当前位置:网站首页>Advanced pointer (I)
Advanced pointer (I)
2022-07-03 00:47:00 【Learn something】
List of articles
Key points of this chapter
1. Character pointer
2. Array pointer
3. Pointer array
4. Array parameter passing and pointer parameter passing
The subject of the pointer , We are in the primary stage of 《 The pointer 》 The chapter has been touched , We know the concept of pointer :
1. A pointer is a variable , It's used to store the address , The address uniquely identifies a piece of memory space .
2. The size of the pointer is fixed 4/8 Bytes (32 Bit platform /64 Bit platform ).
3. Pointers are typed , The type of pointer determines the type of pointer ± Integer step size , The permission of pointer dereference operation .
4. The operation of the pointer .
This chapter , We continue to explore the advanced topic of pointers .
1. Character pointer
Character pointers are pointer variables that point to character data
Among the pointer types, we know that one pointer type is character pointer char *
In general use :
int main()
{
char ch = 'w';
char *pc = &ch;
*pc = 'w';
return 0;
}
We know c There is shaping in language , floating-point , Character , But there is no string type , So we usually use character arrays to store strings .
int main()
{
char arr[] = "abcdef"
char * parr = &arr;
int i = 0;
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
for(i = 0; i<sz; i++)
{
printf("%c",*(parr+i));
}
return 0;
}
in addition , There is another way , The string is represented by a pointer to the string .
int main()
{
char *pstr = "abcdef";
printf("%s",pstr);
}
Code char* pstr = "abcdef" It's very easy for students to think it's a string abcdef Put it in the character pointer pstr In the , It's not . Be careful , Above “abcdef” Represents a constant , It's not about putting "abcdef" Put it in the character pointer , The above code means that the first character of a constant string a The address of is stored in the pointer variable pstr in .
In a string "" The role of is :
1. Apply for space in the constant area , Store string
2. Add ’\0’
3. Return the address of the string
You must have questions , Why can string constants be assigned to character pointer variables ?
Because we define an ordinary character pointer , There is no defined space to store "abcdef", So the compiler will help us find a place to put "abcdef", obviously , Take this "abcdef" As a constant and put it in the constant area of the program is the most appropriate choice for the compiler ."abcdef" The value of is not the character itself , It's the return address , If it is an address, you can receive it with a pointer . So you can assign string constants to character pointer variables .
Be careful , When storing strings with character arrays ,"abcdef" Not a constant string , Defining a character array defines the space for storing strings , Character array is to store characters one by one , So the compiler will char [] = “abcdef” It can be interpreted as char[]={‘a’,b’‘,‘c’,‘d’,‘e’,‘f’,’\0’};
The other thing is that , because "abcdef" Is a constant string , Therefore, its value cannot be modified , Force modification , The program will crash .

We'd better use const Decorate it , The program won't crash ( Because it can't be compiled at all ).

