当前位置:网站首页>Mysql database index study notes
Mysql database index study notes
2022-07-07 09:14:00 【White butterfly】
Preface
The author has been studying database indexing recently , So I want to write a blog to record my learning , If there is a mistake , Please point out .
One 、 Index introduction
1.1 What is the index
The index is a separate 、 Database structure stored on disk , Contains a reference pointer to all records in the data table . Using an index, you can quickly find rows with a specific value in one or more columns , all MySQL All column types can be indexed , Using indexes on related columns is the best way to improve the speed of query operation .
1.2 Advantages and disadvantages of index
advantage :
- Can improve the efficiency of data retrieval , Reduce the IO cost
- Sort data through index columns , To reduce the CPU Consumption of
Inferiority :
- Take up disk space
- When adding data in the table 、 When deleting and modifying , Index should also be maintained dynamically , This reduces the speed of data maintenance .
1.3 When to use index
- When uniqueness is a characteristic of some kind of data itself , Specify a unique index . Using a unique index ensures the data integrity of the defined column , To improve query speed .
- To sort or group frequently ( That is to say group by or order by operation ) Index on the column of , If there are more than one column to sort , You can build composite indexes on these columns .
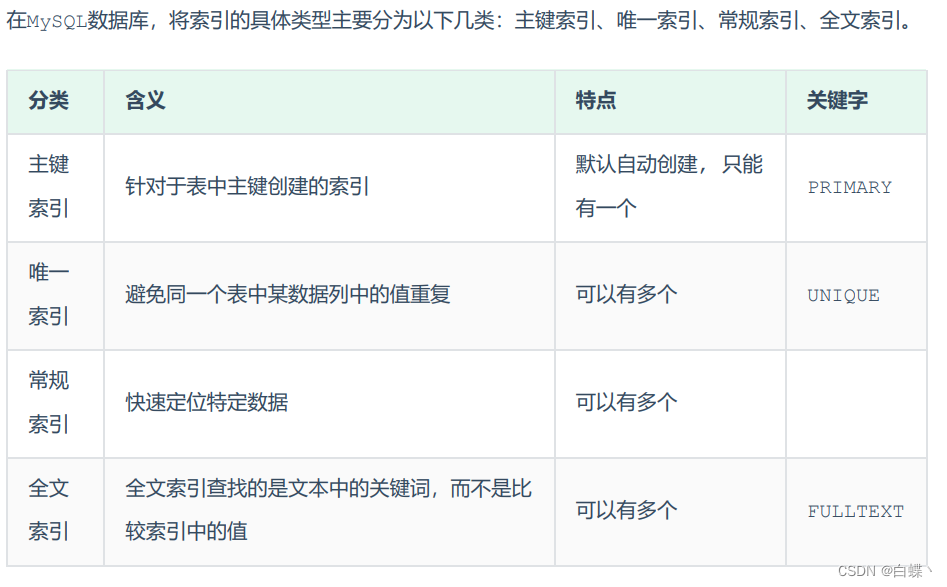
Two 、 Classification of indexes
2.1 Example index
- General index : General index is MySQL The basic index type in , Allows you to insert duplicate and null values in a column that defines an index
- Unique index requires that the value of the index column must be unique , But you can have an empty value . If it's a composite index , The combination of column values must be unique
- Primary key index is a special unique index , No null values are allowed
2.2 Composite index
- Index of multiple field combinations , Only if the left side of these fields is used in the query criteria , Indexes are used . If the intermediate index is not used , Later indexes will also become invalid , When using a composite index, follow the leftmost prefix set
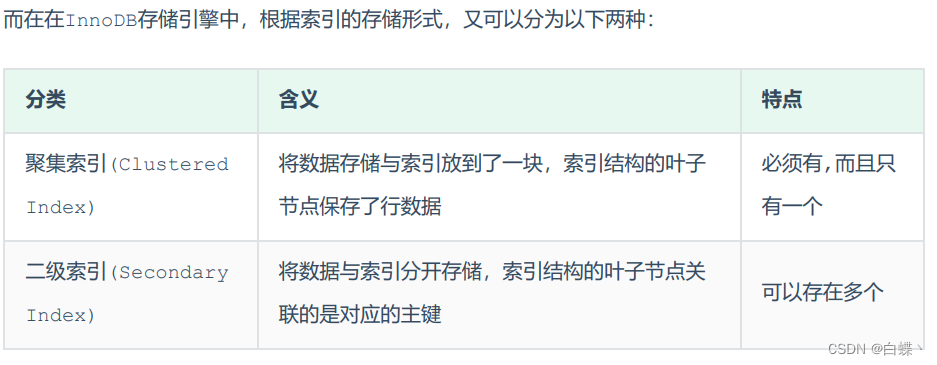
Clustered index selection rules :
- If there is a primary key , A primary key index is a clustered index .
