当前位置:网站首页>Semantic segmentation | learning record (4) expansion convolution (void convolution)
Semantic segmentation | learning record (4) expansion convolution (void convolution)
2022-07-08 02:09:00 【coder_ sure】
List of articles
- Preface
- One 、 Expansion convolution
- Two 、gridding effect
- 3、 ... and 、 When using multiple expansion convolutions , How to set the expansion coefficient ?
- Four 、 Suggestions for setting expansion coefficient
- 5、 ... and 、 Whether it is applied HDC Comparison of segmentation effects of design criteria
- 6、 ... and 、 summary
- Reference material
Preface
This blog mainly introduces the knowledge of dilation convolution , Expansion convolution (Dilated convolution) Also called void convolution (Atrous convolution). When I first came into contact with this word, I really see deeplabv3+ I came across this word when I was writing my thesis , Here is a detailed introduction .
One 、 Expansion convolution
The following figure shows ordinary convolution :k=3,r=1,p=0,s=1
The following figure shows expansion convolution :k=3,r=2,p=0,s=1
We can find that these two convolutions are also used 3*3 Of kernel, But in expansion convolution ,kernel There is a gap , We call it Expansion factor r.
What's the use of expanding convolution ?
- Increase the receptive field
- Keep the original input characteristic graph W,H( Pictured above , In actual use, it will padding Set to 1 In this way, we can ensure that the size of the feature map remains unchanged )
Why use dilation convolution ?
In image classification network, we usually need to carry out multiple down sampling , Compare the following sampling 32 times , After that, the size of the original image will be restored by upsampling , But too much down sampling has a great impact on our restoration to the original image . take VGG16 Take the Internet as an example , stay VGG16 Through the Internet maxpooling Operate to down sample the picture to reduce the length and width , But doing so will lose some details and particularly small goals . And it cannot be restored through up sampling .
