor<s0∧(s,d)T∈Ob,cls(t)}.(20)
s m a x ( t ) = inf { s − Δ c o r ∣ ∀ b ∈ B p r e : s − Δ c o r > s 0 ∧ ( s , d ) T ∈ O b , c l s ( t ) } . \begin{equation*} \begin{split} s_{\mathrm{max}}(t) = \inf \left\lbrace s-\Delta _{\mathrm{cor}}\,|\,\forall b \in \mathcal {B}_{\mathrm{pre}}:s-\Delta _{\mathrm{cor}}>s_0\right.\\ \wedge \left.(s,d)^T\in \mathcal {O}_{b,\mathrm{cls}}(t)\right\rbrace . \end{split} \tag{19} \end{equation*} smax(t)=inf{ s−Δcor∣∀b∈Bpre:s−Δcor>s0∧(s,d)T∈Ob,cls(t)}.(19)
Whole generation process:
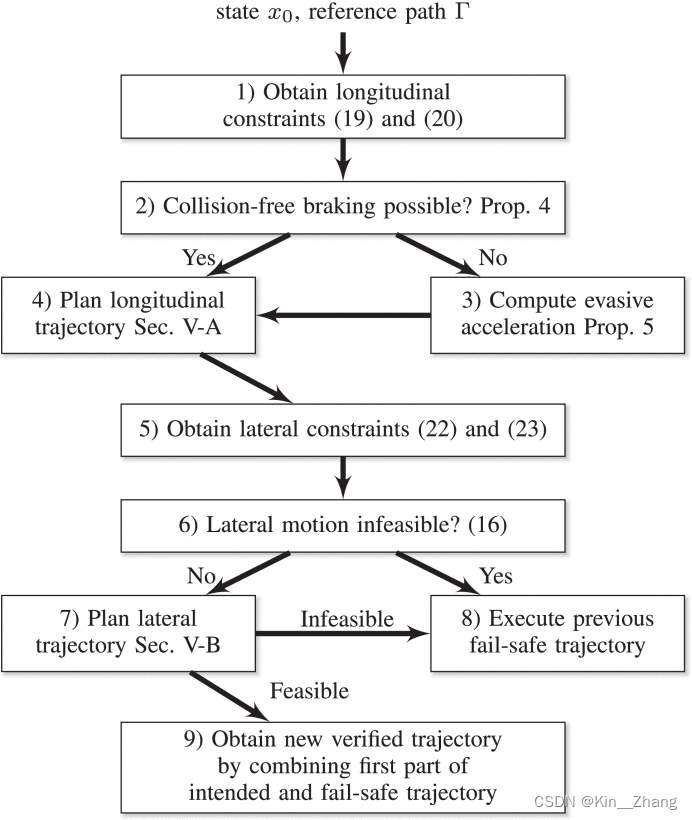
collision avoidance through braking
在初始状态下 Can the emergency brake conditions:Proposition 4
∀ t ∈ [ t 0 , t h ] : s 0 + v 0 ( τ ) − 1 2 ∣ a m a x ∣ max ( τ − δ b r a k e , 0 ) 2 ≤ s m a x ( t ) , τ : = min ( t , v 0 ∣ a m a x ∣ + δ b r a k e ) . \begin{equation*} \begin{split} \forall t\in [t_0,t_h]: &\,s_0+v_0(\tau)-\frac{1}{2}|a_{\mathrm{max}}| \max (\tau -\delta _{\mathrm{brake}},0)^2 \\ &\leq s_{\mathrm{max}}(t), \tau :=\min (t,\frac{v_0}{|a_{\mathrm{max}}|}+\delta _{\mathrm{brake}}). \end{split} \end{equation*} ∀t∈[t0,th]:s0+v0(τ)−21∣amax∣max(τ−δbrake,0)2≤smax(t),τ:=min(t,∣amax∣v0+δbrake).
If a collision is bound to happen,那么guaranteed Time-To-Collision是:
t G T T C : = argmin t ∈ [ 0 , t h ] ∣ ( s 0 + v 0 t ) − s m a x ( t ) ∣ . \begin{equation*} t_{\mathrm{GTTC}}:= \text{argmin}_{t\in [0,t_h]} \big |(s_0+v_0t) - s_{\mathrm{max}}(t)\big |. \end{equation*} tGTTC:=argmint∈[0,th]∣∣(s0+v0t)−smax(t)∣∣.
Evasice AccelerationCan say:Proposition 5
a e v a = 2 ( d e v a − ∣ v l a t ∣ t G T T C ) ( t G T T C − δ s t e e r ) 2 . \begin{equation*} a_{\mathrm{eva}}= \frac{2\left(d_{\mathrm{eva}}-|v_{\mathrm{lat}}|t_{\mathrm{GTTC}}\right)}{(t_{\mathrm{GTTC}}-\delta _{\mathrm{steer}})^2}. \end{equation*} aeva=(tGTTC−δsteer)22(deva−∣vlat∣tGTTC).
Need to meet the distance curve 示意
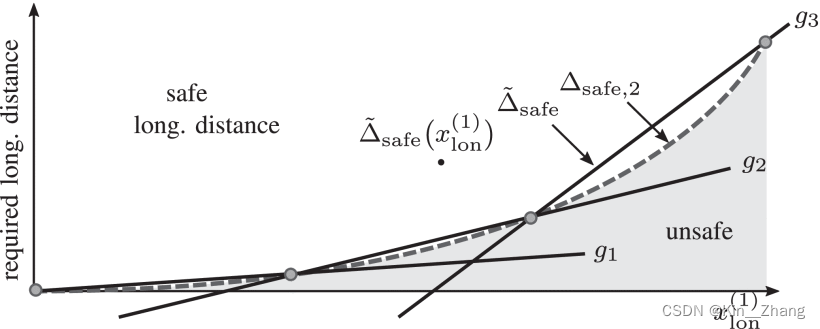
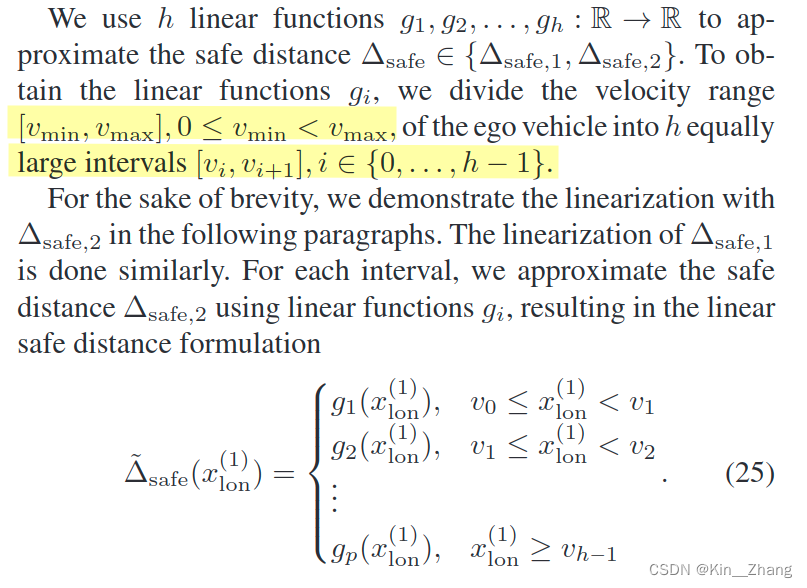
使用h段gThe function to approximate a safe distance Δ s a f e ∈ { Δ s a f e , 1 , Δ s a f e , 2 } \Delta_{safe}\in\{\Delta_{safe,1},\Delta_{safe,2}\} Δsafe∈{ Δsafe,1,Δsafe,2} Then points speed range to geth段
In order to join this optimization process,可以表示为maximum function[88]
Δ ~ s a f e ( x l o n ( 1 ) ) = max ( g 1 ( x l o n ( 1 ) ) , g 2 ( x l o n ( 1 ) ) , … , g h ( x l o n ( 1 ) ) ) . \begin{equation*} \tilde{\Delta }_{\mathrm{safe}}(x_{\mathrm{lon}}^{(1)}) = \max \left(g_1(x_{\mathrm{lon}}^{(1)}), g_2(x_{\mathrm{lon}}^{(1)}), \dots, g_h(x_{\mathrm{lon}}^{(1)})\right). \end{equation*} Δ~safe(xlon(1))=max(g1(xlon(1)),g2(xlon(1)),…,gh(xlon(1))).