- If there is no primary key , The first unique... Will be used (UNIQUE) Index as clustered index .
- If the table does not have a primary key , Or there is no suitable unique index , be InnoDB It will automatically generate a rowid As a hidden gathering rope
lead .
3、 ... and 、 Use of index
3.1 Basic commands for indexing
1. Create index :
create index Index name on Table name ( Field name ( length ));
alter table Table name add index Index name ( Field name ( length ));
2. Delete index :
drop index Index name on Table name ;
3. Look at the index :
show index from Table name
3.2 Determine whether the index is effective
have access to EXPLAIN Statement to see if the index is in use .
explain select * from Table name where Conditions ( Conditions need to be indexed )
The meaning of each field in the execution plan :
3.3 Avoid index invalidation
There are several ways , To avoid index failure :
1. When using composite indexes , Need to follow “ Left most prefix ” principle ;
2. Do nothing on the index column , For example, to calculate 、 function 、 Type conversion , It will cause index invalidation and turn to full table scan ;
3. Try to use overlay index ( Queries that access index columns ), Reduce select * Overwriting the index can reduce the number of table returns ;
4.MySQL In use is not equal to (!= perhaps <>) Unable to use the index will result in a full table scan ;
5.LIKE Start with a wildcard (%abc)MySQL The index will become invalid and become a full table scan operation ;
for example :
select * from company where companyName like ‘% Jiangnan leather is long ’;
It can be changed to
select * from company where reverse(companyName) like reverse(‘% Jiangnan leather is long ’);
6. String without single quotation marks will invalidate the index ( An implicit conversion of the index column may have occurred );
7. When or The conditions of connection , When the left and right fields have indexes , The index will take effect
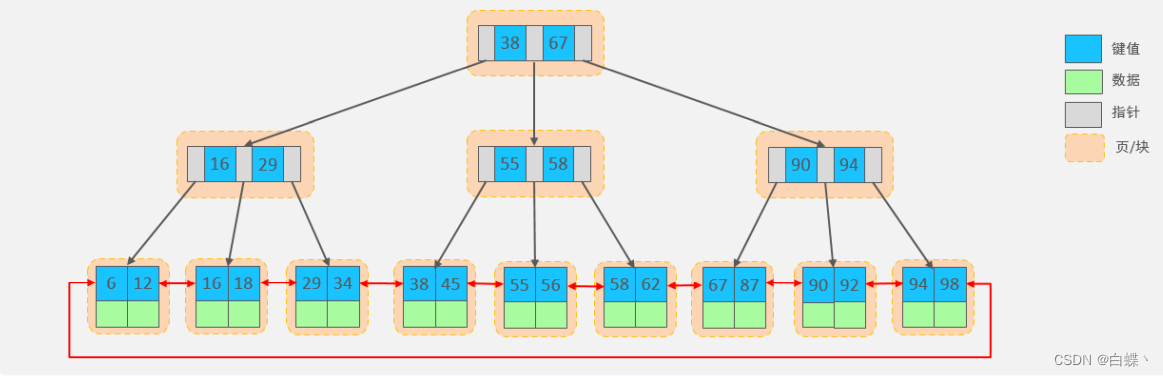
Four 、 Index implementation principle (InnoDB)
stay MySQL In the index structure of , The choice is B+Tree, So what is B+Tree Well ? Say B+Tree Let's introduce it first B-Tree
B-Tree(B Trees ),B A tree is a kind of multi fork road scale search tree , Relative to a binary tree ,B Each node of the tree can have multiple branches , That is, multi fork .