Someone will say , Then we will maxpooling Can you remove the layer ? Get rid of maxpooling Layer is not a good method , This will reduce the receptive field .
So expansion convolution solves this problem , It can increase the receptive field , It can also ensure that the height and width of the input and output characteristic graph will not change .
Two 、gridding effect
Understanding Convolution for Semantic Segmentation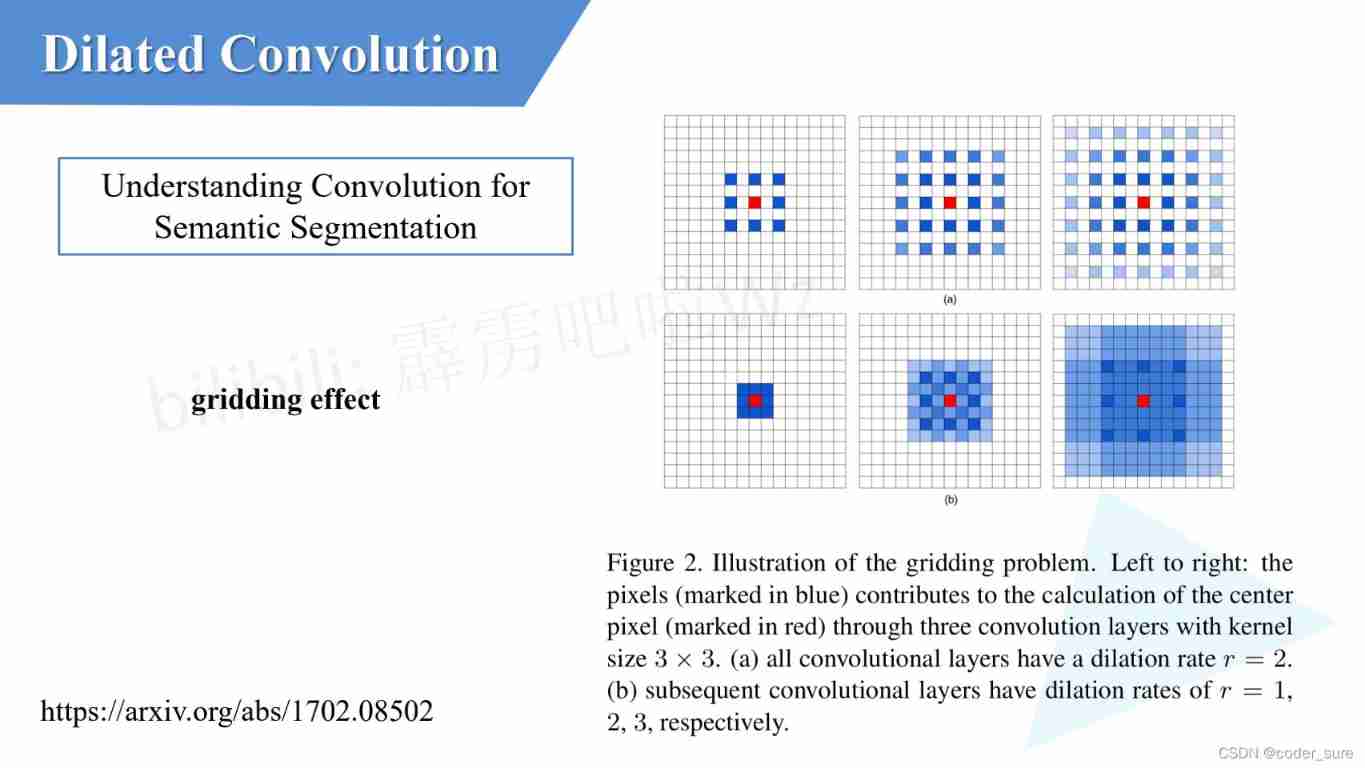
There are four convolutions in the figure below :layer1 To Layer4 the 3 The operational convolution kernel of sub expansion convolution is 3 ∗ 3 3*3 3∗3, The coefficient of expansion is r2
Let's take a detailed look layer2 We used Layer1 What data is on ?
We see layer2 The previous pixel will be used as shown in the following figure 9 individual layer1 Parameters in position 
Look again. layer3 We used Layer1 What data is on ?
