当前位置:网站首页>Bean injection and lifecycle
Bean injection and lifecycle
2022-07-26 20:32:00 【Wei you indulge】
Catalog
1.1 Front work : Configure scan path
1.2 Add annotation storage Bean object
2. obtain Bean object ( Object assembly / Inject )
2.1 Attribute injection ( a key )
2.4 Analysis of advantages and disadvantages of three kinds of injection
3、 ... and 、Bean Life cycle of
1. Instantiation Bean( by Bean Allocate memory space )
2. Set properties (Bean Injection and assembly )
The difference between instantiation and initialization
One 、Bean Inject
1. Storage Bean object
1.1 Front work : Configure scan path
Be careful : You want to successfully store objects in Spring in , We need to configure the scanning package path of the storage object , Only all classes under the configured package , The annotation can be correctly recognized and saved to Spring in .
//ApplicationContext Namely Spring The top level interface of the container
//AnnotationConfigApplicationContext Is one of the implementation classes , Its function is :
//(1) Scan the specified package path , Use Spring Framework annotated classes
//(2) Register these classes into the container => The framework helps us new object , And the dependencies of the injection object ( Attribute assignment )
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("org.example");1.2 Add annotation storage Bean object
Want to store objects in Spring in , There are two annotation types that can be implemented :
1. Class annotation :@Controller、@Service、@Repository、@Component、@Configuration
2. Method notes :@Bean( here , The same type , You can register multiple Bean object )
2. obtain Bean object ( Object assembly / Inject )
2.1 Attribute injection ( a key )
Attribute injection uses @Autowired Realized , take Service Class to Controller Class .
Call relationship : It's usually ,controller Write a method ( Handle http request ) => call service The business method of ( Business logic processing )=> repository Methods ( Database CRUD operation )
@Controller
@Data//lombok annotation : It will generate automatically getter/setter/hashcode/equais/toString
public class UserController {
// Need make Spring Containers , Help us put bean Object is injected into this property
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
}@Service
@Data
public class UserService {
// Attribute injection
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
}@Repository
public class UserRepository {
}2.2 Tectonic injection
@Service
@Data
public class UserService {
private UserRepository userRepository;
// Tectonic injection , And attribute injection , It's the same thing
// The essence is : To put UserService Register in container ( Instantiation ), Is through the construction method , Passed into the container userRepository Object
@Autowired
public UserService(UserRepository userRepository) {
this.userRepository = userRepository;
}
}matters needing attention : If the class has only one constructor , that @Autowired Annotations can be omitted ; If there are multiple constructors in the class , Then you need to add @Autowired To specify exactly which constructor to use .
A type , Multiple bean Injection mode of :
// The same type , Multiple bean Injection mode of
// The first way : Variable name =bean Of id
@Autowired
private Bean object 2 testBean2_1;
// The second way :
@Resource(name = "testBean2_1")
private Bean object 2 bean object 2;
// The third way :
@Autowired
@Qualifier("testBean2_1")//qualifier You can specify bean Of id/ name
private Bean object 2 bean object 2;@Autowired and @Resource The difference between
- Different origins :@Autowired From Spring, and @Resource From JDK Annotations ;
- The parameters set during use are different : Compared with @Autowired Come on ,@Resource Support more parameter settings , for example name Set up , Get... By name Bean.
2.3 Setter Inject
Setter Injection and attribute Setter Method implementation is similar to , Just setting set The method needs to add @Autowired notes
Explain .
private UserRepository userRepository;
//setter Inject
@Autowired
public void setUserRepository(UserRepository userRepository) {