At a maximum degree (max-degree) by 5(5 rank ) Of b-tree For example , So this one B Each node of the tree can store up to 4 individual key,5
A pointer to the :
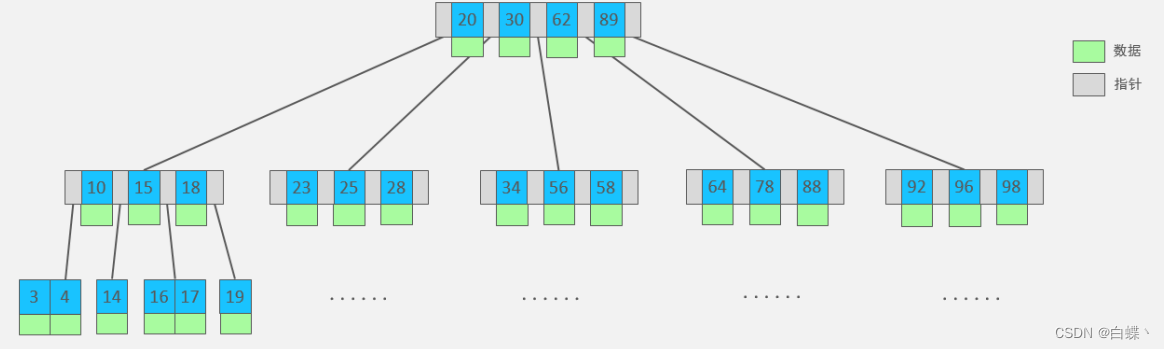
characteristic :
- 5 Step B Trees , Each node can store up to 4 individual key, Corresponding 5 A pointer to the .
- Once the node stores key The quantity has arrived 5, Will fission , The intermediate element splits up .
- stay B In the tree , Both non leaf nodes and leaf nodes store data .
B+Tree yes B-Tree Variants , We have a maximum degree (max-degree) by 4(4 rank ) Of b+tree For example , Come and have a look
The structure diagram is shown below :
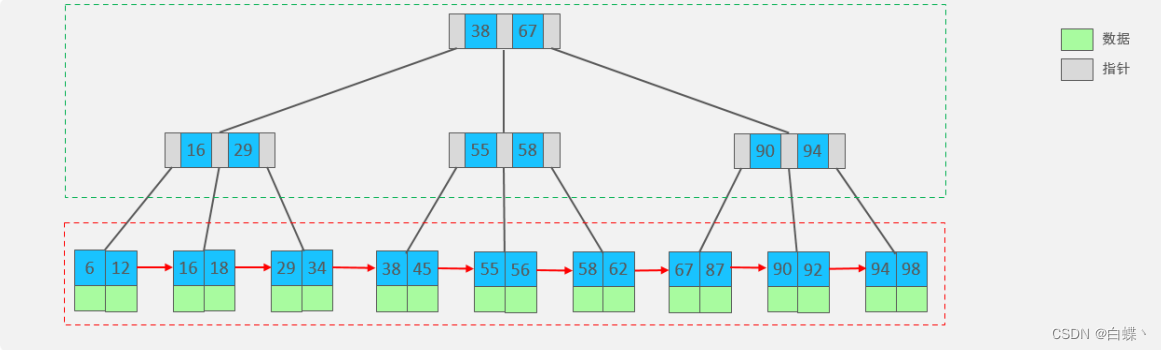
In the end, we see ,B+Tree And B-Tree comparison , There are three main differences :
- All the data will appear in the leaf node .
- Leaf nodes form a one-way linked list .
- Non leaf nodes only serve to index data , The specific data is stored in the leaf node .
