当前位置:网站首页>Mutex lock, spin lock, read-write lock... Clarify their differences and applications
Mutex lock, spin lock, read-write lock... Clarify their differences and applications
2022-07-25 13:27:00 【Brother, between mountains and rivers】
Reprinted address :https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1712307590984312649&wfr=spider&for=pc
In life , We will use locks to protect our property from being stolen , But today's talk “ lock ”, Not for this purpose .
In the world of programming , How to use locks well is one of the basic qualities of programmers . When multithreading accesses shared resources , We can't avoid the problem of data disorder caused by resource competition , Usually in order to solve this problem , Will lock before accessing shared resources . The most commonly used is mutex , Of course, there are many different kinds of locks , For example, spin lock 、 Read-write lock 、 Optimistic lock, etc , Different types of locks are naturally suitable for different scenarios .
If the wrong lock is selected , In some highly concurrent scenarios , May reduce the performance of the system , Impact on user experience . In order to choose the right lock , Not only do you need to know the cost of locking , You also need to analyze how shared resources are accessed in business scenarios , Then we should consider the conflict probability of concurrent access to shared resources . An antidote against the disease , To reduce the impact of locking on high concurrency performance .
Read-write lock (RWMutex)
Read / write locks are mutually exclusive locks for read / write operations . The biggest difference between it and ordinary mutexes is , It can lock and unlock for read operation and write operation respectively . Read and write locks follow different access control rules than mutex locks . Within the jurisdiction of the read-write lock , It allows any read operation to be performed at the same time . But at the same time , It allows only one write operation in progress . also , In the process of a write operation being performed , Reading operation is not allowed . in other words , Multiple write operations under the control of read-write lock are mutually exclusive , And write operations and read operations are mutually exclusive . However, there is no mutually exclusive relationship between multiple read operations . Read the lock : be-all goroutine Can read at the same time , But write lock is not allowed : Only one is allowed goroutine Write , Other goroutine It is not allowed to read or write golang To demonstrate the function of read-write lock , as follows :
The mutex (Mutex)
Use mutexes (Mutex, Full name mutual exclusion) To protect a resource from conflicts caused by concurrent operations , Leading to inaccurate data . The bottom two differences between mutex and spin lock are 「 Mutexes and spinlocks 」, Many advanced locks are implemented based on them , They can be considered as the foundation of various locks , So we have to know the difference and application between them . The purpose of locking is to ensure that shared resources can be locked at any time , Only one thread accesses , In this way, we can avoid the problem of data sharing disorder caused by multithreading . When a thread is already locked , Locking other threads will fail , Mutexes and spinlocks have different ways to handle lock failures .
The overhead cost of mutexes and spinlocks
After the mutex locking fails , The thread will release CPU , To other threads ; After the locking of the rotary lock fails , The thread is busy waiting , Until it gets the lock ; Mutex is a kind of 「 An exclusive lock 」, For example, when a thread A After locking successfully , At this point, the mutex has been locked by the thread A Exclusive , Just threads A No release of the lock in your hand , Threads B Locking will fail , And then it will release CPU Give way to other threads , Since threads B Released CPU, Natural threads B Lock code will be blocked . For mutex locking failure and blocking phenomenon , It's implemented by the operating system kernel . When the lock fails , The kernel will set the thread to 「 sleep 」 state , When the lock is released , The kernel wakes up threads at the right time , When the thread successfully acquires the lock , You can continue to execute .
