当前位置:网站首页>[C language] Analysis of function recursion (3)
[C language] Analysis of function recursion (3)
2022-08-02 13:16:00 【mortal programming biography】
作者:凡人编程传
系列:C语言初阶(适合小白入门)
说明:以凡人之笔墨,书写未来之大梦

₪前言
这一节,We've covered the last two questions about recursion.,The content of the knowledge point of recursion is all completed,好了,废话不多说,Let's get straight to the point!
₪求一个数的阶乘(递归实现)
Are you familiar with this subject?,The exercises in the loop structure article.But this time we're going to do it recursively.那么怎么实现呢?
Here is another introduction to the recursive execution process:The recursive atmosphere is divided into two executions over:pushback and recursion.
1.回推:Pushback is to find similar big complex problems according to the complex problems to be solved,Basic solutions to simple problems.This process needs the value of the system memory stack storage temp;
2.递推:Recursion is based on finding solutions to simple problems to obtain solutions to complex problems,This process is to gradually release the variables saved in the previous stack space,until the solution of the complex problem.
So what is the pushback process for this question??看例子吧:
根据数学知识,The factorial of a number is the factorial of the previous number multiplied by the number itself.如3!(The exclamation mark here is the factorial symbol in mathematics,not logical not)为3!=3*2!
那么我们要求nThe factorial of is as follows:
n!=n * (n-1)
(n-1)!=(n-1) * (n-2)!
(n-2)!=(n-2) * (n-3)!
…
2!=2 * 1!
1!=1* 0!;
0! = 1 (0is the smallest factorial number,规定值为1)
从上述例子可以看出,如果想要知道n的阶乘,Then you must know first(n-1)! * n,想要知道(n-1)!you have to know first,(n-2)! * n(n-1).This process also is the process of function calls itself,以此类推,Until we are back to know the most basic knowledge0!=1,You can start rolling.
递推:
push back to what we know0!=1;
0!=1;
1!=1 * 1 (1!=1 * 0!)
2!=2 * 1. (2!=2 * 1!)
3!=3 * 2 (3!=3 * 2!)
…
n!=n*(n-1)!
根据0!=1This known basic condition,得到1!,2!,3!..最终得到n!
另外再说一点,nmay be negative,Because the smallest factorial is0!.So pay attention to listing branches when writing code.
有了以上知识,We know how to write the code.
code:
#include<stdio.h>
int fac(int k)
{
if(k<0)
{
return -1; //factorial without negative numbers
}
if(0==k)
{
return 1; //0的阶乘为1
}
else
{
return k*fac(k-1);
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int t=fac(n);
if(t<0)
{
printf("参数错误!factorial without negative numbers!\n");
}
else
{
printf("%d!=%d",n,fac(n));
}
return 0;
}
测试结果: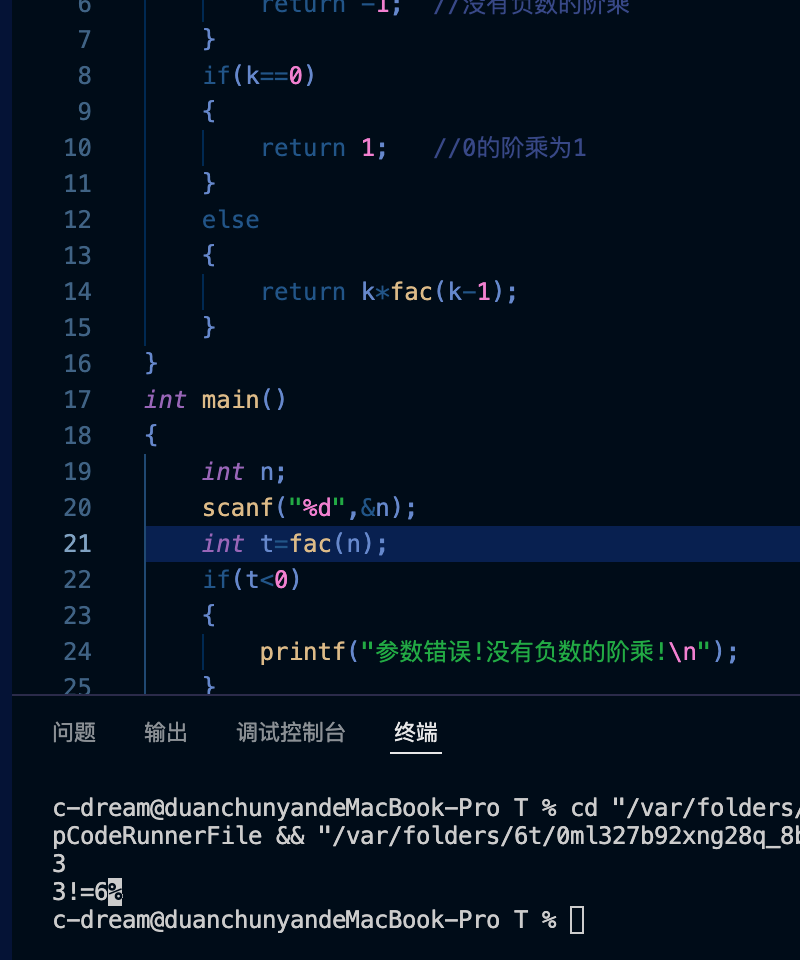
₪求斐波那契数列的第n项
这道题和上一道题很类似,Basic conditions can be known from mathematical knowledge,The first two items of the Fibonacci sequence are1,且从第3项开始,每项是前两项的和.
