当前位置:网站首页>Two schemes of unit test
Two schemes of unit test
2022-07-07 09:00:00 【bboyzqh】
principle
unit testing FIRST The principles are as follows
- Fast (fast): Unit tests should be run quickly , Otherwise, it will cost a lot of development / Deployment time .
- Isolation (isolated): Different test cases are isolated . One test does not rely on another test .
- repeatable (repeatable): Unit tests are repeatable , And when running repeatedly , Unit tests always give the same results ( The system environment is irrelevant ).
- Self verification (self-validating): Unit tests can verify their results , When they all pass , Give a simple “OK” The report , When they fail , You need to output concise details .
- In time (timely): Programmers before the code goes online , They should be written in time , To prevent bug.
Junit+Mockito+H2 database

The overall idea is to serve two parties API、 Configuration data are mock The way , Use a combination of H2 Memory database to initialize data to achieve the purpose of unit testing .
Two party service API use mock The way
To reduce unit test execution time , Need to remove two-party Services api And with mock Object substitution ,api mock The way is usually in Spring At startup mock Inject , namely mock Object replaces the real object . Here you can use Spring Self contained @TestExecutionListeners Annotation to unify mock Second party services api, The execution steps are as follows :

- establish TestContextManager
- Execute each one in turn AbstractTestExecutionListener Example of beforeTestClass Method
- Execute each one in turn AbstractTestExecutionListener Example of prepareTestInstance Method
- Spring Load and parse XML, In this process BeanFactoryPostProcessor
- When executing a test method , Execute each one in turn AbstractTestExecutionListener Example of beforeTestMethod Method
- Perform test methods
- Execute each one in turn AbstractTestExecutionListener Example of afterTestMethod Method
In the above way, press @Mock The objects marked by annotations can be unified mock, Do not load the external environment , Keep the environment isolated 、 The unit test runs fast . The detailed code is as follows :
public class MockitoBeansPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
Map<Class<?>, MockitoBeansTestExecutionListener.MockBeanWrapper> allMockBeans = MockitoBeansTestExecutionListener.resolvedAllMockBeans();
for (Map.Entry<Class<?>, MockitoBeansTestExecutionListener.MockBeanWrapper> mockBeanWrapperEntry : allMockBeans.entrySet()) {
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(mockBeanWrapperEntry.getKey(), mockBeanWrapperEntry.getValue().getMockObject());
beanFactory.registerSingleton(mockBeanWrapperEntry.getValue().getBeanName(), mockBeanWrapperEntry.getValue().getMockObject());
}
}
}
public class MockitoBeansTestExecutionListener extends DependencyInjectionTestExecutionListener {
private static Map<Class<?>, MockBeanWrapper> mockBeans = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private static Map<Class<?>, List<Field>> injectMockBeans = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private static boolean hasInitialized = false;
public static Map<Class<?>, MockBeanWrapper> resolvedAllMockBeans() {
Assert.isTrue(hasInitialized);
return Collections.unmodifiableMap(mockBeans);
}
@Override
public void beforeTestClass(TestContext testContext) throws Exception {
Field[] declaredFields = testContext.getTestClass().getDeclaredFields();
// Get the parent class Mock Method
Field[] superClassFields = testContext.getTestClass().getSuperclass().getDeclaredFields();
List<Field> mockFields = Lists.newArrayList(declaredFields);
if (superClassFields.length > 0) {
mockFields.addAll(Lists.newArrayList(superClassFields));
}
// Will need mock The object is created
for (Field field : mockFields) {
Mock mockAnnon = field.getAnnotation(Mock.class);
if (mockAnnon != null) {
field.setAccessible(true);
MockBeanWrapper wrapper = new MockBeanWrapper();
Class<?> type = field.getType();
wrapper.setMockObject(Mockito.mock(type));
wrapper.setBeanType(type);
wrapper.setBeanName(StringUtils.isEmpty(mockAnnon.value()) ? field.getName() : mockAnnon.value());
mockBeans.putIfAbsent(wrapper.getBeanType(), wrapper);
injectMockBeans.compute(testContext.getTestClass(), (targetClass, waitInjectFields) -> {
if (waitInjectFields == null) {
waitInjectFields = new ArrayList<>();
}
waitInjectFields.add(field);
return waitInjectFields;
});
}
}
hasInitialized = true;
}
@Override
public void beforeTestMethod(TestContext testContext) throws Exception {
Object testInstance = testContext.getTestInstance();
List<Field> fields = injectMockBeans.get(testContext.getTestClass());
if (fields != null) {
for (Field field : fields) {
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(testInstance, mockBeans.get(field.getType()).getMockObject());
}
}
}
@Data
public class MockBeanWrapper {
private String beanName;
private Class<?> beanType;
private Object mockObject;
}
}
// Unit test base class
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = {"classpath:promotion/config/application-unittest.xml"})
@TestExecutionListeners({MockitoBeansTestExecutionListener.class,
TransactionalTestExecutionListener.class,
SqlScriptsTestExecutionListener.class})
public abstract class AbstractTest {
@Mock
protected LogisticService logisticService;
@Mock
protected ItemBatchSpecService itemBatchSpecService;
//......
}
H2 Data initialization of memory database
H2 Database is an embedded memory database , Its grammar and MySQL The grammar is very close to , It is very suitable for unit test data preparation scenarios . So we need to achieve The data in the charge of this application directly depends on H2 Database storage , A single use case uses [email protected] Annotations prepare data separately , That is, the responsible method is not applied mock, From the upper layer to the real database call . The detailed configuration is as follows :
