当前位置:网站首页>JVM garbage collection detailed learning notes (II)
JVM garbage collection detailed learning notes (II)
2022-07-07 09:04:00 【White butterfly】
This blog records personal learning jvm The process of , If there is a mistake , Please correct me
List of articles
One 、 Determine whether the object can be recycled
1. Reference counting
Add a reference counter to the object , Whenever there is a place to quote it , The counter is added 1; When a reference fails , The counter goes down 1; Any time the counter is 0 It is impossible to use the object of .
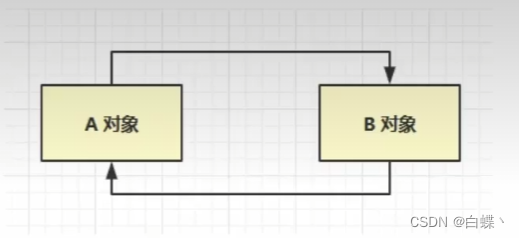
This method is easy to implement , Efficient , But at present, the mainstream virtual machine does not choose this algorithm to manage memory , The main reason is that it is difficult to solve the problem of circular references between objects . As shown in the following code : Except for objects objA and objB Quote each other , There is no more reference between the two objects . But they cite each other , The reference counters that cause them are not 0, So the reference counting algorithm can't notify GC The recyclers recycle them .
public class ReferenceCountingGc {
Object instance = null;
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReferenceCountingGc objA = new ReferenceCountingGc();
ReferenceCountingGc objB = new ReferenceCountingGc();
objA.instance = objB;
objB.instance = objA;
objA = null;
objB = null;
}
}
2. Reachability algorithm
The basic idea of this algorithm is through a series of called “GC Roots” As the starting point , Start with these nodes and drill down , The path a node goes through is called a reference chain , When an object arrives GC Roots If there is no chain of references , Then prove that this object is not available , Need to be recycled .
Image below Object 6 ~ Object 10 Although there is a reference relationship between , But they have to GC Roots Unreachable , So for objects that need to be recycled .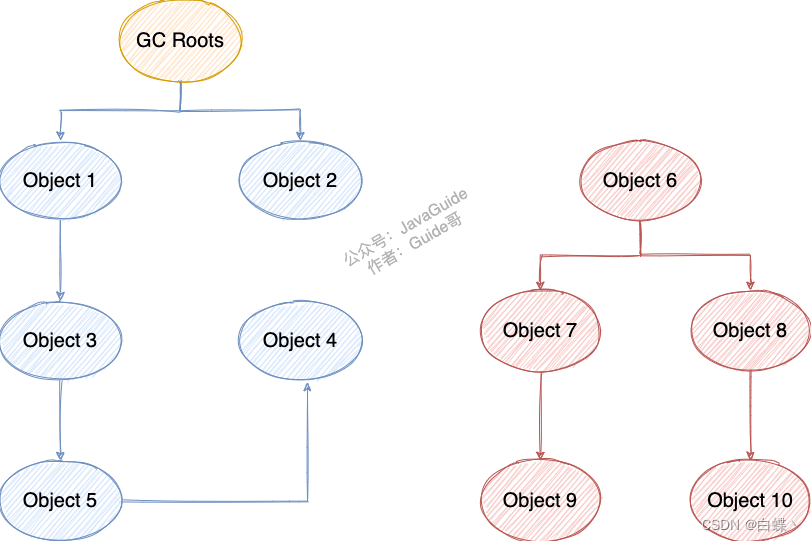
Often as GC Roots The object of
- Virtual machine stack ( Local variables in stack frames ) Object referenced in ( The object here refers to new Out of the objects stored in the heap ).