We see layer3 The previous pixel will be used as shown in the following figure 25 individual layer1 Parameters in position 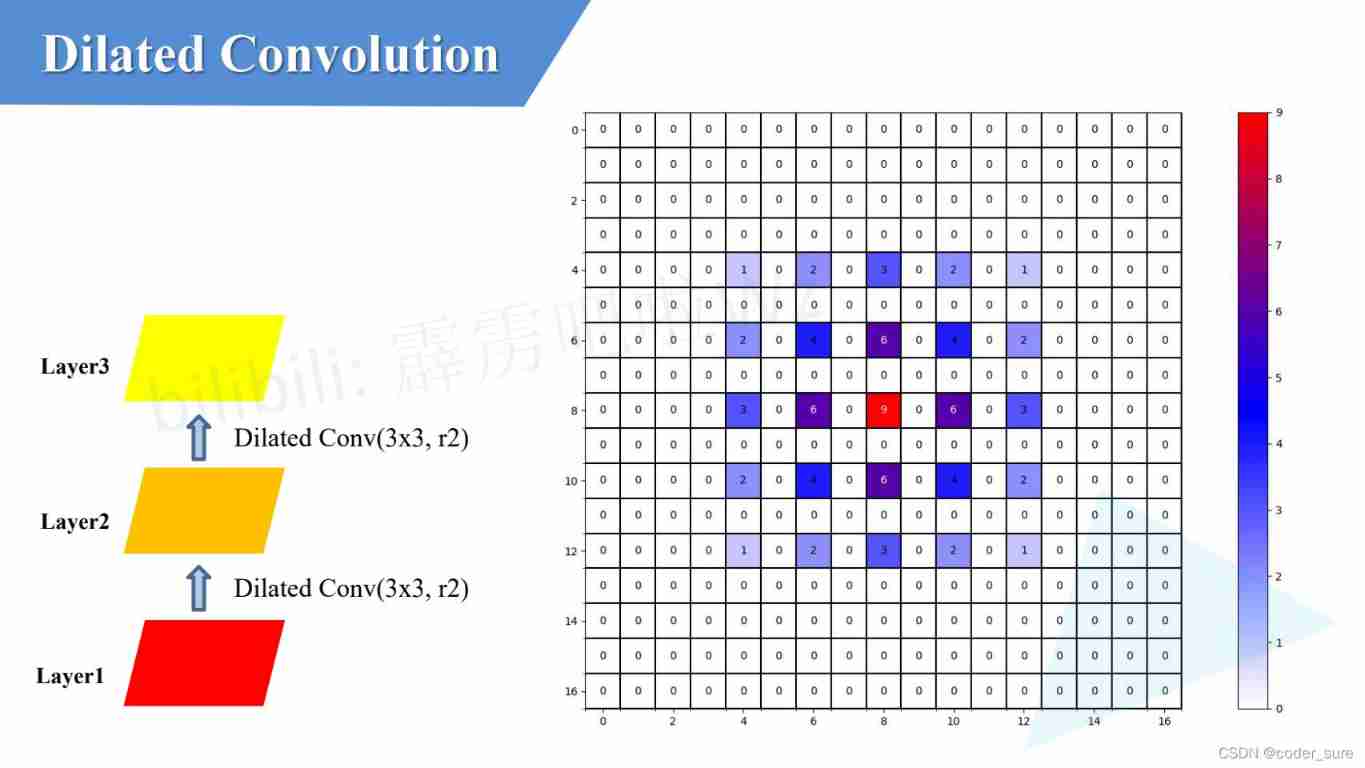
Look again. layer4 We used Layer1 What data is on ?
We see layer4 The previous pixel will be used as shown in the following figure 49 individual layer1 Parameters in position 
At this time, we can observe , The underlying image pixels we use through dilation convolution are not continuous , There is a gap between every non-zero element , This will inevitably lead to the loss of feature information , This is gridding effect problem , We should also try to avoid gridding effect problem .
If we design the expansion factor of the cubic expansion convolution operation in the above figure r1,r2,r3 In the form of :

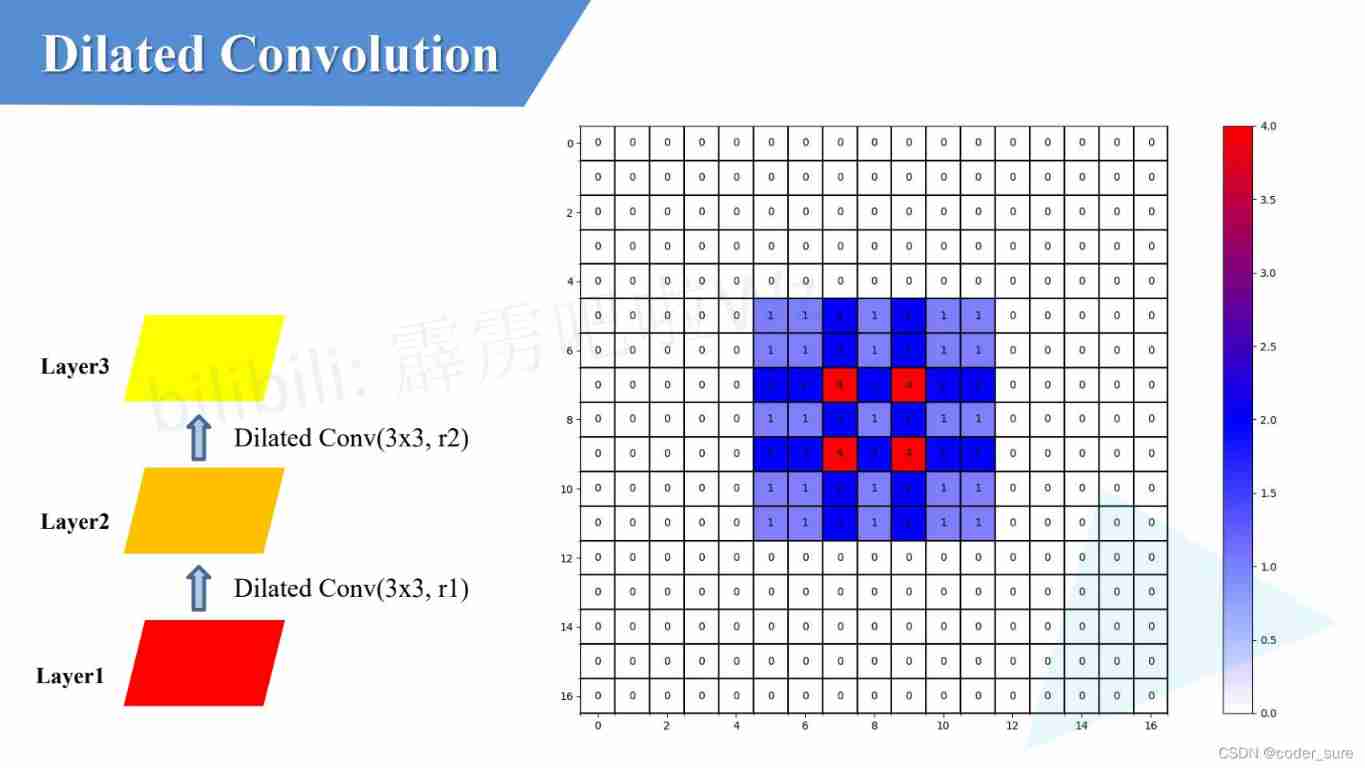
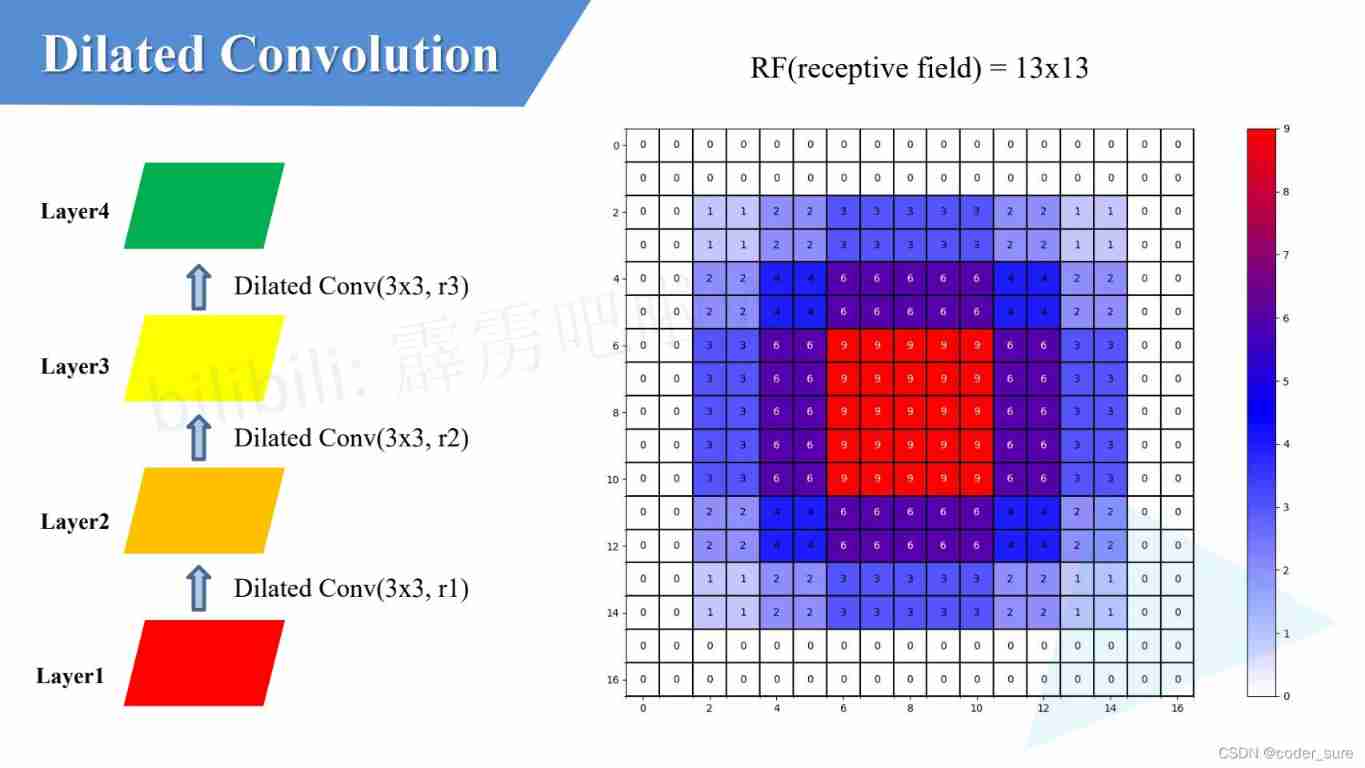
After setting the expansion coefficient in this way , The underlying information we use is continuous !
