当前位置:网站首页>Reading notes of cgnf: conditional graph neural fields
Reading notes of cgnf: conditional graph neural fields
2022-07-02 05:47:00 【Si Xi is towering】
One . An overview of the article
In most GNNs in , The dependency between node labels is not considered . So , The author puts the conditional random field (Conditional Random Fields, CRF) And graph convolution network CGNF(Conditional Graph Neural Network), This model explicitly models the joint probability of the whole node label set , thus The neighborhood label information can be used in the node label prediction task .
Two . Background knowledge
2.1 Figure convolution network
GCN The mathematical form of convolution in the middle map is as follows :
H ( l + 1 ) = σ ( D ~ − 1 2 A ~ D ~ − 1 2 H ( l ) W ( l ) ) \boldsymbol{H}^{(l+1)}=\sigma\left(\tilde{\boldsymbol{D}}^{-\frac{1}{2}} \tilde{\boldsymbol{A}} \tilde{\boldsymbol{D}}^{-\frac{1}{2}} \boldsymbol{H}^{(l)} \boldsymbol{W}^{(l)}\right) H(l+1)=σ(D~−21A~D~−21H(l)W(l))
among A ~ = A + I \tilde{A}=\boldsymbol{A}+\boldsymbol{I} A~=A+I Represents the adjacency matrix with self ring added , D ~ \tilde{D} D~ yes A ~ \tilde{A} A~ The corresponding degree matrix ( Diagonal matrix ), H ( l ) \boldsymbol{H}^{(l)} H(l) It means the first one l l l The node representation of the layer , W ( l ) \boldsymbol{W}^{(l)} W(l) It means the first one l l l Layer weight matrix , σ \sigma σ Is the activation function , The common one is ReLU.
2.2 Conditional random field
Conditional random field (CRF) It's a kind of Undirected probability graph model , Usually used for structural prediction tasks . Given the input characteristics x ∈ R d x \in \mathbb{R}^{d} x∈Rd,CRF To find the maximum conditional probability P ( y ∣ x ) P(\boldsymbol{y} \mid \boldsymbol{x}) P(y∣x) Tag set y \boldsymbol{y} y. On an undirected graph ,CRF The way to calculate the joint probability distribution is Factorization , namely :
P ( y ∣ x ) = 1 Z ( x ) ∏ c Φ a ( x c , y c ) P(\boldsymbol{y} \mid \boldsymbol{x})=\frac{1}{Z(\boldsymbol{x})} \prod_{c} \Phi_{a}\left(\boldsymbol{x}_{c}, \boldsymbol{y}_{c}\right) P(y∣x)=Z(x)1c∏Φa(xc,yc)
among c c c Represents the group in the figure , x c \boldsymbol{x}_{c} xc Express Group c c c Features corresponding to all vertices in , Φ c \Phi_{c} Φc Represents the potential function , Z ( x ) = ∑ y c ′ ∏ c Φ a ( x c , y c ′ ) Z(\boldsymbol{x})=\sum_{\boldsymbol{y}_{c}^{\prime}} \prod_{c} \Phi_{a}\left(\boldsymbol{x}_{c}, \boldsymbol{y}_{c}^{\prime}\right) Z(x)=∑yc′∏cΦa(xc,yc′) Denotes the normalization factor ( It is used to ensure that the calculated probability value is legal ).
Clique refers to a subgraph in which all vertices have edge connections .
