当前位置:网站首页>Shell Function
Shell Function
2022-07-27 06:37:00 【m0_ sixty-nine million five hundred and ten thousand two hundre】
List of articles
One 、shell function
- shell A very important feature is that it can be used as a programming language .
- because shell It's an interpreter , So it cannot compile the program written for it , Instead, explain these programs every time you load them from disk . And the loading and interpretation of the program are very time-consuming .
- In response to this problem , many shell( Such as BourneAgainShell) Both contain shell function ,shell Put these functions in memory , So every time you need to execute them, you don't have to read them from disk .
- shell These functions are also stored in an internal format , So you don't have to spend a lot of time explaining them
- shell Function writes the command sequence together in format
- It is convenient to reuse the command sequence
1、 Definition of function ( Two ways )
function Function name {
command
} # This is a standard way of writing
2
Function name (){ # Most commonly used because of the most concise
command
}
- After the function is defined, it will not execute automatically , You need to call , The advantage is that you can write a piece of function code as a function , Call directly if necessary


- Call second

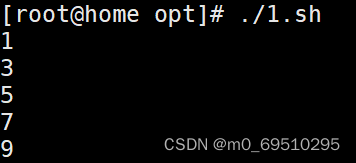
- You can also call all


- It doesn't matter if there are grammatical errors in the definition , If you don't call, you won't report an error
- Of course, the ultimate purpose of writing functions is to call , In order to implement a function block
2、 Function call
Directly define the code block of the function in the script and write the function name to complete the call
#!/bin/bash
function one { // Defines a function called one
echo "hello world" // The function body is to print hello world
}
one // Writing the function name directly will run the code in the function body
Be careful ①: Function name must be unique , If you define a , Use the same name to define , The second will override the function of the first , There are results you don't want , So be careful not to duplicate your name here !
#!/bin/bash
f1 (){
echo hello
}
f1 (){
echo world
}
f1
[[email protected] ~]# . f1.sh
world
Be careful ②: The function must be defined before calling !
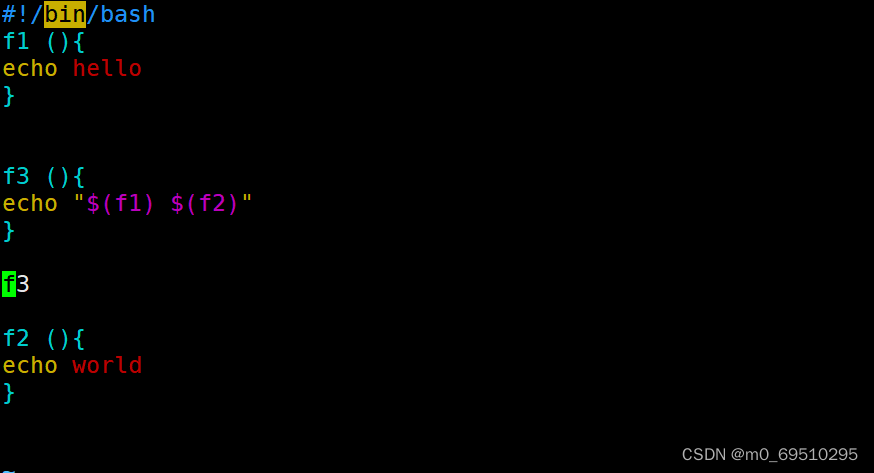

- because f3 Function called f2, Called f3 You don't know f2 The definition of , because f2 Is in f3 After being defined by , So the running script will report an error


This is called ahead of time. f2, however f2 Your function is still running f3 Previously defined, so he can find
3、 Function return value :return
The return value of the function is the status code of the last command running in the function , The default success is 0, Failure is wrong 0 value , Can pass $? see
But you can customize the return code yourself , use return
- return The value range of is 0-255
- encounter return That is, the end function will not execute further
for example


- Judge whether the script runs successfully by the return value
Because sometimes even if the script runs incorrectly , But the return value brought back is still 0


Therefore, you can judge whether there is an error in the script by the return value
- Judge whether the file exists