如: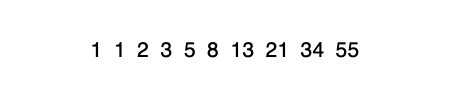
2=1+1
3=2+1
5=2+3
…
n=(n-2)+(n-1)
可以看出,每一项都是前两项之和.Then we can, according to this law and a known basic condition, the first two terms are1,Push back and forth and recurse.
回推:
n=(n-1)+(n-2)
(n-1)=(n-3)+(n-2)
(n-2)=(n-4)+(n-3)
…
Here we draw a diagram to make it easier to understand;
这里假设n为50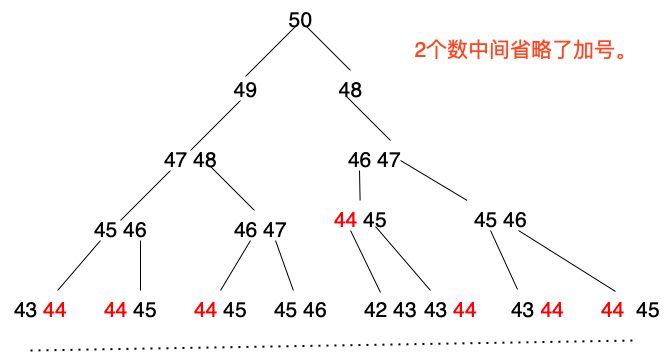
我们可看到,1number to push back two other numbers to sum,还有就是44This number is repeated many times.This is only the first4push back,to push until1,也就是2的49次方,How many times do these data have to be recalculated??This will lead to low efficiency of our.
递推:
Recursion is to push back all the way to the known condition. The first two terms are1,You can start the first3项的(1+1=2),第4项(2+1=3)以此类推到n.That is to say, the reverse of the above picture starts to ask for the item..
有了以上知识,就可以写出代码了
code:
#include<stdio.h>
int Fib(int k)
{
if(k>2) //not the first two,从第3项开始
{
return Fib(k-1)+Fib(k-2);
}
else if(k>=1)
{
return 1; //前两项是1
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("第%d项=%d",n,Fib(n));
return 0;
}
测试结果: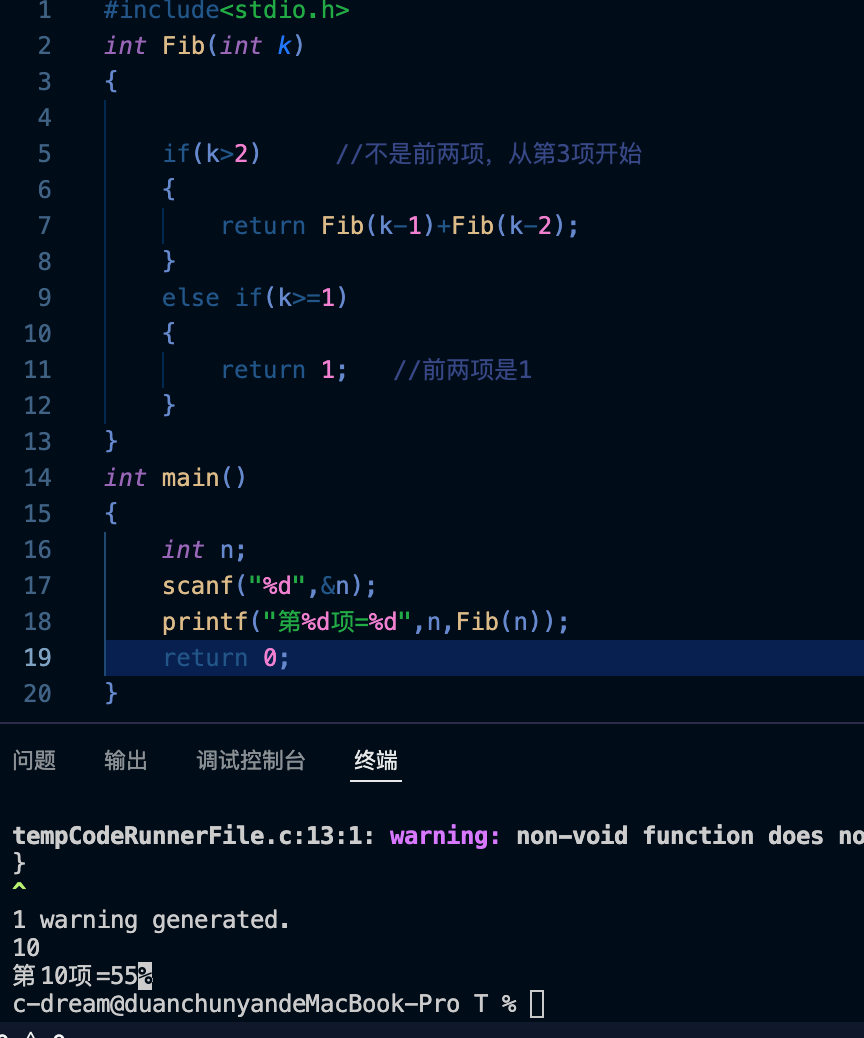
But recursion is too inefficient to use this kind of problem that requires a lot of repeated calculations..If the required item is large, it will take a long time for the computer to calculate it.,Let's test the first40item first3项2被重复计算了多少次
code
#include<stdio.h>
int count=0; //Define global variables to increase lifetime,保证countValid throughout the project
int Fib(int k)
{
if(k==3)
{
count++;
}
if(k>2) //not the first two,从第3项开始
{
return Fib(k-1)+Fib(k-2);
}
else if(k>=1)
{
return 1; //前两项是1
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("第%d项=%d\n",n,Fib(n));
printf("count=%d",count);
return 0;
}
测试结果:
More than 30 million times!It can be seen how different the time complexity is,Efficiency can be seen at a glance.