3、 ... and .CGNF Detailed introduction
First, the symbol table is given for the convenience of subsequent introduction :
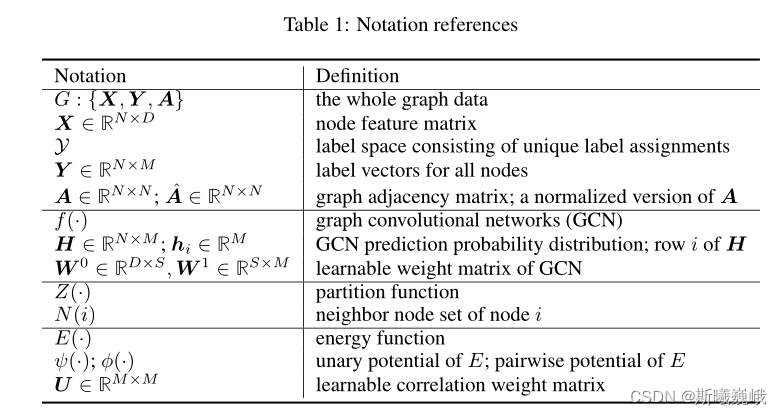
3.1 Training
CGNF The first step is to input the graph G = { X , Y , A } G=\{\boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{Y}, \boldsymbol{A}\} G={ X,Y,A} Later Kipf and Welling Bring up the 2 layer GCN Model , namely :
H = f ( X , A ) = Softmax ( A ^ ReLu ( A ^ X W 0 ) W 1 ) \boldsymbol{H}=f(\boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{A})=\operatorname{Softmax}\left(\hat{\boldsymbol{A}} \operatorname{ReLu}\left(\hat{\boldsymbol{A}} \boldsymbol{X} \boldsymbol{W}^{0}\right) \boldsymbol{W}^{1}\right) H=f(X,A)=Softmax(A^ReLu(A^XW0)W1)
And then , The author considers the influence of node characteristics and label dependency , Define the energy function (energy function) as follows :
E ( Y , X , A ) = E c ( Y c , X c , A ) = ∑ i ψ ( y i , x i ) + γ ∑ ( i , j ) ∈ E , i < j ϕ ( y i , y j , A i , j ) E(\boldsymbol{Y}, \boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{A})=E_{c}\left(\boldsymbol{Y}_{c}, \boldsymbol{X}_{c}, \boldsymbol{A}\right)=\sum_{i} \psi\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i}, \boldsymbol{x}_{i}\right)+\gamma \sum_{(i, j) \in \mathcal{E}, i<j} \phi\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i}, \boldsymbol{y}_{j}, A_{i, j}\right) E(Y,X,A)=Ec(Yc,Xc,A)=i∑ψ(yi,xi)+γ(i,j)∈E,i<j∑ϕ(yi,yj,Ai,j)
among c c c Express Group , E \mathcal{E} E Represents an edge set , ψ ( ⋅ ) \psi(\cdot) ψ(⋅) by The univariate potential function ( Used for policy observation nodes x i x_i xi And labels y i y_i yi Compatibility between compatibility, namely The observed value is x i x_i xi Belong to y i y_i yi The probability of a class ), Pairwise potential function ϕ ( ⋅ ) \phi(\cdot) ϕ(⋅) Used to capture tag Correlation . Based on this energy function , Can export Gibbs Distribution :
P ( Y ∣ X , A ) = exp ( − E ( Y , X , A ) ) ∑ Y ′ ∈ Y exp ( − E ( Y ′ , X , A ) ) = exp ( − E ( Y , X , A ) ) Z ( X , A ) P(\boldsymbol{Y} \mid \boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{A})=\frac{\exp (-E(\boldsymbol{Y}, \boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{A}))}{\sum_{\boldsymbol{Y}^{\prime} \in \mathcal{Y}} \exp \left(-E\left(\boldsymbol{Y}^{\prime}, \boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{A}\right)\right)}=\frac{\exp (-E(\boldsymbol{Y}, \boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{A}))}{Z(\boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{A})} P(Y∣X,A)=∑Y′∈Yexp(−E(Y′,X,A))exp(−E(Y,X,A))=Z(X,A)exp(−E(Y,X,A))
The goal of the author is to maximize the conditional probability , namely :
E ( Y , X , A ) = ∑ i ψ ( y i , h i ) + γ ∑ ( i , j ) ∈ E , i < j ϕ ( y i , y j , A ^ i , j ) = ∑ i ( ψ ( y i , h i ) + γ 2 ∑ j ∈ N ( i ) ϕ ( y i , y j , A ^ i , j ) ) \begin{aligned} E(\boldsymbol{Y}, \boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{A}) &=\sum_{i} \psi\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i}, \boldsymbol{h}_{\boldsymbol{i}}\right)+\gamma \sum_{(i, j) \in \mathcal{E}, i<j} \phi\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i}, \boldsymbol{y}_{j}, \hat{A}_{i, j}\right) \\ &=\sum_{i}\left(\psi\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i}, \boldsymbol{h}_{i}\right)+\frac{\gamma}{2} \sum_{j \in N(i)} \phi\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i}, \boldsymbol{y}_{j}, \hat{A}_{i, j}\right)\right) \end{aligned} E(Y,X,A)=i∑ψ(yi,hi)+γ(i,j)∈E,i<j∑ϕ(yi,yj,A^i,j)=i∑⎝⎛ψ(yi,hi)+2γj∈N(i)∑ϕ(yi,yj,A^i,j)⎠⎞
