当前位置:网站首页>C language pointer (Part 2)
C language pointer (Part 2)
2022-07-07 09:06:00 【A big cat 1201】
author : A big cat 1201
special column :《C Language learning 》
Maxim : You just try to , Leave the rest to time !
C Language pointer ( The next part )
stay C Language pointer ( medium-length ) in , Ben meow introduced some deeper uses of pointers and pointer types , Next, Ben meow will introduce some pointers and usage of more seconds .
Array 、 The pointer passes the parameter
When we call a function , Pointer variable types and arrays are often passed to functions as arguments to achieve the desired purpose .
One dimensional array parameters
We know , When passing parameters to a one-dimensional array , Mainly pass the array name , The array name of a one-dimensional array is essentially the address of the first element of the array , So it's equivalent to sending an address .
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
test(arr);
return 0;
}
We pass such an array to test() Function time , What can formal parameters be ?
- Formal parameters can be arrays
void test(int arr[])
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);// Print elements in an array
}
}
Array access operator ([]) The number of array elements in can be omitted , You can also write .
- Formal parameters can be pointers
void test(int* str)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("%d ", *(str + i));// Print elements in an array
}
}
Arguments are array names , The essence is the first address element , So the address passed is the address of an element , You only need one int * The pointer of type can be received .
- Formal parameters can be array pointers
void test(int(*parr)[10])
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("%d ", *(*(parr)+i));// Print elements in an array
//printf("%d ", *(parr)[i]);
}
}
Of course , The real argument in the main function here is & Array name , Although this method is not often used , But also in a way of one-dimensional array parameter transfer .
The principle of pointer array is the same as that of one-dimensional array , Just different types , Please try it yourself .
Two dimensional array parameters
When transferring parameters to a two-dimensional array , Similarly, the main parameter passed is the array name , The essence of the array name of a two-dimensional array is the address of the first element .
int main()
{
int arr[3][5] = {
1,2,3,4,5,2,3,4,5,6,3,4,5,6,7 };
test(arr);
return 0;
}
Pass the array name of such a two-dimensional array as an argument to test() Function , What can formal parameters be ?
- Formal parameters can be two-dimensional arrays
void test(int arr[3][5])
{
// Print 2D array
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
Formal parameters can be written as two-dimensional arrays , Only rows can be omitted from the subscripts of rows and columns , You can't omit Columns , You can also write . namely
void test(int arr[][5])
void test(int arr[3][5])
and
void test(int arr[3][])
void test(int arr[][])
These two ways of writing are wrong .
- Formal parameters can be array pointer types
{
// Print 2D array
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
printf("%d ", *(*(parr + i) + j));
//printf("%d ", *(parr + i)[j]);
}
}
}
Because the array name of a two-dimensional array is the address of the first element , It's equivalent to having 5 The address of a one-dimensional array of elements , So the formal parameter must be received by the array pointer variable type . This is also the scene where array pointers are often used .
First level pointer parameter transfer
The content in the first level pointer variable is the address of a variable .
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int* pa = &a;
tset(pa);
return 0;
}
When such a pointer variable is used as an argument , Formal parameters can only be of the same pointer variable type .
void test(int* pa)
{
printf("%d\n", *pa);
}
If we only give that the formal parameter type is a pointer variable
void test(int* pa)
What can arguments be ?
int a = 10;
int* pa = &a;
test(pa);
Arguments can be first-order pointer variables .
int a = 10;
test(&a);
An argument can be an address to a variable .
int arr[10] = {0};
test(arr);
The argument can be a int Array name of one-dimensional array of type .
The secondary pointer transmits parameters
The content of the secondary pointer variable is the address of the primary pointer variable .
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int* pa = &a;
int** ppa = &pa;
test(ppa);
return 0;
}
When such a pointer variable is used as an argument , The formal parameter can only be a secondary pointer variable of the same type .
void test(int** ppa)
{
printf("%d\n", **ppa);
}
Similarly, if the type of the formal parameter given to us is a secondary pointer variable type, what can the argument be ?
void test(int** ppa)
So what can the argument be ?
int a = 10;
int* pa = &a;
int** ppa = &pa;
test(ppa);
Arguments can be secondary pointer variables .
int a = 10;
int* pa = &a;
test(&pa);
The argument can be the address of the first level pointer variable .
int* arr[10] = {
0};
test(arr);
The argument can be the array name of the pointer array .
A function pointer
The function pointer is a pointer to a very second , It can make it more convenient for us to call functions .
Let's start with a piece of code :
void test()
{
printf("hehe\n");
}
int main()
{
printf("%p\n", test);
printf("%p\n", &test);
return 0;
}
Print function name and address function name respectively 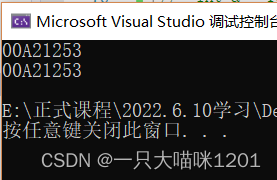
You can see that the result is the same .