Optimistic lock and pessimistic lock
The mutex mentioned earlier 、 spinlocks 、 Read-write lock , All belong to pessimistic lock . Pessimistic lock is more pessimistic , It believes that the probability of multiple threads modifying shared resources at the same time is relatively high , So it's easy to get into conflict , So before accessing shared resources , Lock it first . Contrary , If multiple threads modify shared resources at the same time, the probability is relatively low , You can use the optimistic lock . Optimistic lock is more optimistic , It assumes that the probability of conflict is low , The way it works is : First modify the shared resources , There is no conflict in this period of time , If no other thread is modifying the resource , Then the operation is finished , If you find that other threads have modified this resource , Just give up this operation . How to try again after giving up , This is closely related to the business scenario , Although the cost of retrying is high , But if the probability of conflict is low enough , It's still acceptable . so , The attitude of optimistic lock is , It doesn't matter , Change the resources first . in addition , You will find that optimistic lock is not locked in the whole process , So it's also called lockless programming .
for instance : Online documents can be edited by multiple people at the same time , If pessimistic locks are used , As long as one user is editing the document , At this time, other users cannot open the same document , Of course, the user experience is not good . Realize multi person editing at the same time , It's actually an optimistic lock , It allows multiple users to open the same document for editing , After editing and submitting, verify whether the modified content has conflicts . How to calculate a conflict ? Here's an example , Such as user A First edit the document in the browser , After that users B The same document is opened in the browser for editing , But users B Compared with users A Submit changes , In this process, users A I don't know , When A When submitting the revised content , that A and B There will be a conflict between parallel modifications . How does the server solve this conflict ? Because the probability of conflict is low , So let the user edit the document first , But the browser will record the version number of the document returned by the server when downloading the document ; When a user submits a change , The request sent to the server will carry the original document version number , The server receives it and compares it with the current version number , If the version number is consistent, the modification is successful , Otherwise the submission fails . actually , common SVN and Git It's also the idea of optimism lock , Let the user edit the code first , And then when you submit it , Determine whether there is a conflict by the version number , Where there was a conflict , We need to modify it ourselves , And resubmit . The optimistic lock removes the lock unlock operation , But in case of conflict , The cost of retrying is very high , So only when the probability of conflict is very low , And the locking cost is very high , Just consider using optimistic lock .
边栏推荐
- 0713RHCSA
- 卷积神经网络模型之——AlexNet网络结构与代码实现
- IM系统-消息流化一些常见问题
- Discussion on principle and application technology of MLIR
- 【GCN-RS】Region or Global? A Principle for Negative Sampling in Graph-based Recommendation (TKDE‘22)
- Simple understanding of flow
- 面试官问我:Mysql的存储引擎你了解多少?
- 好友让我看这段代码
- Cv2.resize function reports an error: error: (-215:assertion failed) func= 0 in function ‘cv::hal::resize‘
- QingChuang technology joined dragon lizard community to build a new ecosystem of intelligent operation and maintenance platform
猜你喜欢