among h i h_i hi It's through 2 layer GCN The node representation obtained by the model , A ^ i , j \hat{A}_{i, j} A^i,j Is the original in the regularized adjacency matrix , N ( i ) N(i) N(i) Is the node i i i The neighborhood of . The calculation formula of the two potential functions is as follows :
ψ ( y i , h i ) = − log p ( y i ∣ h i ) = − ∑ k y i , k log h i , k ϕ ( y i , y j , A ^ i , j ) = − 2 A ^ i , j U y i , y j \begin{aligned} \psi\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i}, \boldsymbol{h}_{i}\right) &=-\log p\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i} \mid \boldsymbol{h}_{i}\right)=-\sum_{k} y_{i, k} \log h_{i, k} \\ \phi\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i}, \boldsymbol{y}_{j}, \hat{A}_{i, j}\right) &=-2 \hat{A}_{i, j} U_{y_{i}, y_{j}} \end{aligned} ψ(yi,hi)ϕ(yi,yj,A^i,j)=−logp(yi∣hi)=−k∑yi,kloghi,k=−2A^i,jUyi,yj
It can be seen from the above formula that ψ ( y i , h i ) \psi\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i}, \boldsymbol{h}_{i}\right) ψ(yi,hi) It's actually cross entropy , U y i , y j ∈ U U_{y_{i}, y_{j}} \in \boldsymbol{U} Uyi,yj∈U yes label y i y_i yi and y j y_j yj Learnable correlation weights between . Adopt a similar tradition CRF How to do it , The author uses negative log likelihood as the objective function of training :
− log P ( Y ∣ X , A ) = E ( Y , X , A ) + log Z ( X , A ) = E ( Y , X , A ) + log ∑ Y ′ exp ( − E ( Y ′ , X , A ) ) \begin{aligned} -\log P(\boldsymbol{Y} \mid \boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{A}) &=E(\boldsymbol{Y}, \boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{A})+\log Z(\boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{A}) \\ &=E(\boldsymbol{Y}, \boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{A})+\log \sum_{\boldsymbol{Y}^{\prime}} \exp \left(-E\left(\boldsymbol{Y}^{\prime}, \boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{A}\right)\right) \end{aligned} −logP(Y∣X,A)=E(Y,X,A)+logZ(X,A)=E(Y,X,A)+logY′∑exp(−E(Y′,X,A))
In inferring (inference) When , just min Y E ( Y , X , A ) \min _{\boldsymbol{Y}} E(\boldsymbol{Y}, \boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{A}) minYE(Y,X,A) that will do . But it is more difficult to optimize than the above training objectives , For this reason, the author adopts Pseudo likelihood To approximate it :
P ( Y ∣ X , A ) ≈ P L ( Y ∣ X , A ) = ∏ i P ( y i ∣ y N ( i ) , X , A ) P(\boldsymbol{Y} \mid \boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{A}) \approx P L(\boldsymbol{Y} \mid \boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{A})=\prod_{i} P\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i} \mid \boldsymbol{y}_{N(i)}, \boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{A}\right) P(Y∣X,A)≈PL(Y∣X,A)=i∏P(yi∣yN(i),X,A)
among :
