当前位置:网站首页>ShanDong Multi-University Training #3
ShanDong Multi-University Training #3
2022-07-01 23:22:00 【eyuhaobanga】
The meaning of the title is basically a pile of ants , There is a combat effectiveness value , If the combat effectiveness value of an ant is the divisor of other ants in a certain interval , Then the ant can flow away , Finally, ask l To r How many ants are left in the interval , In fact, it is a segment tree maintenance interval problem , The information maintained is the greatest common divisor in this interval 、 Minimum value and the number of minimum values , Therefore, if the maximum common divisor and the minimum value in a certain interval are the same , Then the ants whose combat effectiveness value is equal to the minimum value will be exiled , Minus is the rest of the ants , If it's not the same , All ants in that range are left
AC Code :
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; int a[100010]; struct node { int gd, minn, cnt; }; node Segtree[100010 << 2]; int gcd(int a, int b) { return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a % b); } node merge(node a, node b) { node c; c.gd = gcd(a.gd, b.gd); c.minn = min(a.minn, b.minn); if (a.minn == b.minn) { c.cnt = a.cnt + b.cnt; } else if (a.minn < b.minn) { c.cnt = a.cnt; } else { c.cnt = b.cnt; } return c; } inline void buildtree(int i, int l, int r) { if (l == r) { Segtree[i].gd = Segtree[i].minn = a[l]; Segtree[i].cnt = 1; return; } int mid = l + r >> 1; buildtree(i << 1, l, mid); buildtree(i << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r); Segtree[i] = merge(Segtree[i << 1], Segtree[i << 1 | 1]); } node query(int i, int l, int r, int x, int y) { if (l > y || r < x) { return {0, (int)1e9, 0}; } if (l >= x && r <= y) { return Segtree[i]; } int mid = l + r >> 1; return merge(query(i << 1, l, mid, x, y), query(i << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r, x, y)); } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int n, q; cin >> n; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { cin >> a[i]; } buildtree(1, 1, n); cin >> q; while (q--) { int l, r; cin >> l >> r; node c = query(1, 1, n, l, r); if (c.minn == c.gd) { cout << r - l + 1 - c.cnt << '\n'; } else { cout << r - l + 1 << '\n'; } } return 0; }Redefinition a To z Dictionary sequence , Then sort according to the new definition , Ask No k Small strings
AC Code :
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; map<char, int> mp; bool cmp(string a, string b) { int len1 = a.size(), len2 = b.size(); for (int i = 0; i < min(len1, len2); i++) { if (mp[a[i]] < mp[b[i]]) { return true; } else if (mp[a[i]] > mp[b[i]]) { return false; } } if (len1 > len2) { return false; } else if (len1 < len2) { return true; } else { return true; } } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); string s; cin >> s; int n, k; cin >> n; vector<string> a(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { cin >> a[i]; } cin >> k; k--; for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) { mp[s[i]] = i; } sort(a.begin(), a.end(), cmp); cout << a[k] << '\n'; return 0; }The general meaning of the title is that there is a,b Two points ,'.' You can go ,'*' You can't go , Every second a and b Do the same action , ask a and b Can we meet , If you meet, you will output the minimum number of steps , So you bfs Search for + Record the steps , Pay attention to the boundary problem and the next if '*‘ Stay where you are ,a and b If the coordinates of are equal, the number of steps is output
AC Code :
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; int n; string mp[55]; bool vis[55][55][55][55]; struct node { int xa, xb, ya, yb, cnt; }; int mov[4][2] = { {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}}; queue<node> qu; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); cin >> n; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { cin >> mp[i]; } node now; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { if (mp[i][j] == 'a') { now.xa = i; now.ya = j; mp[i][j] = '.'; } if (mp[i][j] == 'b') { now.xb = i; now.yb = j; mp[i][j] = '.'; } } } now.cnt = 0; vis[now.xa][now.ya][now.xb][now.yb] = true; qu.push(now); while (!qu.empty()) { node nxt; nxt = now = qu.front(); qu.pop(); if (now.xa == now.xb && now.ya == now.yb) { cout << now.cnt << '\n'; return 0; } now.cnt = nxt.cnt + 1; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { now.xa = nxt.xa + mov[i][0]; now.ya = nxt.ya + mov[i][1]; now.xb = nxt.xb + mov[i][0]; now.yb = nxt.yb + mov[i][1]; if (now.xa >= 0 && now.ya >= 0 && now.xa < n && now.ya < n && mp[now.xa][now.ya] == '.') { } else { now.xa = nxt.xa; now.ya = nxt.ya; } if (now.xb >= 0 && now.yb >= 0 && now.xb < n && now.yb < n && mp[now.xb][now.yb] == '.') { } else { now.xb = nxt.xb; now.yb = nxt.yb; } if (!vis[now.xa][now.ya][now.xb][now.yb]) { vis[now.xa][now.ya][now.xb][now.yb] = true; qu.push(now); } } } cout << "no solution\n"; return 0; }The meaning of the question is to seek ai%aj The maximum of , among ai Be greater than or equal to aj, First, when the sequence is in order , If you traverse directly TLE, Here consider two points to find the maximum possible value , You know ai Greater than or equal to aj, that ai=n*aj+mod, therefore , The maximum possible value must appear in n Times and n+1 The last value between times , direct lower_bound Two points to get n+1 The first value of times , The first one is the maximum possible value to find
AC Code :
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int n; cin >> n; vector<int> a(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { cin >> a[i]; } sort(a.begin(), a.end()); int ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (a[i] != a[i + 1] && i + 1 < n) { int x = lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), 2 * a[i]) - a.begin(); for (int j = 2; j * a[i] <= a[n - 1]; j++) { x = lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), j * a[i]) - a.begin(); ans = max(ans, a[x - 1] % a[i]); } ans = max(ans, a[n - 1] % a[i]); ans = max(ans, a[x - 1] % a[i]); } } cout << ans << '\n'; return 0; }Judgment set a And collection b Are the prefixes of equal , Set hash
AC Code :
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; const i64 mod = 1e9 + 7; i64 n, q; i64 a[200010], b[200010]; set<i64> se; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); cin >> n; i64 s = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { i64 x; cin >> x; if (se.find(x) == se.end()) { s = (s + x * (x + 137) % mod * (x + 997) % mod) % mod; } a[i] = s; se.insert(x); } se.clear(); s = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { i64 x; cin >> x; if (se.find(x) == se.end()) { s = (s + x * (x + 137) % mod * (x + 997) % mod) % mod; } b[i] = s; se.insert(x); } cin >> q; while (q--) { int x, y; cin >> x >> y; if (a[x] == b[y]) { cout << "Yes\n"; } else { cout << "No\n"; } } return 0; }linear dp, You can find that the maximum number of gold coins in your hand is very small , Seeking the minimum walking distance is seeking the maximum riding distance , Then I can deal with the longest distance I can reach by spending how much money that time in advance , Every time I must choose the farthest station , In this way, there is no need to consider the relationship between the last station and the total distance , Because riding must be between two stations , It's impossible to get to the terminal without walking to the next station
AC Code :
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; int dp[1000010][6]; int a[1000010]; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int n, p, s; cin >> n >> p >> s; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { cin >> a[i]; } int k; cin >> k; int ans = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= k; j++) { dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j]); ans = max(ans, dp[i][j]); for (int l = 1; l + j <= k; l++) { int dis = l * s + a[i]; int now = upper_bound(a + 1, a + 1 + n, dis) - a; now--; dp[now][l + j] = max(dp[now][l + j], dp[i][j] + a[now] - a[i]); if (dis > a[n]) { break; } } } } cout << p - ans << '\n'; return 0; }Sieve out all prime numbers , Then we can make a violent sum
AC Code :
