当前位置:网站首页>Analysis of C language [advanced] paid knowledge [II]
Analysis of C language [advanced] paid knowledge [II]
2022-06-09 18:03:00 【Hua Weiyun】
Calculate the length
sizeof:
Calculated variables , Array , The size of the type , Unit is byte ( The operator )
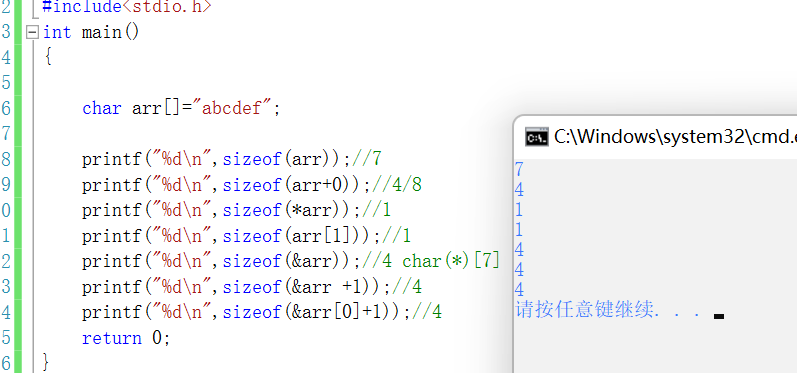
#include<stdio.h>int main(){ //sizeof( Array name )- The array name represents the name of the entire array - It calculates the size of the entire array //& Array name - The array name represents the entire array , It takes out the address of the entire array // besides , All array names are the address of the first element of the array // Shape array int a[]={1,2,3,4}; printf("%d\n",sizeof(a));//16 printf("%d\n",sizeof(a+0));//4/8 a+0 Is the address of the first element ,sizeof(a+0) It calculates the size of the address printf("%d\n",sizeof(*a));//4 *a Is the first element of the array ,sizoef(*a) It calculates the size of the first element printf("%d\n",sizeof(a+1));//4/8 a+1 Is the address of the second element ,sizeof(a+1) The size of the calculated address printf("%d\n",sizeof(a[1]));//4 It calculates the size of the second element printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a));// 4/8 [email protected] Although the address of the array , But it's also the address ,sizeof(&a) It calculates the size of an address printf("%d\n",sizeof(*&a));//16 - Calculate the size of the array //&a -- int(*p)[4]=&a; printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a+1));//4/8 - &a+1-- The address of the space behind the array printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a[0]));//4/8 printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a[0]+1));//4/8 // A character array char arr[]={'a','b','c','d','e','f'}; printf("%d\n",sizeof(arr));//6 printf("%d\n",sizeof(arr+0));//4/8 - Pointer size - The address indicated by the pointer is 4 A byte address printf("%d\n",sizeof(*arr));//1 printf("%d\n",sizeof(arr[1]));//1 printf("%d\n",sizeof(&arr));//4/8 printf("%d\n",sizeof(&arr +1));//4/8 printf("%d\n",sizeof(&arr[0]+1));//4/8 return 0;}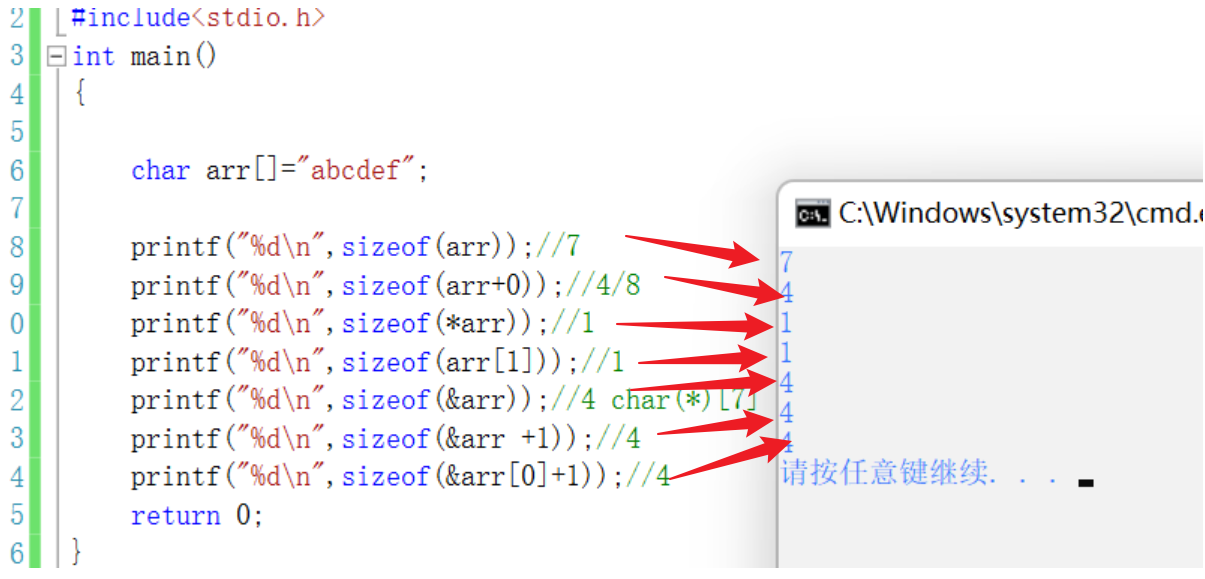
#include<stdio.h>int main(){ //sizeof( Array name )- The array name represents the name of the entire array - It calculates the size of the entire array //& Array name - The array name represents the entire array , It takes out the address of the entire array // besides , All array names are the address of the first element of the array // Shape array int a[]={1,2,3,4}; printf("%d\n",sizeof(a));//16 printf("%d\n",sizeof(a+0));//4/8 a+0 Is the address of the first element ,sizeof(a+0) It calculates the size of the address printf("%d\n",sizeof(*a));//4 *a Is the first element of the array ,sizoef(*a) It calculates the size of the first element printf("%d\n",sizeof(a+1));//4/8 a+1 Is the address of the second element ,sizeof(a+1) The size of the calculated address printf("%d\n",sizeof(a[1]));//4 It calculates the size of the second element printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a));// 4/8 [email protected] Although the address of the array , But it's also the address ,sizeof(&a) It calculates the size of an address printf("%d\n",sizeof(*&a));//16 - Calculate the size of the array //&a -- int(*p)[4]=&a; printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a+1));//4/8 - &a+1-- The address of the space behind the array printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a[0]));//4/8 printf("%d\n",sizeof(&a[0]+1));//4/8 // A character array char arr[]={'a','b','c','d','e','f'}; printf("%d\n",sizeof(arr));//6 printf("%d\n",sizeof(arr+0));//4/8 - Pointer size - The address indicated by the pointer is 4 A byte address printf("%d\n",sizeof(*arr));//1 printf("%d\n",sizeof(arr[1]));//1 printf("%d\n",sizeof(&arr));//4/8 printf("%d\n",sizeof(&arr +1));//4/8 printf("%d\n",sizeof(&arr[0]+1));//4/8 return 0;}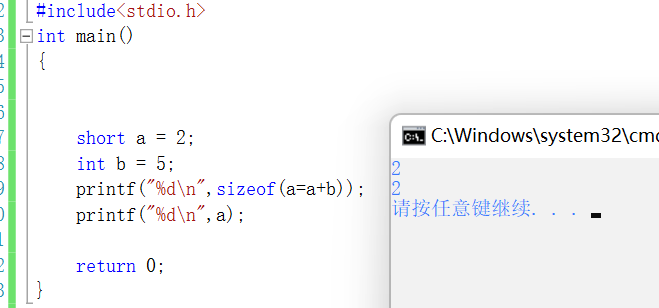
int main(){ int a[3][4] = { 0 }; printf("%d\n", sizeof(a));//48 = 3*4*sizeof(int) printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[0][0]));//4 - a[0][0] - Is the first element in the first line printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[0]));//16 printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[0] + 1));//4 explain :a[0] As an array name, it is not placed separately in sizeof Inside , // I didn't take the address , therefore a[0] It's the first address on the first line //a[0]+1, Is the address of the second element in the first line printf("%d\n", sizeof(*(a[0] + 1)));//4 - explain :*(a[0] + 1) Is the second element in the first line printf("%d\n", sizeof(a + 1));//4 - explain :a Is the array name of a two-dimensional array , No address // It's not alone sizeof Inside , therefore a It represents the address of the first element of the two-dimensional array , namely : The address on the first line //a + 1 Is the address of the second row of the two-dimensional array printf("%d\n", sizeof(*(a + 1)));//16 explain :a+1 Is the address on the second line , therefore *(a+1) It means the second line // So the calculation is the second 2 The size of the line printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a[0] + 1));//4 explain :a[0] Is the array name in the first row , //&a[0] What you take out is the address in the first line ,&a[0]+1 It's the address on the second line printf("%d\n", sizeof(*(&a[0] + 1)));//&a[0]+1 It's the address on the second line //*(&a[0]+1) The second line , So the address of the second line of the calculation printf("%d\n", sizeof(*a));//16 explain :a Array name as a two-dimensional array , No, &, Not alone in sizeof Inside //a Is the address of the first element , That is, the address on the first line , therefore *a It's the first line , It calculates the size of the first line printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[3]));//16 explain :a[3] It's actually the array name on the fourth line ( If any ) // So it doesn't really exist , You can also calculate the size by type printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[-1])); return 0;}strlen
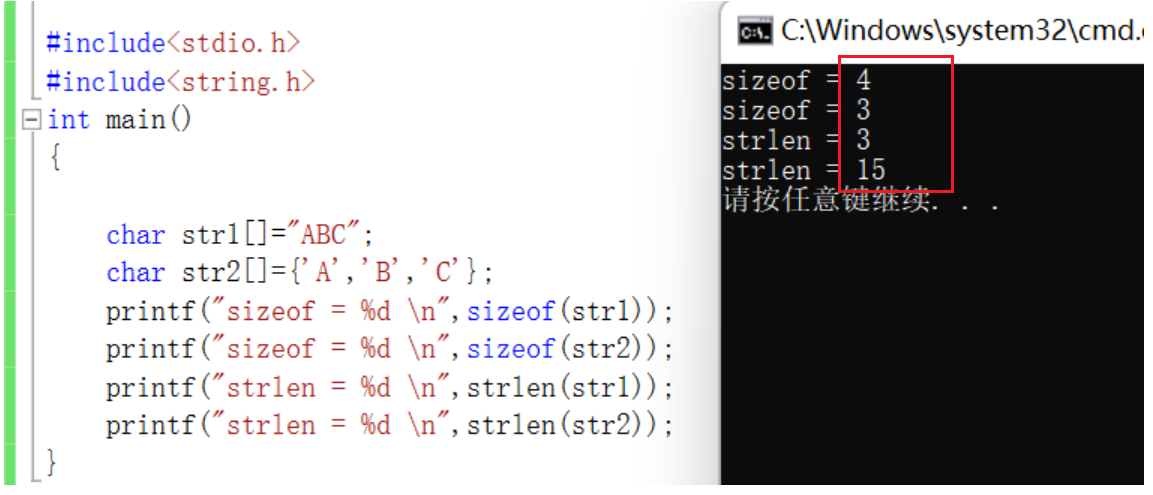
strlen: Is to find the length of the string , Only for string length ( Library function - Use the reference header file )