The address of a function is the address of the function name .
The function name does not take the address , Its essence is also the address of the function .
So when we use function addresses , You can address the function name , You can also not take the address , All we get is the address of the function .
We got the address of a function , You have to put it in a variable , So what kind of variable should the address of the function be placed in ?
void test()
{
printf("hehe\n");
}
int main()
{
void (*pf)() = test;
printf("%p\n", test);
printf("%p\n", &test);
printf("%p\n", pf);
return 0;
}
Or the code above , We create a function pointer variable , Put the address of the function in the function pointer variable .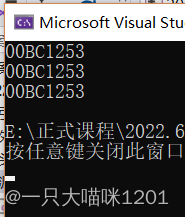
You can see , The value of the function pointer variable is the same as the value of the function name and the address function name .
Such a variable is the function pointer variable .
Function pointer variable creation rules .
void (*pf)() = test;
The left side of the equal sign of this statement can be written in three parts ,void, * pf,().
- pf The first and * It's a combination of , This indicates that this is a pointer variable .
- And then with the back (), That is, the function call operator , It shows that this is a function pointer variable
- and () There is nothing in brackets , It indicates that the formal parameter of the function pointed to by the function pointer has no content .
- void The return type of the function pointed to by the function pointer is void
According to this rule, we will implement a function that adds two numbers
int Add(int x, int y) { return x + y; }The address of is placed in a pointer variable
int main() { int (*pf)(int, int) = Add; return 0; }
After the function pointer variable is created, we will use .
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int (*pf)(int, int) = Add;
int sum1 = pf(a, b);
int sum2 = (*pf)(a, b);
int sum3 = (**pf)(a, b);
printf("sum1 = %d\n", sum1);
printf("sum2 = %d\n", sum2);
printf("sum3 = %d\n", sum3);
return 0;
}
In the above code, we call it through function pointer variables Add function , And print out the results , But we use function pointer variables in three different ways .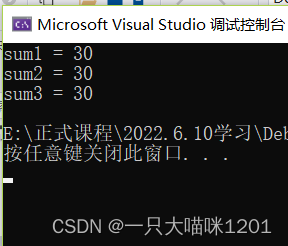
But their results are the same .
When the function takes the address
- Function name whether there is & What we get from the address operator is the address of the function
When using function pointer variables
- Function pointer variable, whether there is * The dereference operator calls this function
So the dereference operator * It's a decoration , Does it , Or there are many that do not affect function calls .
The use of function pointers
We have always used the function name when calling , Feeling and nature are also very convenient , So why should there be function pointer variables ? Is it unnecessary to call functions through function pointer variables ?
We write a simple calculator
#include <stdio.h>
void menu()
{
printf("************************\n");
printf("****1. Add 2. Sub****\n");
printf("****3. Mul 4. Div****\n");
printf("***** 0.exit *****\n");
printf("************************\n");
}
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int Sub(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}
int Mul(int x, int y)
{
return x * y;
}
int Div(int x, int y)
{
return x / y;
}
int main()
{
int input = 0;
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
int sum = 0;
do
{
menu();
printf(" Please select the function :>");
scanf("%d", &input);
switch (input)
{
case 1:
printf(" Please enter two numbers :>");
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
sum = Add(a, b);
printf(" The result is :%d\n", sum);
break;
case 2:
printf(" Please enter two numbers :>");
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
sum = Sub(a, b);
printf(" The result is :%d\n", sum);
break;
case 3:
printf(" Please enter two numbers :>");
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
sum = Mul(a, b);
printf(" The result is :%d\n", sum);
break;
case 4:
printf(" Please enter two numbers :>");
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
sum = Div(a, b);
printf(" The result is :%d\n", sum);
break;
case 0:
printf(" sign out \n");
break;
default:
printf(" Wrong choice \n");
break;
}
}
while (input);
return 0;
}
The above is a program that can realize simple addition, subtraction, multiplication and division 
We can see , stay switch In the sentence , The code in each case has many repetitive parts , Only the functions called are different , In this way, the code will be redundant .
- We can extract different parts of this code
- Then write it as a function
- In each case, just call this function
- In this way, the code will no longer be redundant
void caul(int (*pf)(int, int))
{
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
int sum = 0;
printf(" Please enter two numbers :>");
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
sum = pf(a, b);
printf(" The result is :%d\n", sum);
}
Create a caul function , Formal parameters are function addresses that receive different functions , So you need a function pointer variable type .
Call different function modules through function pointer variables .
In this way , In each case, only different parts are left , The redundant parts are encapsulated in caul Function , And only one .

This is the result of its execution
Through the comparison of the two codes , We found that , Using function pointers to call functions can make the code more concise .