So can we write this question differently??能!The Fibonacci sequence is anywaynThe term is the sum of the first two..Let's once upon a time in the future and not finished,This avoids recalculating a number multiple times,Don't look for the front like recursionncome back to count the number and recalculate that number.
The main key to writing in a loop is to count from the front to the back,先把第n个数用(n-1)+(n-2)算出来,then ask for then+1The number of timen-1改为n-2,n-2又改为n.可能有点看不懂,That's ok let's look at the picture.
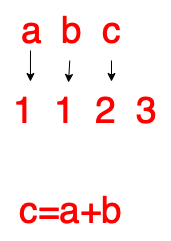
这是求第3项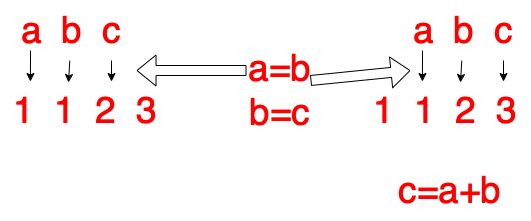
求第4项
还有注意,Calculate a number for each loop,then leavenOne step closer finally asknjust countn-1即可与n-2相加得到n,With the above knowledge, you can type code:
code:
#include<stdio.h>
long long Fib(int k) //test here50项,To prevent integer overflow, set it tolong long 类型
{
long long a=1,b=1,c=1; //already know the first two,c设1duen<-2That is to say, the first two are1,所以设为1
while(k>2)
{
c=a+b;
a=b;
b=c;
k--;
}
return c;
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("第%d项=%lld\n",n,Fib(n));
return 0;
}
运行结果:
The results are coming soon,Because computers don't need a lot of repeated calculations.
₪结言
好了,Function recursive the contents of this section to the end,希望你有收获,Looking forward to the array in the next chapter!
边栏推荐
- 【C语言】明解数组(1)
- JS中的闭包
- 读《IDEO,设计改变一切》有感
- .Net 5.0 Quick Start Redis
- Intouch System Platform IDE-1
- ESP8266模块使用完整教程「建议收藏」
- 网络流详解(流网图一般能够反映什么信息)
- SQL Server 2014 installation tutorial (nanny-level graphic tutorial)
- RISC-V instruction format and 6 basic integer instructions
- [typescript] Use the RangePicker component in antd to implement time limit the previous year (365 days) of the current time
猜你喜欢
Mysql视图

this的绑定指向详细解答
Singleton pattern of seven kinds of writing, you know?
工厂方法模式
自动生成代码器推荐-code-gen
A powerful js pop-up alert plugin
SQL Server 2019 installation error 0 x80004005 service there is no timely response to the start or control request a detailed solution

Get out of the machine learning world forever!
svg balloon rises explosion js special effect
【C语言】虐打循环结构练习题
随机推荐
Do you know Dijkstra of graph theory?
Mysql视图
The uniapp/applet onload method executes the interpretation every time the page is opened
【C语言】细品分支结构——if-else语句
SQL Server database generation and execution of SQL scripts
FreeRTOS experiment -- delete task
ThinkPHP 5.1反序列化分析和poc
【C语言】细品分支结构——switch语句
JS中的闭包
基于华为eNSP的企业网络规划
.Net 5.0快速上手 Redis
【C语言】剖析函数递归(1)
最小割和对偶图(未完成)
There are several ways to jump to js source code, jump on the current page, jump on the blank page
Four seasons of trees realized by svg
第48篇-timestamp2参数分析【2022-08-01】
Win11怎么修改关机界面颜色?Win11修改关机界面颜色的方法
冰箱“扩容”的战事,在今夏格外猛烈
Basic operations of openGauss database (super detailed)
方正璞华“劳动人事法律自助咨询服务平台”在武汉武昌区投入使用!