MySQL Index data structure for classic B+Tree optimized . In the original B+Tree On the basis of , Add a node pointing to adjacent leaves
Linked list pointer , So we have a sequence pointer B+Tree, Improve the performance of interval access , Conducive to sorting .
5、 ... and 、 other
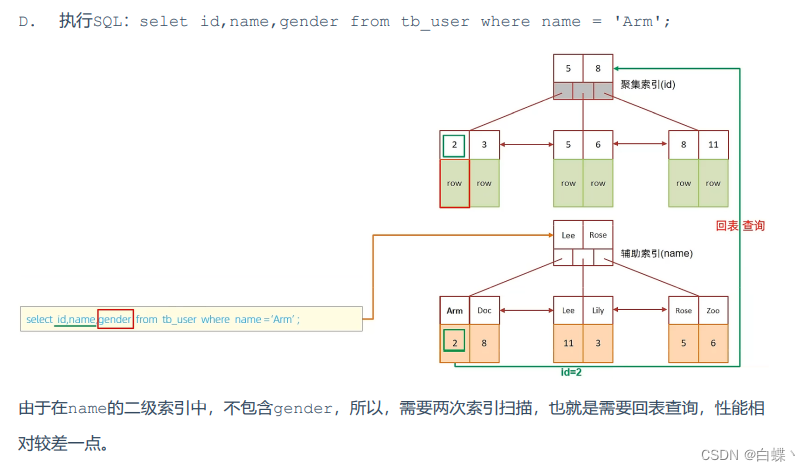
5.1 Return to the table for query
First look for data in the secondary index , Find primary key value , Then it is added to the clustered index according to the primary key value , How to get the data , It is called back to table query .
When we execute the following query statement , The specific process is as follows :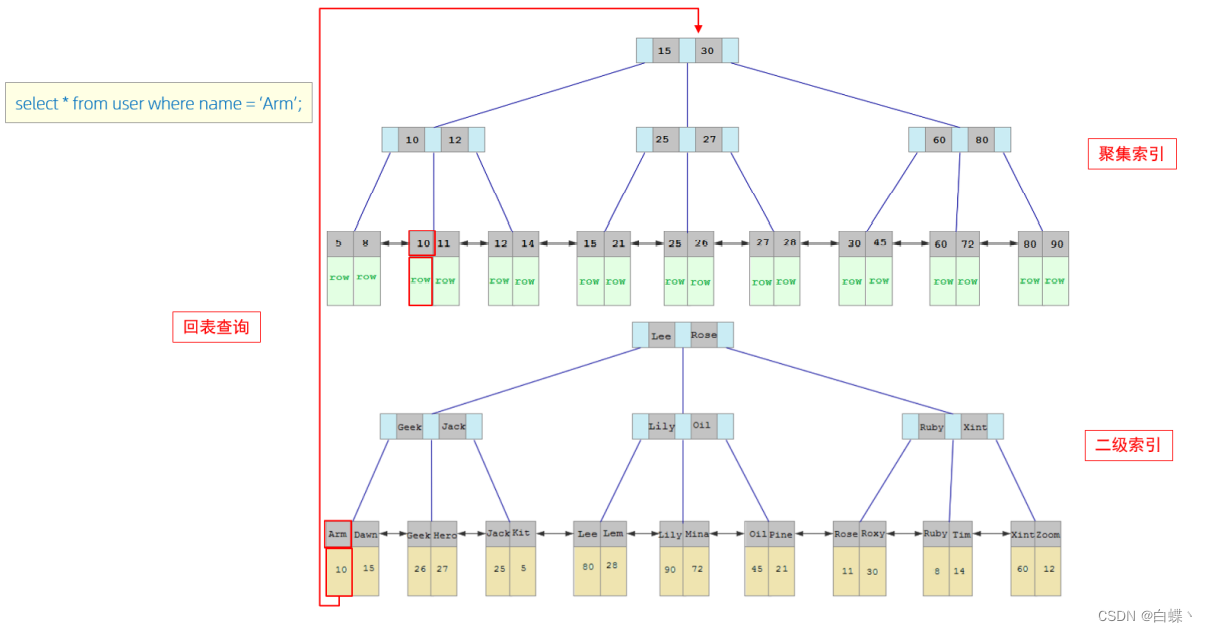
1. Because it's based on name Field to query , So first according to name='Arm’ To name Field in the secondary index
look for . But in the secondary index, you can only find Arm The corresponding primary key value 10.