4、 The scope of the function
stay Shell The execution of the function in the script does not open a new child Shell, But only in the currently defined Shell Effective in the environment .
If Shell The variables in the script are not specially set , The default is valid throughout the script .
When writing scripts , Sometimes you need to limit the value of a variable inside a function , You can use built-in commands local To achieve .
Use of internal variables of functions , It can avoid the influence of variables with the same name inside and outside the function on the script results .
for example
[[email protected] ~]# vim myfun.sh
#!/bin/bash
myfun ()
{
local i # Set local variables
i=8
echo $i
}
i=9
myfun
echo $i
[[email protected] ~]#./myfun.sh
8
9 # Local variables do not affect global variables
Two 、 Arguments to functions
- The parameters of the function
Calculate the location variable $1 and $2 And
#!/bin/bash
add (){
let sum=$1+$2 // The position variable here is the position variable of the function , So write it after the calling function , If it is used when calling the script, it will not succeed
echo $sum
}
add 4 5
- Parameter passing of script


- How to pass and use multiple parameters in functions
- Factorial


- Interactive factorial


3、 ... and 、 Definition of array
An array is a collection of data of the same type , It opens up a continuous space in memory , Usually used together with recycling
The classification of arrays
Normal array : Direct definition without declaration , Subscript index can only be an integer
Associative array : Need to use declare -A Otherwise, the system does not recognize it , The index can be a string
1、 How to define an array
The first one is
Directly enclose the elements to be added to the array in parentheses , Separate... With spaces in the middle
Custom data name =(value0 value1 value2...)
for example :num=(1 2 3 4 5)
The second kind
Precisely define a value for each subscript index and add it to the array , Index numbers can be discontinuous
Array name =([0]=value [1] =value [2] =value...)
for example :num=([0]=1 [1]=2 [2]=3)
The third kind of
First assign all the elements to be added to the array to a variable , Then reference this variable and add it to the array
List name ="value0 value1 value2....”
Array name =($ List name )
for example :list="1 2 3 4"
num=($list)
A fourth
Define according to the subscript
Array name [0]="value0"
Array name [1]="value1"
Array name [2]="value2"
for example :num[0]="1"
num[1]="2"
num[2]="3"
2、 The data types included in the array
1. Gets the length of the array
echo ${# Array name [*]}
echo ${# Array name [@]}

