当前位置:网站首页>Thread process foundation of JUC
Thread process foundation of JUC
2022-07-01 05:09:00 【People below two meters are mortals】
List of articles
1、 Processes and threads
1.1、 process
- A program consists of instructions and data , But these instructions have to run , Read and write data , You have to load the instructions into CPU, Data is loaded into memory . In the process of instruction running, the disk is also needed 、 Network and other equipment . Processes are used to load instructions 、 Manage memory 、 management IO Of
- When a program is run , Load the program's code from disk to memory , At this point, a process begins .
- A process can be considered an instance of a program . Most programs can run multiple instance processes at the same time ( For example, Notepad 、 drawing 、 The browser etc. ), Some programs can only start one instance process ( For example, Netease cloud music 、360 Security guard, etc )
1.2、 Threads
- A process can be divided into one or more threads .
- A thread is a stream of instructions , Give instructions in a certain order to CPU perform
- Java in , Thread as the minimum scheduling unit , Process is the smallest unit of resource allocation . stay windows The middle process is inactive , Just as a container for threads
1.3、 Comparison between processes and threads
- Processes are basically independent of each other , Threads exist in the process , It's a subset of the process
- Processes have shared resources , Such as memory space , For internal threads to share
- Inter process communication is more complex
- The process communication of the same computer is called IPC(Inter-process communication)
- Process communication between different computers , Need to go through the Internet , And abide by a common agreement , for example HTTP
- Thread communication is relatively simple , Because they share memory in the process , An example is that multiple threads can access the same shared variable
- Threads are lighter , The cost of thread context switching is generally lower than that of process context switching
2、 Serial and parallel
2.1、 summary
Single core cpu Next , The thread is actually Serial execution Of . There is a component in the operating system called task scheduler , take cpu Time slice of (windows The next time slice is about 15 millisecond ) among
Different programs use , Just because cpu Between the lines ( The time slice is very short ) The switch is very fast , The human feeling is Simultaneous running . In a word, it is : Micro serial , Macro parallel ,
It's usually Threads take turns using CPU This is called concurrency (
concurrent)Multicore cpu Next , Every nucleus (core) Can schedule running threads , At this time, the thread can be parallel .
2.2、 Comparison between serial and parallel
Concurrent (concurrent) At the same time (dealing with) Ability to do many things
parallel (parallel) It's doing it at the same time (doing) Ability to do many things
2.3、 application
2.3.1、 Asynchronous call
From the perspective of the caller , If :
- Need to wait for the result to return , To continue to run is Sync
FileReader.read("xxxx");
log.debug("do other things ...");
- There is no need to wait for the result to return , Can continue to run, that is asynchronous
new Thread(() -> FileReader.read("xxxx")).start();
log.debug("do other things ...");
For the above two pieces of code , You can feel it clearly , For synchronous calls , If a method takes too long to execute , Specially ,IO Operation does not occupy cpu, Then this thread will do everything
I can't wait , Make the following code can't be executed , But if you use asynchronous calls , Then the target method will use other threads to execute , Its execution no longer blocks the current thread , Make the front line
The process can continue down
2.3.2、 Parallel execution
A four core CPU scenario , The following three calculations need to be performed , Finally, the three calculation results are summarized
Calculation 1 cost 10 ms
Calculation 2 cost 11 ms
Calculation 3 cost 9 ms
Summary needs 1 ms
Serial execution , Simple and clear ,10 + 11 + 9 + 1 = 31ms
Parallel execution , The core 1 Use a thread to perform calculations 1, The core 2 Use a thread to perform calculations 2, The core 3 Use a thread to perform calculations 3, The total running time of the three will only depend on the calculation with the longest execution time
2, That is to say 11ms, Last core 4 Use a thread to summarize three results , Sharing time 11 + 1 = 12ms
Single core cpu Next , Multithreading can't actually improve the running efficiency of programs , Just to be able to switch between different tasks , Different threads take turns to use cpu , Not a thread is always occupied cpu, No other thread
Work by law
Multicore cpu Can run multiple threads in parallel , But whether we can improve the running efficiency of the program depends on the situation
- Some tasks , Well designed , Split the task , Parallel execution , Of course, it can improve the efficiency of the program . But not all computing tasks can be split
- Not all tasks need to be split , If the purpose of the task is different , There's no point in talking about separation and efficiency
3、Java Threads
3.1、 Thread creation
3.1.1、Thread
// The argument to the constructor is to assign a name to the thread , recommend
Thread t = new Thread("t") {
@Override
// run Method implements the task to be executed
public void run() {
log.debug("hello");
}
};
t.start();
3.1.2、Runnable
- One Runnable Represents a runnable task ( The code to be executed by the thread )
// Create task object
Runnable task = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
log.debug("hello");
}
};
// Parameters 1 It's the object of the mission ; Parameters 2 It's the thread name , recommend
Thread t = new Thread(task, "t");
t2.start();
3.1.3、FutureTask
- FutureTask Be able to receive Callable Parameters of type , Used to deal with situations with returned results
// Create task object
FutureTask<Integer> task = new FutureTask<>(() -> {
log.debug("hello");
return 100;
});
// Parameters 1 It's the object of the mission ; Parameters 2 It's the thread name , recommend
new Thread(task, "t").start();
// Main thread blocking , Synchronization waiting task The result of execution
Integer result = task.get();
log.debug(" The result is :{}", result);
3.1.4、Runnable and Thread The relationship between
establish Thread When , If you pass in a Runnable object , that Thread Class will change the current Runnable The object assigns itself a name target In the member variable of