2. Because the data returned by the query is all fields , So at this time , You also need to use the primary key value 10, Find in the clustered index 10 Corresponding records , Finally find 10 The corresponding line row.
3. Finally get the data of this line , Just go back .
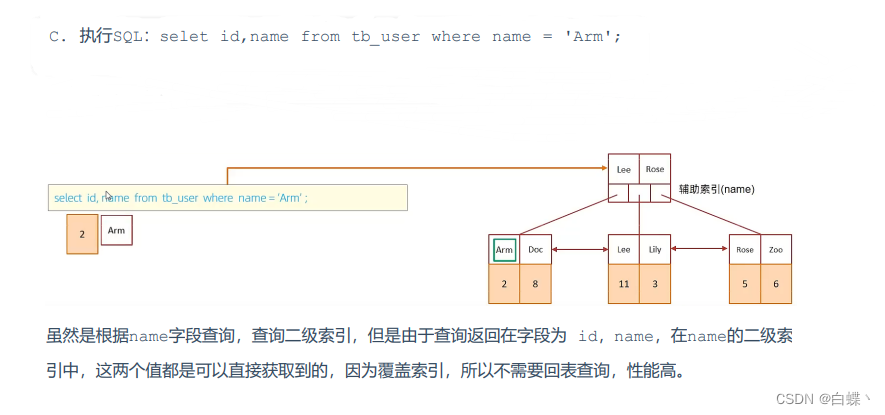
5.2 Overlay index
Overlay index means The query uses an index , And the columns that need to be returned , All can be found in this index .
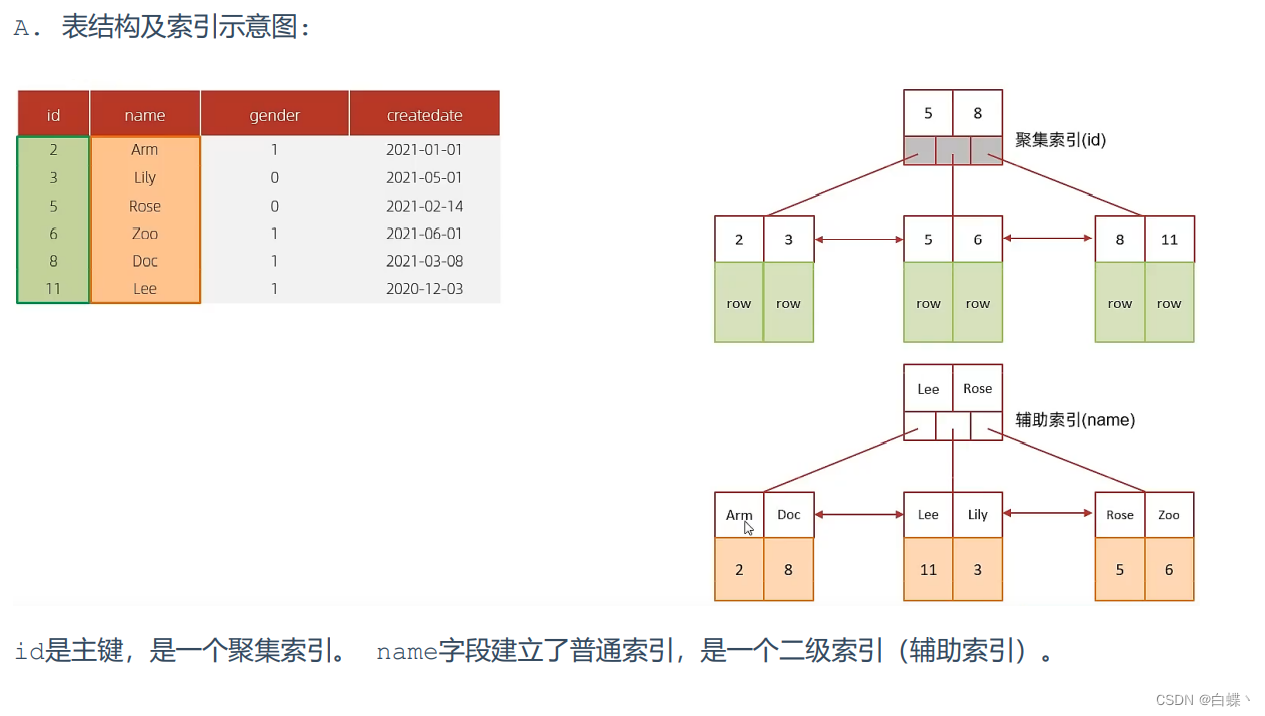
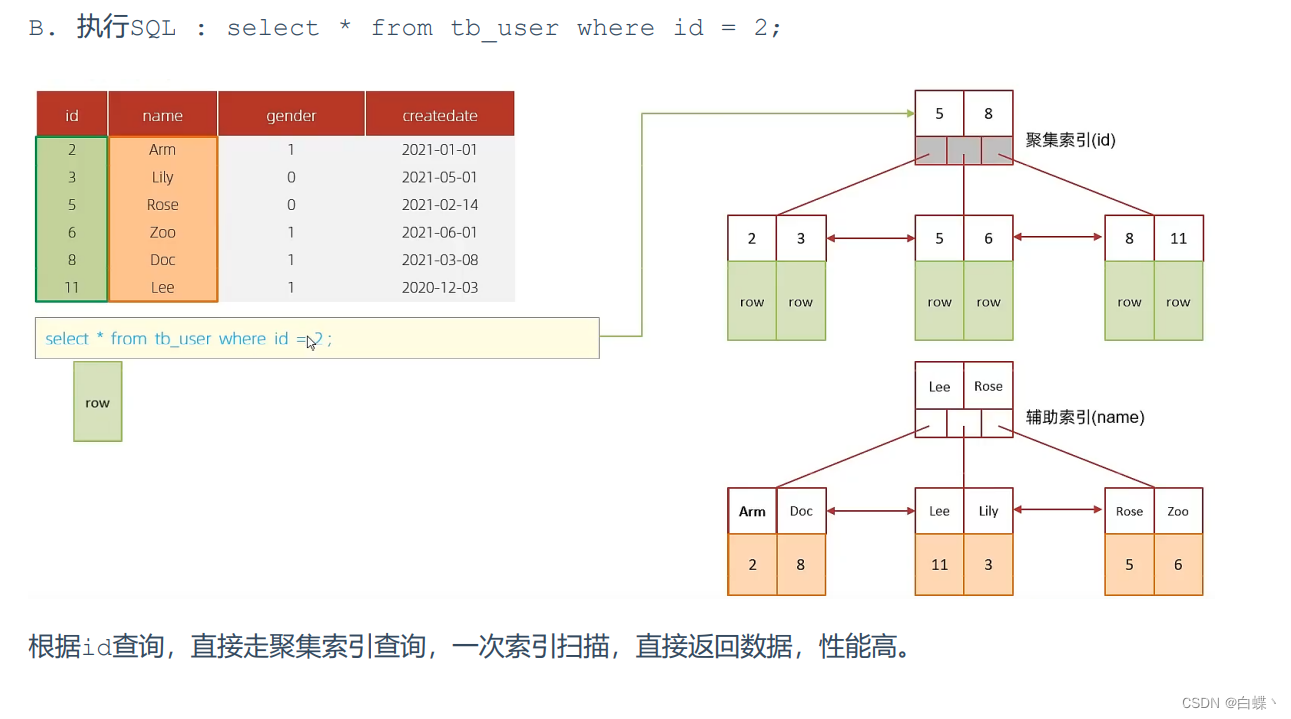
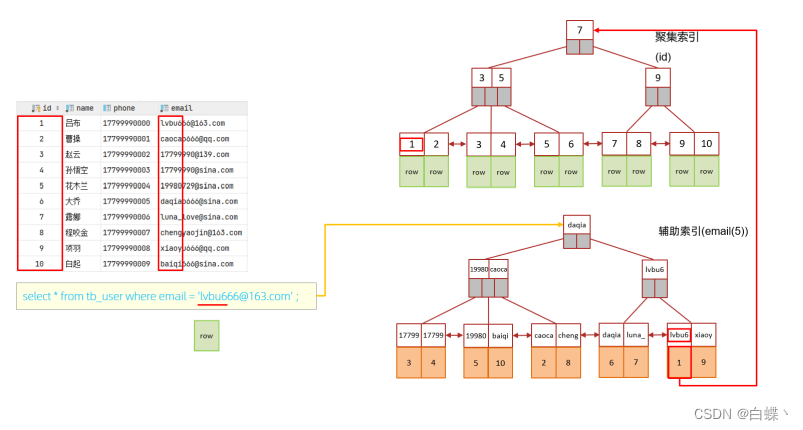
5.3 Prefix index
When the field type is string (varchar,text,longtext etc. ) when , Sometimes you need to index long strings , It will make
The index becomes large , When inquiring , Waste a lot of disk IO, Affecting query efficiency . At this point, you can prefix only part of the string with , build
Vertical index , This can greatly save index space , To improve index efficiency .
create index idx_xxxx on table_name(column(n)) ;
summary
I hope it's lucky
边栏推荐