Let's look at a group of experiments , If you use ordinary convolution :
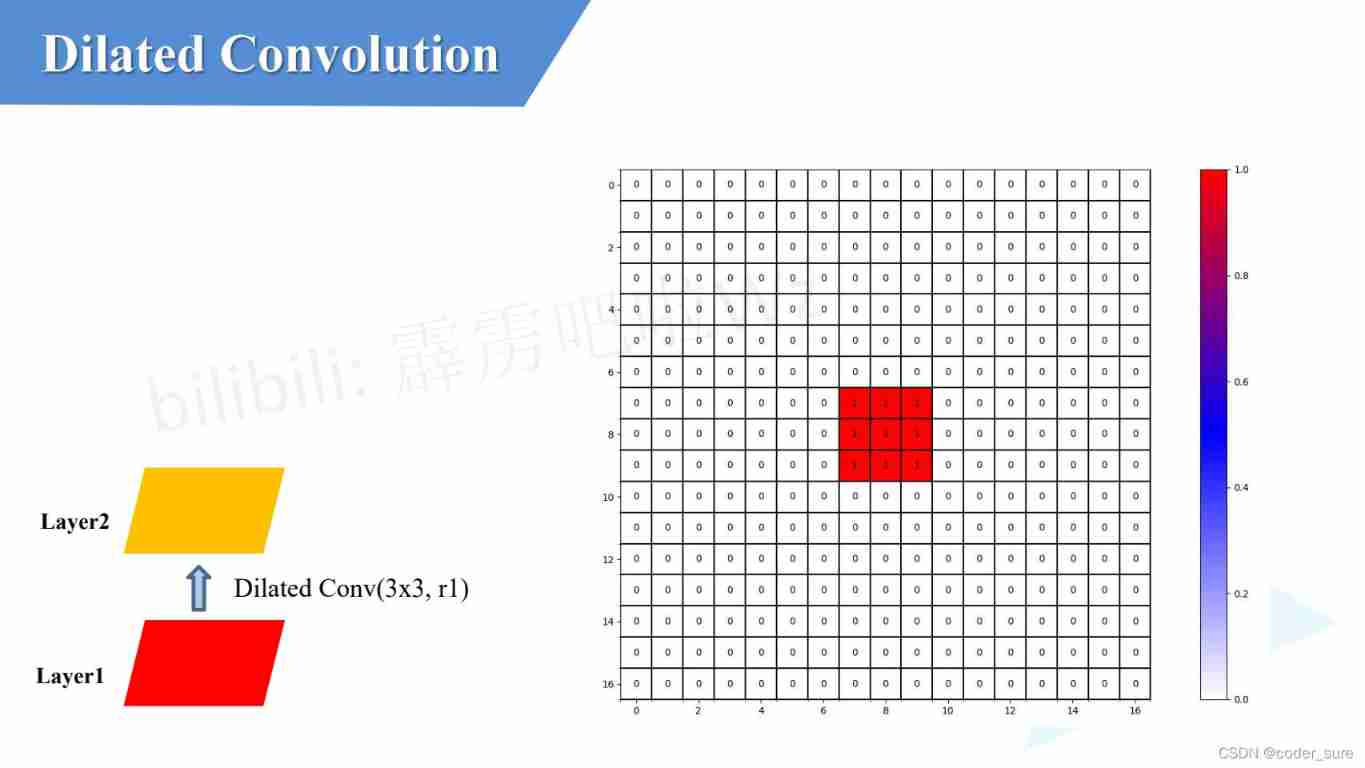


Obviously, we can see that under the same parameters, the receptive field of ordinary convolution is smaller than that of dilated convolution .
3、 ... and 、 When using multiple expansion convolutions , How to set the expansion coefficient ?
Understanding Convolution for Semantic Segmentation The method is given in this paper .