- Native Method Stack (Native Method ) Object referenced in
- Object referenced by a class static property in a method area
- The object referenced by a constant in the method area
- All objects held by synchronous locks
Two 、 Four quotations
The quotation is divided into Strong citation 、 Soft citation 、 Weak reference 、 Virtual reference Four kinds of ( The quoting strength is gradually weakened )
1. Strong citation (StrongReference)
Most of the references we used before are actually strong references , This is the most commonly used quotation . If an object has a strong reference , It's similar to the necessities , The garbage collector will never recycle it . When memory runs out of space ,Java The virtual machine would rather throw OutOfMemoryError error , Causes the program to terminate abnormally , It will not solve the problem of insufficient memory by randomly recycling objects with strong references .
2. Soft citation (SoftReference)
Soft citation , If there's enough memory , The garbage collector won't recycle it , If there's not enough memory , It will reclaim the memory of these objects . As long as the garbage collector doesn't recycle it , This object can be used by the program . Soft references can be used to implement memory sensitive caching .
Soft references can be combined with a reference queue (ReferenceQueue) A combination of , If the object referenced by the soft reference is garbage collected ,JAVA The virtual machine adds the soft reference to the reference queue associated with it . When reclaiming the object pointed to by the soft reference , Soft reference itself Will not be cleaned up , If you want to clean up soft references , Reference queue is required
3. Weak reference (WeakReference)