P ( y i ∣ y N ( i ) , X , A ) = exp ( − ψ ( y i , h i ) − γ ∑ j ∈ N ( i ) ϕ ( y i , y j , A ^ i , j ) ∑ y i ′ ( exp ( − ψ ( y i ′ , h i ) − γ ∑ j ∈ N ( i ) ϕ ( y i ′ , y j , A ^ i , j ) ) = exp ( − log p ( y i ∣ h i ) − 2 γ ∑ j ∈ N ( i ) A ^ i , j U y i , y j ∑ y i ′ ( exp ( − log p ( y i ′ ∣ h i ) − 2 γ ∑ j ∈ N ( i ) A ^ i , j U y i ′ , y j ) \begin{aligned} P\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i} \mid \boldsymbol{y}_{N(i)}, \boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{A}\right) &=\frac{\exp \left(-\psi\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i}, \boldsymbol{h}_{\boldsymbol{i}}\right)-\gamma \sum_{j \in N(i)} \phi\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i}, \boldsymbol{y}_{j}, \hat{A}_{i, j}\right)\right.}{\sum_{\boldsymbol{y}_{i}^{\prime}}\left(\exp \left(-\psi\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i}^{\prime}, \boldsymbol{h}_{\boldsymbol{i}}\right)-\gamma \sum_{j \in N(i)} \phi\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i}^{\prime}, \boldsymbol{y}_{j}, \hat{A}_{i, j}\right)\right)\right.} \\ &=\frac{\exp \left(-\log p\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i} \mid \boldsymbol{h}_{\boldsymbol{i}}\right)-2 \gamma \sum_{j \in N(i)} \hat{A}_{i, j} U_{y_{i}, y_{j}}\right.}{\sum_{\boldsymbol{y}_{i}^{\prime}}\left(\exp \left(-\log p\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i}^{\prime} \mid \boldsymbol{h}_{\boldsymbol{i}}\right)-2 \gamma \sum_{j \in N(i)} \hat{A}_{i, j} U_{y_{i}^{\prime}, y_{j}}\right)\right.} \end{aligned} P(yi∣yN(i),X,A)=∑yi′(exp(−ψ(yi′,hi)−γ∑j∈N(i)ϕ(yi′,yj,A^i,j))exp(−ψ(yi,hi)−γ∑j∈N(i)ϕ(yi,yj,A^i,j)=∑yi′(exp(−logp(yi′∣hi)−2γ∑j∈N(i)A^i,jUyi′,yj)exp(−logp(yi∣hi)−2γ∑j∈N(i)A^i,jUyi,yj
y i ′ \boldsymbol{y}_{i}^{\prime} yi′ Is the node x i \boldsymbol{x}_{i} xi All possible labels . therefore , The new training goal is :
− log P L ( Y ∣ X , A ) = ∑ i − log P ( y i ∣ y N ( i ) , X , A ) = ∑ i ( ψ ( y i , h i ) + γ ∑ j ∈ N ( i ) ϕ ( y i , y j , A ^ i , j ) + log ∑ y i ′ ( exp ( − ψ ( y i ′ , h i ) − γ ∑ j ∈ N ( i ) ϕ ( y i ′ , y j , A ^ i , j ) ) ) = − ∑ i , k ( Y ⊙ log H ) i , k − 2 γ ∑ i , j , i ≠ j ( A ^ ⊙ ( Y U Y T ) ) i , j + ∑ i log ∑ k ( H ⊙ exp ( 2 γ A ^ Y U ) ) i , k \begin{aligned} &-\log P L(\boldsymbol{Y} \mid \boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{A})=\sum_{i}-\log P\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i} \mid \boldsymbol{y}_{N(i)}, \boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{A}\right)= \\ &\sum_{i}\left(\psi\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i}, \boldsymbol{h}_{i}\right)+\gamma \sum_{j \in N(i)} \phi\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i}, \boldsymbol{y}_{j}, \hat{A}_{i, j}\right)+\log \sum_{\boldsymbol{y}_{i}^{\prime}}\left(\exp \left(-\psi\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i}^{\prime}, \boldsymbol{h}_{\boldsymbol{i}}\right)-\gamma \sum_{j \in N(i)} \phi\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i}^{\prime}, \boldsymbol{y}_{j}, \hat{A}_{i, j}\right)\right)\right)\right. \\ &=-\sum_{i, k}(\boldsymbol{Y} \odot \log \boldsymbol{H})_{i, k}-2 \gamma \sum_{i, j, i \neq j}\left(\hat{\boldsymbol{A}} \odot\left(\boldsymbol{Y} \boldsymbol{U} \boldsymbol{Y}^{T}\right)\right)_{i, j}+\sum_{i} \log \sum_{k}(\boldsymbol{H} \odot \exp (2 \gamma \hat{\boldsymbol{A}} \boldsymbol{Y} \boldsymbol{U}))_{i, k} \end{aligned} −logPL(Y∣X,A)=i∑−logP(yi∣yN(i),X,A)=i∑⎝⎛ψ(yi,hi)+γj∈N(i)∑ϕ(yi,yj,A^i,j)+logyi′∑⎝⎛exp⎝⎛−ψ(yi′,hi)−γj∈N(i)∑ϕ(yi′,yj,A^i,j)⎠⎞⎠⎞=−i,k∑(Y⊙logH)i,k−2γi,j,i=j∑(A^⊙(YUYT))i,j+i∑logk∑(H⊙exp(2γA^YU))i,k
⊙ \odot ⊙ Represents element by element multiplication .