When calling Thread Class start() After the method , The operating system will start a thread , This thread is now ready ( Can run ) state , Not running , Once you get it cpu Time slice , We'll start run() Method

Here's how run() Called thread body , It contains the contents of the thread to be executed ,run() End of method run , This thread will terminate .
If we don't pass in Runnable object , But to realize its own run() Method , Then the natural thread will get cpu After the time slice , It will be realized by ourselves run() Method
3.2、 Principle of thread operation
JVM By stack , Pile up , Method area , Stack memory is used by threads , After each thread starts ,JVM Will allocate a stack memory
- Each stack consists of multiple stack frames (Frame) form , Corresponding to the memory occupied by each method call
- The stack frame of the currently executing method , We call it Active stack frame , Each thread has only one active stack frame
/** * @author PengHuanZhi * @date 2021 year 12 month 08 Japan 18:41 */
public class Frames {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
method1();
}
private static void method1() {
int i = method2(1, 2);
System.out.println(i);
}
private static int method2(int a, int b) {
int c = a + b;
return c;
}
}
Observe the commissioning console

In the picture Frames Is corresponding to our Java Virtual machine stack frame , The current code runs to Main Method , Not yet in method1 Method , So there is only one stack frame set main Method , Now enter method1, Observe again
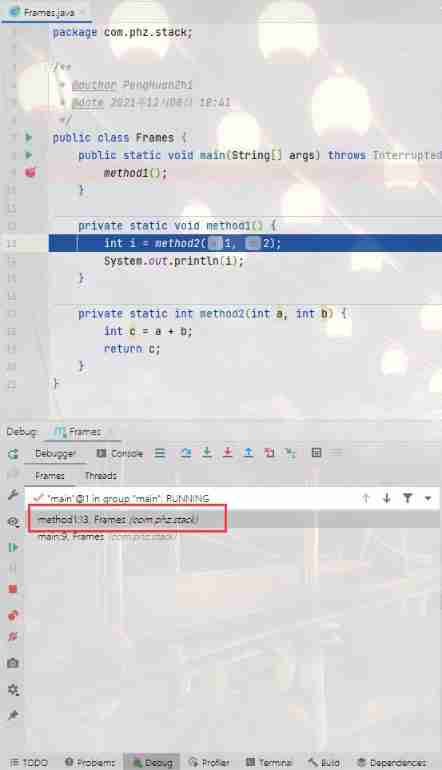
Empathy , Once again into the method2

