当前位置:网站首页>Opencv (I) -- basic knowledge of image
Opencv (I) -- basic knowledge of image
2022-07-27 16:30:00 【Billie studies hard】
Course list :


Catalog
1.4 Application of digital image
2.3 Image resolution and image channel
2.4.2 Three channel histogram drawing
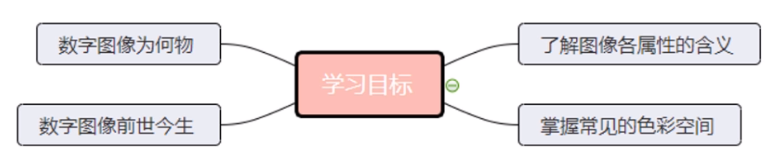
Learning goals :
1. Digital image
1.1 Digital image concept
- Digital image
- Digital image is also called digital image or digital image , yes A two-dimensional image is represented by a finite number of pixels , from Array or matrix Express .
- Digital image can be understood as a two-dimensional function f(x,y), among x and y It's space ( Plane ) coordinate , And the amplitude at any coordinate f Called the intensity or grayscale of the image at that point .
- Purpose of image processing
- Improve the information of the diagram so that people can explain
- For storage 、 Processing of images for transmission and presentation

1.2 Origin of digital image

1.3 Common imaging methods





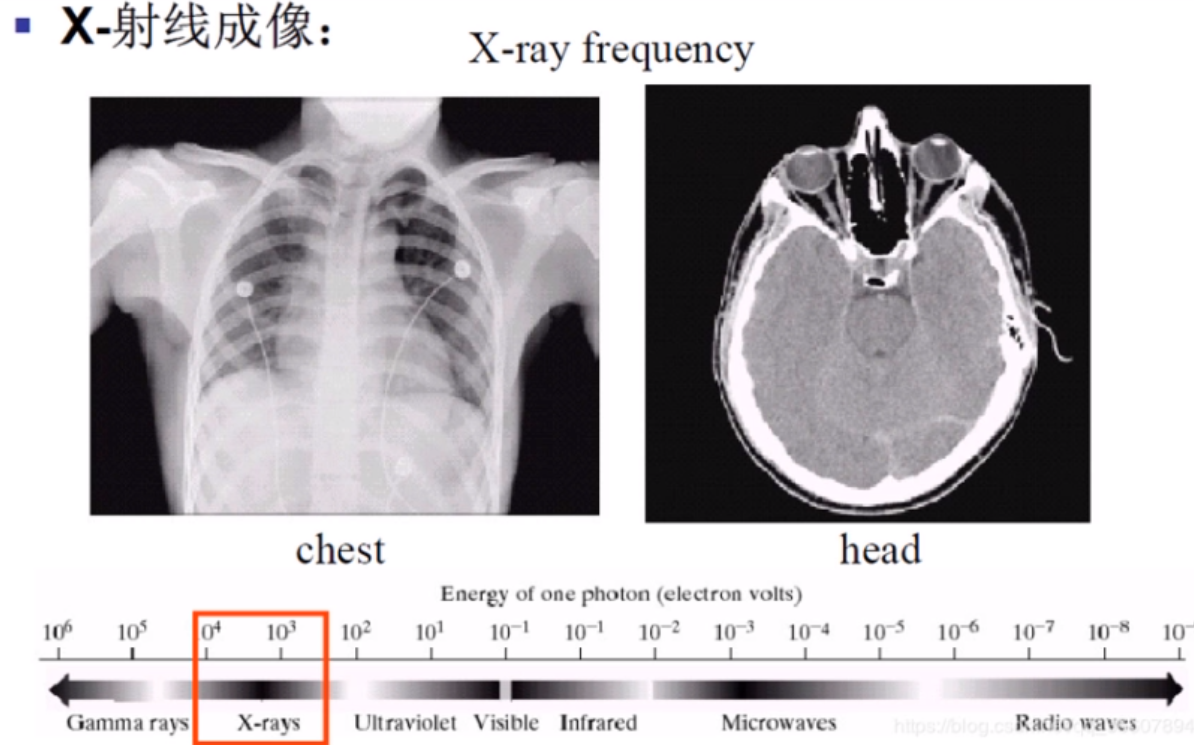











1.4 Application of digital image
The image processing 、 Machine vision 、 AI relationships
- Image processing mainly studies two-dimensional images , The process of dealing with the conversion between an image or a group of images , Include Image filtering , Image recognition , Image segmentation Other questions .
- Computer vision mainly studies the mapping to a single or multiple images Three dimensional scene , Extract abstract semantic information from images , Image understanding is the ultimate goal of computer vision .
- The goal of artificial intelligence in computer vision is to solve the relationship between pixel value and semantics , The main problem is image detection , Image recognition , Image segmentation and image retrieval .
1.5 OpenCV Introduce

2. Image properties
2.1 Image format
- BMP Format :Windows Under the system Standard bitmap format , Uncompressed , General image The files will be bigger . It is widely used in many software .
- JPEG Format : It is also one of the most widely used picture formats , It uses a special Lossy compression algorithm , Achieve a large compression ratio ( Accessible 2:1 even to the extent that 40:1), The most widely used format on the Internet .
- GIF: It can not only be a still picture , It can also be animation , And support transparent background images , Suitable for a variety of operating systems ,“ size ” Very small , A lot of small animations are on the Internet GIF Format . But its color gamut is not too wide , Only support 256 Medium color .
- PNG Format : And JPG The format is similar , Compression ratio higher than GIF, Support image transparency , Support Alpha Channel adjusts the transparency of the image .
- TIFF Format : Its characteristic is that the image format is complex 、 Store more information , stay Mac Widely used in , It is very conducive to the reproduction of the original . Many places will TIFF The format is used for printing .
2.2 Image size
