当前位置:网站首页>IO flow: node flow and processing flow are summarized in detail.
IO flow: node flow and processing flow are summarized in detail.
2022-07-04 14:45:00 【Xiao Li's training record】
Catalog
One 、 Node flow and processing flow
1、BufferedReader Character stream
2、BufferedWriter Character stream
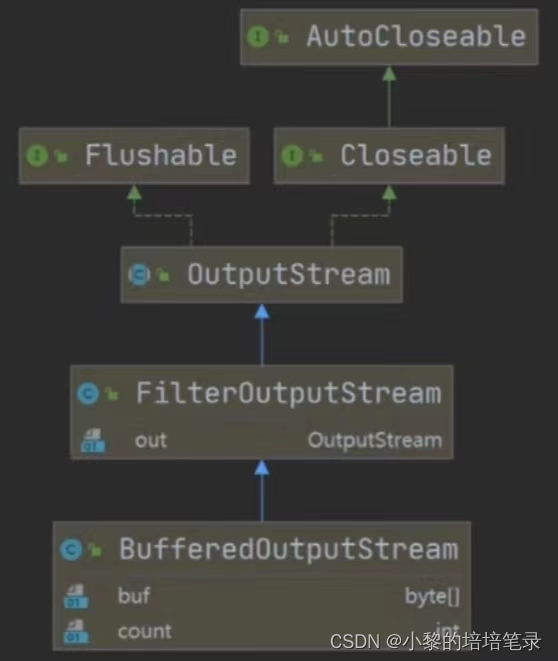
4、BufferedInputStream Byte stream
5、BufferedOutputStream Byte stream
3、 ... and 、ObjectOutputStream、ObjectInputStream
1、 Serialization and deserialization
5、 Standard input and output streams
2、 hold FileInputStream Turn into InputStreamReader
One 、 Node flow and processing flow
(1) Node streams can read and write data from a specific data source
(2) Processing flow ( It's also called packaging flow ) yes “ Connect ” In the existing stream ( Node flow or processing flow ) above , Provide more powerful read and write functions for programs
(3) Sketch Map
(4) The difference between the two
- The node flow is the underlying flow / Low flow , Connect directly to the data source
- Processing flow ( Packaging flow ) Wrapper node flow , It can eliminate the implementation differences of different node flows , You can also provide more
Convenient way to complete input and output .- Processing flow ( It's also called packaging flow ) Wrap the node flow , Decorator design pattern is used , Not directly connected to the data source
(5) The function of processing flow
- Performance improvement : It mainly increases the buffer to improve the efficiency of input and output
- Easy to operate : Processing streams may provide a series of convenient methods to input and output large quantities of data at one time , More flexible and convenient to use
Two 、 Processing flow
- BufferedReader and BufferedWriter Belongs to the character stream , It reads data according to characters
- When the stream is closed , Just turn off the outer flow
- BufferedinputStream It's a byte stream , Creating BufferedlnputStream when , An internal buffer array is created
- BufferedOutputStream It's a byte stream , Implement buffered output stream , Multiple bytes can be written to the underlying output stream , Instead of calling the underlying system for each byte write
1、BufferedReader Character stream
public class BufferedReader_ { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // File path String filePath = "d:\\story.txt"; // establish BufferedReader object BufferedReader bur = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath)); // Read String line;// According to the line read // When to return to null when , Indicates that the file has been read while ((line = bur.readLine()) != null){ System.out.println(line); } // Closed flow , Note here , Just turn off BufferedReader , Because the bottom layer will automatically close the node flow bufferedReader.close(); } }2、BufferedWriter Character stream
public class BufferedWriter_ { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // File path String filePath = "d:\\ok.txt"; // establish BufferedWriter // belt true, Indicates append BufferedWriter bur = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(filePath,true)); bufferedWriter.write("hello, Continue to work hard "); bufferedWriter.newLine();// Insert a system related line break bufferedWriter.write("hello, Continue to work hard "); bufferedWriter.newLine();// Insert a system related line break bufferedWriter.write("hello, Continue to work hard "); // Just turn off the outer flow , Incoming new FileWriter(filePath), Will close at the bottom bufferedWriter.close(); } }3、 Use both for file copying