The difference between weak quotation and soft quotation is : Objects with only weak references have a shorter life cycle . In the process of the garbage collector thread scanning the memory area it governs , Once you find an object with only weak references , Whether the current memory space is enough or not , Will reclaim its memory . however , Because the garbage collector is a low priority thread , So it's not necessarily easy to find objects with only weak references .
Weak references can also be used in conjunction with reference queues
4. Virtual reference (PhantomReference)
Different from other quotations , Virtual references do not determine the life cycle of an object . If an object only holds virtual references , Then it's the same as without any reference , Can be recycled at any time . Virtual references must be used in conjunction with reference queues ( Because after the referenced object is recycled , Its associated direct memory cannot be directly released , Because this direct memory is not affected jvm Control and control , Therefore, in order to reclaim the direct memory, we need to use the virtual reference together with the queue )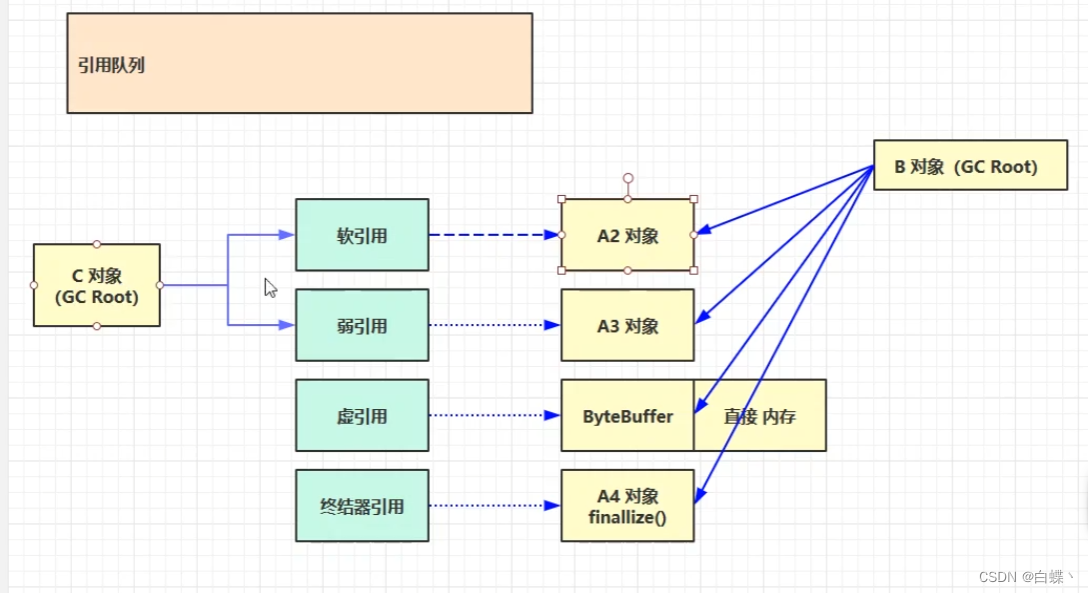
Soft reference use cases
package com.atguigu.test8;
import com.sun.scenario.effect.impl.sw.sse.SSEBlend_SRC_OUTPeer;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.ref.SoftReference;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Demo1 {
public static int _4MB = 4 * 1024 * 1024;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
method1();
}
// Set up -Xmx20m , Demo heap out of memory ,
public static void method1() throws IOException {
ArrayList<byte[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
list.add(new byte[_4MB]);
}
System.in.read();
}
// demonstration Soft citation
public static void method2() throws IOException {
// Use soft reference objects list and SoftReference There are strong references between , and SoftReference and byte Between arrays are soft references