- The length and width of image size are in pixels .
- Pixels (pixel)
- Pixel is the basic unit of digital image , Each pixel is a small dot , And the dots of different colors gather to become a moving picture .
- The range of gray pixel values is 0-255 Between ,0 It means black ,255 It means white , Other values indicate between black and white .
- The color map is represented by a two-dimensional matrix of red, green and blue channels . Each value is also in 0-255 Between ,0 Represents the corresponding primary color , and 255 Represents the maximum value of the corresponding primary color in the pixel .
function :cv2.imread()
Parameter description :
- The first parameter is the path to be read
- The second parameter is the reading mode , There are three common reading methods


# Import opencv Of python Version dependent Library cv2
import cv2
# Use opencv in imread Function to read pictures ,
#0 Represents the grayscale image ,1 Represents color form open
img = cv2.imread('split.jpg',1)
print(img.shape)
#print(img)function :cv2.imshow()
Parameter description :
- Parameter one , The name of the window
- Parameter two , Image data name

# Import opencv Dependency Library
import cv2
# Read images , The reading method is color reading
img = cv2.imread('split.jpg',1)
#
cv2.imshow('photo',img)
# Waiting time , if 0, Then type and exit
k = cv2.waitKey(0)
if k == 27: # Input ESC Key to exit
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
elif k == ord('s'): # Input S Key to save the picture and exit
cv2.imwrite('split_.jpg',img)
# Destruction of the window
cv2.destroyAllWindows()function :cv2.imwrite()
Parameter description :
- Parameter one , Image name ( Including format )
- Parameter two , The variable name of the image data to be written

2.3 Image resolution and image channel
- The resolution of the : The number of pixels expressed or intercepted in unit length . Number of pixels per inch of image , The unit is pixels per inch (PPI). The higher the image resolution , The higher the pixel density , The clearer the image .
- The channel number : Graphic Bit depth , It refers to describing each... In the image pixel The number of binary digits occupied by the value . The greater the bit depth, the more colors the image can represent , The richer the color, the more realistic .
- 8 position : Single channel image , That is, grayscale , Gray value range 2^8=256
- 24 by : Three channels 3*8=24
- 32 position : Three channels plus transparency Alpha passageway

2.3.1 Grayscale conversion
- Purpose : Put the three channel image ( Color picture ) Convert to single channel image ( grayscale ).
- The formula :
- 3-->1:GRAY = B * 0.114 + G * 0.587 + R * 0.299
- 1-->3:R = G = B = GRAY; Alpha = 0
- function :cv2.cvtColor(img,flag)
- Parameter description
- Parameter one : Image to be converted
- Parameter two :flag Is to transform the mode ,
- cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY: Color to grayscale
- cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR: Single channel to three channels