Practice it , An interview question :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char str1[] = "hello world";
char str2[] = "hello world";
const char *str3 = "hello world";
const char *str4 = "hello world";
if(str1 ==str2)
printf("str1 and str2 are same\n");
else
printf("str1 and str2 are not same\n");
if(str3 ==str4)
printf("str3 and str4 are same\n");
else
printf("str3 and str4 are not same\n");
return 0;
}
The final output here is :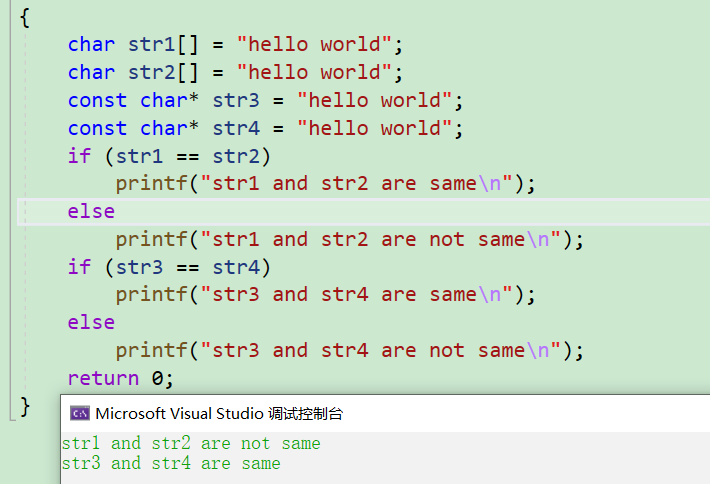
Conclusion : We know "hello world" Is a constant string , Stored in the constant area , And it can't be modified , The address is certain , The address here is the first element a The address of , here str3 and str4 Points to the same constant string ,C/C++ The constant string is stored in a separate memory area , When several pointers point to the same string , They actually point to the same block of memory . But when initializing different arrays with the same constant string, different memory spaces will be opened up , therefore str1 and str2 Different ,str3 and str4 Different .
2. Pointer array
stay 《 Initial order of pointer 》 We also learned about pointer arrays in this chapter , Pointer array is an array of pointers ,
Interested students , You can check it out .
3. Array pointer
3.1 Definition of array pointer
Array pointers are pointers ? Or arrays ?
The answer is : The pointer . From the perspective of Chinese , Array is a modifier , The pointer is the subject . such as , Peppa Pig , Page is the subject , Piglet is a modifier . The above is all my nonsense , Ha ha ha ha , My Chinese is very poor , Anyway, that's what I understand .
We are already familiar with :
Shaping the pointer : int * pi—> A pointer that can point to shaped data —> Can store plastic address
Character pointer : char * pc—> A pointer that can point to character data —> Can store character addresses
The array pointer should be : A pointer to an array —> The address where the array can be stored
Which of the following code is an array pointer ?
int *p1[10];
int (*p2)[10];
//p1, p2 What are the differences ?
explain :
int *p1[10];
explain :p1 The first and [10] combination , explain p1 Is an array , Storage 10 Elements , The type of each element is int *, therefore p1 Stored in is a pointer ,p1 It's an array of pointers .
int (*p2)[10];
explain :p2 The first and * combination , explain p2 Is a pointer variable , Then point to a size of 10 An array of integers . therefore p2 It's a pointer , Point to a number
Group , It's called array pointer .
Pay attention here :[] Priority is higher than * The no. , So we have to add () To guarantee p The first and * combination .
3.2& Array name VS Array name
For the following array :
int arr[10];
arr and &arr and &arr[0] What's the difference ?
We know arr It's an array name , The array name indicates the address of the first element of the array .
that &arr Array name and &arr What is the first element of the array ?
Let's look at a piece of code :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {
0};
printf("%p\n", arr);
printf("%p\n", &arr);
printf("%p\n",&arr[0]);
return 0;
}
The operation results are as follows :
Let's take another look at the code :
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {
0 };
printf("%p\n", arr);
printf("%p\n", arr + 1);
printf("\n");
printf("%p\n", &arr[0]);
printf("%p\n", &arr[0] + 1);
printf("\n");
printf("%p\n", &arr);
printf("%p\n", &arr + 1);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
The operation results are as follows :
According to the above code, we find that , Actually &arr and arr, Although the values are the same , But the meaning should be different .
actually : &arr It means Address of array , Instead of the address of the first element of the array ,&arr[0] and arr It means Are the address of the first element of the array .( Feel it carefully )