from method2 Method , Look again , You can find ,method2 It was ejected

3.3、 Thread context switch
Thread context switching refers to the following reasons cpu The current thread is no longer executed , Instead, execute the code of another thread
Thread cpu I ran out of time
Garbage collection
Higher priority threads need to run
The thread called itself sleep、yield、wait、join、park、synchronized、lock Other methods
When thread context switching occurs , The state of the current thread needs to be saved by the operating system , And restore the state of another thread ,Java The corresponding concept in It's the program counter ( Its function is to remember the next item JVM The execution address of the instruction , Threads are private
Status includes program counters 、 Information of each stack frame in virtual machine stack , Such as local variables 、 The stack of operands 、 Return address, etc
Frequent thread context switching can affect performance
4、 Common methods
| Method name | static | Functional specifications | Be careful |
|---|---|---|---|
| start() | Start a new thread , Run in a new thread run The code in the method | start The method is simply to put the thread into ready , The code inside does not necessarily run immediately (CUP He hasn't been given a time slice yet ). Per thread object start Method can only be called once , Occurs if called multiple times IllegalThreadStateException | |
| run() | The method that will be called after the new thread is enabled | If in construction Thread Object Runnable Parameters , After the thread is started, call Runnable Medium run Method , Otherwise, no operation will be performed by default . But you can wear Thread Subclass object of , To override the default behavior | |
| join() | Wait for the thread to finish running | ||
| join(long n) | Wait for the thread to finish running , Waiting for the most n millisecond | ||
| getId() | Get thread length integer id | id only | |
| getName() | Get the thread name | ||
| setName(String) | Modify the thread name | ||
| getPriority() | Get thread priority | ||
| getPriority(int) | Modify thread priority | java The priority specified in is 1~10 The integer of , A higher priority can improve the efficiency of the thread CPU The probability of calling | |
| getState() | Get thread status | Java Thread status in 6 individual enum Express , Respectively : NEW, RUNNABLE, BLOCKED, WAITING, TIMED_WAITING, TERMINATED | |
| isInterrupted() | Determine whether you were beaten break , | It won't clear “ Break mark ” | |
| isAlive() | Is the thread alive ( It's not finished yet BI ) | ||
| interrupt() | Interrupt thread | If the interrupted thread is sleep,wait,join Can cause interruption The thread threw InterruptedException, And get rid of Interrupt mark remember ; If you interrupt a running thread , Will set up Interrupt mark remember ;park Thread interrupted , It will also set up Break mark | |
| interrupted() | static | Determine whether the current thread is No, interrupted | Will clear Break mark |
| currentThread() | static | Get currently executing Thread of line | |
| sleep(long n) | static | Let the currently executed line Cheng dormancy n millisecond , Give up when dormant cpu Time slice for others Threads | |
| yield() | static | Prompt thread scheduler Release the current thread pair CPU Use | Mainly for testing and debugging |
4.1、run and start
For these two methods , It's about Runnable and Thread The relationship between Have mentioned , I won't repeat it here
4.2、getState
This method can get the status of the current thread ,Java Thread status in 6 individual enum Express , Respectively :
NEW: A new thread object is created , But it's not called yet start() Method .
RUNNABLE:JAVA The thread will be ready (ready) And in the operation of the (running) The two states are generally called “ function ”.
BLOCKED: Blocking , Indicates that the thread is blocked by a lock
WAITING: wait for , A thread entering this state needs to wait for some specific action from another thread ( Notification or interruption ).
TIMED_WAITING: Finite waiting state ( Time limited , Corresponding sleep Method sleep time )
TERMINATED: End
Just have a simple look
Thread t = new Thread(() -> System.out.println("invoke..."), "t");
System.out.println(t.getState());
t.start();
System.out.println(t.getState());

The same thread cannot be called more than once , Otherwise, an error thread state exception will be thrown IllegalThreadStateException
4.3、sleep
call sleep Will cause the current thread to Running Get into Timed Waiting state ( Finite waiting state )
After sleep, the thread may not be executed immediately
Suggest using TimeUnit Of sleep Instead of Thread Of sleep For better readability
@SneakyThrows
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
//Do Nothing
}
}, "t");
System.out.println(t.getState());
t.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(t.getState());
}