# Import opencv
import cv2
# Read in the original image , Use cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED
img = cv2.imread("girl.jpg",cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED)
# View the of the printed image shape
shape = img.shape
print(shape)
# Judge whether the number of channels is 3 Channel or 4 passageway
if shape[2] == 3 or shape[2] == 4 :
# Convert the color map into a single channel map
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.imshow("gray_image",img_gray)
cv2.imshow("image", img)
cv2.waitKey(1000)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()2.3.2 RGB And BGR
use opencv What I read is BGR The format of , If you use plt Show pictures , You need to change the picture from BGR To RGB Format .
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread("test2.png", cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
cv2.imshow("Opencv_win", img)
# use opencv Bring your own way to
img_cv_method = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# use numpy turn ,img[:,:,::-1] Columns flip left and right
img_numpy_method = img[:,:,::-1] # It was originally BGR Now in reverse order , become RGB
# use matplot drawing
plt.subplot(1,3,1)
plt.imshow(img_cv_method)
plt.subplot(1,3,2)
plt.imshow(img_numpy_method)
plt.subplot(1,3,3)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.savefig("./plt.png")
plt.show()
# Save the picture
cv2.imwrite("opencv.png", img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows() 
2.3.3 The channel separation
- Purpose : Color image , Divide into B、G、R Three monochrome channel images . For our convenience BGR The three channels operate separately .
- function :cv2.split(img)
- Parameter description
- Parameter one : Image of the channel to be separated
# load opencv
import cv2
src=cv2.imread('split.jpg')
cv2.imshow('before',src)
# Call channel separation
b,g,r=cv2.split(src)
# The three channels are displayed separately
cv2.imshow('blue',b)
cv2.imshow('green',g)
cv2.imshow('red',r)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()The output is all three grayscale images

