当前位置:网站首页>Group counting_ Structure and workflow of CPU
Group counting_ Structure and workflow of CPU
2022-06-24 11:05:00 【xuchaoxin1375】
List of articles
cpu Structure and workflow of

Contents
cpu Make up the structure
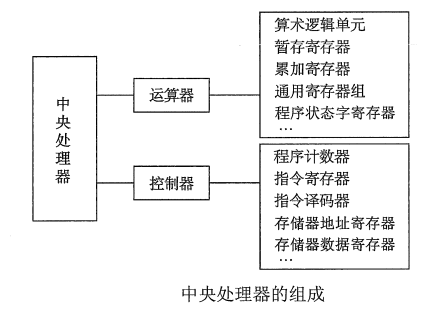

- Block diagram of a basic uniprocessor-CPU computer. Black lines indicate data flow, whereas red lines indicate control flow; arrows indicate flow directions.
Arithmetic unit
- Arithmetic unit Receive from Commands from the controller And perform the corresponding actions , To process and process data .
- Arithmetic unit is the center of data processing by computer , It is mainly composed of
- Arithmetic logic unit (ALU)、
- Temporary register 、
- Accumulation register (ACC)、
- General register group 、
- Program status word register (PSW)、
- Shifter 、
- Counter (CT) Other components .
- 1) Arithmetic logic unit . The main function is to do arithmetic / Logical operations .
2) Temporary register .- Used to temporarily store data read from main memory , This data cannot be stored in a general-purpose register , Otherwise, it will destroy its original content .
- Temporary registers are transparent to application programmers .
- 3) Accumulation register . It's a General registers , For temporary storage ALU The result information of the operation , It can be used as an input of addition operation .
- 4) General register group .
- Such as AX、BX、CX、DX、SP etc. , Used to store operands ( Including source operands 、 Destination operands and intermediate results ) And all kinds of address information, etc .
- SP It's a stack pointer , Used to indicate the address at the top of the stack .
- 5) Program status word register (PSW).
- All kinds of state information established by the result of arithmetic logic operation instruction or test instruction are retained , Such as
- Overflow sign (OF)、
- sign indicator (SF)、
- Zero mark (ZF)、
- Carry mark (CF) etc. .
- PSW These bits in participate in and decide Micromanipulation The formation of .
- All kinds of state information established by the result of arithmetic logic operation instruction or test instruction are retained , Such as
- 6) Shifter . The operation of an operand or the result of an operation Shift operation .
- 7) Counter . That controls multiplication and division Operation steps .
controller
The whole command system is the central controller , Under the control of the controller , Arithmetic unit 、 Memory and input / Output device and other functions
Components form an organic whole , Command the whole aircraft to coordinate work according to the requirements of the instruction . The basic function of the controller is to execute instructions , Each instruction is executed by a set of micro operations issued by the controller .
The controller has Hardwired controllers and Microprogrammed controllers Two types of
The controller consists of
- Program counter (PC)、
- Instruction register (IR)、
- Instruction decoder 、
- Memory address register (MAR)、
- Memory data register (MDR)、
- Timing system and micromanipulation signal generator Other components .
1) Program counter . Used to indicate the location of the next instruction in main memory .
- CPU according to PC To get instructions from main memory . Because the instructions in the program ( Usually ) It's sequential , therefore PC It has self increasing function .
2) Instruction register . It is used to save the currently executing instruction .
3) Instruction decoder . only For opcode fields Decoding , towards The controller provides specific operating signals .
4) Memory address register . The address used to store the main memory unit to be accessed .
5) Memory data register . Used to store information written to or read from main memory .
6) Sequential systems . Used to produce various Timing signal , They are made by Unified clock (CLOCK) frequency division obtain .
7) Micromanipulation signal generator .
- according to R The content of ( Instructions )、PSW The content of ( State information ) Just in time signals , produce Various control signals required to control the whole computer system ,
- Its structure has Combinatorial logic type and Storage logical type Two kinds of .
- The operating principle of the controller is , according to Command opcode 、 The directive Execution steps ( Micro command sequence ) and Condition signal To form the control signals to be used by various components of the current computer .
- The hardware system of the computer works together under the control of these control signals , Produce the expected results of execution .
Be careful :CPU Inside Registers can be roughly divided into two categories :
- One is the user visible register , Such registers can be programmed , Such as
- General register group 、
- Program status word register ;
- The other is registers that are invisible to the user , Transparent to users , Such registers cannot be programmed , Such as
- Memory address register 、
- Memory data register 、
- Instruction register .
- One is the user visible register , Such registers can be programmed , Such as
Memory management unit (MMU)
Main article: Memory management unit
Many microprocessors (in smartphones and desktop, laptop, server computers) have a memory management unit, translating logical addresses into physical RAM addresses, providing memory protection and paging abilities, useful for virtual memory. Simpler processors, especially microcontrollers, usually don’t include an MMU.