ArrayList<SoftReference<byte[]>> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
SoftReference<byte[]> ref = new SoftReference<>(new byte[_4MB]);
System.out.println(ref.get());
list.add(ref);
System.out.println(list.size());
}
System.out.println(" The loop ends :" + list.size());
for(SoftReference<byte[]> ref : list) {
System.out.println(ref.get());
}
}
}
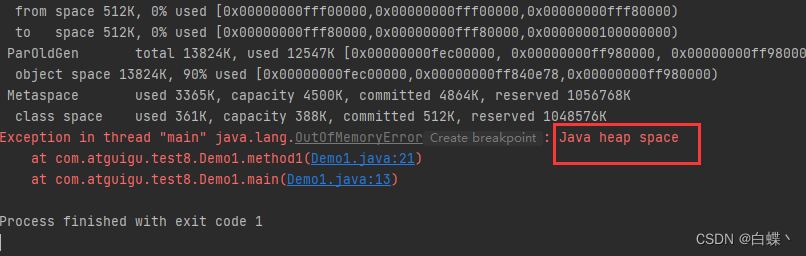
Before we test , You have to set it jvm Parameters , Set the size of heap memory to 20mb, And print GC Information
-Xmx20m -XX:+PrintGCDetails -verbose:gc
function method1, because list Is a strong quote ,jvm Instead of recycling, an exception is reported
function method2, At this point we are list In the collection Soft reference objects , On the fifth trip list When you store data in , Insufficient memory will trigger full gc, Recycle soft referenced objects 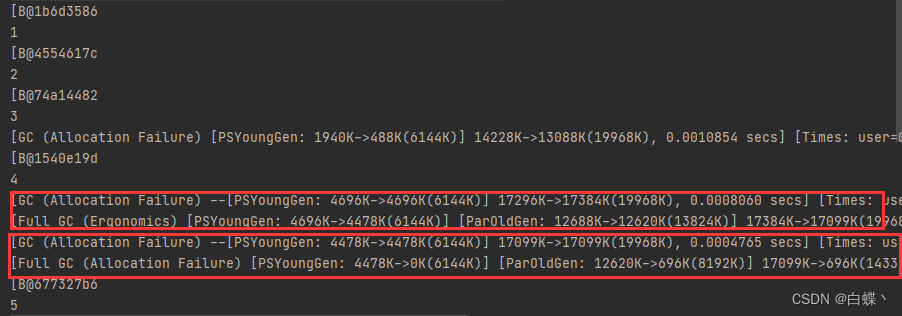
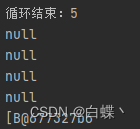
The above does not recycle the soft reference itself , Recycling soft references requires the use of reference queues , Modify the code as follows 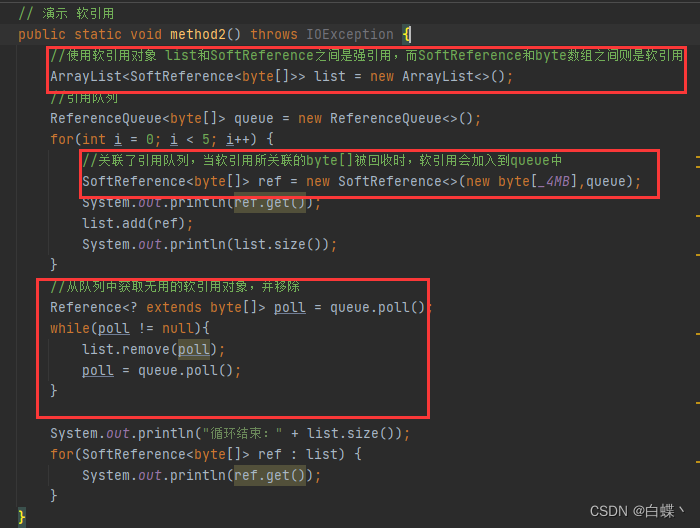
3、 ... and 、 Garbage collection algorithm
1. Mark - Clear algorithm
The algorithm is divided into “ Mark ” and “ eliminate ” Stage : First mark all objects that do not need to be recycled , After the completion of the marking, all unmarked objects will be recycled . It's the most basic collection algorithm , The follow-up algorithm is to improve its shortcomings to get . This garbage collection algorithm will generate memory fragments
The blue color in the figure below is marked , Objects that do not need recycling 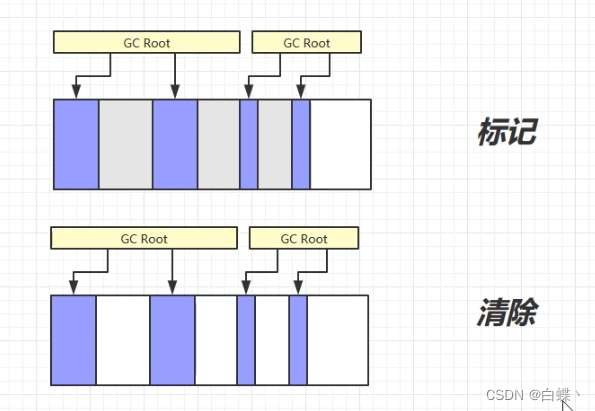
2. Mark - Copy algorithm