4.4、interrupt
4.4.1、 Interrupt a sleeping thread
Other threads can use interrupt Method to interrupt the sleeping thread , At this time sleep Method will throw InterruptedException Thus, the sleep thread executes again
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
log.info("sleep...");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000); // wait, join
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "t");
t1.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.info("interrupt");
t1.interrupt();
log.info(" Break mark :{}", t.isInterrupted());
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.info(" Break mark :{}", t.isInterrupted());

about sleep、wait、join The thread of , Break it , The thread will re-enter a WAITING state , The interrupt state changes to... In the thread WAITING It will be emptied
4.4.2、 Interrupt a running thread
Other threads can use interrupt Method to break a running thread , Normal running threads can also be divided into blocked threads and executing threads
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
boolean interrupted = Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted();
if (interrupted) {
log.info(" Interrupted , Exit loop ");
break;
}
}
}, "t");
t.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.info("interrupt");
t.interrupt();

4.4.3、 interrupt park Threads
LockSupport Medium park() Method can also stop the current thread
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
log.info("park...");
LockSupport.park();
log.info("unpark...");
log.info(" Interrupt state :{}", Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
log.info("unpark...");
}, "t");
t.start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
t.interrupt();

park The method has one characteristic , That is, it has been park After the thread is interrupted , Re execution park Method , The current thread cannot stop
park The reason why the method fails is that it only applies to the interrupt state false Thread of takes effect , After the first interruption , The interruption state changes to true , If you still want park The method works , This can be done using
interrupted Method to reset the interrupt state
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
log.info("park...");
LockSupport.park();
log.info("unpark...");
log.info(" Interrupt state :{}", Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
Thread.interrupted();
log.info(" Interrupt state :{}", Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
LockSupport.park();
log.info("unpark...");
}, "t");
t.start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
t.interrupt();

4.5、yield
The original intention is to give up
call yield Will cause the current thread to Running Get into Runnable Ready state , Then schedule other threads.
The specific implementation depends on the task scheduler of the operating system , If the current system resources are abundant , Then the task scheduler of the operating system will still hand over the time slice to the current thread for execution
The difference in sleep, perform yield Method thread , The next time slice still has the opportunity to execute , But to perform sleep Method thread , Only after a certain amount of time can we have the opportunity to implement , And not immediately
Runnable task1 = () -> {
int count = 0;
for (; ; ) {
System.out.println("---->1 " + count++);
}
};
Runnable task2 = () -> {
int count = 0;
for (; ; ) {
System.out.println("---->2 " + count++);
}
};
Thread t1 = new Thread(task1, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(task2, "t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();

to t1 Add one... Per loop yield Method
Runnable task1 = () -> {
int count = 0;
for (; ; ) {
Thread.yield();
System.out.println("---->1 " + count++);
}
};
Re execution

4.6、setPriority
- Thread priority will prompt (hint) The scheduler schedules the thread first , But it's just a hint , The scheduler can ignore it
- If cpu Busy , The thread with higher priority will get more timeslices , but cpu Leisure time , Priority has little effect
Runnable task1 = () -> {
int count = 0;
for (; ; ) {
System.out.println("---->1 " + count++);
}
};
Runnable task2 = () -> {
int count = 0;
for (; ; ) {
System.out.println("---->2 " + count++);
}
};
Thread t1 = new Thread(task1, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(task2, "t2");
t1.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
t2.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
t1.start();
t2.start();
Above code , The author's equipment can't detect much difference , If the reader needs proof , You can try to run the above code on a single core CPU On the virtual machine of , The end result should be t2 The number of executions of is higher than t1
4.7、join
Blocking waits for the target thread to finish running
private static int r = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(" Start ");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
r = 10;
System.out.println(" end ");
});
t1.start();
System.out.println(" The result is :" + r);
}
The result is
The result is :0
Start
end
The specific reason is
- Because the main thread and thread t1 Is executed in parallel ,t1 Thread needs 1 It takes seconds to figure out r=1, And the main thread starts printing r Result , So you can only print it out r=0
There are two solutions
- The main thread uses sleep, But this is not recommended , because t1 The execution time is often not fixed
- The main thread uses t1.join(), After the main thread executes this step , It's going to block , until t1 completion of enforcement ,join Method can add a timeout parameter , If the timeout occurs, the main thread unblocks and continues to execute downward
private static int r = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(" Start ");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
r = 10;
System.out.println(" end ");
});
t1.start();
t1.join();
System.out.println(" The result is :" + r);
}
The result is
Start
end
The result is :10
4.8、 Outdated methods
These methods are outdated , Easy to break synchronous code blocks , Cause thread deadlock
| Method name | Functional specifications |
|---|---|
| stop() | Stop the thread running |
| suspend() | Hang up ( Pause ) Thread running |
| resume() | Thread recovery |
- stop May adopt Two phase termination of termination mode To replace
- suspend Methods can be used Object.wait Method to better suspend threads
- resume You can also use Object.notify Method to better wake up threads
5、 Main thread and guard thread
By default ,Java The process needs to wait for all threads to finish running , It's over .
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
break;
}
}
log.info(" end ");
}, "t");
t.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.info(" end ");