<jdbc:embedded-database id="dataSource" type="H2">
<jdbc:script location="classpath:common/common_schema.sql"/>
</jdbc:embedded-database>
<bean id="h2SqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:common/mybatis-config.xml"/>
<property name="mapperLocations">
<list>
<value>classpath:mapper/brule/Promotion*.xml</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="mapperScannerConfigurer" class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.yt.smc.dal.flashbuy.mapper,com.yt.smc.dal.brule.mapper"/>
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="h2SqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
Unit test examples
The unit test class only needs to inherit the unit test base class AbstractTest that will do , The sample code is as follows :
public class NoBatchPlaceOrderTest extends AbstractTest {
@Autowired
private TradeService tradeService;
@Sql("classpath:promotion/db/trade/placeorder/nobatch_place_order_01.sql")
@Test
public void testplaceOrderFinishTest1() {
Mockito.when(itemPriceService.skuPrice(any())).thenReturn(getNoBatchSkuPriceMap());
SmcResultData<List<CouponOwnerShareDTO>> smcResultData = new SmcResultData<>();
smcResultData.setData(Lists.newArrayList());
Mockito.when(couponTradeService.shareCouponOwner(any(), any())).thenReturn(smcResultData);
SmcResultData<PaceOrderFinishReDTO> paceOrderFinishResult = new SmcResultData<>();
PaceOrderFinishReDTO paceOrderFinishReDTO = new PaceOrderFinishReDTO();
paceOrderFinishResult.setData(paceOrderFinishReDTO);
Mockito.when(promotionPlaceExecuteService.placeOrderFinishPromotion(any(), any())).thenReturn(paceOrderFinishResult);
Mockito.when(itemSqueryAdapter.listItemByIds(Mockito.any())).thenReturn(getItemDetailList());
PlaceOrderRequestDTO requestDTO = buildPlaceOrderRequest1();
PlaceOrderResponseDTO responseDTO = tradeService.placeOrderFinish(requestDTO);
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(responseDTO));
Assert.assertNotNull(responseDTO);
Assert.assertEquals(1, responseDTO.getPromotionPlaceOrderDTOS().size());
Assert.assertEquals(16900, responseDTO.getPromotionPlaceOrderDTOS().get(0).getOrderPrice().longValue());
Assert.assertEquals(1, responseDTO.getPromotionPlaceOrderDTOS().get(0).getPromotionPlaceActivityDTOs().size());
Assert.assertEquals(3000, responseDTO.getPromotionPlaceOrderDTOS().get(0).getPromotionPlaceActivityDTOs().get(0).getActivityCreatePrice().longValue());
}
Spock+Mockito+H2 database
use Spock Their ideas are basically the same Juit Think the same , The difference is in using groovy Language for writing unit tests . Use groovy Conduct unit testing based on behavior driven development (BDD) Thought , During unit testing, use cases need to be mapped to given、when and then, And Junit Compared with this way, it is closer to business expression . First, introduce dependencies as follows ( Pay attention to the matching version , Inconsistent versions may cause unit tests to fail ):
<!--Spock The test framework -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.spockframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spock-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.3-groovy-2.5</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.codehaus.groovy</groupId>
<artifactId>groovy-all</artifactId>
<version>2.4.4</version>
</dependency>Based on the above mock Idea creation AbstractSpockTest Base class , as follows :
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:promotion/config/application-unittest.xml")
@TestExecutionListeners([
MockitoBeansTestExecutionListener.class,
TransactionalTestExecutionListener.class,
SqlScriptsTestExecutionListener.class
])
abstract class AbstractSpockTest extends Specification {
@Mock
protected ItemBatchSpecService itemBatchSpecService;
//......
}
Examples of unit tests are as follows :
class UserTaskServiceSpockTest extends AbstractSpockMockTest {
@Autowired
private UserTaskService userTaskService;
@Sql("classpath:db/share/query_share_detail_info.sql")
@Unroll
def " The shared person scans the sharing code details unit test "() {
given:
Mockito.when(activityService.checkActivityById(any(), any())).thenReturn(getCheckReturnResult())
Mockito.when(activityService.checkUser(any(), any(), any())).thenReturn(getCheckReturnResult())
Mockito.when(iSnsUserServiceWrapper.getSnsUserById(any())).thenReturn(getSnsTaoBaoUserDTO())
ShareDetailQueryRequest shareDetailQueryRequest = new ShareDetailQueryRequest(shareCode: shareCode, userId: userId)
expect:
ServiceResult<ScanShareResultVO> result = userTaskService.queryShareDetailInfo(shareDetailQueryRequest)
result.getData().getSelf() == self
result.getData().getSourceUserId() == sourceUserId
where:
shareCode | userId | self | sourceUserId
"da0f4a99c41ff8cc3634830552239c8fb5503076ab" | 3L | false | 5L
"da0f4a99c41ff8cc3634830552239c899e683076ab" | 4L | true | 5L
}
}summary
The principles of the two implementation methods are the same , In terms of style "Spock+Mockito+H2 database " This method has less code 、 Closer to business expression , recommend !
边栏推荐
- OpenGL frame buffer
- 模拟卷Leetcode【普通】1705. 吃苹果的最大数目
- Output a spiral matrix C language
- Tronapi wave field interface - source code without encryption - can be opened twice - interface document attached - package based on thinkphp5 - detailed guidance of the author - July 6, 2022 - Novice
- Greenplum 6.x monitoring software setup
- JVM 垃圾回收 详细学习笔记(二)
- NCS Chengdu Xindian interview experience
- Enterprise manager cannot connect to the database instance
- QT charts use (rewrite qchartview to realize some custom functions)
- Alibaba P8 teaches you how to realize multithreading in automated testing? Hurry up and stop
猜你喜欢

