当前位置:网站首页>Sed explanation of shell script (SED command, sed -e, sed s/ new / old /...)
Sed explanation of shell script (SED command, sed -e, sed s/ new / old /...)
2022-06-11 09:17:00 【Jerry00713】
( One )
Sed Is a non interactive text flow editor . It edits a text copy of a file or standard input export .vi The regular expression command in sed Most of them can be used in general .
##sed Common options
-e script Appoint sed Edit command
-f scriptfile In the specified file is sed Edit command
-n Silent mode , Suppress from sed Redundant output information during command execution , For example, only the changed rows are displayed .
-i[SUFFIX], –in-place[=SUFFIX] Replace and back up source files
edit files in place (makes backup if extension supplied)
##1. Parameters p: Print matching lines
$ sed -n ’2p’/etc/passwd Print out the 2 That's ok
$ sed -n ’1,3p’/etc/passwd Print out the 1 To the first 3 That's ok
$ sed -n ‘$p’/etc/passwd Print out the last line
$ sed -n ‘/user/p’ /etc/passwd Print it out with user The line of
$ sed -n ‘/\$/p’ /etc/passwd Print it out with $ Metacharacter lines ,$ It means the last line
$ sed -n ‘$=’ ok.txt Print the total number of rows ##2. Parameters a and i: Insert text and additional text ( Insert a new line )
$ sed -n ‘/FTP/p’/etc/passwd Print out FTP The line of
$ sed ‘/FTP/a\ 456′ /etc/passwd It contains FTP Insert a new line after the line of , The content is 456
$ sed ‘/FTP/i\ 123′ /etc/passwd It contains FTP Insert a new row before the row of , The content is 123
$ sed ‘/FTP/i\ “123″’ /etc/passwd It contains FTP Insert a new row before the row of , The content is ”123″
$ sed ’5 a\ 123′ /etc/passwd In the 5 Insert a new line after the line , The content is 123
$ sed ’5 i\ “12345″’ /etc/passwd In the 5 Insert a new line before the line , The content is ”123 expression 45″sed- Add embedded code after search results
#!/bin/bash
#export LANG=zh_CN
find ./ -name “*.html” -exec grep 10000008/100 ‘{}’ \; -exec sed -i ‘/10000008/a\<\!--\# include file=\"\/code.html\"--\>‘ {} \;
###3. Parameters d: Delete text
Delete spaces
sed -i ‘s/[ ]*//g’ ~/$cid.txtDelete empty lines without content
sed ‘/^$/d’ file.conf > file.new.conf
sed -i ‘/^$/d’ ~/$cid.txtDelete the first line
sed -i ’1d’ ~/$cid.txtDelete the first two lines
sed -i ’1,2d’ ~/$cid.txt
del Multiple lines
cat SCTP.log |sed ’1d;2d;$d’
Delete last line :
sed -e ‘$d’ file
Delete the last two lines :
sed ‘N;$!P;D’ file
sed ‘N;$!P;$!D;$d’ fileDelete last n That's ok :
$vi sed.sh
$!/bin/bash
A=$(sed -n ‘$=’ file)
sed $(($A-n+1)),${A}d file
$ sed ‘/user/d’/etc/passwdDelete with string The line of (del include love row head)
sed -i ‘/^love/d’ file
sed -i ‘/love/d’ filevi Delete include strings front 4 That's ok , after 34 That's ok
:/strings/-4,+34d
Delete... From the configuration file # No. comment line
sed ‘s#\#.*##’ file.conf > file.new.conf
sed ‘s,\#.*,,’Delete... From the configuration file // No. comment line
sed ‘s#//.*##’ file.conf > file.new.conf
sed ‘[email protected]//.*@@’Delete by spaces and Tab And become a blank line
sed ‘/^[[:space:]]*$/d’ file.conf > file.new.conf
sed ‘/^[[:space:]]*$/d’Delete the space in the last line
sed -e ‘s/.$//’ file > file.new.conf
Add... At the end of the line 1 A space
sed ‘s/[0-9]$/& /g’ file > flile.new.conf
##4. Parameters s: replace text , The replace command replaces the specified mode with the replacement mode , The format is :
[ a d d r e s s [,address]] s/pattern-to-find/replacement-pattern/[g p w n]
$ sed ‘s/user/USER/’/etc/passwd Will be the first 1 individual user Replace with USER,g Indicates global substitution
$ sed ‘s/user/USER/g’/etc/passwd Will all user Replace with USER
$ sed ‘s/user/#user/’/etc/passwd Will be the first 1 individual user Replace with #user, For example, it is used for shielding
$ sed ‘s/user//’/etc/passwd Will be the first 1 individual user Replace with empty
$ sed ‘s/user/&11111111111111/’/etc/passwd If you want to append or modify a very long string , have access to ( &) command ,& The command saves the discovery pattern in order to recall it , Then put it in the replacement string , Here is the handle. & Put it in the front
$ sed ‘s/user/11111111111111&/’/etc/passwd Here is the general & Put it back Contains the string test On any line of , take 111 Replace with 222