There is a special thread called the guardian thread , As long as other non daemon threads run , Even if the code of the daemon thread is not finished , It'll be forced to end , Just use setDaemon(true) You can set a thread as a daemon thread .
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
break;
}
}
log.info(" end ");
}, "t");
t.setDaemon(true);
t.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.info(" end ");

The garbage collector thread is a kind of guardian thread
Tomcat Medium Acceptor ( Accept the request ) and Poller ( Distribute the requests ) Threads are all guard threads , therefore Tomcat Received shutdown After the command , Won't wait Wait until they finish processing the current request
6、 State of thread
6.1、 Five states
At the operating system level , Threads have five states
- The initial state : Only thread objects are created at the language level , Not yet associated with an operating system thread
- Ready state ( Operational state ): Indicates that the thread has been created ( Associated with the operating system thread ), Can be CPU Scheduling execution
- Running state : Refers to the acquisition of CPU Time slice running state , When CPU I ran out of time , Will transition to ready state , The thread will perform context switching
- Blocked state : Blocked threads , As long as you don't wake up , The scheduler will never consider scheduling them , For example, call BIO Read and write files , because IO Operation will not use CPU So the current thread will perform context switching , Go into blocking mode , Only when IO End of operation , The operating system will wake it up , Then switch to ready state
- Termination status : Indicates that the thread has finished executing , The life cycle is over , No more transitions to other states
6.2、 Six states
from JAVA API Level description , Threads have six states , Please refer to Thread.State
public enum State {
/** * Thread state of a thread that has not been started */
NEW,
/** * The thread state of a runnable thread . The thread in the runnable state is Java Execute... In virtual machine , * But it may be waiting for other resources from the operating system , For example, processor . */
RUNNABLE,
/** * Thread blocking thread state waiting for lock . The blocked thread is waiting to unlock and then enter the synchronization block method * Or call Object.wait Then re-enter the synchronization block method . */
BLOCKED,
/** * Wait for the thread state of the thread . Due to calling one of the following methods , The thread is in a wait state : * Object.wait * Thread.join * LockSupport.park * * The waiting thread is waiting for another thread to perform a specific operation . * * for example : * Called on an object Object.wait() Your thread is waiting for another thread to call * Object.notify() or Object.notifyAll() On that object . * * Already called Thread.join() Is waiting for the specified thread to terminate . */
WAITING,
/** * Thread state of a waiting thread with a specified waiting time . Because one of the following methods is called with the specified waiting time , The thread is in a timed wait state : * Thread.sleep(long timeout) * Object.wait(long timeout) * Thread.join(long timeout) * LockSupport.parkNanos(long timeout) * LockSupport.parkUntil(long timeout) */
TIMED_WAITING,
/** * Thread state of terminated thread . Thread has finished executing . */
TERMINATED;
}
NEW: Thread just created , But not yet called start() Method
RUNNABLE: When a thread is called start() After method ,Java API Level of RUNNABLE It covers the state of the operating system 【 Ready state 】、【 Running state 】 and 【 Obstructive
state 】( because BIO Thread blocking caused by , stay Java There's no way to distinguish between them , Still considered operational )
BLOCKEDWAITINGTIMED_WAITING: All are Java API Face to face 【 Blocked state 】 Subdivision of
TERMINATED: When the thread code ends running
Example :
Thread t1 = new Thread("t1") {
@Override
public void run() {
log.info("running...");
}
};
Thread t2 = new Thread("t2") {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
// runnable
}
}
};
t2.start();
Thread t3 = new Thread("t3") {
@Override
public void run() {
log.info("running...");
}
};
t3.start();
Thread t4 = new Thread("t4") {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (Test.class) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000000); // timed_waiting
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
};
t4.start();
Thread t5 = new Thread("t5") {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
t2.join(); // waiting
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
t5.start();
Thread t6 = new Thread("t6") {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (Test.class) {
// t4 The lock has been taken but not released , So here we will blocked
try {
Thread.sleep(1000000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
};
t6.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("t1 state {}", t1.getState());
log.info("t2 state {}", t2.getState());
log.info("t3 state {}", t3.getState());
log.info("t4 state {}", t4.getState());
log.info("t5 state {}", t5.getState());
log.info("t6 state {}", t6.getState());

