当前位置:网站首页>Promise+ handwritten promise
Promise+ handwritten promise
2022-06-12 12:33:00 【Fashion_ Barry】
Preface
1、Promise The meaning of ?
stay javascript In the world of , All code is executed in a single thread , Because of this “ defects ”, Lead to JavaScript All network operations for , Browser Events , All must be performed asynchronously .Ajax Can solve this problem , But it is not easy to reuse .JQuery The chain call of can also solve , Each call returns a JQuery object . In order to better handle Promise There is , also ECMAScript It has been standardized .
2、PromiseA+ What is the norm ?
Actually
PromiseThere are a lot of norms , Such asPromise/A,Promise/B,Promise/Das well asPromise/AUpgraded versionPromise/A+.ES6 ( Also called ES2015) Have adopted thePromise/A+standard .
Catalog
Two 、Promise Status( Three states and their relationships )
3、 ... and 、Promise then Method And its return value
1. Specification of parameters
4. onFulfilled and onRejected It should be executed in the micro task phase
5. then Methods can be called multiple times
5、 ... and 、 Realization promise Specific steps ( About nine steps );
1. promise It should be a constructor or class
4. Realization resolve and reject
5. For instantiation promise Input parameter processing at
8. resolvePromise The concrete implementation of the method
9. onFulfilled and onRejected Is executed in a micro task
Here we are ordinary promise It's done , You can simply test
One 、 The term
1. promise Yes then Object or function of method ;
2. thenable Is a then Object or function of a method ;
3. value promise The value when the status is successful , resolve(value), It can be any data type (String Number Boolean undefined thenable promise);
4. reason promise The value when the state fails , reject(reason);
Two 、Promise Status( Three states and their relationships )
1. pending
1.1 The initial state , You can change .
1.2 stay resolve and reject I was in this state before .
1.3 adopt resolve --> fulfilled state .
1.4 adopt reject --> rejected state .
2. fulfilled
2.1 The final state , It can't be changed .
2.2 One promise By resolve Change to this state .
2.3 You have to go through a value value , Value after success .
3. rejected
3.1 The final state , It can't be changed ;
3.2 One promise By reject Change to this state ;
3.3 You have to have a reason , That is the reason for the failure ;
summary :
pending --> resolve(value) --> fulfilled
pending --> reject(reason) --> rejected

3、 ... and 、Promise then Method And its return value
promise should (promiseA+ standard , The standard proposed , So it should be ) Provide a then Method , Used to access the final results , No matter what value still reason.
promise.then(onFuilled,onRejected)Four 、 standard
1. Specification of parameters
1.1 onFulfilled Must be a function type , If it's not a function type , Should be ignored ( Ignore here means to give a default value , It is not neglect in the true sense );
1.2 onRejected Must be a function type , If it's not a function type , Should be ignored ( ditto );
2. onFulfilled characteristic
2.1 stay promise become fulfilled when , Should be called onFulfilled , Parameter is value;(onFulfilled Execution time of ?)
2.2 stay promise become fulfilled Before , Should not call onFulfilled;
2.3 Can only be called once , You can register several callback functions (promise.then().then().then()....);( How to realize only one call ?)
3. onRejected characteristic
3.1 stay promise become rejected when , call onRejected , Parameter is reason;
3.2 stay promise become rejected Before , Should not call onRejected.
3.3 It can only be called once
4. onFulfilled and onRejected It should be executed in the micro task phase
Why does the micro task phase execute ?
Be sure to wait until the previous task is completed , Before calling . A micro task is executed after a round of macro tasks ;
5. then Methods can be called multiple times
5.1 promise become fulfilled after , be-all onFulfilled Callbacks should be executed in the order of registration , It can also be understood as following .then() Sequential execution ;
example :
promise.then(onFulfilled , onRejected).then(onFulfilled1 => ( )).then(....)5.2 promise become rejected after , be-all onRejected Callbacks should be executed in the order of registration , It can also be understood as following .then() Sequential execution ;
6. Return value
It's defined in the specification then It's time to return to one promise
const promise2 = promise( onFulfilled , onRejected );
6.1 onFulfilled or onRejected Execution results by x( Anything : Value or promise), call resolvePromise;
6.2 onFulfilled or onRejected Exception thrown during execution ,promise2 Need to be reject;
6.3 If onFulfilled Not a function ,promise2 Should take promise1 Of value Trigger fulfilled;
6.4. If onRejected Not a function ,promise2 Should take promise1 Of reason Trigger fulfilled
7. resolvePromise
promise2: The first one at the moment promise The return value of ;
X: Whether it's onFulfilled still onRejected The results of the implementation of
resolve、reject : Change method
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject)7.1 If promise2 and x equal reject typeError;
7.2 If x It's a promise
If x yes pending state ,promise Must be in pending state , until x Change of state of .