# Import opencv modular
import numpy as np
import cv2
image=cv2.imread("split.jpg")# Read the picture to be processed
cv2.imshow("src",image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
B,G,R = cv2.split(image)# Separate the image B,R,G Color channel
zeros = np.zeros(image.shape[:2],dtype="uint8")# Create with image A zero matrix of the same size
cv2.imshow("BLUE",cv2.merge([B,zeros,zeros]))# Show (B,0,0) Images
cv2.imshow("GREEN",cv2.merge([zeros,G,zeros]))# Show (0,G,0) Images
cv2.imshow("RED",cv2.merge([zeros,zeros,R]))# Show (0,0,R) Images
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
2.3.4 Channel merging
- Purpose : The channels are separated into B、G、R after , Modify individual channels , Finally, the modified three channels are merged into color images .
- function :cv2.merge(List)
- Parameter description
- Parameter one : Number of channels to be merged , With list Form input
# load opencv
import cv2
src=cv2.imread('split.jpg')
cv2.imshow('before',src)
# Call channel separation
b,g,r=cv2.split(src)
# take Blue Change the channel value to 0
g[:] = 0
# Merge the modified channels
img_merge=cv2.merge([b,g,r])
cv2.imshow('merge',img_merge)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
2.4 Image histogram
- Image histogram : Image histogram (Image Histogram) Is a histogram used to represent the brightness distribution in a digital image , The number of pixels of each luminance value in the image is plotted . In this histogram , In abscissa The left side is pure black 、 Darker areas , and The right side is brighter 、 Pure white areas .
- The meaning of image histogram :
- Histogram is a graphical representation of the intensity distribution of pixels in an image
- It counts the number of pixels per intensity value
- CV The field often uses image histogram to realize image Two valued
2.4.1 Histogram drawing
- Purpose : Histogram is the statistical distribution of image pixels , It counts each pixel (0-255) The number of
- function :cv2.calcHist(images,channels,mask,histSize,ranges)
- Parameter description :
- Parameters 1: Images to be counted , Use square brackets
- Parameters 2: Channel to be calculated
- Parameters 3:Mask, It's not used here , So use None
- Parameters 4:histSize, Indicates how many parts the histogram is divided into
- Parameters 5: Is the value of each pixel in the histogram ,[0.0,256.0] The representation histogram can represent pixel values from 0.0 To 256 The pixel . Histogram is the statistical distribution of image pixels , It counts each pixel (0 To 255) The number of .
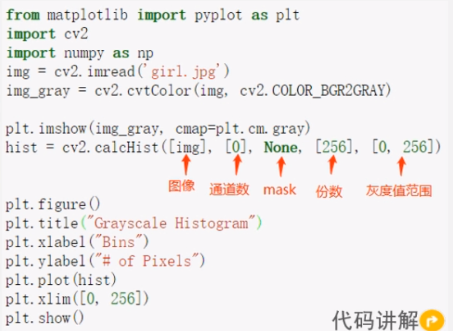
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('girl.jpg')
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
plt.imshow(img_gray, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
hist = cv2.calcHist([img], [0], None, [256], [0, 256])
plt.figure()
plt.title("Grayscale Histogram")
plt.xlabel("Bins")
plt.ylabel("# of Pixels")
plt.plot(hist)
plt.xlim([0, 256])
plt.show()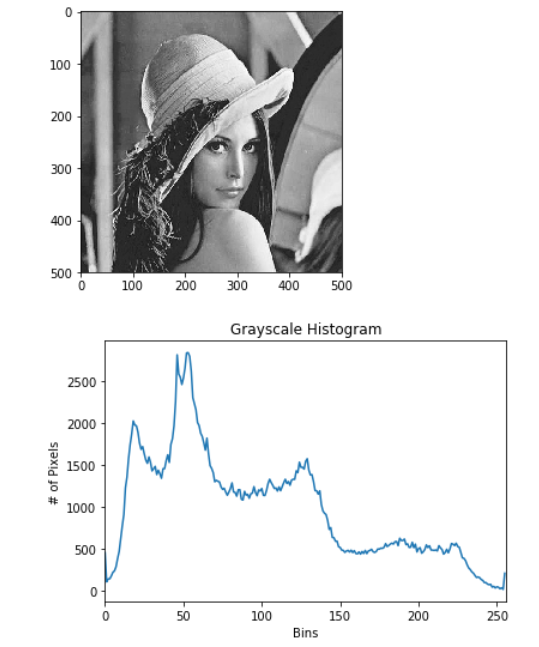
2.4.2 Three channel histogram drawing
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import cv2
girl = cv2.imread("girl.jpg")
cv2.imshow("girl", girl)
color = ("b", "g", "r")
# Use for Loop traversal color list ,enumerate Enumeration returns indexes and values
for i, color in enumerate(color):
hist = cv2.calcHist([girl], [i], None, [256], [0, 256])
plt.title("girl")
plt.xlabel("Bins")
plt.ylabel("num of perlex")
plt.plot(hist, color = color)
plt.xlim([0, 260])
plt.show()
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()

2.5 Image color space
- Concept
- Color space is also called color model ( Also known as color space or color system ), Its purpose is to describe color in a generally acceptable way under certain standards .
- Common color spaces :RGB、HSV、HSI、CMYK
(1)RGB Color
- RGB Color space concept
- Mainly used in computer graphics , Create according to the color recognized by human eyes , Every pixel in the image has R、G、B Three color components , The sizes of these three components are [0,255]. Usually it means a certain color , Write it in the form of a three-dimensional vector (110,150,130).
- Color model
- The color corresponding to the origin is black dot , Its three component values are 0
- The color of the vertex farthest from the origin is white , The three component values are 1
- The gray values from black to white are distributed on the line between the two points , The dotted line is called the gray line
- The rest of the cube has different colors , That is, three primary colors of red 、 green 、 Blue and its mixture yellow 、 magenta 、 Cyan .