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; using u64 = unsigned long long; #define M 10000000 int cnt = 0; i64 a[M + 5]; bool is_prime[M + 5]; void init(){ is_prime[0] = is_prime[1] = false; for (int i = 2; i <= M; i++) { if (is_prime[i]) { a[++cnt] = i; for (int j = 2; j * i <= M; j++) { is_prime[i * j] = false; } } } } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); memset(is_prime, true, sizeof(is_prime)); i64 n, ans = 0; init(); cin >> n; for (int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) { for (int j = i + 1; j <= cnt; j++) { if (a[j] * a[j] > n / a[i] / a[j]) { break; } ans++; } } cout << ans << "\n"; return 0; }The meaning of the question is to put chocolate with a given length and width into a box with a given length and width , Can you put it all in , One box can only hold one chocolate , And long to long , Width to width , Greedy to think that it must be more appropriate to put it in the box, so it must be more appropriate to put it in the box , This requires fixed length or fixed width sorting , Then go to the other side , It happens to be multiset characteristic , Automatic sorting + No weight removal
AC Code :
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int n, m; cin >> n >> m; vector<pair<int, int>> a(n), b(m); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { cin >> a[i].first; } for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { cin >> a[i].second; } for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { cin >> b[i].first; } for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { cin >> b[i].second; } sort(a.begin(), a.end()); sort(b.begin(), b.end()); multiset<int> ms; for (int i = n - 1, j = m - 1; i >= 0; i--) { while (j >= 0 && b[j].first >= a[i].first) { ms.insert(b[j].second); j--; } multiset<int>::iterator x; x = ms.lower_bound(a[i].second); if (x == ms.end()) { cout << "No\n"; return 0; } ms.erase(x); } cout << "Yes\n"; return 0; }Ask how many points are not leading to the ring , Reverse diagram + A topological sort , The picture is reversed , The degree of 0 It must not lead to the ring , Because the positive graph must have only in degrees but not out degrees , The inverse graph can only be out of degree but not in degree , Such a point must not , Then sort the topology according to these points , All other degrees from it are 0 All points must be points that cannot lead to the ring
AC Code :
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; vector<int> G[200010]; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); int n, m; cin >> n >> m; vector<int> deg(n + 1); for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { int u, v; cin >> u >> v; G[v].push_back(u); deg[u]++; } queue<int> qu; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { if (deg[i] == 0) { qu.push(i); } } int ans = n; while (!qu.empty()) { int u = qu.front(); qu.pop(); ans--; for (auto it : G[u]) { if (--deg[it] == 0) { qu.push(it); } } } cout << ans << '\n'; return 0; }Ordinary Mo team question , Block thought
AC Code :
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; using i64 = long long; i64 s; struct query { i64 l, r, idx; }; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); i64 n, m; cin >> n >> m; s = sqrt(n) + 1; vector<i64> a(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { cin >> a[i]; } vector<query> q(m); vector<i64> v(m); for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { i64 L, R; cin >> L >> R; L--, R--; q[i].l = L, q[i].r = R, q[i].idx = i; } sort(q.begin(), q.end(), [&](query a, query b) { pair<i64, i64> x = {a.l / s, a.r}; pair<i64, i64> y = {b.l / s, b.r}; return x < y; }); vector<i64> cnt(1000010, 0); i64 ans = 0; i64 l = 0, r = 0; cnt[a[0]] = 1; ans = a[0]; for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { i64 L = q[i].l, R = q[i].r, I = q[i].idx; while (l > L) { l--; ans -= cnt[a[l]] * cnt[a[l]] * a[l]; cnt[a[l]]++; ans += cnt[a[l]] * cnt[a[l]] * a[l]; } while (l < L) { ans -= cnt[a[l]] * cnt[a[l]] * a[l]; cnt[a[l]]--; ans += cnt[a[l]] * cnt[a[l]] * a[l]; l++; } while (r > R) { ans -= cnt[a[r]] * cnt[a[r]] * a[r]; cnt[a[r]]--; ans += cnt[a[r]] * cnt[a[r]] * a[r]; r--; } while (r < R) { r++; ans -= cnt[a[r]] * cnt[a[r]] * a[r]; cnt[a[r]]++; ans += cnt[a[r]] * cnt[a[r]] * a[r]; } v[I] = ans; } for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { cout << v[i] << '\n'; } return 0; }
边栏推荐
- Redis data types and application scenarios
- 数字化转型道阻且长,如何迈好关键的第一步
- 【嵌入式系统课设】单个按键控制LED灯
- CADD course learning (3) -- target drug interaction
- 上海炒股开户选择手机办理安全吗?
- CKS CKA ckad change terminal to remote desktop
- AirServer最新Win64位个人版投屏软件
- 共享电商的背后: 共创、共生、共享、共富,共赢的共富精神
- [micro service sentinel] @sentinelresource details
- 距离度量 —— 汉明距离(Hamming Distance)
猜你喜欢

What is the mosaic tailgate?
Advanced skills of testers: a guide to the application of unit test reports

硅谷产品实战学习感触
CADD课程学习(3)-- 靶点药物相互作用

什么是马赛克?