In this case &arr The type is : int(*)[10], Is an array pointer type
**&arr It takes out the address of the entire array ,p2 and * combination , Indicates that it is a pointer , It points to an array arr, Group arr Yes 10 Elements , therefore ( p2) and [10] combination ,arr The type of each element in the array is int , therefore int ( p2)[10] = &arr;
* Not a dereference operator , It's about explaining p2 It's a pointer
Address of array +1, Skip the size of the entire array , therefore &arr+1 be relative to &arr The difference is 40.
Analogy exercise :
*&arr2 It takes out the address of the entire array ,parr and * combination , Indicates that it is a pointer , It points to an array arr2, Array arr2 Yes 5 Elements , therefore ( p2) and [5] combination ,arr2 The type of each element in the array is char * , therefore char ( p2)[10] = &arr;
3.3 The use of array pointers
How do you use array pointers ?
Since the array pointer points to an array , The array pointer should store the address of the array .
Look at the code :
int main()
{
int arr[] = {
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
int (*p)[10] = &arr;
int i = 0;
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
for(i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%d ", *(*p + i));//p Is pointing to an array ,*p In fact, it is equivalent to the array name , The array name is the address of the first element of the array
// therefore *p It is essentially the address of the first element of the array *p == arr
}
return 0;
}
We find this very awkward , Generally, we don't use it like this , Instead, use the following code .
int main()
{
int arr[] = {
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
int i = 0;
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
for(i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%d ",*(arr + i));
}
return 0;
}
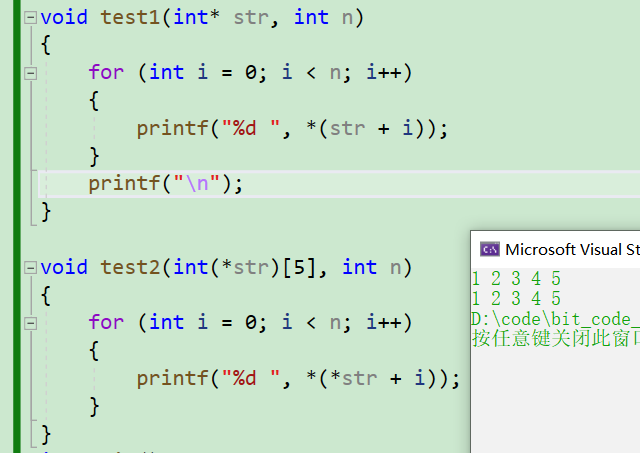
Look at the code :
void test1(int* str,int n)
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("%d ",*(str + i));
}
}
void test2(int (*str)[5],int n);
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("%d ",*(*str + i));
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[5] = {
1,2,3,4,5};
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
test1(arr,sz);
test2(&arr,sz);
return 0;
}
So let's talk about that , When we pass parameters to a function ,&arr The effect is not arr good . We said before &arr Is the address of the entire array , You can't print it out with one quotation . and arr One dereference is enough . This is because you dereference the address of the entire array to get the array name of a one-dimensional array , The array name here is the address of the first element of the array , At this time, it is similar to passing directly in the function call arr The result is the same .
The use of an array pointer :
void print_arr1(int arr[3][5], int r, int c)
{
int i = 0;
for(i=0; i < r; i++)
{
for(j=0; j < c; j++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void print_arr2(int (*arr)[5], int r, int c)
{
int i = 0;
for(i=0; i<r; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<c; j++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i][j]);//*(*(arr+i)+j)
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[3][5] = {
1,2,3,4,5,2,3,4,5,6,3,4,5,6,7};
print_arr1(arr, 3, 5);
// Array name arr, Represents the address of the first element
// But the first element of a two-dimensional array is the first row of a two-dimensional array
// So the message here is arr, It's actually equivalent to the address on the first line , Is the address of a one-dimensional array
// You can use an array pointer to receive
print_arr2(arr, 3, 5);
return 0;
}
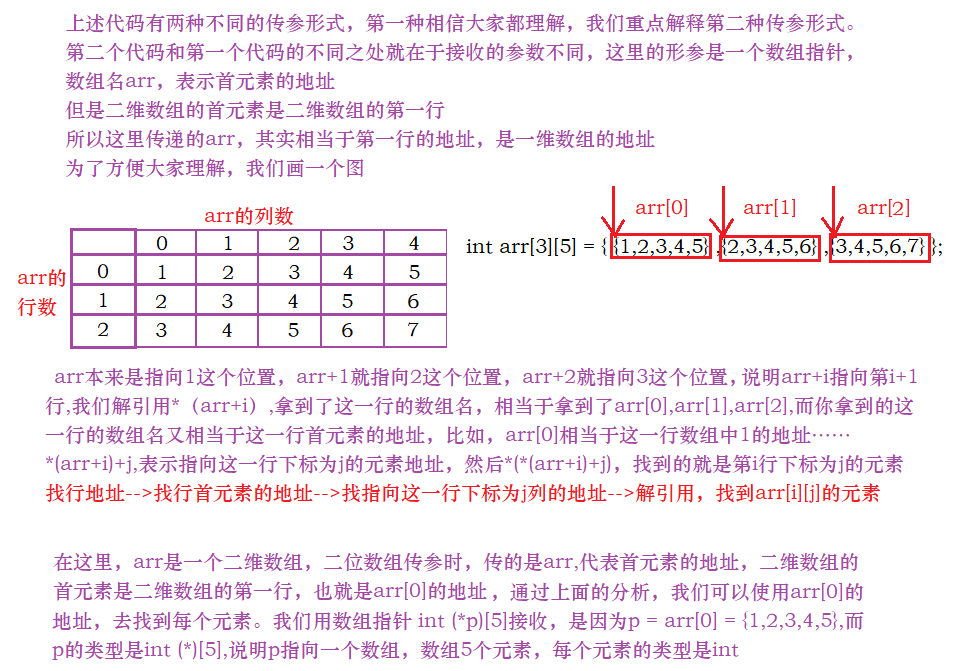
After learning pointer array and array pointer, let's review and see what the following code means :
int arr[5];
int *parr1[10];
int (*parr2)[10]
int (*parr3[10])[5];