If x yes fulfilled ,value --> fulfilled
If x yes rejected ,reason --> rejected
7.3 If x It's a Object perhaps Function
To get x.then(), If you make a mistake ,reject reason
If then It's a function ,then.call(x, resolvePromiseFn, rejectPromiseFn)
Why call change this The pointer , perhaps then May lead to The pointer changes , So use call Continue with the previous logic
5、 ... and 、 Realization promise Specific steps ( About nine steps );
1. promise It should be a constructor or class
const promise = new promise();newly build promise-class.js, Today we use class To achieve promise
class MPromise{
constructor(){
}
}2. Define three states
const PENDING = 'pending';
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled';
const REJECTED = 'rejected';
class MPromise{
constructor(){
}
}3. Initialization status
const PENDING = 'pending';
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled';
const REJECTED = 'rejected';
class MPromise{
constructor(){
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = null;
this.reason = null;
}
}4. Realization resolve and reject
4.1 These two methods need to be changed status, from pending become fulfilled / rejected
4.2 The parameters are value and reason
const PENDING = 'pending';
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled';
const REJECTED = 'rejected';
class MPromise{
constructor(){
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = null;
this.reason = null;
}
resolve(value){
// The final state cannot be changed , So we need to add a judgment
// Only when status It can only be changed when it is in the initial state
if(this.status === PENDING){
this.status = FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
}
}
reject(reason){
if(this.status === PENDING){
this.status = REJECTED;
this.reason= reason;
}
}
}5. For instantiation promise Input parameter processing at
5.1 The input parameter is a function
const promise = new promise((resolve,reject)=>{
})5.2 Accept resolve and rejected Two parameters
5.3 initialization promise Will be Sync Execute this function , And any error must be reported through reject Throw out
const promise = new promise((resolve,reject)=>{
axios.get('www.baidu.com')
}).then(result=>{
// There's a little bit of caution here , Where it was created, it was executed
// It's not a call .then() Only when
// Synchronous execution , So you can cache one promise , When you need it, you can take the value directly
// At the time of acquisition The request will not be sent again , So don't worry about traffic sneaking away And Performance issues
})const PENDING = 'pending';
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled';
const REJECTED = 'rejected';
class MPromise{
constructor(fn){
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = null;
this.reason = null;
// You need to call from inside , If you report an error, you need to throw it out immediately
try{
// Consider rigor , change this Point to the current environment
fn(this.resolve.bind(this), this.reject.bind(this));
} catch(e){
this.reject(e)
}
}
resolve(value){
// The final state cannot be changed , So we need to add a judgment
// Only when status It can only be changed when it is in the initial state
if(this.status === PENDING){
this.status = FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
}
}
reject(reason){
if(this.status === PENDING){
this.status = REJECTED;
this.reason= reason;
}
}
}6. Realization then Method
6.1 then Accept Two parameters onFulfilled and onRejected
6.2 Check and process parameters , If the parameter is not a function Just ignore it
6.3 According to the current promise The state of , Call different functions
If promise yes fulfilled When We need to call onFulfilled
If promise yes rejected When We need to call onRejected
6.4 First get all the callbacks , Because when the state changes , Whether it is success or failure, we need to implement the corresponding Callback ; Create two new arrays , Store successful and failed callbacks respectively , call then When , If still pending The status is stored in the array .