VIM tip: always show line numbers

基于百问网IMX6ULL_PRO开发板驱动AP3216实验

Introduction to web security UDP testing and defense
![[Video] Markov chain Monte Carlo method MCMC principle and R language implementation | data sharing](/img/20/bb43ab1bc447b519c3b1de0f809b31.png)
[Video] Markov chain Monte Carlo method MCMC principle and R language implementation | data sharing
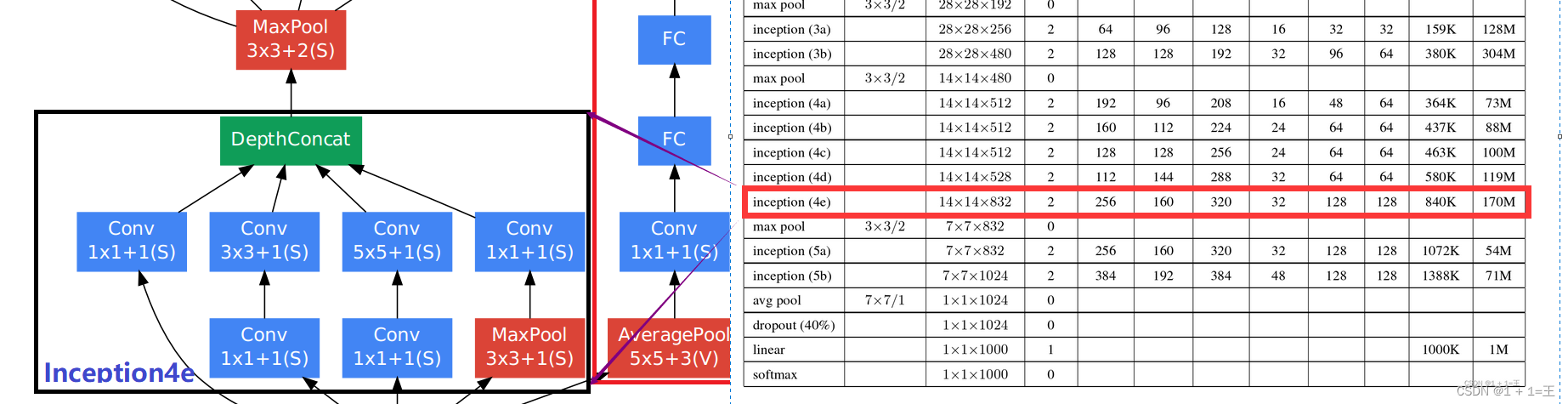
卷积神经网络模型之——GoogLeNet网络结构与代码实现
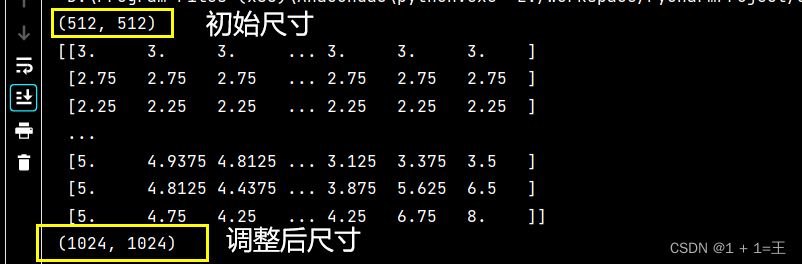
cv2.resize函数报错:error: (-215:Assertion failed) func != 0 in function ‘cv::hal::resize‘

Convolutional neural network model -- alexnet network structure and code implementation

【视频】马尔可夫链蒙特卡罗方法MCMC原理与R语言实现|数据分享

mysql函数汇总之日期和时间函数
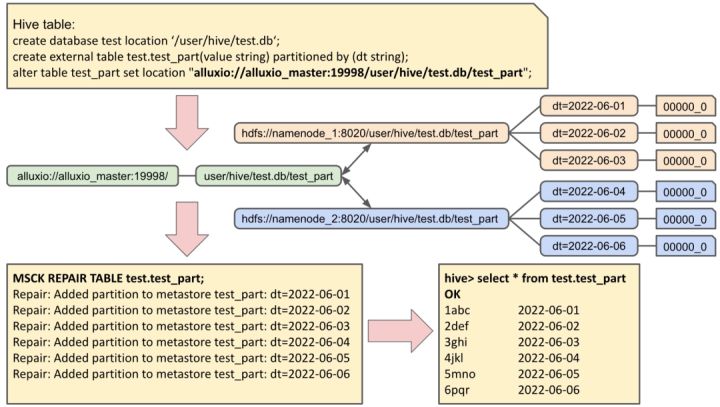
The whole process of 6w+ word recording experiment | explore the economical data storage strategy of alluxio
随机推荐
pytorch创建自己的Dataset加载数据集
说说对hashcode和equals方法的理解?
手写jdbc的使用步骤?
卷积神经网络模型之——VGG-16网络结构与代码实现
How to solve the problem of taking up too much space when recording and editing videos?
领域驱动模型设计与微服务架构落地-模型设计
Shell common script: check whether a domain name and IP address are connected
Machine learning strong foundation program 0-4: popular understanding of Occam razor and no free lunch theorem
机器学习强基计划0-4:通俗理解奥卡姆剃刀与没有免费午餐定理
0719RHCSA
2022全球开发者中,你的收入排多少?
Common operations for Yum and VIM
外围系统调用SAP的WebAPI接口
int数组获取重复数据
Friends let me see this code
Simple understanding of flow
Install mujoco and report an error: distutils.errors DistutilsExecError: command ‘gcc‘ failed with exit status 1
hcip第八天实验
Blindly expanding the scale of the meta universe has deviated from the development logic of the meta universe
详解浮点数的精度问题