$ sed ‘/test/s/111/222/g’ sample.txt##5. Quick one line regular expression command Here are some one-line command sets .([ ] Said the blank space ,[TAB] Express t a b key )
‘s/\ . $//g’ End with a period
‘-e/abcd/d’ Delete include a b c d The line of
‘s/[ ] [ ] [ ] */[ ]/g’ Remove more than one space , Use a space instead of
‘s/^ [ ] [ ] *//g’ Remove the space at the beginning of the line
‘s/\ . [ ] [ ] */[ ]/g’ Delete a period followed by two or more spaces , Replace it with a space
‘/^ $/d’ Delete blank lines
‘s/^ .//g’ Delete the first character
‘s/COL \ ( . . . \ )//g’ Delete and follow C O L The last three letters of
‘s/^ \///g’ Remove the first... From the path \
‘s/[ ]/[TAB]//g’ Delete all spaces and use t a b Key substitution
‘S/^ [TAB]//g’ Delete all at the beginning of the line t a b key
‘s/[TAB] *//g’ Delete all t a b key ##6、 use sed Remove line breaks from files , You don't need an ox knife to kill a chicken ?
tr -d ‘\n’ file
Really need to sed
sed -nr ‘ H;
$ {
x;
s/\n//g;
p
}’##7、sed obtain ip
[[email protected] ~]# ifconfig eth0|sed -ne ‘s/^.*addr:\([0-9.]*\).*$/\1/p’
192.168.100.180
[[email protected] ~]# ifconfig eth0 | sed -e ‘/inet/!d’ -e ‘s/.*addr://’ -e ‘s/[ ].*//’
192.168.100.180##8、\/ Escape character
echo /usr/local/bin | sed ‘s/\/usr\/local\/bin/\/common\/bin/’
find . -name “*.html” |xargs sed -i ‘s#/canApp/evaluation/html/ index.html#http://www.wallcopper.com/eva/#g’
Can put the current directory .c .h In the document TAB Replace with 4 A space .
find . -name “*.[c|h]” | xargs sed -i ‘s/\t/ /g’##9、 Parameters f:
The following three commands are equal , First, include the string test On any line of , take 111 Replace with 222, And then the character f Replace with hello
$ sed ‘/test/s/111/222/g ; s/f/hello/g’ sample.txt
$ sed -e ‘/test/s/111/222/g’ -e ‘s/f/hello/g’ sample.txtOptions -f: Put all the compilation commands to be executed into the file
$ more scher
/test/s/111/222/g
s/f/hello/g’ sample.txt
$ sed -f scher sample.txt##10、 Parameters q: Means to jump away sed. It can be matched with at most one address parameter .
Print it out with a or b Lines of characters , Once you come across a number , Stop printing now .
$ sed -n -e ‘/[0-9]/q’ -e ‘/[a b]/p’
To china quit
sed ‘china/q’ myfile.txt##11、 Parameters -i suffix : Replace and change the source file backup to suffix
$ sed -i.bak ‘s/123/efg/g’ a.txt Back up the source file
##12、 Parameters r: Insert a file on a line
$ sed -i ’2 r readfile.txt’ writefile.txt
##13、 Parameters w: The contents of the read file are stored in another file (temp.txt). It can be matched with at most one address parameter .
take sample.txt File contains test Data line of string ,copy to temp.txt File ( primary temp.txt There's nothing in it )
$ sed -e ‘/test/w temp.txt’ sample.txt##14、 Parameters y: Convert characters in data . It can be matched with two address parameters at most .
1. Replace the lowercase letters in the file with the uppercase letters .
$ sed -e ‘y/abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz/ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ/’ sample.txt
The number of characters must be the same .
##15、 Parameters !: Indicates that the function parameters are not executed . Remove from the file important character string , Delete the rest .
$ sed -e ‘/important/!d’ sample.txt
##16、 Parameters =: Indicates the number of rows of printed data . It can be matched with two address parameters at most . 1. Print out the document data and display the number of lines .
$ sed -e ‘=’ sample.txt
Calculate the total number
$ sed -n ‘$=’ a.txt
##17、 Other parameters Parameters #: Indicates a comment on the text .
Parameters N: Means to add the next data to pattern space Inside . It can be matched with two address parameters at most .( Add next : After adding a piece of information , Continue to add the next row of this data to pattern space Inside ) 1, Merge the data in the file . The contents of the document are as follows : UNIX LINUX
$ sed -e ‘N’ -e’s/\n/\,/g’ sample.txtgive the result as follows : UNIX,LINUX
Parameters D: Said to delete pattern space The first row of data in . It can be matched with two address parameters at most .
Parameters P: Print out pattern space The first row of data in .
$ sed -n -e ‘N’ -e ‘P’ sample.txt
