当前位置:网站首页>【LeetCode每日一题】——103.二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
【LeetCode每日一题】——103.二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
2022-08-02 01:57:00 【IronmanJay】
一【题目类别】
- 二叉树
二【题目难度】
- 中等
三【题目编号】
- 103.二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
四【题目描述】
- 给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 锯齿形层序遍历 。(即先从左往右,再从右往左进行下一层遍历,以此类推,层与层之间交替进行)。
五【题目示例】
示例 1:
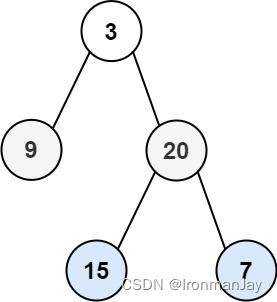
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:[[3],[20,9],[15,7]]示例 2:
输入:root = [1]
输出:[[1]]示例 3:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
六【题目提示】
- 树中节点数目在范围 [0, 2000] 内
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
七【解题思路】
- 层序遍历肯定使用的是BFS(广度优先搜索)
- 基于这个思路进行层序遍历,对于层序遍历比较简单,直接扫描这一层的元素在队列弹出然后加入到结果数组中即可
- 但是题目要求存储的左右顺序不停的反转,所以设置一个标志位,一开始从左到右存储,然后每存储完一层之后,修改标志位,让其从右到左存储。通过不停的修改标志位来达到左右顺序不同的层序存储
八【时间频度】
- 时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n),其中 n n n为树的节点个数
- 空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n),其中 n n n为树的节点个数
九【代码实现】
- Java语言版
package Tree;
import java.util.*;
public class p103_ZigzagOrderTraversalOfBinaryTrees {
int val;
p103_ZigzagOrderTraversalOfBinaryTrees left;
p103_ZigzagOrderTraversalOfBinaryTrees right;
public p103_ZigzagOrderTraversalOfBinaryTrees() {
}
public p103_ZigzagOrderTraversalOfBinaryTrees(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
public p103_ZigzagOrderTraversalOfBinaryTrees(int val, p103_ZigzagOrderTraversalOfBinaryTrees left, p103_ZigzagOrderTraversalOfBinaryTrees right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
p103_ZigzagOrderTraversalOfBinaryTrees root = new p103_ZigzagOrderTraversalOfBinaryTrees(3);
p103_ZigzagOrderTraversalOfBinaryTrees left = new p103_ZigzagOrderTraversalOfBinaryTrees(9);
p103_ZigzagOrderTraversalOfBinaryTrees right = new p103_ZigzagOrderTraversalOfBinaryTrees(20);
p103_ZigzagOrderTraversalOfBinaryTrees right1 = new p103_ZigzagOrderTraversalOfBinaryTrees(15);
p103_ZigzagOrderTraversalOfBinaryTrees right2 = new p103_ZigzagOrderTraversalOfBinaryTrees(7);
root.left = left;
root.right = right;
right.left = right1;
right.right = right2;
List<List<Integer>> res = zigzagLevelOrder(root);
System.out.println("res = " + res);
}
public static List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(p103_ZigzagOrderTraversalOfBinaryTrees root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
boolean flag = true;
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
Queue<p103_ZigzagOrderTraversalOfBinaryTrees> queue = new ArrayDeque<p103_ZigzagOrderTraversalOfBinaryTrees>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
Deque<Integer> list = new LinkedList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
p103_ZigzagOrderTraversalOfBinaryTrees temp = queue.poll();
if (flag) {
list.offerLast(temp.val);
} else {
list.offerFirst(temp.val);
}
if (temp.left != null) {
queue.offer(temp.left);
}
if (temp.right != null) {
queue.offer(temp.right);
}
}
res.add(new LinkedList<Integer>(list));
if (flag) {
flag = false;
} else {
flag = true;
}
}
return res;
}
}
- C语言版
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
struct TreeNode
{
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
};
int** zigzagLevelOrder(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes)
{
int** res = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * 2001);
*returnColumnSizes = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 2001);
*returnSize = 0;
struct TreeNode* queue[2001];
int front = 0;
int rear = 0;
bool flag = true;
if (root == NULL)
{
(*returnColumnSizes)[*returnSize] = 0;
return res;
}
queue[rear++] = root;
while (front != rear)
{
res[*returnSize] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 2001);
(*returnColumnSizes)[*returnSize] = 0;
int size = (rear - front + 2001) % 2001;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
struct TreeNode* temp = queue[front++];
if (flag)
{
res[*returnSize][count] = temp->val;
}
else
{
res[*returnSize][size - count - 1] = temp->val;
}
if (temp->left != NULL)
{
queue[rear++] = temp->left;
}
if (temp->right != NULL)
{
queue[rear++] = temp->right;
}
count++;
}
(*returnColumnSizes)[*returnSize] = count;
*returnSize = *returnSize + 1;
if (flag)
{
flag = false;
}
else
{
flag = true;
}
}
return res;
}
/*主函数省略*/
十【提交结果】
Java语言版