- Original collection of hardware bear (updated on June 2022)
- Interpretation of MySQL optimization principle
- Locust performance test 2 (interface request)
- 硬件大熊原创合集(2022/05更新)
- Pytest+request+allure+excel interface automatic construction from 0 to 1 [five nails / flying Book notice]
- Locust performance test 3 (high concurrency, parameter correlation, assembly point)
- [chaosblade: node CPU load, node network delay, node network packet loss, node domain name access exception]
- Several stages of PMP preparation study
- systemd
- When inputting an expression in the input box, an error is reported: incorrect string value:'\xf0\x9f... ' for column 'XXX' at row 1
猜你喜欢
2022-07-06 unity core 9 - 3D animation

2020 year end summary
![[istio introduction, architecture, components]](/img/2b/f84e5cdac6ed9b429e053ffc8dbeb0.png)
[istio introduction, architecture, components]
Confitest of fixture py

PMP examination experience sharing
Goldbach conjecture C language

C language pointer (Part 2)

C语言指针(下篇)
使用Typora编辑markdown上传CSDN时图片大小调整麻烦问题
Ppt template and material download website (pure dry goods, recommended Collection)
随机推荐
How to use Arthas to view class variable values
寄存器地址名映射
2022-07-06 Unity核心9——3D动画
Reading notes of pyramid principle
[istio introduction, architecture, components]
How long does the PMP usually need to prepare for the exam in advance?
[chaosblade: node CPU load, node network delay, node network packet loss, node domain name access exception]
STM32的时钟系统
DRF defines views and routes
Several methods of calculating the average value of two numbers
【ChaosBlade:根据标签删除POD、Pod 域名访问异常场景、Pod 文件系统 I/O 故障场景】
STM32串口寄存器库函数配置方法
PMP examination experience sharing
[chaosblade: node disk filling, killing the specified process on the node, suspending the specified process on the node]
MySql数据库-事务-学习笔记
Upgrade Alibaba cloud RDS (relational database service) instance to com mysql. jdbc. exceptions. Troubleshooting of jdbc4.communicationsexception
JVM garbage collection detailed learning notes (II)
OpenGL frame buffer
H3C VXLAN配置
Serial port experiment - simple data sending and receiving