#include<stdio.h>#include<string.h>int main(){ char arr[]={'a','b','c','d','e','f'}; printf("%d\n",strlen(arr));// Random value - encounter ‘\0’ end printf("%d\n",strlen(arr+0));// Random value //printf("%d\n",strlen(*arr));//err //printf("%d\n",strlen(arr[1]));//err printf("%d\n",strlen(&arr));// Random value printf("%d\n",strlen(&arr+1));// Random value - 6 printf("%d\n",strlen(&arr[0]+1));// Random value - 1 return 0;}because strlen Just find the length of the string , Random values are generated for characters
The pointer
The size of the pointer variable
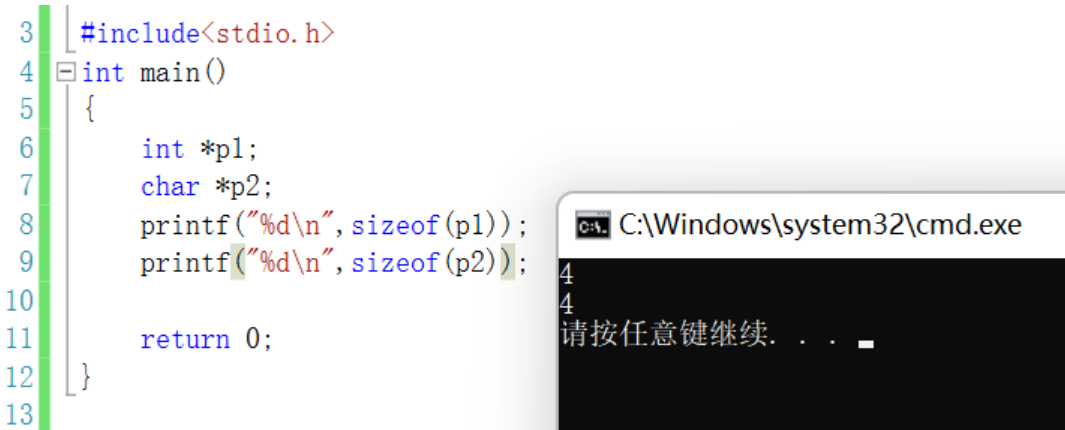
32 Bit computer system The integer pointer accounts for 4 Bytes , The actual parameter is passed to the character parameter 4 Bytes
void test1 (char ch)//char *ch{
printf("%d\n",sizeof(ch));//4 Bytes , Because the first address of the character is passed in , That's the pointer char *ch , The length of the pointer is 4, therefore char The passed parameter of character type is the passed pointer byte}char arr[10]={0};printf("%d\n",sizeof(char));//10test1(ch);// The first element of the character array
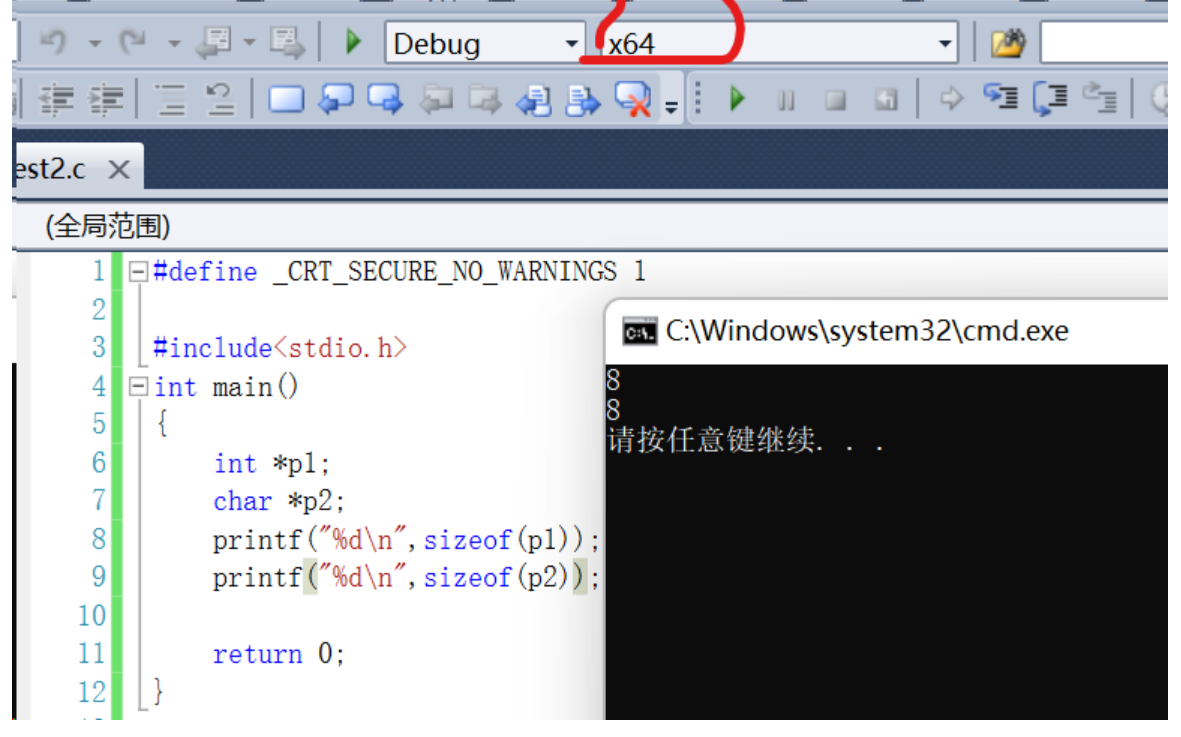
- As long as 32 Bit operating environment , No matter what type , All are 4 Bytes
- stay 64 Bit environment
Declaration pointer
int* a,b,c; In fact, only variables are declared a It's the pointer type If you want to declare three pointers :int a ,b, *c;

Structure
. : Structural variable . member
-> : Structure pointer -> member

#include<stdio.h>#include<string.h>struct Book{ char book_name[20]; int price;};int main(){ struct Book b={"c Language programming ",55}; struct Book* p = &b; // Change price (*p).price=19;// Equate to p->price printf("%d\n",b.price); // Change book title // Use library function strings to copy functions //b1.name="c++";//error strcpy(p->book_name,"C++");// because book_name