this.userRepository = userRepository;
}2.4 Analysis of advantages and disadvantages of three kinds of injection
- The advantage of attribute injection is simplicity , Easy to use ; The disadvantage is that it can only be used for IoC Containers , If it is right or wrong IoC Container not available , And only when used NPE( Null pointer exception ).
- Construction method injection is Spring Recommended injection method , Its disadvantage is that if there are multiple injections, it will appear bloated , But in this case, you should consider whether the current class conforms to the design pattern of single responsibility of the program , Its advantage is versatility , Ensure that the injected class is not empty before use .
- Setter The way is Spring The injection method recommended in the previous version , But the generality is not as good as the construction method , all Spring The current version has recommended the use of constructor injection for class injection .
Two 、 Scope
1. Scope definition
Limiting the available range of variables in a program is called scope , In other words, an area in the source code that defines variables is called a scope .
and Bean The scope of refers to Bean stay Spring Some kind of behavior pattern in the whole framework , such as singleton Single case scope , It means Bean Throughout Spring Only one of them , It is globally shared , So when someone else changes this value , What the other person reads is the modified value .
2. Bean Of 6 Species scope
Spring The container is initializing a Bean When an instance of the , The scope of the instance is also specified .Spring Yes 6 Species scope , The last four are based on Spring MVC Effective :
- singleton: Single case scope
- prototype: Prototype scope ( Multiple scope )
- request: Request scope
- session: Callback scope
- application: Global scope
- websocket:HTTP WebSocket Scope
![]()
2.1 singleton
- describe : Under this scope Bean stay IoC There is only one instance in the container : obtain Bean( That is, through applicationContext.getBean And so on ) And assembly Bean( That is, through @Autowired Inject ) It's all the same thing .
- scene : Usually stateless Bean Use this scope . Stateless means Bean The property state of the object does not need to be updated
- remarks :Spring The scope is selected by default
// The following four notes , Are class annotations , Used for registration Bean object
// How to register , default Bean ID( name ), It's the first letter of a class in lowercase
@Controller
//@Service
//@Repository
//@Component
public class Bean object 1 {
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println("Hello");
}
}![]()
2.2 prototype
- describe : Every time you make a comparison of Bean All requests will create new instances : obtain Bean( That is, through applicationContext.getBean And so on ) And assembly Bean( That is, through @Autowired Inject ) Are all new object instances .
- scene : Usually stateful Bean Use this scope
@Controller
@Scope("prototype")
public class Bean object 1 {
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println("Hello");
}
}
2.3 request
- describe : Every time http The request creates a new Bean example , Be similar to prototype
- scene : once http Sharing of requests and responses Bean
- remarks : limit SpringMVC Use in
2.4 session
- describe : In a http session in , Define a Bean example
- scene : Sharing of user replies Bean, such as : Record a user's login information
- remarks : limit SpringMVC Use in
3、 ... and 、Bean Life cycle of
The so-called life cycle refers to the whole life process of an object from birth to destruction , We call this process of life cycle .
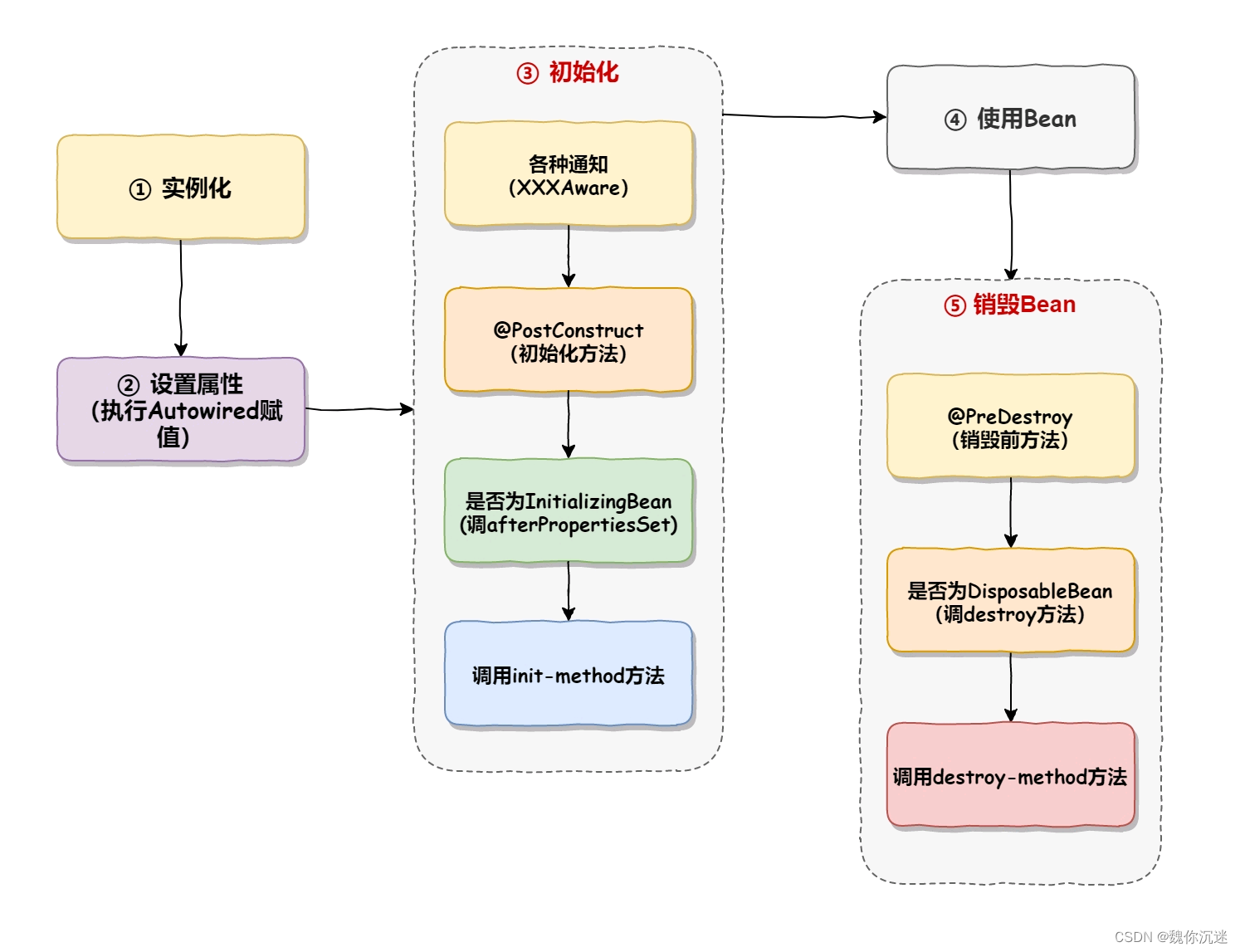
Bean The life cycle of is divided into the following 5 Most of the :
1. Instantiation Bean( by Bean Allocate memory space )
Like us new object
2. Set properties (Bean Injection and assembly )
Dependency injection : attribute assembly
3.Bean initialization
It means that we need to initialize a lot of content , Can be used