6.3、 Thread state switch
6.3.1、NEW -> RUNNABLE
- call start Method
6.3.2、RUNNABLE -> WAITING
- Thread use synchronized(obj) After getting the object lock , call obj.wait() When the method is used
- Current thread call t.join() When the method is used , Note that the current thread is t Wait on the monitor of the thread object
- Current thread call LockSupport.park()
6.3.3、WAITING -> RUNNABLE
- t End of thread run
- Thread use synchronized(obj) After getting the object lock , call obj.notify() , obj.notifyAll() , t.interrupt() when , And the competition lock is successful ( Otherwise it becomes BLOCKED)
- call LockSupport.unpark( Target thread )
6.3.4、RUNNABLE -> TIMED_WAITING
- Thread use synchronized(obj) After getting the object lock , call obj.wait(long n) When the method is used
- Current thread call t.join(long n) When the method is used , Note that the current thread is t Wait on the monitor of the thread object
- Current thread call Thread.sleep(long n)
- Current thread call LockSupport.parkNanos(long nanos) or LockSupport.parkUntil(long millis) when
6.3.4、TIMED_WAITING -> RUNNABLE
- t End of thread run
- Thread waiting time exceeded n millisecond , Or call obj.notify() , obj.notifyAll() , t.interrupt() when , And the competition lock is successful ( Otherwise it becomes BLOCKED)
- call LockSupport.unpark( Target thread )
6.3.5、RUNNABLE -> BLOCKED
- Thread use synchronized(obj) If the race fails when an object lock is acquired
6.3.6、BLOCKED -> RUNNABLE
- a obj The synchronization block of the lock thread is executed , Will wake up all BLOCKED The threads of the , If one t Thread contention succeeded , from BLOCKED --> RUNNABLE , Other failed threads still BLOCKED
6.3.7、RUNNABLE -> TERMINATED
- All the code of the current thread is running , Get into TERMINATED
*7、 application - As a whole
attach : Hua Luogeng 《 The co-ordination method 》
The co-ordination method , It is a mathematical method of arranging the work process . It has a wide range of applications , In enterprise management and capital construction , And the organization and management of complex scientific research projects , Can be applied to .
How to apply it ? The main thing is to arrange the process well .
such as , I want to make a pot of tea . So here's what happened : There is no boiling water ; The kettle needs washing , teapot 、 The teacup needs washing ; The fire has started , Tea also has . What do I do ?
- Method a : Wash the kettle , Fill with cold water , Put it on the fire ; While waiting for the water to boil , Wash the teapot 、 Wash tea cups 、 Take the tea ; When the water boils , Make tea and drink .
- Method B : Do some preparatory work first , Wash the kettle , Wash the teapot and teacup , Take the tea ; Everything is ready. , Water and boil ; Wait until the water boils , Make tea and drink .
- Method C : Wash the kettle , Fill with cold water , Put it on the fire , Wait for the water to boil ; When the water boils , Rush to find tea , Wash the teapot and teacup , Make tea and drink .
Which way to save time ? We can see at a glance , The first way is good , Both of the latter two methods have been abandoned .
It's a small thing , But this is the introduction , It can lead to useful methods in production management and so on .
The kettle doesn't wash , Don't boil water , Therefore, washing the kettle is the premise of boiling water . No boiling water 、 No tea 、 Don't wash teapots and cups , You can't make tea , So these are the prerequisites for making tea . Their interrelationship , You can use the following diagram to show :
You can see at a glance from this picture , Method a requires a total of 16 minute ( And method b 、 C need 20 minute ). If you want to shorten the working hours 、 Improve work efficiency , We should mainly focus on the link of boiling water , Instead of grabbing tea and other links . meanwhile , Wash the teapot and teacup 、 The total amount of tea is only 4 minute , Great use “ When the water boils ” Time to do .
Yes , It's like bullshit , There is no high theory of inferiority . It's like walking on two legs , Eat one mouthful at a time , Everyone knows these principles . But a little change , A situation of being obsessed with things , It often exists . In the complex technological process of modern industry , Often it's not as simple as making tea . There are so many tasks , Hundreds of thousands , There are even tens of thousands of tasks . There's more to it , Perplexing , a multitude of things , It often appears that “ Everything is done To prepare , Only east wind ” The situation of . Because one or two parts are not finished , Delayed the delivery time of a complex machine . Or often because it's not the key , Three shifts a night , In a hurry , After completing this link , You have to wait for the next link to assemble . Wash the teapot , Wash tea cups , Take the tea , Or first or later , Not much to do with , And it's the same person's job , So it can be merged into :
It seems that this is “ big deal ”, But when there are too many work links , This is very necessary . This is mainly about time , But in the specific production practice , There are many other things . Although this method may not be direct Solve all the problems , however , We use this method to consider the problem , It is also beneficial .
In fact, the article has been analyzed very clearly , The code implementation is also extremely simple
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
log.info(" Wash the kettle ");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
log.info(" The boiling water ");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, " Lao Wang ");
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
log.info(" Wash the teapot ");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
log.info(" Wash tea cups ");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
log.info(" Take the tea ");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
t1.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info(" Make tea ");
}, " Xiao Wang ");
t1.start();
t2.start();