We can see in the experiment just now , The expansion coefficients used are 1,2,3 The effect of continuous convolution is better than that of convolution with the same expansion coefficient . So how to design the coefficient ? The author puts forward HDC Design criteria :
Let's use the actual code to test these two groups of examples of setting the expansion convolution coefficient in the paper :
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import LinearSegmentedColormap
def dilated_conv_one_pixel(center: (int, int),
feature_map: np.ndarray,
k: int = 3,
r: int = 1,
v: int = 1):
""" The center of the expanded convolution kernel is in the specified coordinate center Location time , Count which pixels are used , And an increment is added at the utilized pixel position v Args: center: The coordinates of the center of the expanded convolution kernel feature_map: A characteristic diagram that records the number of times each pixel is used k: Expansion convolution kernel kernel size r: Dilated convoluted dilation rate v: Use times increment """
assert divmod(3, 2)[1] == 1
# left-top: (x, y)
left_top = (center[0] - ((k - 1) // 2) * r, center[1] - ((k - 1) // 2) * r)
for i in range(k):
for j in range(k):
feature_map[left_top[1] + i * r][left_top[0] + j * r] += v
def dilated_conv_all_map(dilated_map: np.ndarray,
k: int = 3,
r: int = 1):
""" According to which pixels in the output characteristic matrix are used and how many times they are used , With expansion convolution k and r Calculate which pixels of the input characteristic matrix are used and how many times they are used Args: dilated_map: Record the characteristic diagram of the number of times each pixel is used in the output characteristic matrix k: Expansion convolution kernel kernel size r: Dilated convoluted dilation rate """
new_map = np.zeros_like(dilated_map)
for i in range(dilated_map.shape[0]):
for j in range(dilated_map.shape[1]):
if dilated_map[i][j] > 0:
dilated_conv_one_pixel((j, i), new_map, k=k, r=r, v=dilated_map[i][j])
return new_map
def plot_map(matrix: np.ndarray):
plt.figure()
c_list = ['white', 'blue', 'red']
new_cmp = LinearSegmentedColormap.from_list('chaos', c_list)
plt.imshow(matrix, cmap=new_cmp)
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_xticks(np.arange(-0.5, matrix.shape[1], 1), minor=True)
ax.set_yticks(np.arange(-0.5, matrix.shape[0], 1), minor=True)
# Show color bar
plt.colorbar()
# Mark the quantity in the drawing
thresh = 5
for x in range(matrix.shape[1]):
for y in range(matrix.shape[0]):
# Notice the matrix[y, x] No matrix[x, y]
info = int(matrix[y, x])
ax.text(x, y, info,
verticalalignment='center',
horizontalalignment='center',
color="white" if info > thresh else "black")
ax.grid(which='minor', color='black', linestyle='-', linewidth=1.5)
plt.show()
plt.close()
def main():
# bottom to top
dilated_rates = [1, 2, 3]
# init feature map
size = 31
m = np.zeros(shape=(size, size), dtype=np.int32)