utilize N The next row of data ( namely : Even number line ) Add to pattern space Inside , Using P Print out odd lines . Explain the process : because N The role of , Make it possible to add one piece of data to each time pattern space after , Do not perform the operation first , Instead, continue to add the next line of this data to pattern space Inside , then P Parameter print out the first row of data .
Parameters h: Indicates temporary storage pattern space From the content of hold space( Cover ). It can be matched with two address parameters at most .
Parameters H: Indicates temporary storage pattern space From the content of hold space( add to ). It can be matched with two address parameters at most .
Parameters g: It means that you will hold space Put the contents of back to pattern space Inside .( Overwrite the original pattern space The data in )
Parameters G: It means that you will hold space Put the contents of back to pattern space Inside .( Add large to original pattern space After the data )
Delete all blank lines in the file , And add a blank line after each line .
$ sed ‘/^$/d;G’ sample.txt
Delete all blank lines in the file , Add two blank lines after each line .
$ sed ‘/^$/d;G;G’ sample.txt
Parameters x: It means exchange hold space And pattern space The data in .
Replace the data in the third line of the file with the data in the first line .
$ sed -e ’1h’ -e ’3x’ sample.txt
Parameters b:
Parameters t:
If you use sed Filter files , It's best to break the problem down into several steps , Step by step , And test results while executing .
Experience tells us , This is the most effective way to perform a complex task .
Reference resources :
http://www.2cto.com/os/201111/112217.html
http://markmail.org/download.xqy?id=w5pncjwnrs77lz3s&number=2
http://www.grymoire.com/Unix/Sed.html
http://sed.sourceforge.net/sed1line.txt
from :
http://www.wallcopper.com/linux/769.html
( Two )
One , Basic overview
(1) Basic introduction
sed It's a stream editing tool , Used to filter and replace text , sed Read the contents of the file through input , But read only one line at a time and output after some instruction processing ,sed It is more suitable for processing big data files .
(2) working principle
sed When dealing with text files , A schema space is created in memory , Then call each line of this file into the schema space and process it with the corresponding command , Finished processing output ; Next line , Until the last .
(3) And vim The difference between
vim It is necessary to inform which lines of the file will be processed ,sed All lines of the file are processed by default , Unless you tell it which lines it doesn't handle .
Two , sed Basic syntax
(1)sed [ Options ] [ Address commands] [inputfile]
About addressing :
The address can be 0 individual 、1 individual 、2 individual ; notice sed Which lines of the file to process .
0 individual : No address , Process all lines of the file
1 individual : Line number , Process the line where the line number is located
2 individual : Line number 、 Regular expressions , Handle lines wrapped in line numbers or regular expressions
(2)
Options :
--version Show sed edition hao
--help Show help documents
-n Turn off default output , All lines will be automatically printed by default
-e Multi point editing , Allow multiple script instructions to be executed .
-r Support extended regularization + ? () {} |
-i You can modify the original file , Use with caution !
-f Support the use of scripts
command :
p Print row
d Delete row
s Replace
n Replace the contents of the first few matches
w Save as
a Then add a line
i Insert text before the current line
y Replace matching content
3、 ... and , Explain the actual case
(1)p( And -n share )
see passwd Of documents 1~3 That's ok
@1, Print one to three lines
[[email protected] ~]# cp /etc/passwd /t1
[[email protected] ~]# cat -n t1 | sed -n '1,3p'
1root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
2bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
3daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
@2, see passwd Of documents lp~halt That's ok
[[email protected] ~]# cat -n t1 |sed -n '/lp/,/halt/p'
5lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
6sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
7shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
8halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
@3, Print cardinality lines ( Start with the first line , Output every other line )