public class BufferedCopy_ { public static void main(String[] args) { // File path String srcFilePath = "d:\\story.txt"; String destFilePath = "d:\\story2.txt"; // Create objects separately BufferedReader br = null; BufferedWriter bw = null; // According to the line read String line; try { // Get the path object respectively br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(srcFilePath)); bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(destFilePath)); //readLine() Press the line to get while ((line = br.readLine()) != null){ // Read one line at a time , Just write bw.write(line); // Insert a line break bw.newLine(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // Both streams should be closed try { if (br != null){ br.close(); } if (bw != null){ bw.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }Be careful :
- BufferedReader and BufferedWriter It is operated by characters
- Don't manipulate binaries [ video , voice ,doc,PDF etc. ], May cause file damage
4、BufferedInputStream Byte stream
5、BufferedOutputStream Byte stream
public class BufferedCopy02 { public static void main(String[] args) { // File path String srcFilePath = "d:by.png"; String destFilePath = "d:newby.png"; // Create objects BufferedInputStream bis = null; BufferedOutputStream bos = null; try { // because FileInputStream yes InputStream Subclasses of bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFilePath)); bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destFilePath)); // Create array , Read and write in an array byte[] buff = new byte[1024]; // file length int readLen = 0; // When to return to -1 when , It means that the file is read while ((readLen = bis.read(buff)) != -1){ // Write while reading bos.write(buff,0,readLen); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // Closed flow try { if (bis != null){ bis.close(); } if(bos != null){ bos.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
3、 ... and 、ObjectOutputStream、ObjectInputStream
1、 Serialization and deserialization
- Serialization is when you save data , Save data values and data types
- Deserialization is when recovering data , Recover data values and data types
- You need to stop an object from supporting the serialization mechanism , Then its class must be serializable , To make a class serializable , The class must implement one of the following two interfaces :
①Serializable ②Externalizable- function : Provides methods for serializing and deserializing basic types or object types
2、 ObjectOutputStream
public class ObjectOutStream_ { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // File path String filePath = "d:\\data.txt"; // Create objects ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(filePath)); // Serialize data to e:\data.dat oos.writeInt(100); // int -> Integer ( Realized Serializable) oos.writeBoolean(true); //boolean -> Boolean ( Realized Serializable) oos.writeChar('a'); //char -> Character ( Realized Serializable) oos.writeDouble(9.5); //double -> Double ( Realized Serializable) oos.writeUTF(" Study hard "); //String ( Realized Serializable) // Save one dog object oos.writeObject(new Dog(" The small white ",10)); oos.close(); System.out.println(" Save completed "); } }Be careful : After serialization , Saved file format , Not storing text , It is saved according to its format
3、ObjectInputStream
public class ObjectInputStream_ { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ // Specify the file path of deserialization String filePath = "d:\\data.txt"; // Create objects ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filePath)); // Read ( Deserialization ) The order in which data needs to be and saved ( serialize ) In the same order , Otherwise, an exception will be reported System.out.println(ois.readInt()); System.out.println(ois.readBoolean()); System.out.println(ois.readChar()); System.out.println(ois.readDouble()); System.out.println(ois.readUTF()); Object o = ois.readObject(); System.out.println(" Run type =" + o.getClass()); System.out.println("dog Information =" + o); // Particularly important details : We need to Dog The definition of a class , Put it where it can be referenced Dog dog = (Dog)o; System.out.println(dog.getName()); // Closed flow , Just turn off the outer flow , The bottom will close FileInputStream flow ois.close(); } }4、 matters needing attention