C语言版

边栏推荐
- Multi-Party Threshold Private Set Intersection with Sublinear Communication-2021: Interpretation
- Chengdu openGauss user group recruit!
- Redis 持久化 - RDB 与 AOF
- Hash collisions and consistent hashing
- Constructor instance method inheritance of typescript37-class (extends)
- 有效进行自动化测试,这几个软件测试工具一定要收藏好!!!
- volatile原理解析
- LeetCode brush diary: LCP 03. Machine's adventure
- 力扣 1374. 生成每种字符都是奇数个的字符串
- swift项目,sqlcipher3 -&gt; 4,无法打开旧版数据库有办法解决吗
猜你喜欢
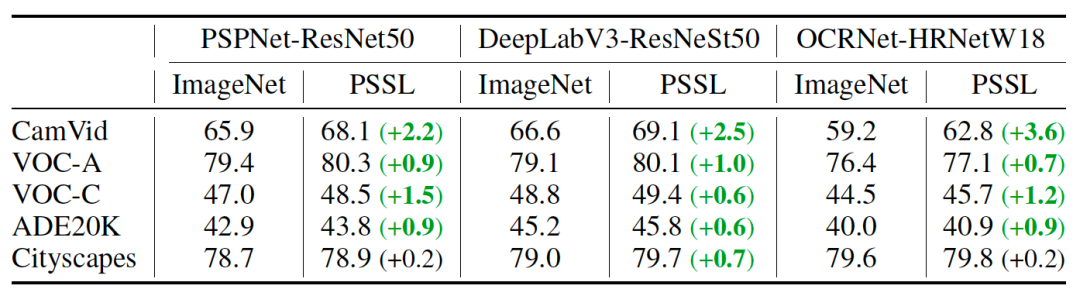
The ultra-large-scale industrial practical semantic segmentation dataset PSSL and pre-training model are open source!
YGG 公会发展计划第 1 季总结

Day116. Shangyitong: Details of appointment registration ※

『网易实习』周记(三)
检查IP或端口是否被封

typescript33-typescript高级概述

成都openGauss用户组招募啦!
3.Bean的作用域与生命周期

飞桨助力航天宏图PIE-Engine地球科学引擎构建
【图像融合】基于加权和金字塔实现图像融合附matlab代码
随机推荐
Garbage Collector CMS and G1
LeetCode刷题日记:74. 搜索二维矩阵
Constructor of typescript35-class
YGG 公会发展计划第 1 季总结
Multi-Party Threshold Private Set Intersection with Sublinear Communication-2021: Interpretation
typescript36-class的构造函数实例方法
The ultra-large-scale industrial practical semantic segmentation dataset PSSL and pre-training model are open source!
MySQL optimization strategy
『网易实习』周记(二)
typescript33-typescript高级概述
超大规模的产业实用语义分割数据集PSSL与预训练模型开源啦!
Effects of Scraping and Aggregation
JDBC PreparedStatement 的命名参数实现
《自然语言处理实战入门》 基于知识图谱的问答机器人
Entry name ‘org/apache/commons/codec/language/bm/gen_approx_greeklatin.txt’ collided
创新项目实战之智能跟随机器人原理与代码实现
密码学的基础:X.690和对应的BER CER DER编码
6-25 Vulnerability Exploitation - irc Backdoor Exploitation
PHP 使用 PHPRedis 与 Predis
【ORB_SLAM2】void Frame::ComputeImageBounds(const cv::Mat &imLeft)