1、 Preface
It's time for gold, silver and four again , Everyone can't stand the inner agitation , I'm here to share with you a knowledge point encountered in the previous interview (MQ Application scenarios of ), If there is any deficiency , Welcome the big guys to give advice .
Application background of message oriented middleware
To improve the performance of the system, the first consideration is the optimization of the database , But for historical reasons , Lateral expansion is a very complicated project , So we usually try to block the traffic before the database . Whether it's unlimited scale out servers , Or vertically block the traffic to the database , It's all about that . Blocking traffic to the database , Cache component and message component are two major killers .
2、MQ brief introduction
MQ:Message queue, Message queue , It's a container that holds messages .
Now commonly used MQ The components are activeMQ、rabbitMQ、rocketMQ, Of course, it's hot in recent years kafka, In some cases , It's also MQ, however kafka Is more powerful , Although different MQ All have their own characteristics and advantages , however , Whatever it is MQ, There are MQ Some of its own characteristics .
Comparison of common message queues
| characteristic | ActiveMQ | RabbitMQ | RocketMQ | Kafka |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Producer consumer model | Support | Support | Support | Support |
| Publish subscribe mode | Support | Support | Support | Support |
| Request response mode | Support | Support | I won't support it | I won't support it |
| Api completeness | high | high | high | high |
| Multilingual support | Support | Support | java | Support |
| Single machine throughput | All level | All level | All level | One hundred thousand |
| Message delay | nothing | microsecond | millisecond | millisecond |
| Usability | high ( Master-slave ) | high ( Master-slave ) | Very high ( Distributed ) | Very high ( Distributed ) |
| Lost message | low | low | In theory, it won't be lost | In theory, it won't be lost |
| Completeness of documents | high | high | Jiaogao | high |
| Provides a quick start | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Community activity | high | high | in | high |
| Commercial support | nothing | nothing | Business cloud | Business cloud |
3、MQ characteristic
fifo
fifo , Is the most obvious feature of the queue . The order of message queues is basically determined when they enter the queue , Generally, there is no need for human intervention . and , most important of all , Data is only one piece of data in use . This is also MQ The reason why it is used in many scenes .
Publish subscribe
Publish and subscribe is a very efficient way of handling , If there is no blockage , Basically, it can be regarded as synchronous operation . This processing method can effectively improve the server utilization , This kind of application scenario is very extensive .
Persistence
Persistence ensures MQ It's not just a partial scene aid , Rather let MQ Can store core data like a database , Guarantee MQ The reliability of the .
Distributed
In the current large flow 、 In the use scenario of big data , The server software that only supports single application can't be used , Support distributed deployment , To be widely used . and ,MQ Positioning is a high-performance middleware .
4、 Application scenarios
Message Queuing Middleware is an important component of distributed system , The main solution is application decoupling , Asynchronous messaging , Flow cutting 、 Massive log data synchronization 、 Distributed transactions and so on , Achieve high performance , High availability , Scalable and ultimately consistent architecture .
4.1 The application of decoupling
The scene that : After the user orders , Order system needs to inform inventory system . The traditional way is , Interface between order system and inventory system .

Disadvantages of traditional models : If the inventory system is not accessible , Order inventory reduction will fail , Which leads to order failure , High coupling between order system and inventory system , Prone to avalanche accidents .
Scheme after introducing application message queue :

Order system : After the user orders , Order system completes persistent processing , Write message to message queue , Return to user's order successfully placed .
inventory system : Subscribe to the message of the order , use pull/push The way , Get order information , Inventory system according to order information , Inventory operation .
Key steps to solve problems : The inventory system cannot be used normally when placing an order , It does not affect normal order , Because after placing the order , When the order system writes to the message queue, it no longer cares about other subsequent operations , As long as final agreement is reached . Realize the application decoupling of order system and inventory system .
4.2 Asynchronous messaging
The scene that : After user registration , Need to send registration email and SMS . There are two traditional approaches : Serial mode 、 Parallel mode .
Serial mode : After successfully writing the registration information to the database , Send registration email , Resend registration SMS . After all the above three tasks are completed , Return to the client .

Parallel mode : After successfully writing the registration information to the database , Send registration email at the same time , Send registration SMS . After the above three tasks are completed , Return to the client . The difference with serial is , Parallel processing can improve processing time .

Problem analysis :
Suppose three business nodes each use 50 Milli second , No consideration of network and other expenses , The time of serial mode is 150 millisecond , Parallel time may be 100 millisecond .
because CPU The number of requests processed in unit time is certain , hypothesis CPU1 Throughput per second is 100 Time . Serial mode 1 Seconds CPU The number of requests that can be processed is 7 Time (1000/150). The number of requests processed in parallel is 10 Time (1000/100)
As described in the above case , Performance of traditional way system ( Concurrency , throughput , response time ) There will be bottlenecks. .The steps of sending registration email and registration SMS are decoupled through message queue :