边栏推荐
- Pytoch (III) -- function optimization
- Global and Chinese market of search engine optimization (SEO) software 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- Global and Chinese markets of gps/gnss receiver modules 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- Use of STM32 expansion board temperature sensor and temperature humidity sensor
- [hardware ten treasures catalogue] - reprinted from "hardware 100000 whys" (under continuous update ~ ~)
- LeetCode_ 58 (length of last word)
- Global and Chinese market of high-end home theater 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- How to meet the requirements of source code confidentiality and source code security management
- Pytoch (I) -- basic grammar
- 工业导电滑环的应用
猜你喜欢

Manually implement a simple stack

How to meet the requirements of source code confidentiality and source code security management
How to traverse massive data in redis

C read / write application configuration file app exe. Config and display it on the interface

Pytoch (III) -- function optimization

Causes of short circuit of conductive slip ring and Countermeasures
![解决:Thread 1:[<*>setValue:forUndefinedKey]:this class is not key value coding-compliant for the key *](/img/88/0b99d1db2cdc70ab72d2b3c623dfaa.jpg)
解决:Thread 1:[<*>setValue:forUndefinedKey]:this class is not key value coding-compliant for the key *
![[summer daily question] Luogu p5886 Hello, 2020!](/img/ac/4be05f80aab7fb766674e6e2d16fbc.png)
[summer daily question] Luogu p5886 Hello, 2020!

LeetCode316-去除重复字母-栈-贪心-字符串

Actual combat: gateway api-2022.2.13
随机推荐
1076 Forwards on Weibo
Global and Chinese markets of InGaAs APD arrays 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
RuntimeError: mean(): input dtype should be either floating point or complex dtypes. Got Long instead
Global and Chinese market of paper machine systems 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Unity drags and modifies scene camera parameters under the editor
How to traverse massive data in redis
Pytorch convolution operation
Buffer stream and transform stream
Pytorch neural network construction template
字符输入流与字符输出流
Application of industrial conductive slip ring
打印流与System.setout();
Daily question -leetcode1175- permutation of prime numbers - Mathematics
Data loading and preprocessing
Spanner 论文小结
QDataStream的简单读写验证
每日一题-LeetCode1175-质数排列-数学
FileOutPutStream
【暑期每日一题】洛谷 P1568 赛跑
[daily question in summer] first time, second time, deal!