当前位置:网站首页>09 MySQL lock
09 MySQL lock
2022-06-11 19:30:00 【Runaway mine】
1 The type of lock
1.1 Row-level locks
MySQL Two standard levels of row level locks are provided
- Shared lock (S Lock): Allow a transaction to read a row of data
- Exclusive lock (X Lock): Allow transactions to delete or update a row of data
Compatibility between exclusive locks and shared locks
| X | S | |
|---|---|---|
| X | Conflict | Conflict |
| S | Conflict | compatible |
1.2 Intent lock
InnoDB Support Multi granularity locking , Allow locks at row level and table level to exist at the same time
InnoDB It also supports additional locking methods , According to the Intent locks , yes surface Level lock , Used to reveal the type of lock requested by the next row in a transaction
- Intention sharing lock (IS Lock): The transaction wants to obtain the shared lock of some rows in the table
- Intention exclusive lock (IX Lock): The transaction wants to obtain exclusive locks for certain rows in the table
The intent lock shall be subject to the following protocol :
- Before the transaction acquires the shared lock of a row , First get IS A lock or stronger lock
- Before a transaction acquires an exclusive lock on a row , First, get... On the table IX lock
| IS | IX | S | X | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS | compatible | compatible | compatible | Are not compatible |
| IX | compatible | compatible | Are not compatible | Are not compatible |
| S | compatible | Are not compatible | compatible | Are not compatible |
| X | Are not compatible | Are not compatible | Are not compatible | Are not compatible |
X Locks are not compatible with any locks ,S Lock and IX Locks are not compatible , The rest are compatible
Intentional locks only block table level locks , Row level locks are not blocked
InnoDB Two kinds of locking operation of storage engine :
- select … for update: Add a... To the read line X lock , Other transaction locking will be blocked
- select … lock in share mode: Add a... To the read row record S lock , Other business can add S lock , But for the X The lock will be blocked
1.3 Self increasing lock
The transaction is inserted into the with AUTO-INC A special table level lock for columns , When a transaction is inserted , A self incrementing lock must be obtained to obtain the value of the self incrementing column
innodb_autoinc_lock_mode Parameters
- value 0: stay 5.1 Implementation of self growth before version , Locked by watch AUTO-INC Locking The way
- value 1( Default ): about Simple Inserts, Use mutexes to accumulate counters in memory , about Bulk Inserts, Using traditional watch lock AUTO-INC Locking The way
- value 2: This mode can be used at any time Row-Base Replication, The maximum concurrent performance and Replication Data synchronization
1.4 Locking mechanism of foreign keys
To insert and update a foreign key, you need to query the parent table record first , If the row record is added by another transaction X Lock not committed , Then subsequent insert operations will first add S lock , The insert operation will be blocked , Data inconsistency will also occur after submission
2 Lock algorithm
InnoDB Three row lock algorithms :
- Record Lock: Lock of single line record
- Gap Lock: Clearance lock , Lock a range , Does not include the record itself
- Next-Key Lock: Lock a range , Include the record itself , The default row record locking algorithm at the repeatable read isolation level
3 The lock problem
Lost update
Multiple transactions modify a row data at the same time , Cause the modification of a transaction to be overwritten
Dirty reading
Dirty data concept : Pages whose buffers have been modified , The data on the disk has not been written
Dirty reading : Under different affairs , Read uncommitted data from other transactions , Exists at the read uncommitted isolation level
It can't be read repeatedly
In the same thing , If data is modified and committed by another transaction , The data read twice will be inconsistent , Violation of the principle of transaction consistency
stay InnoDB in , adopt Next-Key Lock The algorithm avoids the problem of non repeatable reading , stay mysql Is defined as Phantom Problem( Fantasy reading ),Next-key The algorithm will lock the scanned and gaps , Avoid inserting in scope , Avoid the problem of non - repeatable reading
4 Blocking
The lock in one transaction needs to wait for the lock in another transaction to release the occupied resources , Use mutex The data structure implements the blocking mechanism
InnoDB Using parameter innodb_lock_wait_timeout Control the waiting time of the lock , Parameters innodb_rollback_on_timeout Set whether to rollback , Default OFF Does not roll back ,lock Parameters can be dynamically adjusted during database operation , and rollback Parameters are static , Can only be adjusted at startup
5 Deadlock
The database may deadlock in parallel , The mutual waiting between two resources
InnoDB After a deadlock is detected , The transaction will be rolled back . Such as oracle, Deadlocks often occur when an index is not added to a foreign key , and InnoDB The engine will automatically add , Do not delete the foreign key index , Therefore, this problem has been solved better
6 Lock escalation
Definition : Reduce the granularity of the current lock , For example, put the... Of a table 100 A row lock is upgraded to a page lock , Or page lock is upgraded to table lock , To avoid lock overhead , Lock escalation occurs frequently
mssql stay 05 Row lock is supported after version , When one SQL The number of locks on an object exceeds the threshold 5000 Or lock resources occupy more memory than 40% Lock escalation will occur
InnoDB There is no lock escalation problem in ,MySQL The cost of internal locking is independent of the quantity , similar Oracle The design of the
边栏推荐
- 2022各大厂最新总结的软件测试宝典,看完不怕拿不到offer
- 09-MySQL锁
- 【图像去噪】基于马尔可夫随机场实现图像去噪附matlab代码
- 【Laravel系列7.5】事件系统
- 懂机器学习如何入门量化交易?
- Database design graduation information management
- WinCC flexible 2008项目移植到博途WinCC的具体方法
- Understand how to get started with machine learning to quantify transactions?
- 激活函数公式、导数、图像笔记
- ASEMI的MOS管25N120在不同应用场景的表现
猜你喜欢