- All kinds of Aware Method of notification , Such as BeanNameAware、BeanFactoryAware、ApplicationContextAware Interface method of ;(bean After implementing these notification interfaces , At this moment , The corresponding interface methods will be executed in turn )( Execute sequentially Aware Method of notification interface )
- perform BeanPostProcessor Initialize the pre method ;(BeanPostProcessor A method in an interface (XXXbeforeXXX))
- perform @PostConstruct Initialization method , After the dependency injection operation is executed ;( Initialization method )
- Execute your own designated init-method Method ( If there is a designation );( Initialization method )
- perform BeanPostProcessor Initialize the post method .(BeanPostProcessor A method in an interface (XXXafterXXX))
4. Use Bean
5. The destruction Bean
Various methods of destroying containers , Such as @PreDestroy、DisposableBean Interface method 、destroy-method.
The first three steps are completed ,Bean The registration is successful .
- Create the object ;
- Dependency injection ( Property initialization );
- Other initialization contents ;
- hold Bean Objects into containers .
package org.lifecycle.config;
import org.lifecycle.model.MyBean;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class LifecycleConfig implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Bean(initMethod = " Initialization method 2", destroyMethod = " Destruction method 2")//initMethod Value , Is the name of the method in the object
public MyBean bean(){
return new MyBean();
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor Life cycle : Initialize the pre method ");
return BeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessBeforeInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor Life cycle : Initialize the post method ");
return BeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
}package org.lifecycle.model;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.*;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
//@Service
public class MyBean implements BeanNameAware,
BeanFactoryAware,
ApplicationContextAware,
InitializingBean,
DisposableBean {
public MyBean(){
System.out.println("Bean Object instantiation ");
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("BeanNameAware Life cycle approach ");
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanFactoryAware Life cycle approach ");
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("ApplicationContextAware Life cycle approach ");
}
@PostConstruct
public void Initialization method 1(){
System.out.println("Bean Initialization method of :@PostConstruct");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Bean Initialization method of :InitializingBean");
}
public void Initialization method 2(){
System.out.println("Bean Initialization method of :@Bean(initMethod= Name of this method )");
}
@PreDestroy
public void Destruction method 1(){
System.out.println("Bean How to destroy :@PreDestroy");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Bean How to destroy :DisposableBean");
}
public void Destruction method 2(){
System.out.println("Bean How to destroy :@Bean(destroyMethod= Name of this method )");
}
}package org.lifecycle;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Spring Container startup class _ Observe Bean Life cycle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("org.lifecycle");
// Destruction of the container , Will execute bean How to destroy
context.close();
}
}The difference between instantiation and initialization
Instantiation and property settings are Java Level system “ event ”, The operation process cannot be manually intervened or modified ; Initialization is provided for developers , After instantiation , Customize the class before loading it “ event ” Handle
边栏推荐
- gospel! Wechat personal official account can be renamed!
- Definition and use of one-dimensional array
- smoothscroll-polyfill插件的用法
- Parallel execution (II). Multiprocessing
- Game partner topic: breederdao and ultiverse have established a new metauniverse
- GBase学习-安装GBase 8a MPP Cluster V95
- STM32F103 active buzzer driver
- Week 6 Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
- 解决IBGP的水平分割和BGP选路原则
- Servlet
猜你喜欢