center = size // 2
m[center][center] = 1
# print(m)
# plot_map(m)
for index, dilated_r in enumerate(dilated_rates[::-1]):
new_map = dilated_conv_all_map(m, r=dilated_r)
m = new_map
print(m)
plot_map(m)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
r=[1,2,3]:
r=[1,2,5]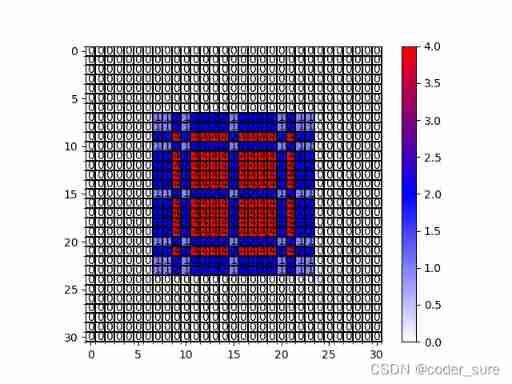
r=[1,2,9]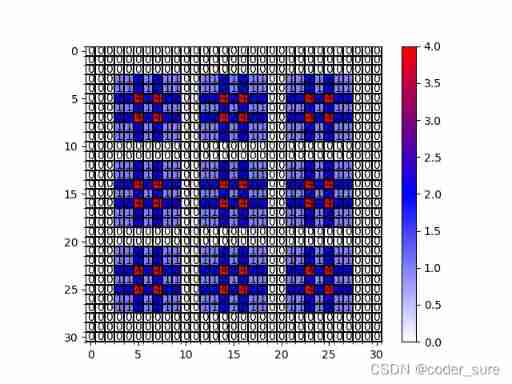
Four 、 Suggestions for setting expansion coefficient
- The suggestion is to dilation rates Set to sawtooth structure , for example
[1,2,3,1,2,3] - The common divisor of the expansion coefficient is not greater than 1
for example r=[2,4,8]: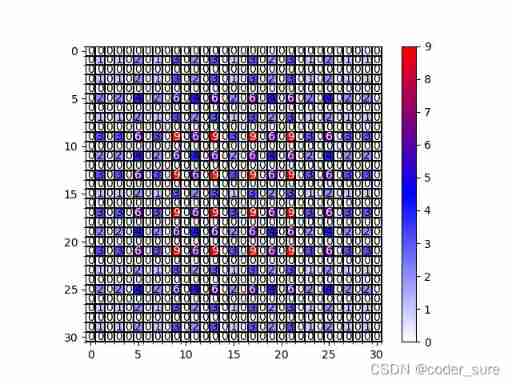
If the expansion coefficient is set in this way , The feature map we get is not zero pixels nor continuous .
5、 ... and 、 Whether it is applied HDC Comparison of segmentation effects of design criteria

The first line is GT, The second line is ResNet-DUC model, The third line is application HDC Design criteria , It is obvious that the scientific setting of expansion coefficient has a positive impact on the segmentation effect .
6、 ... and 、 summary
- Introduced what is expansion convolution
- The role of expansion convolution
- Why use expansion convolution
- Determination method and influence of expansion convolution expansion coefficient
Reference material
up Lord thunderbolt Wz Original video
Source code of the program
Understanding Convolution for Semantic Segmentation
边栏推荐
- 力扣6_1342. 将数字变成 0 的操作次数
- The way fish and shrimp go
- Apache multiple component vulnerability disclosure (cve-2022-32533/cve-2022-33980/cve-2021-37839)
- Ml self realization /knn/ classification / weightlessness
- Redission源码解析
- 需要思考的地方
- QT -- create QT program
- Apache多个组件漏洞公开(CVE-2022-32533/CVE-2022-33980/CVE-2021-37839)
- How mysql/mariadb generates core files
- leetcode 865. Smallest Subtree with all the Deepest Nodes | 865.具有所有最深节点的最小子树(树的BFS,parent反向索引map)
猜你喜欢

C语言-Cmake-CMakeLists.txt教程
metasploit

快手小程序担保支付php源码封装

leetcode 873. Length of Longest Fibonacci Subsequence | 873. 最长的斐波那契子序列的长度

进程和线程的退出

喜欢测特曼的阿洛

Introduction to grpc for cloud native application development
咋吃都不胖的朋友,Nature告诉你原因:是基因突变了
Ml self realization /knn/ classification / weightlessness
常见的磁盘格式以及它们之间的区别
随机推荐
Ml self realization /knn/ classification / weightlessness
银行需要搭建智能客服模块的中台能力,驱动全场景智能客服务升级
nmap工具介绍及常用命令
metasploit
Partage d'expériences de contribution à distance
Application of slip ring in direct drive motor rotor
Redisson分布式锁解锁异常
Alo who likes TestMan
Little knowledge about TXE and TC flag bits
I don't know. The real interest rate of Huabai installment is so high
Exit of processes and threads
关于TXE和TC标志位的小知识
node js 保持长连接
From starfish OS' continued deflationary consumption of SFO, the value of SFO in the long run
分布式定时任务之XXL-JOB
系统测试的类型有哪些,我给你介绍
【错误】加载h5权重出错AttributeError: ‘str‘ object has no attribute ‘decode‘
CorelDRAW2022下载安装电脑系统要求技术规格
JVM memory and garbage collection-3-direct memory
The generosity of a pot fish