4. Array parameters 、 Pointer parameter
When writing code, it is inevitable to 【 Array 】 perhaps 【 The pointer 】 Pass to function , How to design the parameters of the function ?
4.1 One dimensional array parameters
#include <stdio.h>
1.void test(int arr[])//ok?
{
}
2.void test(int arr[10])//ok?
{
}
3.void test(int *arr)//ok?
{
}
4.void test2(int *arr[20])//ok?
{
}
5.void test2(int **arr)//ok?
{
}
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {
0};
int *arr2[20] = {
0};
test(arr);
test2(arr2);
}
ask : The above parameter passing form , Whether it is right ?
answer : All right
We know , When passing parameters to a one-dimensional array , Mainly pass the array name , The array name of a one-dimensional array is essentially the address of the first element of the array , So it's also equivalent to sending an address .
We pass the array name to test() function , there arr Is an array that stores shaping data
1. Formal parameters can be arrays , Notice the array access operator ([]) The number of array elements in can be omitted , You can also write .
2. Formal parameters can also be pointers , We repeatedly emphasize that the array name is the address of the first element , So what is passed is essentially the address of an element , It can be used int* Pointer reception of type .
We pass the array name to test2() function , there arr2 It's a storage int * An array of type data
3. Formal parameters can be arrays , Notice the array access operator ([]) The number of array elements in can be omitted , You can also write .
4. Formal parameters can also be secondary pointers , In this case arr2 The type of each element of is int *, It shows that it is an array of pointers ,arr2 Address representing the first element of the array , It means to take arr2 The first address in the element , explain arr2 Is the address of the address , So you can use a secondary pointer int **arr receive .
4.2 Two dimensional array parameters
1.void test(int arr[3][5])//ok?
{
}
2.void test(int arr[][])//ok?
{
}
3.void test(int arr[][5])//ok?
{
}
// summary : Two dimensional array parameters , Function parameter design can only omit the first [] The number of .
// Because for a two-dimensional array , I don't know how many lines there are , But you have to know how many elements in a row .
// So it's easy to calculate .
4.void test(int *arr)//ok?
{
}
5.void test(int* arr[5])//ok?
{
}
6.void test(int (*arr)[5])//ok?
{
}
7.void test(int **arr)//ok?
{
}
int main()
{
int arr[3][5] = {
0};
test(arr);
}
ask : Whether the above parameter transfer form is correct ?
answer :1,3,6 correct , Other mistakes .
We know , When passing parameters to a two-dimensional array , Mainly pass the array name , The array name of a two-dimensional array is essentially the address of the first element of the array , But here The address of the first element of the array is equivalent to the address of the first row of the two-dimensional array , Is the address of a one-dimensional array .
We pass the array name to test() function , there arr It is a two-dimensional array storing shaping data
1. Formal parameters can be two-dimensional arrays , Note that only the first [] The number of , Because for a two-dimensional array , I don't know how many lines there are , But you have to know how many elements in a row , Easy to calculate .
2. Formal parameters cannot be integer pointers , It's here arr Is the address of a one-dimensional array , The integer pointer cannot receive .
3. The formal parameter cannot be a one-dimensional integer pointer array , It should pass two-dimensional pointer array or pointer .
4. Formal parameters can be array pointers ,arr Is the address of a one-dimensional array , This one-dimensional array happens to have 5 Elements , and int (*arr)[5] Can point to a 5 An array of shaping elements .
5. Formal parameters cannot be secondary pointers , The address of a one-dimensional array cannot be received with a secondary pointer .
4.3 First level pointer parameter transfer
#include <stdio.h>
void print(int *p, int sz)
{
int i = 0;
for(i=0; i<sz; i++)
{
printf("%d\n", *(p+i));
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
int *p = arr;
int sz = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
// First level pointer p, Pass to function print
print(p, sz);
return 0;
}
reflection :
When the parameter part of a function is a first-order pointer , What parameters can a function take ?
such as :
void test1(int *p)
{
}
//test1 What parameters can a function take ?
// If the parameter part of the function is a first-order pointer
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int *ptr = &a;
int arr[10];
test1(&a);// Address of the integer variable
test1(ptr);// Pointer to the address of the integer variable
test1(arr);// Address of the first element of the integer variable
return 0;
}
4.4 The secondary pointer transmits parameters
void test(int** ptr)
{
printf("num = %d\n", **ptr);
}
int main()
{
int n = 10;
int*p = &n;
int **pp = &p;
test(pp);
test(&p);
return 0;
}
reflection :
When the parameter of the function is a secondary pointer , What parameters can be received
void test(char **p)
{
}
//test What parameters can a function take ?
// If the parameter of the function is a secondary pointer
int main()
{
char c = 'b';
char*pc = &c;//pc Is the first level pointer
char**ppc = &pc;//ppc It's a secondary pointer
char* arr[10];
// The secondary pointer transmits parameters
test(&pc);// Pass the secondary pointer variable
test(ppc);// Pass the address of the first level pointer variable
test(arr);//Ok? Ok
// Pass the address of the first element of the pointer array
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- leetcode-2280:表示一个折线图的最少线段数
- Solution to the problem of abnormal display of PDF exported Chinese documents of confluence
- 2022 list of manufacturers of Chinese 3D vision enterprises (guided positioning and sorting scenes)
- 【AutoSAR 五 方法论】
- Overlay of shutter (Pop-Up)
- University of Oslo: Li Meng | deep reinforcement learning based on swing transformer
- 腾讯云免费SSL证书扩展文件含义
- 微信小程序获取某个元素的信息(高、宽等),并将px转换为rpx。
- FAQ | FAQ for building applications for large screen devices
- Extension of flutter
猜你喜欢