Then add the longitudinal distance constraint in the 公式(9)
x l o n ( 0 ) ( t ) + Δ ~ s a f e ( x l o n ( 1 ) ) ≤ s m a x ( t ) . \begin{align*} x_{\mathrm{lon}}^{(0)}(t) + \tilde{\Delta }_{\mathrm{safe}}(x_{\mathrm{lon}}^{(1)}) \leq s_{\mathrm{max}}(t). \tag{26} \end{align*} xlon(0)(t)+Δ~safe(xlon(1))≤smax(t).(26)
Because the solver cannot solve withmax的函数,所以加入hA less than or equal to constraints, hShould not be too big 也不能太小,The former can increase the computing burden,The latter will have larger error
x l o n ( 0 ) ( t ) + ( g i ( x l o n ( 1 ) ) + δ b r a k e x l o n ( 1 ) ) ≤ s m a x ( t ) . \begin{align*} x_{\mathrm{lon}}^{(0)}(t) + \left(g_{i}(x_{\mathrm{lon}}^{(1)})+\delta _{\mathrm{brake}}x_{\mathrm{lon}}^{(1)}\right) \leq s_{\mathrm{max}}(t). \tag{27} \end{align*} xlon(0)(t)+(gi(xlon(1))+δbrakexlon(1))≤smax(t).(27)
3. 实验及结果
使用了Python和C++,Optimal solution is used by the library:CVXPY, ECOS and CVXPY-CODEGEN
Invariably safe set of the scenario
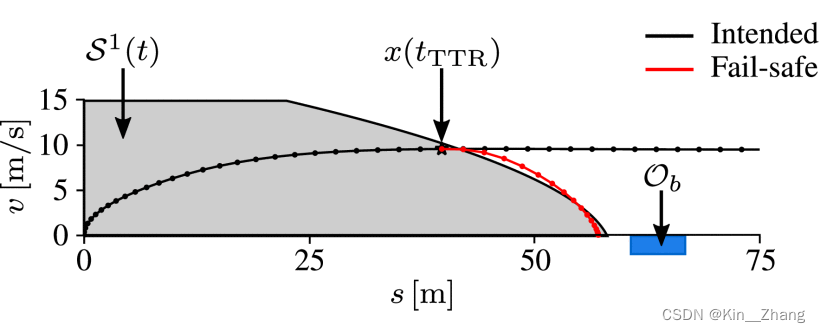
Then mainly experiment a few specific scenarios 去验证 fail-safe The trajectory of operation:
静态障碍物、In front of the vehicle brakes、Pedestrians rush out
4. Conclusion
提出了fail-safe motion planning 来保证AV不会发生事故
对比于其他的verification,Our approach is the first inarbitrary traffic situations使用的;同时保证了40msIn computing time,Can with any othermotion plan相结合
Our solution does not makeAVIn the excessive conservative strategy
If the relevant laws and regulations be extended,我们的verificationAlso can automatically adapt to.通过提供的occupancy setsTo capture other traffic participants all legal actions
碎碎念
一开始,abSaid that this is a conservative strategy,Is to consider the worst case;But while on a first reading in the said Don't take overly conservative strategy,A later start didn'tget到这个点,Until askedjg的时候发现slack variable和weights的一些trick设计,也就是并不是 非0即1 But can over constraint
对于fail-safeIs the concept of first by theTTR生成状态,Then according to the flowchart to determine whether the longitudinal brake can,Not possible in transverse obstacle avoidance;Overall is a solving optimization problem,Just constraints such as determined by a series of states to
赠人点赞 手有余香 ;正向回馈 才能更好开放记录 hhh
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
Bytebase database schema change management tool