3.2 infer
As mentioned above , When inferring, you only need to optimize the following objectives :
min Y ^ t e E ( Y ^ t e , X , A , Y t r ) = min Y ^ t e [ − log p ( Y ^ t e ∣ H ) − γ ∑ i ≠ j ( A ^ ⊙ ( Y ^ U Y ^ T ) ) i , j ] \min _{\hat{\boldsymbol{Y}}_{t e}} E\left(\hat{\boldsymbol{Y}}_{t e}, \boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{A}, \boldsymbol{Y}_{t r}\right)=\min _{\hat{\boldsymbol{Y}}_{t e}}\left[-\log p\left(\hat{\boldsymbol{Y}}_{t e} \mid \boldsymbol{H}\right)-\gamma \sum_{i \neq j}\left(\hat{\boldsymbol{A}} \odot\left(\hat{\boldsymbol{Y}} \boldsymbol{U} \hat{\boldsymbol{Y}}^{T}\right)\right)_{i, j}\right] Y^teminE(Y^te,X,A,Ytr)=Y^temin⎣⎡−logp(Y^te∣H)−γi=j∑(A^⊙(Y^UY^T))i,j⎦⎤
among Y ^ = \hat{\boldsymbol{Y}}= Y^= concatenate ( Y t r , Y ^ t e ) \left(\boldsymbol{Y}_{t r}, \hat{\boldsymbol{Y}}_{t e}\right) (Ytr,Y^te). The author mentioned two inference methods in his paper .
3.2.1 Inference method 1
The simplest inference method is to ignore the correlation between tags , namely :
y i = arg min y j E ( y i , Y t r , X , A ) = arg min j [ − log ( h i ) − 2 γ A ^ t r Y U T ] j y_{i}=\underset{y_{j}}{\arg \min } E\left(\boldsymbol{y}_{i}, \boldsymbol{Y}_{t r}, \boldsymbol{X}, \boldsymbol{A}\right)=\underset{j}{\arg \min }\left[-\log \left(\boldsymbol{h}_{i}\right)-2 \gamma \hat{\boldsymbol{A}}_{t r} \boldsymbol{Y} \boldsymbol{U}^{T}\right]_{j} yi=yjargminE(yi,Ytr,X,A)=jargmin[−log(hi)−2γA^trYUT]j
3.2.2 Inference method 2
The second scheme is to use dynamic programming method to find the optimal value . This method will randomly select a test node as the start , And randomly sort other test nodes , Then follow the order of sorting test nodes beam search(beam The size is K K K, That is, you can get K K K Best set ). Repeat the process T T T word , Then select the best of all search results , The algorithm is summarized as follows :

Four . experiment
The author in Cora、Pubmed、Citeseer and PPI Experiment on four data sets , And compared with others baseline Good performance has been achieved , The corresponding results are as follows :

Conclusion
Reference material :
边栏推荐
- 【论文翻译】GCNet: Non-local Networks Meet Squeeze-Excitation Networks and Beyond
- centos8安裝mysql8.0.22教程
- 7. Eleven state sets of TCP
- 【技术随记-08】
- JVM class loading mechanism
- How matlab marks' a 'in the figure and how matlab marks points and solid points in the figure
- GRBL 软件:简单解释的基础知识
- Fabric. JS compact JSON
- 中小型项目手撸过滤器实现认证与授权
- Lantern Festival gift - plant vs zombie game (realized by Matlab)
猜你喜欢
6. Network - Foundation

VSCode paste image插件保存图片路径设置

Technologists talk about open source: This is not just using love to generate electricity

Fabric. JS iText superscript and subscript

Pytorch Basics
Record sentry's path of stepping on the pit
![[personal test] copy and paste code between VirtualBox virtual machine and local](/img/ce/eaf0bd9eff6551d450964da72e0b63.jpg)
[personal test] copy and paste code between VirtualBox virtual machine and local

KMP idea and template code

idea开发工具常用的插件合集汇总
Youth training camp -- database operation project
随机推荐
我所理解的DRM显示框架
Youth training camp -- database operation project
Cambrian was reduced by Paleozoic venture capital and Zhike shengxun: a total of more than 700million cash
Sliding window on the learning road
在线音乐播放器app
Lantern Festival gift - plant vs zombie game (realized by Matlab)
Reflection of the soul of the frame (important knowledge)
Go language web development is very simple: use templates to separate views from logic
2022-2-14 learning xiangniuke project - Section 7 account setting
[technical notes-08]
1036 Boys vs Girls
Visual Studio導入
Online English teaching app open source platform (customized)
Technologists talk about open source: This is not just using love to generate electricity
vite如何兼容低版本浏览器
Balsamiq wireframes free installation
ERP management system development and design existing source code
Foreign trade marketing website system development function case making
Thread pool overview
c语言中的几个关键字