You probably haven't noticed the very important testing strategy in your work
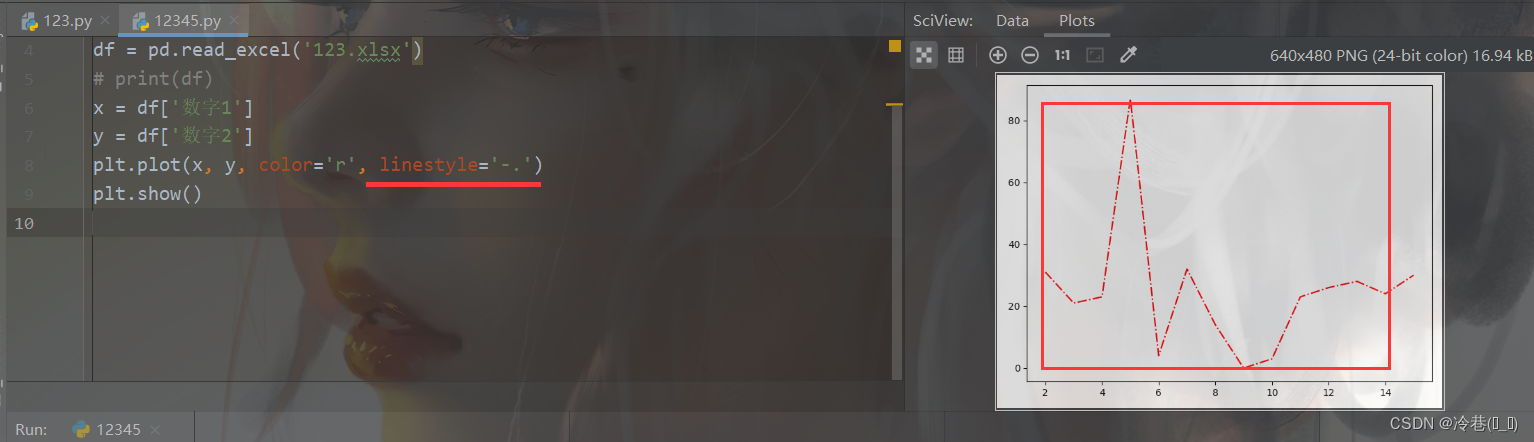
Matplotlib常用設置
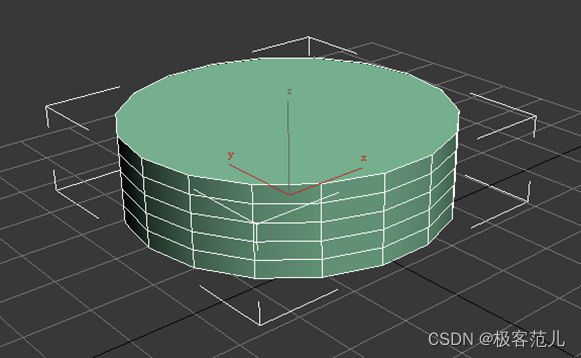
Use 3DMAX to make a chess piece
![Jerry's burning of upper version materials requires [chapter]](/img/65/fcd804e00dc08a2bd056e8e6493829.png)
Jerry's burning of upper version materials requires [chapter]

【嵌入式系统课设】单个按键控制LED灯
随机推荐
The digital summit is popular, and city chain technology has triggered a new round of business transformation
Jielizhi, production line assembly link [chapter]
Jerry's burning of upper version materials requires [chapter]
win 10 mstsc连接 RemoteApp
每日三题 6.28
马赛克后挡板是什么?
Business visualization - make your flowchart'run'up
Treatment of insufficient space in the root partition of armbain system
Programming English vocabulary notebook
dat. GUI
Istio, ebpf and rsocket Broker: in depth study of service grid
会声会影2022智能、快速、简单的视频剪辑软件
Multiple smart pointers
SWT / anr problem - SWT causes low memory killer (LMK)
Is it safe to choose mobile phone for stock trading account opening in Shanghai?
[kotlin third party] coil koltin collaboration picture loading library coil glide like picture loading third party
CKS CKA CKAD 将终端更改为远程桌面
OpenVINO 模型性能评估工具—DL Workbench
Commemorate becoming the first dayus200 tripartite demo contributor
plain framework的实际应用和扩展