(2)HSV Color
- HSV Color space concept
- HSV(Hue,Saturation,Value) According to the intuitive characteristics of color A.R.Smith stay 1978 A color space created in , The parameters of color in this model are : tonal (H)、 saturation (S)、 Lightness (V).
- Color model
- H passageway :Hue, tonal / color , This channel represents color
- S passageway :Saturation, saturation , Value range 0%~100%, The bigger the value is. , The more saturated the color
- V passageway :Value, Light and shade , The higher the value , The brighter ,0%( black ) To 100%( white )

RGB turn HSV

import cv2
# Color space conversion function
def color_space_demo(image):
gray=cv2.cvtColor(image,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.imshow('gray',gray)
hsv=cv2.cvtColor(image,cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
#print(hsv)
cv2.imshow('hsv',hsv)
# Read in a color picture
src=cv2.imread('girl.jpg')
cv2.imshow('before',src)
# call color_space_demo Function to transform color space
color_space_demo(src)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()(3)HSI
- HSI Color space concept
- HSI The model is made by American colorist Munsell and 1915 Put forward in , It reflects the way the human visual system perceives color , In tone 、 Saturation and Strength Three basic feature quantities to perceive color .
- The advantages of the model
- When processing color images , Only for I Component processing , The result does not change the color type in the original image
- HSI The model completely reflects the basic properties of human perception of color , It corresponds to the result of human perception of color one by one

(4)CMYK Color
- CMYK Color space concept
- CMYK Color space is used in the printing industry , The printing industry through the green (C)、 product (M)、 yellow (Y) The overprint of three primary color inks with different dot area ratio shows rich and colorful colors and tones , This is three primary colors CMY Color space .

