当前位置:网站首页>[notes of wuenda] fundamentals of machine learning
[notes of wuenda] fundamentals of machine learning
2022-06-24 21:52:00 【Zzu dish】
Fundamentals of machine learning
What is machine learning ?
A program is thought to be able to learn from experience E Middle school learning , Solve the task T, Performance metrics reached P, If and only if , Experience gained E after , after P judge , The program is processing T Improved performance when .
I think experience E It is the experience and task of tens of thousands of self-practice procedures T Is playing chess . Performance metrics P Well , It's when it plays against some new opponents , Probability of winning the game .
Supervised Learning Supervised learning

Supervised learning : There are more than features in a dataset feature-X, And labels target-Y
We'll talk about an algorithm later , It's called support vector machine , There is a clever mathematical skill , It allows the computer to process an infinite number of features .
Unsupervised Learning Unsupervised learning

Unsupervised learning : There are only features in the dataset feature
clustering algorithm : Separate audio at different distances , Distinguish whether the mailbox is a junk mailbox, etc
[W,s,v] = svd((repmat(sum(x.*x,1),size(x,1),1).*x)*x');
Self supervised learning
Explain a : Self supervised learning enables us to obtain high-quality representation without large-scale annotation data , Instead, we can use a large number of unlabeled data and optimize predefined pretext Mission . We can then use these features to learn about new tasks that lack data .
Explain two : self-supervised learning It's a kind of unsupervised learning , The main purpose is to learn a common feature expression for downstream tasks . The main way is to supervise yourself , For example, remove a few words from a paragraph , Use his context to predict missing words , Or remove some parts of the picture , Rely on the information around it to predict the missing patch.
effect :
Learn useful information from unlabeled data , For subsequent tasks .
Self monitoring tasks ( Also known as pretext Mission ) We are asked to consider the supervisory loss function . However , We usually don't care about the final performance of the task . actually , We are only interested in the intermediate representations we have learned , We expect these representations to cover good semantic or structural meaning , And it can be beneficial to various downstream practical tasks .
Linear Regression with One Variable Linear regression of single variable
Univariate linear regression :
- One possible expression is : h θ ( x ) = θ 0 + θ 1 x h_\theta \left( x \right)=\theta_{0} + \theta_{1}x hθ(x)=θ0+θ1x, Because it contains only one feature / The input variable , So this kind of problem is called univariate linear regression problem .
Selling a house : Already know the price of the previous sale , Based on the previous data set, predict the price at which your friend's house can be sold .
Training Set( Training set ) as follows :

m m m Represents the number of instances in the training set
x x x On behalf of the characteristic / The input variable
y y y Represents the target variable / Output variables
( x , y ) \left( x,y \right) (x,y) Represents an instance of a training set
( x ( i ) , y ( i ) ) ({ {x}^{(i)}},{ {y}^{(i)}}) (x(i),y(i)) On behalf of the i i i Two observation examples

h h h Solutions or functions that represent learning algorithms are also called assumptions (hypothesis)
Cost Function Cost function
The cost function is also called the square error function , Sometimes called the square error cost function . The reason why we ask for the sum of squares of errors , Because the square cost function of the error , For most problems , Especially the problem of return , Is a reasonable choice . There are other cost functions that work well , But the square error cost function is probably the most common way to solve regression problems .
The cost function makes us h θ ( x ) = θ 0 + θ 1 x h_\theta \left( x \right)=\theta_{0} + \theta_{1}x hθ(x)=θ0+θ1x Better choice of parameters **parameters ** θ 0 θ 1 \theta_{0}\theta_{1} θ0θ1, So that the most possible lines and data fit each other .

Our goal is to select the model parameters that minimize the sum of squares of modeling errors .
- Even if you get the cost function J ( θ 0 , θ 1 ) = 1 2 m ∑ i = 1 m ( h θ ( x ( i ) ) − y ( i ) ) 2 J \left( \theta_0, \theta_1 \right) = \frac{1}{2m}\sum\limits_{i=1}^m \left( h_{\theta}(x^{(i)})-y^{(i)} \right)^{2} J(θ0,θ1)=2m1i=1∑m(hθ(x(i))−y(i))2 Minimum .
θ 0 \theta_{0} θ0 and θ 1 \theta_{1} θ1 and J ( θ 0 , θ 1 ) J(\theta_{0}, \theta_{1}) J(θ0,θ1) Visualization of relationships

At present, the global minimum cost function is obtained , Simplify θ 0 = 0 \theta_{0}=0 θ0=0

Yes θ 1 \theta_{1} θ1 Continuously assign values to get the corresponding J ( θ 1 ) J(\theta_{1}) J(θ1), obtain J ( θ 1 ) J(\theta_{1}) J(θ1) and θ 1 \theta_{1} θ1 Relationship