- Read and write in the same order
- Require serialization or deserialization of objects , Need to achieve Serializable Interface
- It is recommended to add... To the serialized class SerialVersionUID, To improve version compatibility
- When serializing objects , All attributes are serialized by default , But in addition to static keyword or transient keyword Decorated member
- When serializing objects , It is required that the type of the attribute inside also needs to implement the serialization interface
- Serialization is inheritable , That is, if a class has implemented serialization , Then all its subclasses have implemented serialization by default
5、 Standard input and output streams
public class InputAndOutput { public static void main(String[] args) { //System Class public final static InputStream in null; //System.in Compile type InputStream //System.in Run type BufferedInputStream // Represents standard input keyboard System.out.println(System.in.getClass()); //System.out -> public static final PrintStream out = null; // Compile type PrintStream // Run type PrintStream // Indicates standard output Monitor System.out.println(System.out.getClass()); } }
Four 、 Converted flow
1、 Basic introduction
InputStreamReader : Reader Subclasses of , Can be InputStream( Byte stream ) package
Pretend to be Reader( Character stream )OutputStreamWriter : Writer Subclasses of , The implementation will OutputStream( Byte stream )
Package as Writer( Character stream )When dealing with plain text data , If you use character stream, it is more efficient , And it can effectively solve Chinese
problem , Therefore, it is recommended to convert byte stream into character streamYou can specify the encoding format when using ( such as utf-8,gbk,gb2312 etc. )
2、 hold FileInputStream Turn into InputStreamReader
// Specified encoding gbk InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(filePath),"gbk"); // hold InputStreamReader Pass in BufferedReader BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr); // Read String s = br.readLine(); System.out.println(" Read the content ="+s); // Shut down the outer stream br.close();// Create a flow object OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("d:\\a.txt") , "gbk" ); // write in osw.write("hello, Continue to work hard "); // close osw.close();
5、 ... and 、 Print stream
1、PrintWriter
//PrintWriter pw= new PrintWriter(System.out); PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("e:\\f2.txt"));2、PrintStream
PrintStream out = System.out; // By default ,PrintStream The position of output data is standard output , That's the monitor// because print The bottom layer uses write, So we can call write Print / Output out.write(" Study hard ".getBytes()); out.close();// We can change the position of the print stream output / equipment System.setOut(new PrintStream("e:\\f1.txt")); System.out.println(" Study hard ");
6、 ... and 、Properties class
(1) Collection class for reading and writing configuration files
The format of the configuration file : key = valueBe careful : Key value pairs do not need spaces , Values do not need to be enclosed in quotation marks , The default type is String
ip=192.168.0.13 user=root pwd=12345(2)Properties Common ways to do it