Function pointer array ( Transfer table )
Ben meow introduced pointer arrays in previous articles , Replace the element types in the pointer array with function pointers of the same type , The result is an array of function pointers .
int (*arr[5])(int, int) = {
0,Add,Sub,Mul,Div };
This code is the address of the four functions of the calculator function above and one 0 The address is placed in the function pointer array arr in .
Function pointer array creation rule
int (*arr[5])(int, int) = { 0,Add,Sub,Mul,Div }; This statement can be split into two parts
- arr[5] and int (*)(int, int)
arr The first and [] combination , After the combination is an array , Array has 5 Elements .
Get rid of arr[5] The rest is the type of the elements in the array .
- The rest int (*)(int, int) Is a function pointer type
- The return type of the function pointed to by this pointer is int type , The types of the two formal parameters are also int type
So we know a specific situation of the array .
Use of function pointer array
Or the code of the calculator above , Let's implement the same function in another way .
int main()
{
int (*arr[5])(int, int) = {
0,Add,Sub,Mul,Div };// To correspond to menu functions , Complement in array 1 individual 0
int input = 0;
do
{
menu();
printf(" Please select the function :>");
scanf("%d", &input);
if (input == 0)
{
printf(" sign out \n");
break;
}
else if (input >= 1 && input <= 4)
{
caul(arr[input]);
}
else
{
printf(" Wrong choice \n");
}
}
while (input);
return 0;
}
Just modify the code in the main function , Others can also realize the function of calculator without moving .
- The valid number entered is 1 To 4
- Numbers 1 To 4 Respectively corresponding to Add Function to Div Address of function
- Just pass the function pointer of the corresponding digital element to caul Function can call the corresponding function
This way is like looking up a table , The function pointer array is the table , So it is also called transfer table .
A pointer to an array of function pointers
A pointer to an array of function pointers —— Pointer to function array
It's a pointer , Same as pointer to array pointer array , It is also similar to the process of dolls .
int main()
{
int (*arr[5])(int, int) = {
0,Add,Sub,Mul,Div };
int (*(*parr)[5])(int, int) = &arr;
return 0;
}
The above code is to make a pointer variable parr Point to the function pointer array composed of calculator function modules .
Create rules
int (*(*parr)[5])(int, int) = &arr; The statement can be divided into two parts .
- (* parr)[5] and int (*)(int, int)
parr successively * It's a combination of , After the combination is a pointer variable
(* parr) And again [5] combination , After the combination is an array pointer , There are in the array pointed to 5 Elements , Type is a function pointer variable type
int (*)(int, int)
And the return type of the function pointer variable pointing to the function is int type , Both parameters are int type .
When we write code, we seldom write such code , Just recognize that this is a pointer to the function pointer array when encountering .
边栏推荐
- 年薪50w阿裏P8親自下場,教你如何從測試進階
- 2022-07-06 Unity核心9——3D动画
- PMP experience learning and sharing process
- Full link voltage test of the e-commerce campaign Guide
- [chaosblade: node CPU load, node network delay, node network packet loss, node domain name access exception]
- Synchronized underlying principle, volatile keyword analysis
- 模拟卷Leetcode【普通】1706. 球会落何处
- Upgrade Alibaba cloud RDS (relational database service) instance to com mysql. jdbc. exceptions. Troubleshooting of jdbc4.communicationsexception
- Panel display technology: LCD and OLED
- Alibaba P8 teaches you how to realize multithreading in automated testing? Hurry up and stop
猜你喜欢
【Istio Network CRD VirtualService、Envoyfilter】

PMP examination experience sharing
C language for calculating the product of two matrices

LeetCode 715. Range module

为不同类型设备构建应用的三大更新 | 2022 I/O 重点回顾
外部中断实现按键实验
Pointer advanced, string function
Goldbach conjecture C language
Two schemes of unit test
Explain Huawei's application market in detail, and gradually reduce 32-bit package applications and strategies in 2022
随机推荐
Full link voltage test of the e-commerce campaign Guide
Original collection of hardware bear (updated on June 2022)
LeetCode 715. Range 模块
面试题:高速PCB一般布局、布线原则
Simulation volume leetcode [general] 1557 The minimum number of points that can reach all points
Simple use of Xray
Analysis of Hessian serialization principle
端口复用和重映像
STM32串口寄存器库函数配置方法
systemd
PMP experience learning and sharing process
Enterprise manager cannot connect to the database instance
Goldbach conjecture C language
ChaosBlade:混沌工程简介(一)
串口實驗——簡單數據收發
Mountaineering team (DFS)
C语言指针(特别篇)
How long does the PMP usually need to prepare for the exam in advance?
面板显示技术:LCD与OLED
Calf problem