Contour map : Corresponding θ 0 = 360 \theta_{0}=360 θ0=360, θ 1 = 0 \theta_{1}=0 θ1=0, Corresponding to the position in the contour map

Gradient Descent gradient descent
gradient descent : To solve the cost function J ( θ 0 , θ 1 ) J(\theta_{0}, \theta_{1}) J(θ0,θ1) Minimum value θ 0 \theta_{0} θ0, θ 1 \theta_{1} θ1
The idea behind the gradient drop is : At first, we randomly choose a combination of parameters ( θ 0 , θ 1 , . . . . . . , θ n ) \left( {\theta_{0}},{\theta_{1}},......,{\theta_{n}} \right) (θ0,θ1,......,θn), Computational cost function , Then we look for the next parameter combination that can reduce the cost function value the most . We keep doing this until we find a local minimum (local minimum), Because we haven't tried all the parameter combinations , So it's not sure if the local minimum we get is the global minimum (global minimum), Choose different combinations of initial parameters , Different local minima may be found .

Gradient descent algorithm

- a a a It's the learning rate (learning rate), It determines how far down we go in the direction where the cost function can go down the most , In the decline of batch gradients , Each time we subtract all the parameters from the learning rate times the derivative of the cost function .

- The right is right , Assign values after all values are calculated , The left side is wrong
The gradient descent algorithm is as follows :
θ j : = θ j − α ∂ ∂ θ j J ( θ ) {\theta_{j}}:={\theta_{j}}-\alpha \frac{\partial }{\partial {\theta_{j}}}J\left(\theta \right) θj:=θj−α∂θj∂J(θ)
describe : Yes $\theta Fu value , send have to assignment , bring Fu value , send have to J\left( \theta \right) Press ladder degree Next drop most fast Fang towards Into the That's ok , One straight Overlapping generation Next Go to , most end have to To game Ministry most Small value . Its in Proceed in the direction of fastest gradient descent , And you keep iterating , You end up with a local minimum . among Press ladder degree Next drop most fast Fang towards Into the That's ok , One straight Overlapping generation Next Go to , most end have to To game Ministry most Small value . Its in a$ It's the learning rate (learning rate), It determines how far down we go in the direction where the cost function can go down the most .

If only consider θ 1 \theta_{1} θ1, θ 0 = 0 \theta_{0}=0 θ0=0 when , α ∂ ∂ θ 1 J ( θ ) \alpha \frac{\partial }{\partial {\theta_{1}}}J\left(\theta \right) α∂θ1∂J(θ), The front is the learning rate , Then comes the cost function J ( θ ) J\left( \theta \right) J(θ) About θ 1 \theta_{1} θ1 The derivative of .
Cost function J ( θ 1 ) J\left( \theta_{1} \right) J(θ1) and θ 1 \theta_{1} θ1 Image ,
If the learning rate is too small , More iterations
If the learning rate is too high , May cross the local minimum , Back and forth oscillation deviates from the local minimum value point .
take Gradient descent and cost function combination , And apply it to the specific linear regression algorithm of fitting straight line .
Gradient descent algorithm and linear regression algorithm are shown in the figure below :

For our previous linear regression problem, we use the gradient descent method , The key is to find the derivative of the cost function , namely :
∂ ∂ θ j J ( θ 0 , θ 1 ) = ∂ ∂ θ j 1 2 m ∑ i = 1 m ( h θ ( x ( i ) ) − y ( i ) ) 2 \frac{\partial }{\partial { {\theta }_{j}}}J({ {\theta }_{0}},{ {\theta }_{1}})=\frac{\partial }{\partial { {\theta }_{j}}}\frac{1}{2m}{ {\sum\limits_{i=1}^{m}{\left( { {h}_{\theta }}({ {x}^{(i)}})-{ {y}^{(i)}} \right)}}^{2}} ∂θj∂J(θ0,θ1)=∂θj∂2m1i=1∑m(hθ(x(i))−y(i))2
j = 0 j=0 j=0 when : ∂ ∂ θ 0 J ( θ 0 , θ 1 ) = 1 m ∑ i = 1 m ( h θ ( x ( i ) ) − y ( i ) ) \frac{\partial }{\partial { {\theta }_{0}}}J({ {\theta }_{0}},{ {\theta }_{1}})=\frac{1}{m}{ {\sum\limits_{i=1}^{m}{\left( { {h}_{\theta }}({ {x}^{(i)}})-{ {y}^{(i)}} \right)}}} ∂θ0∂J(θ0,θ1)=m1i=1∑m(hθ(x(i))−y(i))
j = 1 j=1 j=1 when : ∂ ∂ θ 1 J ( θ 0 , θ 1 ) = 1 m ∑ i = 1 m ( ( h θ ( x ( i ) ) − y ( i ) ) ⋅ x ( i ) ) \frac{\partial }{\partial { {\theta }_{1}}}J({ {\theta }_{0}},{ {\theta }_{1}})=\frac{1}{m}\sum\limits_{i=1}^{m}{\left( \left( { {h}_{\theta }}({ {x}^{(i)}})-{ {y}^{(i)}} \right)\cdot { {x}^{(i)}} \right)} ∂θ1∂J(θ0,θ1)=m1i=1∑m((hθ(x(i))−y(i))⋅x(i))
Then the algorithm is rewritten to :
Repeat {
θ 0 : = θ 0 − a 1 m ∑ i = 1 m ( h θ ( x ( i ) ) − y ( i ) ) {\theta_{0}}:={\theta_{0}}-a\frac{1}{m}\sum\limits_{i=1}^{m}{ \left({ {h}_{\theta }}({ {x}^{(i)}})-{ {y}^{(i)}} \right)} θ0:=θ0−am1i=1∑m(hθ(x(i))−y(i))
θ 1 : = θ 1 − a 1 m ∑ i = 1 m ( ( h θ ( x ( i ) ) − y ( i ) ) ⋅ x ( i ) ) {\theta_{1}}:={\theta_{1}}-a\frac{1}{m}\sum\limits_{i=1}^{m}{\left( \left({ {h}_{\theta }}({ {x}^{(i)}})-{ {y}^{(i)}} \right)\cdot { {x}^{(i)}} \right)} θ1:=θ1−am1i=1∑m((hθ(x(i))−y(i))⋅x(i))
**}
Refer to https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/328261042