@4, Print uid yes 0 or 1 The line of
[[email protected] ~]# sed -n '/x:[01]:/p' t1
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
(2)d Delete
@1, Delete first line

@2, Delete the first and third lines ( And -e The options apply )
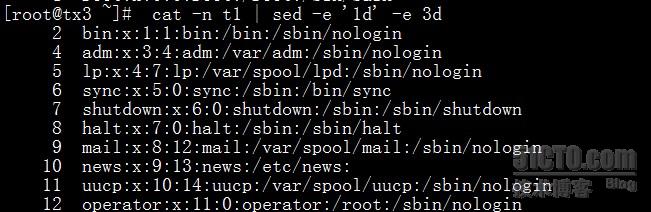
@3,; Use of options and -e equally

@4, Take the opposite :!
[[email protected] ~]# cat -n t1 | sed '1!d'
1root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
(3)s Search and replace s///
grammar :
'[address]s/pattern/replacement/flags'
old new
flags:
n:1-512 Positive integer between , Indicates the number of occurrences in the replacement mode
p: Print
g: Global modification
w: Save as
These options can be combined , But write something meaningful .(pg ;nw)
notes : Here is partial interception
@1 By default, it will replace the... In the line 1 A match
[[email protected] ~]# sed 's/root/ROOT/' t1
ROOT:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
@2 All replacement
[[email protected] ~]# sed 's/root/ROOT/g' t1
ROOT:x:0:0:ROOT:/ROOT:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
@3 Replacement section 2 A match
[[email protected] ~]# sed 's/root/ROOT/2' t1
root:x:0:0:ROOT:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
@4 Print
[[email protected] ~]# sed 's/root/ROOT/p' t1
ROOT:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
ROOT:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin‘
[[email protected] ~]# sed -n 's/root/ROOT/p' t1
ROOT:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
operator:x:11:0:operator:/ROOT:/sbin/nologin
@5 Save as
[[email protected] ~]# sed -n 's/root/ROOT/w /tx' t1
[[email protected] ~]# cat /tx
ROOT:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
operator:x:11:0:operator:/ROOT:/sbin/nologin
@6 Add... Before each line of the file # notes
[[email protected] ~]# sed 's/^/#/' t1
#root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
#bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
#daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
@7 Delete section of the document 1 Characters
[[email protected] ~]# sed 's/^.//1' t1
oot:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
in:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
aemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
@8 Delete section of the document 2 Characters
[[email protected] ~]# sed 's/.//2' t1
rot:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bn:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
(4)i Insert... From the current line
Insert... Before the first line hello
[[email protected] ~]# sed '1i hello' t1
hello
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
(5)a Add... After the current line
Add... After the first line hello
[[email protected] ~]# sed '1a hello' t1
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
hello
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
(6)-r Support extended regularization
[[email protected] ~]# sed -r 's/^(.)(.)/\1/' t1
rot:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash // It is equivalent to replacing the first two characters with the first one , This enables the deletion of the second character
bn:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
demon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
Other methods :
@1#sed 's/.//2' t1
@2#sed 's/^..../\1/' t1
(7)y Replace , Match and replace by position y/// Don't recognize re
[[email protected] ~]# sed 'y/abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz/ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ/' t1
ROOT:X:0:0:ROOT:/ROOT:/BIN/BASH
BIN:X:1:1:BIN:/BIN:/SBIN/NOLOGIN
DAEMON:X:2:2:DAEMON:/SBIN:/SBIN/NOLOGIN
(8) Replace matching lines
@1[[email protected] ~]# sed -n '1c ROOT' t1
ROOT
(9)q sign out
[[email protected] ~]# sed '1q ' t1
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
(10)-i You can modify the original file