Operation
The fundamental operation of most CPUs, regardless of the physical form they take, is to execute a sequence of stored instructions that is called a program.
The instructions to be executed are kept in some kind of computer memory.
Nearly all CPUs follow the fetch, decode and execute steps in their operation, which are collectively known as the instruction cycle.( Instruction cycle )
After the execution of an instruction, the entire process repeats, with the next instruction cycle normally fetching the next-in-sequence instruction because of the incremented value in the program counter.
If a jump instruction was executed, the program counter will be modified to contain the address of the instruction that was jumped to and program execution continues normally.
In more complex CPUs, multiple instructions can be fetched, decoded and executed simultaneously.
This section describes what is generally referred to as the “classic RISC pipeline”, which is quite common among the simple CPUs used in many electronic devices (often called microcontrollers).
It largely ignores the important role of CPU cache, and (therefore )the access stage of the pipeline.
Some instructions manipulate the program counter rather than producing result data directly;
such instructions are generally called “jumps” and facilitate program behavior like loops, conditional program execution (through the use of a conditional jump), and existence of functions.[c]
In some processors, some other instructions change the state of bits in a “flags” register.
- These flags can be used to influence how a program behaves, since they often indicate the outcome of various operations.
- For example, in such processors a “compare” instruction evaluates two values and sets or clears bits in the flags register to indicate which one is greater or whether they are equal;
- one of these flags could then be used by a later jump instruction to determine program flow.
Fetch
- The first step, fetch, involves retrieving an instruction (which is represented by a number or sequence of numbers) from program memory.
- The instruction’s location (address) in program memory is determined by the program counter (PC; called the “instruction pointer” in Intel x86 microprocessors), which stores a number that identifies the address of the next instruction to be fetched.
- After an instruction is fetched, the PC is incremented by the length of the instruction so that it will contain the address of the next instruction in the sequence.[d]
- Often, the instruction to be fetched must be retrieved from relatively slow memory, causing the CPU to stall(stop or cause to stop making progress) while waiting for the instruction to be returned.
- This issue is largely addressed(dealt with) in modern processors by caches and pipeline architectures (see below).
Decode
- Further information: Instruction set architecture § Instruction encoding
The instruction that the CPU fetches from memory determines what the CPU will do.
In the decode step, performed by binary decodercircuitry([ˈsɜrkɪtri]) known as the instruction decoder, the instruction is converted into signals that control other parts of the CPU.
The way in which the instruction is interpreted is defined by the CPU’s instruction set architecture (ISA).[e]
Often, one group of bits (that is, a “field”) within the instruction, called the opcode, indicates which operation is to be performed,
while the remaining fields usually provide supplemental information required for the operation, such as the operands.
Those operands may be specified as
a constant value (called an immediate value),
or as( the location of a value that may be a processor register or a memory) address, as determined by some addressing mode.
In some CPU designs the instruction decoder is implemented as a hardwired, unchangeable binary decoder circuit. In others, a microprogram is used to translate instructions into sets of CPU configuration signals that are applied sequentially over multiple clock pulses.
In some cases the memory that stores the microprogram is rewritable, making it possible to change the way in which the CPU decodes instructions.
Execute
- After the fetch and decode steps, the execute step is performed.
- Depending on the CPU architecture, this may consist of a single action or a sequence of actions. During each action, control signals electrically enable or disable various parts of the CPU so they can perform all or part of the desired operation.
- The action is then completed, typically in response to a clock pulse.
- Very often the results are written to an internal CPU register for quick access by subsequent instructions.
- In other cases results may be written to slower, but less expensive and higher capacitymain memory.
- For example, if an addition instruction is to be executed, registers containing operands (numbers to be summed) are activated, as are the parts of the arithmetic logic unit (ALU) that perform addition.
- When the clock pulse occurs, the operands flow from the source registers into the ALU, and the sum appears at its output.
- On subsequent clock pulses, other components are enabled (and disabled) to move the output (the sum of the operation) to storage (e.g., a register or memory).
- If the resulting sum is too large (i.e., it is larger than the ALU’s output word size), an arithmetic overflow flag will be set, influencing the next operation.