The marking process is still associated with “ Mark - eliminate ” Algorithm is the same , But the next step is not to recycle the recyclable objects directly , It's about moving all the living objects to one end , Then directly clean up the memory outside the end boundary , Low efficiency 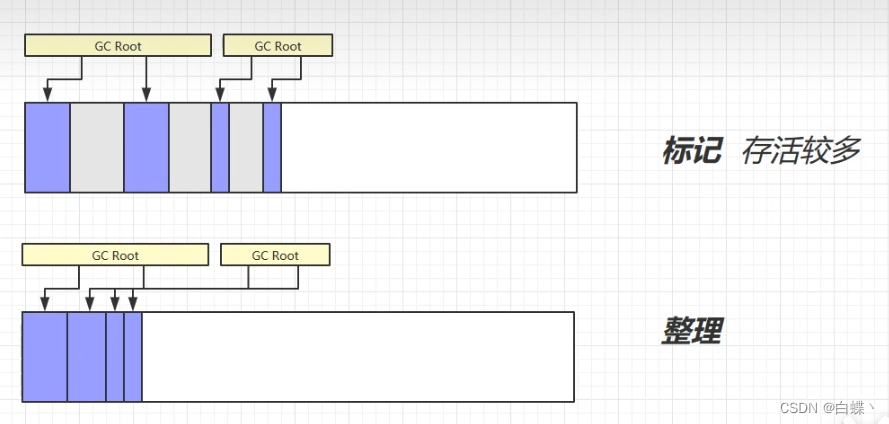
3. Mark - Copy algorithm
To solve the problem of efficiency ,“ Mark - Copy ” The collection algorithm appears . It can divide memory into two blocks of the same size , Use one of them at a time . When this block of memory is used up , Copy the surviving objects to another piece , Then clean up the used space once more . In this way, every time the memory is recycled, half of the memory interval is recycled , The disadvantage is that more memory is needed ( double )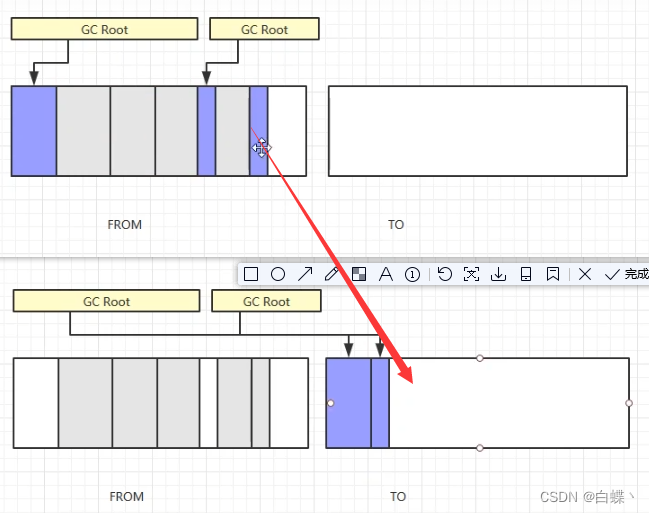
4. Generational collection algorithm
At present, the garbage collection of virtual machine adopts the generational collection algorithm , It divides the memory into several blocks according to the different life cycle of the object . Generally will java The heap is divided into the new generation and the old generation , In this way, we can choose the appropriate garbage collection algorithm according to the characteristics of each era .
For example, in the new generation , A lot of objects die in every collection , So you can choose ” Mark - Copy “ Algorithm , Each garbage collection can be completed with a small amount of object replication cost . In the old age, the survival rate of objects is relatively high , And there's no extra space to guarantee its distribution , So we have to choose “ Mark - eliminate ” or “ Mark - Arrangement ” Algorithm for garbage collection .
The following are the specific steps of the generational collection algorithm
1. The new object enters the garden of Eden 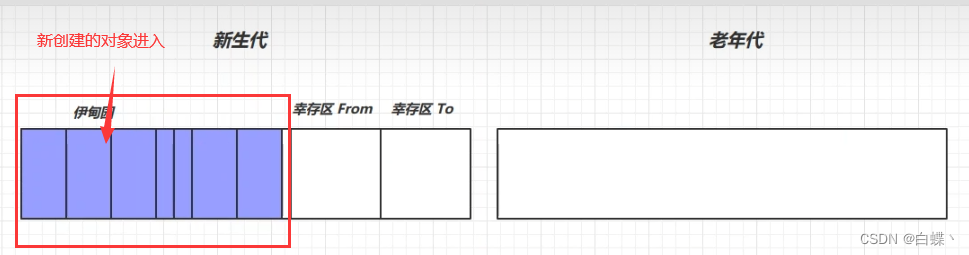
2. When the memory in Eden is full , Trigger MirrorGC, Can use replication algorithm , Copy living objects into To District , And life plus 1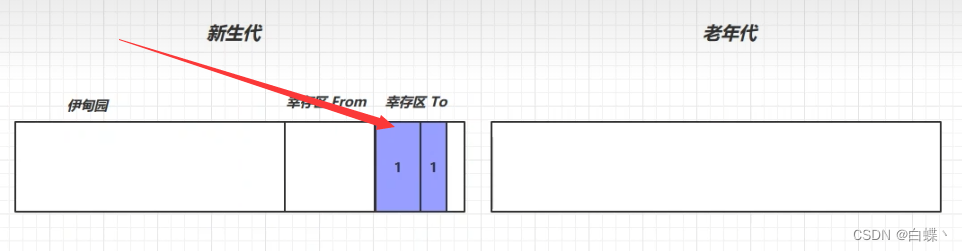