(11)-f Support script

Four .sed How to process data
PATT: Mode space , Process the input line of the file , Space for processing files , Save at most 8192 byte , Equivalent to workshop sed Process the stream content here .
HOLD: Reserved space , Used to save input lines that have been processed ; Save at most 8192 byte ; There is a blank line by default , It's like a warehouse , The processed semi-finished products are temporarily stored here .
COMM: command
h: The content in the pattern space , Copy to reserved space , Cover the original content >
H: The content in the pattern space , Append to reserved space , Keep the original content >>
g: The contents of the space will be reserved , Copy to schema space , Cover the original content
G: The contents of the space will be reserved , Append to the schema space , Keep the original content
n: Process the next line of the matching line
x: Swap the contents of the schema space and reserved space
(1)h;G
@1. Put the first line after three lines

@2. Add... After each line 1 Empty rows
notes :1. There is a blank line in the reserved space by default .2,‘G’ The default process is global

@3. The first 1 Go to the first place 4 The data of row is copied to 5 After line
notes :1h To cover the blank lines in the reserved space

@4. The first 1 Go to the first place 4 The data of the row is cut to 5 After line

(2)n Process the next line of the matching line

(3)x Swap the contents of the schema space and reserved space

This article from the “tanxin” Blog , Please make sure to keep this source Shell The script sed Detailed explanation _tanxin Technology blog _51CTO Blog
Reproduced in :https://www.cnblogs.com/tureno/articles/6677942.html
边栏推荐
- Tissu. JS définit dynamiquement la taille de la police
- [share] how do enterprises carry out implementation planning?
- OpenCV CEO教你用OAK(四):创建复杂的管道
- 206. reverse linked list
- openstack详解(二十二)——Neutron插件配置
- Device = depthai Device(““, False) TypeError: _init_(): incompatible constructor arguments.
- 19. delete the penultimate node of the linked list
- Type-C docking station adaptive power supply patent protection case
- 1721. 交换链表中的节点
- 机器学习笔记 - 使用TensorFlow的Spatial Transformer网络
猜你喜欢

Openstack explanation (XXIII) -- other configurations, database initialization and service startup of neutron

OpenCV CEO教你用OAK(四):创建复杂的管道
![报错[DetectionNetwork(1)][warning]Network compiled for 6 shaves,maximum available 10,compiling for 5 s](/img/54/f42146ae649836fe7070ac90f2160e.png)
报错[DetectionNetwork(1)][warning]Network compiled for 6 shaves,maximum available 10,compiling for 5 s

Shandong University project training (IV) -- wechat applet scans web QR code to realize web login

openstack详解(二十四)——Neutron服务注册

Install jupyter in the specified environment

Talk about how to customize data desensitization

Openstack explanation (24) -- registration of neutron service
MSF基于SMB的信息收集

ArcGIS 10.9.1 地质、气象体元数据处理及服务发布调用
随机推荐
83. delete duplicate elements in the sorting linked list
Sword finger offer II 041 Average value of sliding window
Modularnotfounderror: no module named 'find_ version’
Type-C docking station adaptive power supply patent protection case
OpenCV CEO教你用OAK(五):基于OAK-D和DepthAI的反欺骗人脸识别系统
Install jupyter in the specified environment
Sword finger offer 31 Stack push and pop sequence
[ERP system] how much do you know about the professional and technical evaluation?
How to deal with these problems in the factory production process?
682. baseball game
Openstack explanation (21) -- installation and configuration of neutron components
MySQL啟動報錯“Bind on TCP/IP port: Address already in use”
山东大学项目实训(四)—— 微信小程序扫描web端二维码实现web端登录
Telecommuting best practices and Strategies
206. reverse linked list
Typescript high level feature 1 - merge type (&)
kubelet Error getting node 问题求助
[scheme development] sphygmomanometer scheme pressure sensor sic160
ArcGIS 10.9.1 geological and meteorological volume metadata processing and service publishing and calling
Award winning survey streamnational sponsored 2022 Apache pulsar user questionnaire