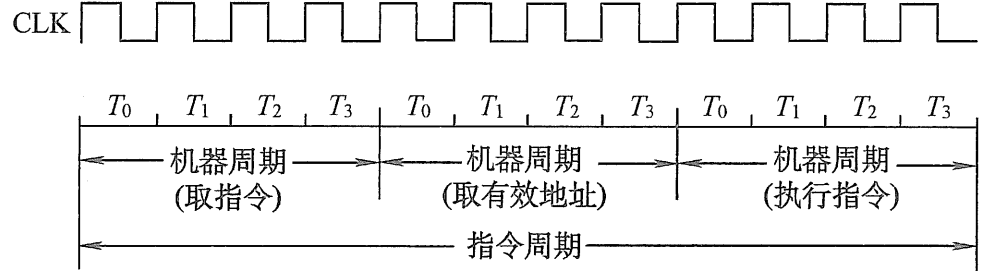
Operation flow of central processing unit
CPU The main operating principle of , Regardless of its appearance , It's all about execution ( Stored in a program ) A series of instructions .
What is discussed here is to follow the general feng · Neumann structure (von Neumann architecture) Designed equipment .
The program is stored on the computer in a series of numbers Memory in .
Almost all Feng · Neumann CPU The operating principle of can be divided into
- Four stages : extract 、 decode 、 perform and Write back to .
The first stage , extract , Retrieve... From program memory Instructions ( Is a number or a series of numbers ).
from Program counter Specify the location of the program memory , The program counter stores a value that identifies the current program location .
In other words , The program counter records CPU Traces in the current program .
After extracting the instruction ,PC Increase the memory unit according to the instruction length [iwordlength].
The extraction of instructions often has to look up from relatively slow memory , Lead to CPU Waiting for instructions to be sent . This problem is mainly discussed in the cache and pipeline architecture of modern processors ( See below ).
CPU The execution behavior is determined according to the instructions extracted from the memory .
stay decode Stage , Instructions are broken down into meaningful fragments .
- according to CPU Of Instruction set architecture (ISA(architecture)) The definition translates values into instructions [isa].
- Part of the instruction value is Operation code , It indicates which operations to perform .
- Other values usually provide the necessary information for the command , Like a Add The operation target of the operation . Such an objective may provide a constant value ( Immediate value ), Or the addressing value of a space : register or Memory address , With Addressing mode decision . In the old design ,CPU The instruction decoding part of the is a hardware device that cannot be changed . But in many abstract and complex CPU and ISA in , One Microprograms It is often used to help convert instructions into signals of various forms . These microprograms are used in finished products CPU Can often be rewritten , It is convenient to change the decoding instruction .
After the extraction and decoding phase , Then enter the perform Stage . In this stage , Connect to all kinds of... That can perform the required operations CPU parts . for example , Requires an addition operation , Arithmetic logic unit Will be connected to a set of inputs and a set of outputs . The input provides the value to add , And the output will contain the sum result .ALU Embedded circuit system , In order to complete simple general operation and logic operation at the output end ( Such as addition and Bit operation ). If the addition operation produces a pair of CPU Results that are too large for processing , In the flag register , overflow Flags may be set ( See numerical accuracy discussion below ).
The final stage , Write back to , Simply write the results of the execution phase back in a certain format . The result of the operation is often written into CPU Internal registers , For quick access by subsequent instructions . In other cases , The operation result may be written in slowly , For example, those with large capacity and low cost Main memory . Some types of instructions operate on program counters , Instead of directly generating result data . These are commonly referred to as “ Jump ” And bring... In the program loop Behavior 、 Conditional execution ( Jump through conditions ) and function [jumps]. Many instructions also change the status bits of the flag register . These flags can be used to influence program behavior , Because they often show various operation results . for example , With a “ Compare ” The instruction determines the size of two values , Set a value on the flag register according to the comparison result . This flag can be used to determine the program direction by subsequent jump instructions .
After executing the instruction and writing back the result data , The value of the program counter is incremented , Repeat the whole process , The next instruction cycle normally extracts the next sequential instruction . If a jump instruction is completed , The program counter will be modified to jump to the instruction address , And the program continues to execute normally . A lot of complicated CPU You can extract multiple instructions at once 、 decode , And at the same time . This part generally involves “ classic RISC Assembly line ”, Those are actually simple in many uses CPU The rapid spread of electronic equipment ( Often called Micro controller )[riscpipeline].
边栏推荐
- Preparation for a series of courses on WordPress applet generation
- How to convert an array to an object, and how to convert an object to an array
- 88. merge ordered arrays
- Quick completion guide for manipulator (III): mechanical structure of manipulator
- Centripetalnet: more reasonable corner matching, improved cornernet | CVPR 2020 in many aspects
- Cook a delicious cli
- The nodejs service global timeout callback failed to get process Domain problem
- What is a voice assistant? What will the future voice assistant look like?
- What is the resource search platform and how resource search works
- Besides technology, programmers also need to master a skill - self marketing ability
猜你喜欢