Is a character array name , The array itself is an address , and price It's a variable. printf("%s\n",(*p).book_name); printf("%s\t %d\n",p->book_name,p->price); printf("%s\t%d\n",(*p).book_name,(*p).price);//(*p).book_name,(*p).price Equate to p->book_name,p->price printf("%s\n",b.book_name); printf("%d\n",b.price); return 0;}Array element address
1.sizeof( Array name ), Calculate the size of the entire array ,sizeof Put a separate array name inside , The array name represents the entire array 2.& Array name , The address of the extracted array .& Array name , The array name represents the entire array .
In addition to this 1,2 Except for two cases , All array names represent the address of the first element of the array
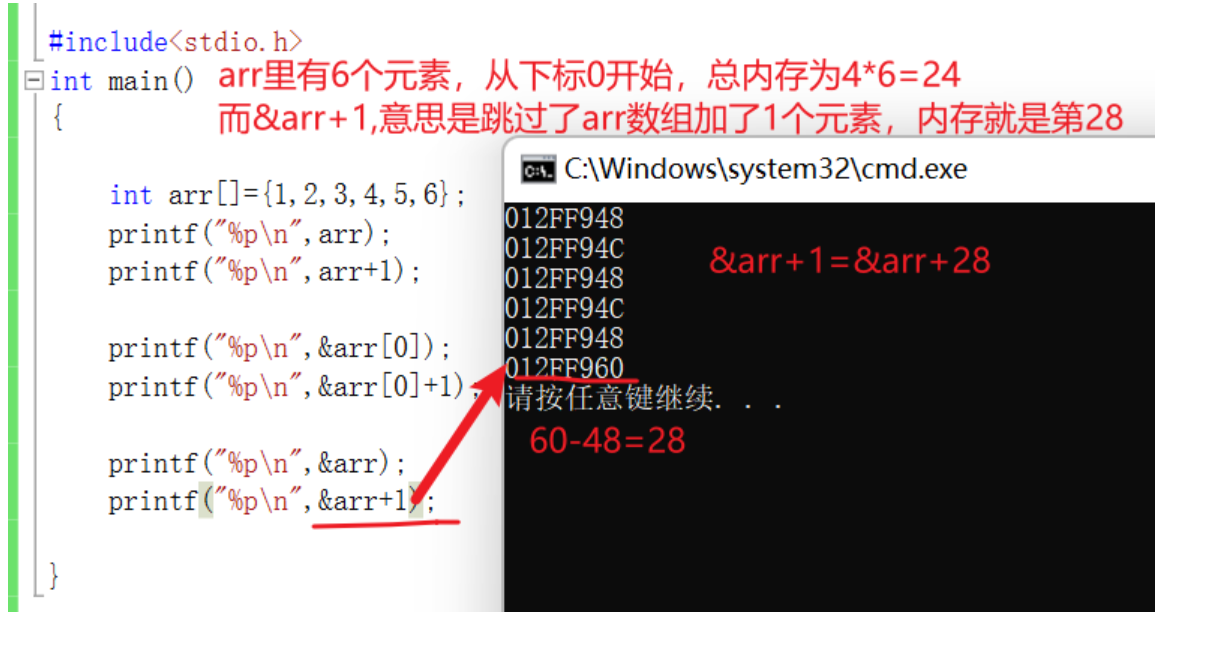
character string
String comparison
stract(str1,str1); //err, Because I will add that I will '\0' overwrite , No, it hasn't been '\0' Go back and forth
You can't compare two strings to make them equal , You should use the string example :
char password[20]={0};sacnf("%s",password);//if(pwssword == "123456")//errif(strcmp(password,"123456")==0)printf(" identical ");Copy of string
Copy the string to the destination address , Debugging we found , encounter '\0' End copy
// Change book title // Use library function strings to copy functions //b1.name="c++";//error strcpy(p->book_name,"C++");// because book_name Is a character array name , The array itself is an address 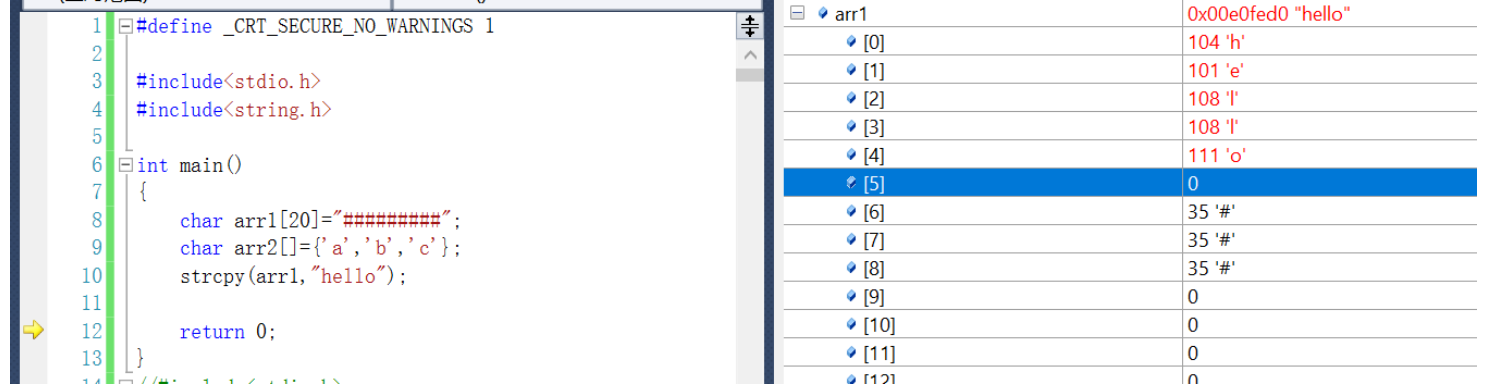
When the copy is not '\0' end , Program running error
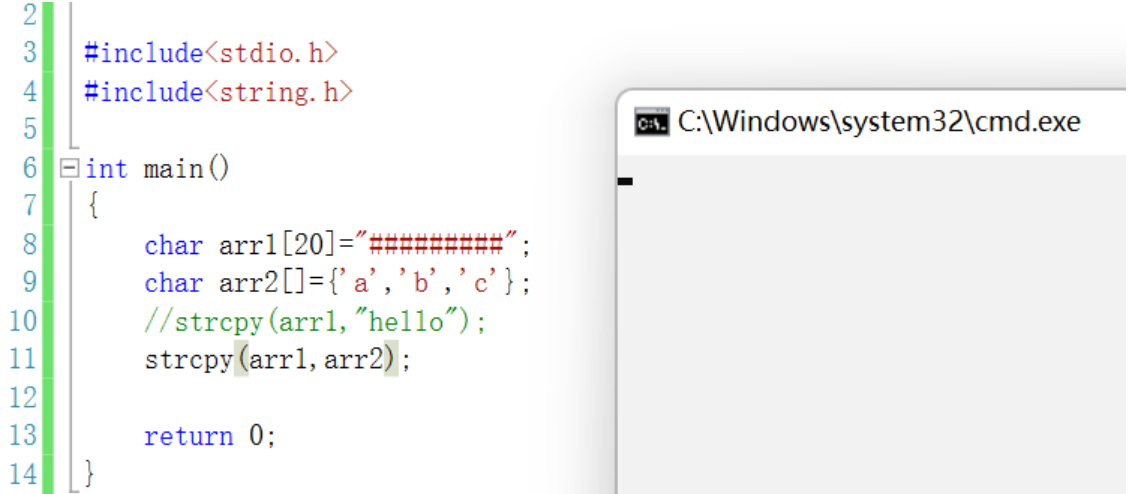
The source string must be in '\0' end .