From the above Architecture , The response time of the user is equal to the time when the registration information is written to the database , That is to say 50 millisecond . Registered mail , After SMS is written to message queue , Go straight back to , So writing to message queues is fast , Basically negligible , So the response time of the user may be 50 millisecond . So after the architecture changes , System throughput increased to per second 20 QPS. Better than serial 3 times , Twice as much as parallel .
4.3 Flow cutting
Traffic cutting is also a common scenario in message queuing , Generally, it is widely used in seckill or group robbery activities .
The scene that : Seckill activity , Generally, it will be caused by excessive flow , Resulting in a surge in flow , Application or database hang up . To solve this problem , In general, it is necessary to join the message queue in the front end of the application .
The structure is as follows :

The benefits of joining the message queue :
- Number of people who can control the activity
- It can alleviate the application of high flow collapse in a short time
User's request , After server receives , Write message queue first . If the message queue length exceeds the maximum number , Discard the user request or jump to the error page directly .
Seckill service according to the request information in the message queue , Follow up .
4.4 Massive log data synchronization
The scene that : Under the microservice system , Projects are often deployed in clusters , Then you need a unified log platform to query the logs of each instance , However, the log information in the cluster is often massive data , A single log collection tool cannot meet the needs of business , Therefore, message queuing needs to be used in log processing , such as Kafka Application , Solve the problem of a large number of log transfers .
The architecture is simplified as follows :
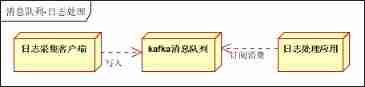
Architecture description :
- Log collection client , Responsible for log data collection , Timed write to write Kafka queue
- Kafka Message queue , Responsible for receiving log data , Store and forward
- Log processing application : Subscribe and consume kafka Log data in queue
4.5 Distributed things
Distributed transactions are divided into strong consistency , Weak agreement , And final conformity
Strong consistency :
When the update operation is complete , Any subsequent process or thread access will return the latest updated value . This is the most user-friendly , It's what the user wrote the last time , Make sure you can read something next time . according to CAP theory , This implementation requires sacrificing availability .
Weak agreement :
The system does not guarantee that the access of continuation process or thread will return the latest updated value . After the data is written successfully , Do not promise to read the latest written value immediately , It won't be a specific commitment for how long to read .
Final agreement :
The specific form of weak consistency . The system guarantees that without subsequent updates , The system finally returns the value of the last update operation . Without failure , The time of inconsistent window is mainly delayed by communication , System load and number of replicas impact .DNS It's a typical final consistency system .
In distributed systems , At the same time satisfy “CAP The laws of ” Consistency in 、 Availability and partition fault tolerance are almost impossible . Most of the scenes in the Internet field , All need to sacrifice strong consistency for high availability of the system , Systems often only need to guarantee “ Final consistency ”, As long as the final time is within the acceptable range of users , At this time, we only need to use a short period of data inconsistency to achieve the effect we want .
The scene that : For example, there are orders , Inventory two data , A process of placing an order is simplified as , Add an order , One less inventory . Orders and inventory are independent services , How to ensure data consistency .
The most frustrating thing about remote calls is , There are 3 Kind of , success 、 Failures and timeouts . If the timeout , Success and failure are all possible . The general solution , Most of it is with the help of mq To make the final agreement .
Achieve final agreement :

Through the above architecture, you may think of these problems :
Local execution first , Send a message when the execution is successful , The consumer side gets the message and performs its own business .
such as a,b Two services , service a Asynchronous call service b, If the service b failed , Or success , Or a timeout , How to use it mq Let them finally agree ?
Referring to the concept of local transaction, this scenario can be divided into three situations to solve :
- Case one : hypothesis a,b It's all working , Then the whole business ends normally ;
- The second case : hypothesis b Overtime , You need to MQ to b Resend message (b Service should be idempotent ), If the resend fails , It depends on the situation , It's service interruption , Or continue to resend , Even human intervention ;
- The third case : hypothesis a,b One of them failed , Failed service utilization MQ Send messages to other services , Other services receive messages , Query the local transaction log , If the local government fails , Delete received messages ( The message consumption is successful ), If local success , You need to call the compensation interface to compensate ( Each service needs to provide a business compensation interface ).
Special attention required :
MQ There's a pit here , It is usually only applicable to scenarios where only the first operation is allowed to fail , That is to say, after the first success, we must ensure that there are no business obstacles for the following operations , Otherwise, the back will fail and the front will not roll back , Only system exception failures are allowed , Business failure is not allowed , Usually, after a business failure, it is unlikely to succeed , If the failure is caused by network or downtime, it can be solved by retrying , If the business is abnormal , Then you can only send messages to the service a Let them make up for it ? Usually through a third party to compensate , Each service needs to provide compensation interface , The design paradigm usually does not allow downstream business failure .
5、 summary
MQ It is used more and more in the scenario of distributed system development , The business ability of processing is also getting stronger and stronger , So master MQ The usage scenario is necessary . By mastering MQ, Can solve most business scenarios , You can also add points in the interview , Improve your core competitiveness .
Last , It's not easy to go out to work , I hope you guys find your favorite job , Hair in the year of the tiger !
I also hope brothers can pay attention to 、 give the thumbs-up 、 Collection 、 Comments support a wave of , Thank you very much !