Multithreaded applications - improve efficiency

【本周六活动】.NET Day in China
![[JS reverse sharing] community information of a website](/img/71/8b77c6d229b1a8301a55dada08b74f.png)
[JS reverse sharing] community information of a website

Apple's legendary design team disbanded after jobs refused to obey cook

Maui's way of learning -- Opening

使用Process Monitor工具监测进程对注册表和文件的操作
历史上的今天:图灵诞生日;互联网奠基人出生;Reddit 上线

脚本之美│VBS 入门交互实战

Moving Tencent to the cloud cured their technical anxiety

Any 与 TypeVar,让 IDE 的自动补全更好用
随机推荐
[activities this Saturday] NET Day in China
图片的可视化呈现有效增强大屏吸引力
First acquaintance with string+ simple usage (I)
Functions of document management what functions does the document management software have
【毕业季·进击的技术er】绕树三匝,何枝可依?
喜欢就去行动
I just did it! Visualization of character relationships in Douluo continent
Mongodb index operation
Tencent's open source project "Yinglong" has become a top-level project of Apache: the former long-term service wechat payment can hold a million billion level of data stream processing
Introduction to the use of splice() method
What is wireless WiFi? What are the benefits of wireless WiFi
Today in history: Turing's birth day; The birth of the founder of the Internet; Reddit goes online
突然想到老家的木屋
Why should we make the best use of the external chain in SEO?
When the data security law comes, how can enterprises prepare for a rainy day? Tencent security has something to say
The record of 1300+ times of listing and the pursuit of ultimate happiness
@RequestBody注解
Stack Title: exclusive time of function
How to use arbitrarygen code generator what are the characteristics of this generator
服乔布斯不服库克,苹果传奇设计团队解散内幕曝光