云平台建设解决方案
3D 语义分割——2DPASS
《数字经济全景白皮书》金融数字用户篇 重磅发布!

Conditional Statements for Shell Programming
电商秒杀系统

Software testing is seriously involution, how to improve your competitiveness?

node连接mysql数据库报错:Client does not support authentication protocol requested by server

Zilliz 2023 Fall Campus Recruitment Officially Launched!
易观分析:2022年Q2中国网络零售B2C市场交易规模达23444.7亿元
随机推荐
Diazo Biotin-PEG3-DBCO | Diazo Compound Modified Biotin-Tripolyethylene Glycol-Dibenzocyclooctyne
重发布实验报告
SPOJ 2774 Longest Common Substring(两串求公共子串 SAM)
How many way of calling a function?
获国际权威认可 | 云扩科技入选《RPA全球市场格局报告,Q3 2022》
Causes of Mysql Disk Holes and Several Ways to Rebuild Tables
七夕活动浪漫上线,别让网络拖慢和小姐姐的开黑时间
直播预告 | 构建业务智联,快速拥抱财务数字化转型
物联网新零售模式,引领购物新潮流
Codeup刷题笔记-简单模拟
encapsulation, package, access modifier, static variable
Interpretation of ML: A case of global interpretation/local interpretation of EBC model interpretability based on titanic titanic rescued binary prediction data set using interpret
Testng listener
网络基础学习系列四(网络层,数据链路层和一些其他重要协议或技术)
牛客2022 暑期多校3 H Hacker(SAM + 线段树查询区间内部最大子段和)
Work Subtotal QT Packing
【论文阅读】TRO 2021: Fail-Safe Motion Planning for Online Verification of Autonomous Vehicles Using Conve
完全二叉树问题
软测人每个阶段的薪资待遇,快来康康你能拿多少?
pikachu Over permission