Crop disease detection using image processing technology and convolutional neural network (CNN)

30讲 线性代数第二讲 矩阵
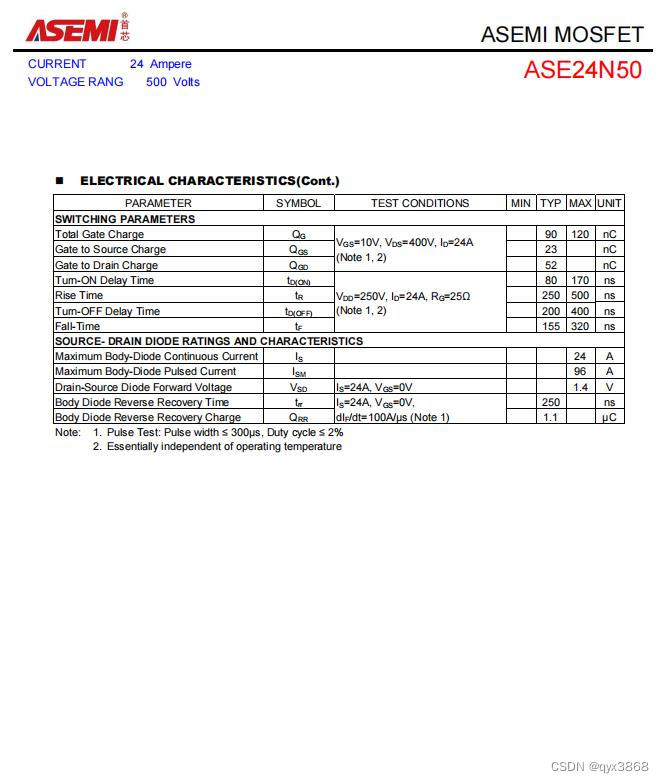
MOS transistor 24n50 parameters of asemi, 24n50 package, 24n50 size

Use Mysql to determine the day of the week
![[Multisim Simulation] using operational amplifier to generate sawtooth wave](/img/98/27086746dc552ada25fd36a82cb52b.png)
[Multisim Simulation] using operational amplifier to generate sawtooth wave
![[assembly] analysis of Experiment 7 of the fourth edition of assembly language](/img/ac/a3c5bfeb2dcb93b123dd337993bab3.jpg)
[assembly] analysis of Experiment 7 of the fourth edition of assembly language

Find the maximum 3 same digits in the string

Replace the backbone of target detection (take the fast RCNN as an example)

vs2010链接sql2008数据库时无法打开

【Multisim仿真】利用运算放大器产生方波、三角波发生器
随机推荐
【图像去噪】基于马尔可夫随机场实现图像去噪附matlab代码
30讲 线性代数第二讲 矩阵
First acquaintance with enterprise platform
[Lao Wang's fallacy of brain science] Why do blind people "seem" to be more "sensitive" than normal people?
无监督图像分类《SCAN:Learning to Classify Images without》代码分析笔记(1):simclr
Today's sleep quality record is 60 points
Anaconda installation, jupyter notebook default startup path modification and nbextensions plug-in installation
"Case sharing" based on am57x+ artix-7 FPGA development board - detailed explanation of Pru Development Manual
E-commerce (njupt)
WinCC flexible 2008项目移植到博途WinCC的具体方法
使用canvas给页面添加文字水印
Introduction to go language (VI) -- loop statement
YOLOv3 Pytorch代码及原理分析(二):网络结构和 Loss 计算
Highcharts sets the histogram width, gradient, fillet, and data above the column
关于富文本储存数据库格式转译问题
Cf:c. restoring the duration of tasks
PyMySQL利用游标操作数据库方法封装!!!
Bottomsheetdialog usage details, setting fillet, fixed height, default full screen, etc
金字塔测试原理:写好单元测试的8个小技巧,一文总结
Internet_ Business Analysis Overview