分组卷积(Group Converlution)

内网渗透学习(二)信息收集

How to implement an asynchronous task queue system that can handle massive data (supreme Collection Edition)

Intranet penetration learning (II) information collection

【面试必刷101】动态规划1
Summary of message queue knowledge points

81.(cesium之家)cesium修改灰色背景(默认蓝色)
BUU刷题记-网鼎杯专栏2

游戏合作伙伴专题:BreederDAO 与 Ultiverse 建立了一个新的元宇宙

Task 2 kaggle diabetes detection
随机推荐
Gartner发布最新《中国AI初创企业市场指南》,弘玑Cyclone再次被评为代表性企业
如何优雅地赞美他人?不妨尝试下这几种方式
App uploader download and installation
Chat software project development 2
Principle and application of one click login of local number (glory Collection Edition)
The Sandbox 和艺术家 Alec Monopoly 达成合作
Small scenes bring great improvement! Baidu PaddlePaddle easydl helps AI upgrade of manufacturing assembly line
解决IBGP的水平分割和BGP选路原则
arpspoof 安装和使用
T246836 [lsot-1] potatoes of Tyrannosaurus Rex
Using questpdf operation to generate PDF is faster and more efficient!
nmap安装和使用
Auto.js 旋转图标
Typescript asynchronous function promise use
AI 技术,让复杂世界简单化 | TeaTalk·Online 应用实战系列第 2 期
This point - super classic interview questions
HM中如何获取CU块划分信息并用Matlab绘图
Where are the single dogs in the evening of 5.20?
任务一 报告
How to build a super interface collaboration platform: count the six weapons of apifox