Batch gradient descent , All training sets are used for each gradient descent
summary
1. Hypothesis function (Hypothesis)
A linear function is used to fit the sample data set , It can be simply defined as :

among
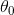
and

Is the parameter .
2. Cost function (Cost Function)
Measure the... Of a hypothetical function “ Loss ”, Also known as “ Square sum error function ”(Square Error Function), The following definitions are given :

amount to , Sum up the square of the difference between the assumed value and the true value of all samples , Divide by the number of samples m, Get an average of “ Loss ”. Our task is to find out
and

Make this “ Loss ” Minimum .
3. gradient descent (Gradient Descent)
gradient : The directional derivative of a function at that point is maximized in that direction , That is, the rate of change at this point ( Slope ) Maximum .
gradient descent : Make the argument

Along make

Move in the direction of the fastest descent , Get... As soon as possible

The minimum value of , The following definitions are given :

In wuenda's course, I learned , Gradient descent requires all independent variables to be simultaneously “ falling ” Of , therefore , We can translate it into separate pairs

and

Find the partial derivative , It's fixed

take

Take the derivative as a variable , The opposite is true of

equally .
We know that the cost function is

, among

, that , According to the derivation principle of composite function ,dx/dy=(*du/dy)*∗(dx/du), That is to translate it into :

Finally, the results of the course :


边栏推荐
- Advanced secret of xtransfer technology newcomers: the treasure you can't miss mentor
- 二叉搜索树模板
- socket(1)
- Redis+Caffeine两级缓存,让访问速度纵享丝滑
- 应用实践 | 海量数据,秒级分析!Flink+Doris 构建实时数仓方案
- Shengzhe technology AI intelligent drowning prevention service launched
- Memcached comprehensive analysis – 3 Deletion mechanism and development direction of memcached
- Multi task model of recommended model: esmm, MMOE
- Blender FAQs
- Byte software testing basin friends, you can change jobs. Is this still the byte you are thinking about?
猜你喜欢

CondaValueError: The target prefix is the base prefix. Aborting.

Blender FAQs

面试官:你说你精通Redis,你看过持久化的配置吗?

Data link layer & some other protocols or technologies

XTransfer技术新人进阶秘诀:不可错过的宝藏Mentor

【产品设计研发协作工具】上海道宁为您提供蓝湖介绍、下载、试用、教程
架构实战营 第 6 期 毕业设计

C语言实现DNS请求器

Installing Oracle without graphical interface in virtual machine centos7 (nanny level installation)

字节的软件测试盆友们你们可以跳槽了,这还是你们心心念念的字节吗?
随机推荐
基于 KubeSphere 的分级管理实践
123. the best time to buy and sell shares III
【无标题】
openGauss内核:简单查询的执行
leetcode:1504. 统计全 1 子矩形的个数
SAP接口debug设置外部断点
[camera Foundation (I)] working principle and overall structure of camera
2022 international women engineers' Day: Dyson design award shows women's design strength
leetcode_1470_2021.10.12
C语言实现DNS请求器
MySQL optimizes query speed
Pattern recognition - 0 introduction
how to install clustershell
Intelligent fish tank control system based on STM32 under Internet of things
[camera Foundation (II)] camera driving principle and Development & v4l2 subsystem driving architecture
Li Kou daily question - day 25 -496 Next larger element I
架构实战营 第 6 期 毕业总结
leetcode-201_2021_10_17
并查集+建图
(待补充)GAMES101作业7提高-实现微表面模型你需要了解的知识