【AutoSAR 七 工具链简介】

Explain in detail the significance of the contour topology matrix obtained by using the contour detection function findcontours() of OpenCV, and how to draw the contour topology map with the contour t
Basic use of shell script
![[MCU project training] eight way answering machine](/img/a3/6a50619cd16269bf485a4a273677aa.jpg)
[MCU project training] eight way answering machine

【AutoSAR 二 AppL概述】

Linux Software: how to install redis service

Multiprocess programming (I): basic concepts
University of Toronto: Anthony coach | the conditions of deep reinforcement learning can induce dynamic risk measurement

Sentry developer contribution Guide - configure pycharm
可下载《2022年中国数字化办公市场研究报告》详解1768亿元市场
随机推荐
Web2.0 giants have deployed VC, and tiger Dao VC may become a shortcut to Web3
图解网络:什么是虚拟路由器冗余协议 VRRP?
NC24325 [USACO 2012 Mar S]Flowerpot
lex && yacc && bison && flex 配置的問題
Introduction and use of ftrace tool
利亚德:Micro LED 产品消费端首先针对 100 英寸以上电视,现阶段进入更小尺寸还有难度
Vulkan并非“灵药“
Graduation summary
node_ Modules cannot be deleted
微信小程序获取某个元素的信息(高、宽等),并将px转换为rpx。
Teach you JDBC hand in hand -- structure separation
leetcode-2280:表示一个折线图的最少线段数
leetcode-224:基本计算器
Rust ownership (very important)
[MCU project training] eight way answering machine
University of Oslo: Li Meng | deep reinforcement learning based on swing transformer
【luogu P4320】道路相遇(圆方树)
kubernetes编写yml简单入门
There is an unknown problem in inserting data into the database
【AutoSAR 九 C/S原理架构】