3. take To Area and From Zone Exchange ( It's the replication algorithm ), Always keep To The area is empty 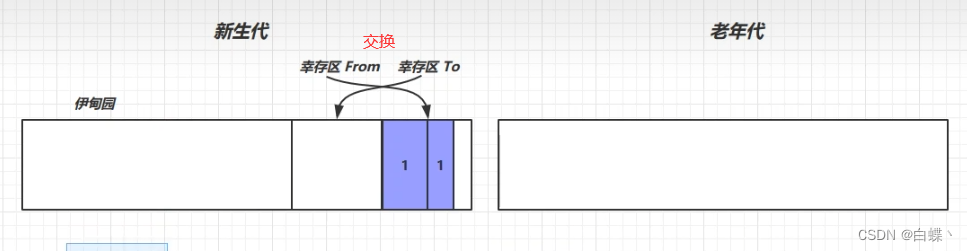
The next one 2 Change to 1( embarrassed )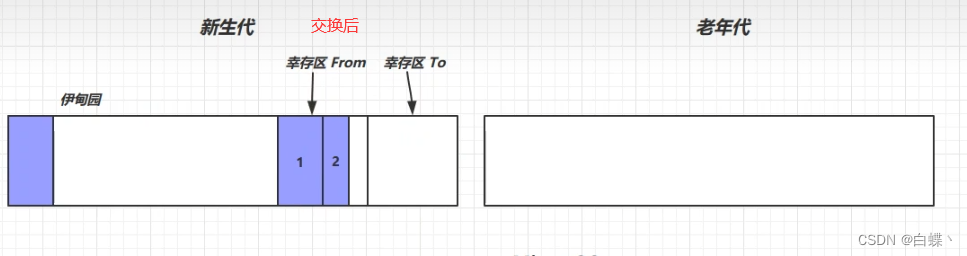
4. Go round and begin again , When someone reaches 15( Not absolutely ) Object still alive , Will enter the elderly generation area 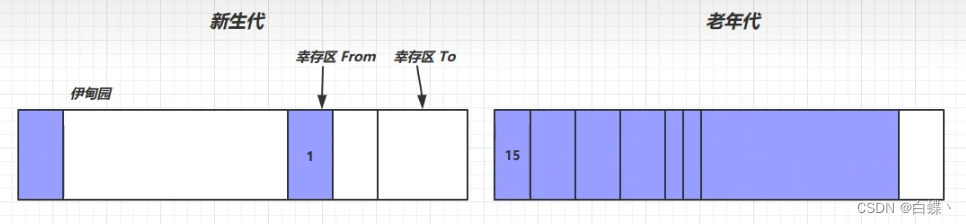
5. If the memory of the new generation and the old generation is full , It will trigger first Minor GC, Trigger again Full GC, Scan all objects that are no longer used in the new and old generations and recycle ;
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
H3C vxlan configuration
Expérience de port série - simple réception et réception de données
selenium自动化集成,八年测试经验软测工程师,一篇文章带你学懂
Enterprise manager cannot connect to the database instance
Calf problem
Original collection of hardware bear (updated on May 2022)
Count the number of words in the string c language
Simulation volume leetcode [general] 1706 Where does the ball meet
外部中断实现按键实验
PPT模板、素材下载网站(纯干货,建议收藏)
The essence of high availability
Nanjing commercial housing sales enabled electronic contracts, and Junzi sign assisted in the online signing and filing of housing transactions
数据在内存中的存储
On December 8th, 2020, the memory of marketing MRC application suddenly increased, resulting in system oom
面试题:高速PCB一般布局、布线原则
[chaosblade: delete pod according to the tag, pod domain name access exception scenario, pod file system i/o failure scenario]
Simulation volume leetcode [general] 1557 The minimum number of points that can reach all points
RuntimeError: Calculated padded input size per channel: (1 x 1). Kernel size: (5 x 5). Kernel size c
最长上升子序列模型 AcWing 1017. 怪盗基德的滑翔翼
Recommended by Alibaba P8, the test coverage tool - Jacobo is very practical