Complete code
import cv2
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
#=============================cv2.imread Open the picture ===========================#
flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag == 1:
# Use opencv in imread Function to read pictures ,
# 0 Represents the grayscale image ,1 Represents color form open
img = cv2.imread('girl.jpg',1)
print(img.shape)
#=============================cv2.imshow display picture ==========================#
#=============================cv2.imwrite Save the picture ==========================#
flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag == 1:
# Read color pictures
img = cv2.imread('girl.jpg', 1)
# Window name and picture parameters
cv2.imshow('girl',img)
# Waiting time , if 0, Then type any key and exit
key = cv2.waitKey(0)
# Type , Exit after operation
if key == 27: # Input ESC Key to exit
#imshow A temporary address will be created on the desktop , After use, you need to manually destroy the window
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
elif key == ord('s'): # Input S Key to save the picture and exit
# Save the picture : Picture address and picture name , Picture parameters
# Be careful , Add an extension to the picture name , Otherwise, the report will be wrong
# The file is saved in the same level as this file
cv2.imwrite('save_girl.jpg',img)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
#=============================cv2.cvtColor Realize the mutual transformation of three channel image and single channel gray image ==========================#
flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag == 1:
#-1 It means not to change the picture
img = cv2.imread('girl.jpg',-1)
# Get the shape
shape = img.shape
## Judge whether the number of channels is 3 Channel or 4 passageway
if shape[2] == 3 or shape[2] == 4:
# Convert the color map into a single channel map
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.imshow('girl_gray',img_gray)
cv2.imshow('girl',img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag == 1:
img_gray = cv2.imread('girl_gray.jpg',-1)
shape = img_gray.shape
# Single channel gray image is converted to three channels
img = cv2.cvtColor(img_gray,cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
# Although it turns to three channels , The result of single output is still a gray image
cv2.imshow('img',img)
cv2.imshow('img_gray',img_gray)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
#=============================BGR And RGB Conversion between ==========================#
flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag == 1:
# use cv Read BGR Images
img = cv2.imread('test_image.png', 0)
# use matplotlib Exhibition RGB picture ,gray It's a grayscale image
plt.imshow(img)
# hide X、Y The scale on the axis
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag == 1:
'''
because cv Read in BGR Images ,matplotlib Output RGB Images , Then the output image color does not match the original image
So you need to be in plt.imshow Previously, the channel of the picture was transformed :BGR-->RGB
'''
img_BGR = cv2.imread('girl.jpg',-1)
# adopt opencv Built in method conversion
img_cv_RGB = cv2.cvtColor(img_BGR,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# use numpy turn , take img[:,:,::-1] Columns flip left and right
img_numpy_RGB = img_BGR[:, :, ::-1]
# use matplotlib drawing
# Define rows and columns ,(1,3) Represents a window with one row and three columns , the last one 1 Represents the first image
plt.subplot(1,3,1)
plt.imshow(img_BGR)
plt.subplot(1,3,2)
plt.imshow(img_cv_RGB)
plt.subplot(1,3,3)
plt.imshow(img_numpy_RGB)
# use plt Display the image without manually destroying the window
plt.show()
#============================= Use split Yes BGR The channel separation ==========================#
flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag == 1:
'''
You can see , The output result is three grayscale images with different depths , After separation, each picture is single channel , There is only one value to represent , The color map needs more than three channels
'''
img = cv2.imread('girl.jpg',-1)
# The separation channel
b,g,r = cv2.split(img)
# Display the separated channels
cv2.imshow('blue',b)
cv2.imshow('green',g)
cv2.imshow('red',r)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
#============================= Manual channel separation ==========================#
flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag == 1:
img = cv2.imread('girl.jpg', -1)
# The separation channel
b, g, r = cv2.split(img)
# Create with img The same two-dimensional zero matrix
zero = np.zeros(img.shape[:2],dtype='uint8')
#cv2.merge For merging channels
cv2.imshow('blue',cv2.merge([b,zero,zero])) # Show (B,0,0) Images
cv2.imshow('green', cv2.merge([zero, g , zero])) # Show (0,G,0) Images
cv2.imshow('red', cv2.merge([zero, zero, r])) # Show (0,0,R) Images
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
#============================= Draw a gray histogram ==========================#
flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag == 1:
img = cv2.imread('girl.jpg',-1)
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# Draw histogram , The parameters are img、 passageway 、mask、 Additional copies 、 Gray value range
# Square brackets must be added
hist = cv2.calcHist([img],[0],None,[256],[0,256])
# Create a canvas , You can customize the size ,figsize = ?
plt.figure('gray_hist')
# Canvas name
plt.title('gray_hist')
plt.xlabel('grayhist')
plt.ylabel('pixel')
plt.plot(hist)
plt.xlim([0,256])
plt.show()
# flag = 0
flag = 1
if flag == 1:
img = cv2.imread('girl.jpg',-1)
# girl.ravel() The function is to reduce the three digit group of the image to one dimension ,
# 256 by bins Number of ,[0, 256] For the scope
plt.hist(img.ravel(),256,[0,256])
plt.show()
#============================= Draw three channel histogram ==========================#
flag = 0
# flag = 1
if flag == 1:
img = cv2.imread('girl.jpg',-1)
color = ('b','g','r')
# Use for Loop traversal color list ,enumerate Enumeration returns indexes and values
for i , color in enumerate(color):
hist = cv2.calcHist([img],[i],None,[256],[0,256])
plt.title('gray_hist')
plt.xlabel('grayhist')
plt.ylabel('pixel')
plt.plot(hist,color = color)
plt.xlim([0, 256])
plt.show()
边栏推荐
- Cubemx联合IAR工程移植
- 第一章 马克思主义哲学是科学的世界观和方法论
- Analysis of PHP keyword replacement classes (avoid repeated replacement, keep and restore the original links)
- Two methods of generating excel table with PHP
- 2.2 JMeter基本元件
- 【论文阅读】Single- and Cross-Modality Near Duplicate Image PairsDetection via Spatial Transformer Compar
- 2021-03-09
- DRF learning notes (IV): DRF view
- Pychart imports the existing local installation package
- Crmeb Pro v1.4 makes the user experience more brilliant!
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
The method of inserting degree in word
MapReduce instance (II): Average
Excel提取重复项
Script file ‘D:\programs\anaconda3\Scripts\pip-script.py‘ is not present.
Implementation of ByteDance service grid based on Hertz framework
OpenCV(一)——图像基础知识
IO流简介
第31回---第52回
收藏!0基础开源数据可视化平台FlyFish大屏开发指南
Axure install Icon Font Catalog
Some queries of TP5
training on multiple GPUs pytorch
Leetcode25 question: turn the linked list in a group of K -- detailed explanation of the difficult questions of the linked list
2021-03-09
Flowable process custom attribute
【论文阅读】Single- and Cross-Modality Near Duplicate Image PairsDetection via Spatial Transformer Compar
TP5 paging some small points
201403-1
爬取常见英文名
Solve the problem that Flink cannot be closed normally after startup