In the source string '\0' Copy to target space .
The target space has to be large enough , To ensure that the source string can be stored .
The target space has to be variable .
Learn to simulate . Be careful : The source character must be a character array or a pointer to an array of dynamically allocated memory , Cannot use string constants !
Structure
Memory alignment
On the whole :
Memory alignment of structures is a way of trading space for time . rise .
S1 and S2 The type of members as like as two peas , however S1 and S2 There are some differences in the amount of space taken up .
// for example :struct S1{char c1;int i;char c2;};struct S2{char c1;char c2;int i;};Change the default alignment number
We met before #pragma This preprocessing instruction , Here we use again , We can change our default alignment number .
// for example :struct S1{ char c1; int i; char c2;};struct S2{ char c1; char c2; int i;};#include <stdio.h>#pragma pack(8)// Set the default alignment number to 8struct S1{ char c1; int i; char c2;};#pragma pack()// Unset the default number of alignments , Restore to default #pragma pack(1)// Set the default alignment number to 1struct S2{ char c1; int i; char c2;};#pragma pack()// Unset the default number of alignments , Restore to default int main(){ // What is the result of the output ? printf("%d\n", sizeof(struct S1)); printf("%d\n", sizeof(struct S2));边栏推荐
- 君可归烈士寻亲系统开发实战
- 【玩转华为云】基于华为云图像识别标签实战
- Vulkan规范笔记(一) 第一章至第六章
- How to realize face verification quickly and accurately?
- slurm program running without multiprocess instead run individually
- js中性能优化之函数防抖
- MySQL并行复制(MTS)原理(完整版)
- Mediapipe body and hand key points
- Epigentek染色质可及性检测试剂盒原则与程序
- How to learn the process of KD tree construction and search with cases?
猜你喜欢

Macro definition CV with parameters in opencv_ Role of assert()

14届数独-真题标准数独-Day 6-20220121(补)

Operation manual of abbexa PCR super mixture

微信小程序根据经纬度获取省市区信息

Reconstruction practice of complex C-end projects

nlp网络中两种残差结构对网络的影响

NLP - Keyword Extraction - textrank

NLP keyword extraction overview

NLP-RNN

Some interesting b+ tree optimization experiments
随机推荐
【玩转华为云】MapReduce服务初体验
About concurrency and parallelism, are the fathers of go and Erlang wrong?
ZigBee组网从未如此简单!
华为云原生之数据仓库服务GaussDB(DWS)的深度使用与应用实践【这次高斯不是数学家】
梦醒
Wake up from a dream
Vulkan specification notes (I) Chapter 1 to Chapter 6
Real topic of the 13th provincial competition of the Blue Bridge Cup in 2022 - block painting
How to ensure personal and property safety when traveling
NLP- 关键词提取 - 综述
解决Chrome提示:“您的连接不是私密连接“,且无继续访问选项问题
Function throttling for performance optimization in JS
Reconstruction practice of complex C-end projects
sqllite create a database
[work with notes] multiple coexistence of ADB, sound card, network card and serial port of Tina system
可以用来nlp任务评估的计算方法(语意相近计算)
Abbexa PCR 超级混合液使用说明书
I/O流
腾讯云数据库TDSQL|像这样的高考,其实我们每天都在经历
谁说Redis不能存大key