2. Get the data list
echo ${ Array name [*]}
echo ${ Array name [@]}

3. Read a subscript
arr=${num[3]}
echo $arr

4. Element slice
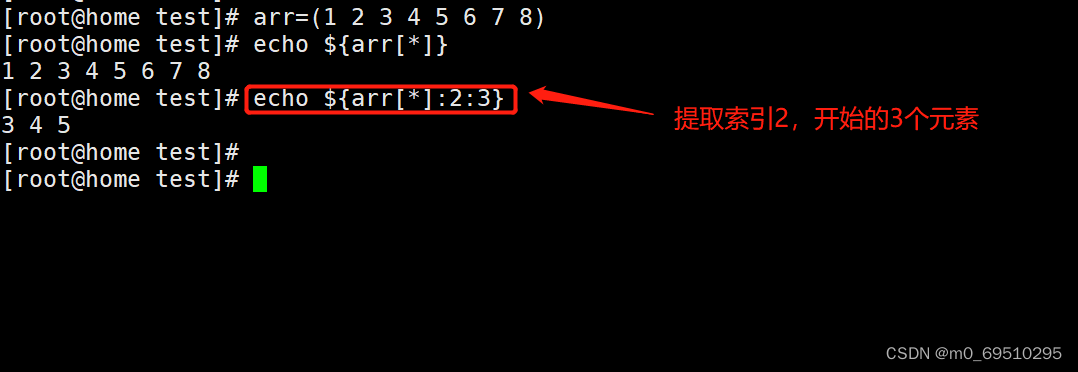
5. Array ( Elements ) Replace
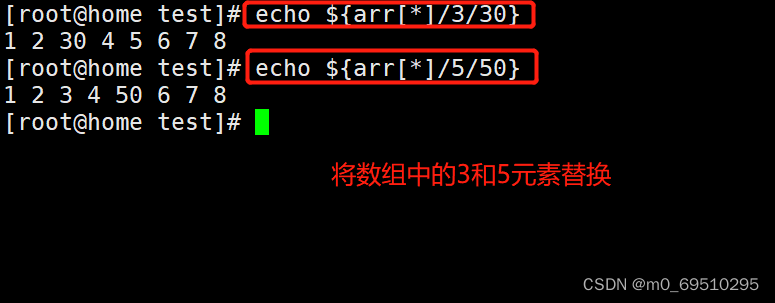
6. Array delete
unset Array name # Delete the specified array
arr=(1 2 3 4)
unset arr[4] # Delete the fourth element
3、 Array sorting algorithm : Bubble sort
It's like a bubble rising , Will move the data in the array from small to large or from large to small .
The basic idea of bubble sorting is to compare the values of two adjacent elements , Exchange element values if conditions are met , Move the smaller elements to the front of the array , Move large elements to the back of the array ( That is, to exchange the positions of two elements ), So the smaller elements rise from the bottom to the top like bubbles .
Algorithm ideas
- The bubble algorithm is implemented by a two-layer loop , The external loop is used to control the number of sorting rounds , Generally, the length of the array to be sorted minus 1 Time , Because there's only one array element left in the last loop , There's no need to compare , At the same time, the array has finished sorting . The inner loop is mainly used to compare the size of each adjacent element in the array , To determine whether to swap positions , The number of comparisons and exchanges decreases with the number of sorting rounds .
Algorithm
#!/bin/bash
array=(34 56 21 90 89 78)
# Show unordered arrays
echo " The current array is :${array[*]}"
# Define array length ; The current array length is 6
lt=${#array[*]}
# Define outer loop
# Define the number of comparison rounds , The number of comparison rounds is the length of the array minus 1, from 1 Start
for ((i=1;i<$lt;i++))
do
# Internal circulation for comparison
# Determine the position of the comparison element , Compare two adjacent elements , Put the larger number back , The number of comparisons decreases with the number of rounds
for ((j=0;j<$lt-i;j++))
do
# Define the value of the first element
first=${array[$j]}
# Define the value of the second element
k=$[$j+1]
second=${array[$k]}
# If the first element is larger than the second element, it is interchangeable
if [ $first -gt $second ]
then
# Save the first element value to a temporary variable
temp=$first
# Assign a value to the first element
array[$j]=$second
# Put the temporary variable ( That is, the original value of the first element ) Assign to the second element
array[$k]=$temp
fi
done
done
# Output sorted array
echo " Order from small to large :${array[*]}"


- From big to small


- Interactive arrangement
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-b57nBXqR-1657543697855)(

边栏推荐
- Introduction to Wireshark graphical interface
- 测试基础概括
- ROS distributed communication
- Array and subscript index
- Interface test process and interview questions
- Source code compilation and installation LNMP and discuz Forum
- Robot navigation
- Three ways to get RPM packages using yum
- Using markdowm
- 5g network identity - detailed explanation of 5g Guti
猜你喜欢

Li Kou daily question leetcode 513. find the value in the lower left corner of the tree

shell脚本之函数调用

QGIS series (1) -qgis (server APACHE) win10 installation

Launch file of ROS operation management

Seven sorting details

Briefly remember the top ten orders

正则表达式

七大排序详解
Source code compilation and installation LNMP and discuz Forum

logging日志的封装
随机推荐
Shell脚本备份MySQL数据库
Wireshark function introduction
源码编译安装LAMP和DISCUZ论坛
Ram of IP core
Related knowledge of internal classes
shell--自定义变量与赋值
shell脚本循环
Wireshark IP address domain name resolution
面试常问的问题总结【呕心沥血熬了一个晚上总结的】
Robot navigation implementation
Binary tree - search tree
ROS workspace coverage
如何规范式编写yaml文件
This is my blog
Ulcl function --5gc
C language - Custom structure type
互联网简单协议概括
FTP服务器的搭建
英语基础知识: 并列结构
shell--变量的运算