Method function load Load the key value of the configuration file to Properties object list Display data to the specified device getProperty(key) Get value from key setProperty(key , value) Set key value to Properties object store take Properties The key value pairs in are stored in the configuration file , stay idea in , Save information to configuration file , If it contains Chinese , Will be stored as unicode code
// establish Properties object Properties pr = new Properties(); // Loads the specified configuration file pr.load(new FileReader("src\\mysql.properties")); // hold key-value Display console pr.list(System.out); // according to key Get the corresponding value String user = pr.getProperty("user"); String pwd = pr.getProperty("pwd"); System.out.println(" user name ="+user); System.out.println(" The password is ="+pwd);// Use Properties Class to create a configuration file , Modify the configuration file contents Properties pr = new Properties(); // establish //1. If the file does not key Is to create //2. If the file has key, Is to modify pr.setProperty("charset","utf8"); pr.setProperty("user"," Tom ");// Note that when saving , It's Chinese. unicode Code value pr.setProperty("pwd","888888"); // take key-value Just store it in a file pr.store(new FileOutputStream("src\\mysql2.properties"),null);
边栏推荐
- Sqlserver functions, creation and use of stored procedures
- Red envelope activity design in e-commerce system
- LVGL 8.2 LED
- LeetCode 1200 最小绝对差[排序] HERODING的LeetCode之路
- 为什么国产手机用户换下一部手机时,都选择了iPhone?
- A collection of classic papers on convolutional neural networks (deep learning classification)
- EventBridge 在 SaaS 企业集成领域的探索与实践
- Codeforce:c. sum of substrings
- openresty 限流
- Real time data warehouse
猜你喜欢
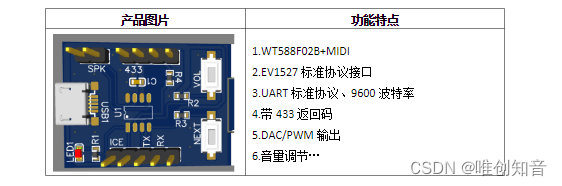
Wt588f02b-8s (c006_03) single chip voice IC scheme enables smart doorbell design to reduce cost and increase efficiency

Digi XBee 3 rf: 4 protocols, 3 packages, 10 major functions
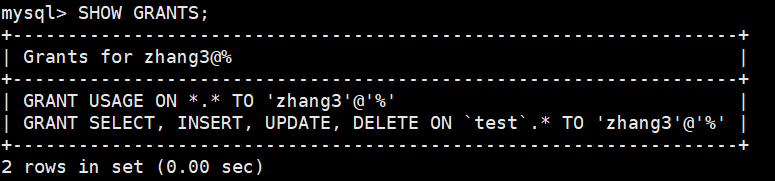
【MySQL从入门到精通】【高级篇】(四)MySQL权限管理与控制

Codeforce:c. sum of substrings
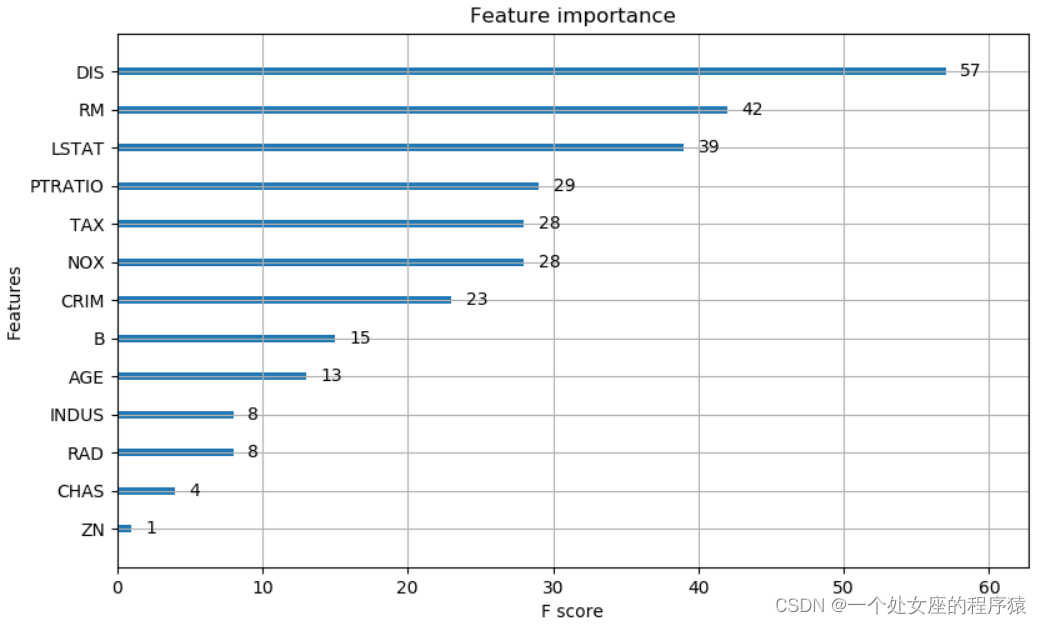
ML之shap:基于boston波士顿房价回归预测数据集利用shap值对XGBoost模型实现可解释性案例
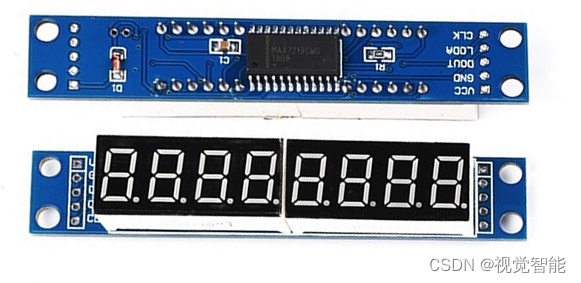
Stm32f1 and stm32subeide programming example -max7219 drives 8-bit 7-segment nixie tube (based on GPIO)
阿里被裁员工,找工作第N天,猎头又传来噩耗...
Transplant tinyplay for imx6q development board QT system
Pandora IOT development board learning (RT thread) - Experiment 3 button experiment (learning notes)

Test evaluation of software testing
随机推荐
Is it safe to open an account online for stock speculation? Will you be cheated.
WT588F02B-8S(C006_03)单芯片语音ic方案为智能门铃设计降本增效赋能
Deep learning 7 transformer series instance segmentation mask2former
5g TV cannot become a competitive advantage, and video resources become the last weapon of China's Radio and television
Free, easy-to-use, powerful lightweight note taking software evaluation: drafts, apple memo, flomo, keep, flowus, agenda, sidenote, workflow
Intelligence d'affaires bi analyse financière, analyse financière au sens étroit et analyse financière au sens large sont - ils différents?
Visual Studio调试方式详解
Yyds dry goods inventory # solve the real problem of famous enterprises: continuous maximum sum
AI and Life Sciences
关于miui12.5 红米k20pro用au或者povo2出现问题的解决办法
Explain of SQL optimization
Ultrasonic distance meter based on 51 single chip microcomputer
LVGL 8.2 Line wrap, recoloring and scrolling
UFO:微软学者提出视觉语言表征学习的统一Transformer,在多个多模态任务上达到SOTA性能!...
潘多拉 IOT 开发板学习(RT-Thread)—— 实验3 按键实验(学习笔记)
C language programming
LVGL 8.2 keyboard
C language set operation
[MySQL from introduction to proficiency] [advanced chapter] (V) SQL statement execution process of MySQL
Expose Ali's salary and position level