Oracle makes it clear at one time that a field with multiple separators will be split into multiple rows, and then multiple rows and columns. Multiple separators will be split into multiple rows, and
Ppt template and material download website (pure dry goods, recommended Collection)

LeetCode 715. Range module

C语言指针(下篇)

Expérience de port série - simple réception et réception de données
Explain Huawei's application market in detail, and gradually reduce 32-bit package applications and strategies in 2022
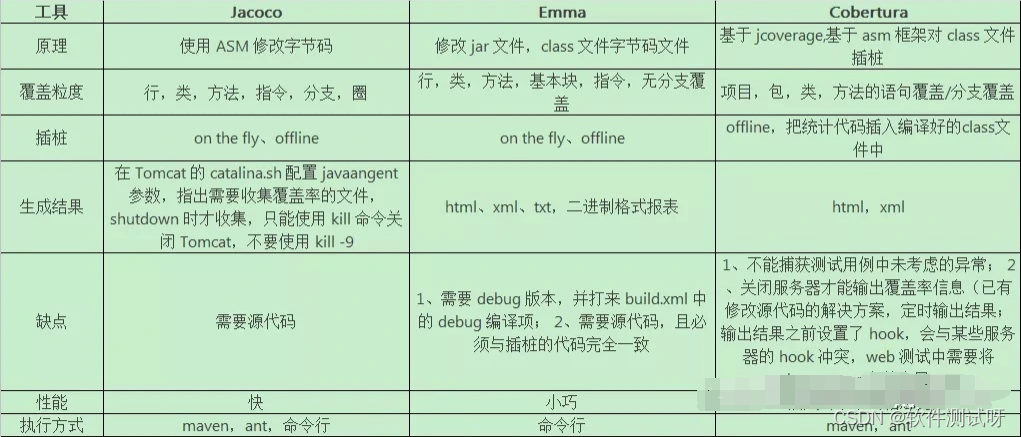
Recommended by Alibaba P8, the test coverage tool - Jacobo is very practical
2022-07-06 unity core 9 - 3D animation

Nanjing commercial housing sales enabled electronic contracts, and Junzi sign assisted in the online signing and filing of housing transactions
C语言指针(习题篇)
随机推荐
Greenplum 6.x build_ install
Explain Huawei's application market in detail, and gradually reduce 32-bit package applications and strategies in 2022
Opencv converts 16 bit image data to 8 bits and 8 to 16
Expérience de port série - simple réception et réception de données
Category of IP address
数字三角形模型 AcWing 275. 传纸条
UnityShader入门精要个人总结--基础篇(一)
Introduction to data fragmentation
Simulation volume leetcode [general] 1557 The minimum number of points that can reach all points
C语言指针(中篇)
go mod module declares its path as: gtihub. com/xxx-xx but was required as:xx-xx
面板显示技术:LCD与OLED
NCS Chengdu Xindian interview experience
Skills that testers must know: Selenium's three waiting ways are interpreted clearly
Count the number of words C language
测试人一定要会的技能:selenium的三种等待方式解读,清晰明了
串口实验——简单数据收发
实现自定义内存分配器
Unity Shader入门精要初级篇(一)-- 基础光照笔记
数字三角形模型 AcWing 1027. 方格取数