6.5 stay status When it changes , Execute the corresponding callback . Here we use es6 Of getter setter, monitor status The change of , Do the corresponding operations when changes occur ;
Let's say if it is ES5 No, getter setter, Then we can directly resolve and reject There are two ways to change status The state of ; Use getter setter It can be better maintained later , No need to pay attention status ;
const PENDING = 'pending';
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled';
const REJECTED = 'rejected';
class MPromise{
// Just live two arrays directly , The array here will not be modified Will only be push Come in
// Status complete list
FULFILLED_CALLBACK_LIST = [];
// Status failed list
REJECTED_CALLBACK_LIST = [];
// Storage initialization status
_status = PENDING;
constructor(fn){
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = null;
this.reason = null;
// You need to call from inside , If you report an error, you need to throw it out immediately
try{
// Consider rigor , change this Point to the current environment
fn(this.resolve.bind(this), this.reject.bind(this));
} catch(e){
this.reject(e)
}
}
get status(){
// All the real status
return this._status;
}
set status(newStatus){
this._status = newStatus;
// Judge different states Execute different logic
switch(newStatus){
case FULFILLED: {
// then The method has been used to judge whether it is function So there is no need to judge
// stay status When it changes , Execute the corresponding callback .
this.FULFILLED_CALLBACK_LIST.forEach(callback=>{
callback(this.value)
});
break;
}
case REJECTED: {
this.REJECTED_CALLBACK_LIST.forEach(callback=>{
callback(this.reason)
});
break;
}
}
}
resolve(value){
// The final state cannot be changed , So we need to add a judgment
// Only when status It can only be changed when it is in the initial state
if(this.status === PENDING){
this.value = value;
this.status = FULFILLED;
}
}
reject(reason){
if(this.status === PENDING){
this.reason= reason;
this.status = REJECTED;
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected){
const fulFilledFn = this.isFunction(onFulfilled) ? onFulfilled : (value) => value
const rejectedFn = this.isFunction(onRejected) ? onRejected : (reason) => throw(reason)
switch(this.status){
case FULFILLED: {
fulFilledFn(this.value);
break;
}
case REJECTED: {
rejectedFn(this.reason);
break;
}
case PENDING: {
this.FULFILLED_CALLBACK_LIST.push(fulFilledFn);
this.REJECTED_CALLBACK_LIST.push(rejectedFn);
break;
}
}
}
isFunction(param){
return typeof param === 'function';
}
}7. then The return value of
7.1 If onFulfilled perhaps onRejected Throw an exception e , So new promise must reject e;
7.2 The return value should be a promise
7.3 If onFulfilled It's not a function , And promise1 success (resolve state ) perform ,promise2 Must return to the same status and value;( As defined in the specification )
7.4 If onRejected It's not a function , And promise1 Refuse to enforce ,promise2 Must return to the same status and reason;
7.5 If onFulfilled perhaps onRejected Returns a value x , function resolvePromise Method .
const PENDING = 'pending';
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled';
const REJECTED = 'rejected';
class MPromise{
// Just live two arrays directly , The array here will not be modified Will only be push Come in
// Status complete list
FULFILLED_CALLBACK_LIST = [];
// Status failed list
REJECTED_CALLBACK_LIST = [];
// Storage initialization status
_status = PENDING;
constructor(fn){
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = null;
this.reason = null;
// You need to call from inside , If you report an error, you need to throw it out immediately
try{
// Consider rigor , change this Point to the current environment
fn(this.resolve.bind(this), this.reject.bind(this));
} catch(e){
this.reject(e)
}
}
get status(){
// All the real status
return this._status;
}
set status(newStatus){
this._status = newStatus;
// Judge different states Execute different logic
switch(newStatus){
case FULFILLED: {
// then The method has been used to judge whether it is function So there is no need to judge
// stay status When it changes , Execute the corresponding callback .
this.FULFILLED_CALLBACK_LIST.forEach(callback=>{
callback(this.value)
});
break;
}
case REJECTED: {
this.REJECTED_CALLBACK_LIST.forEach(callback=>{
callback(this.reason)
});
break;
}
}
}
resolve(value){
// The final state cannot be changed , So we need to add a judgment
// Only when status It can only be changed when it is in the initial state
if(this.status === PENDING){
this.value = value;
this.status = FULFILLED;
}
}
reject(reason){
if(this.status === PENDING){
this.reason= reason;
this.status = REJECTED;
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected){
const fulFilledFn = this.isFunction(onFulfilled) ? onFulfilled : (value) => value
const rejectedFn = this.isFunction(onRejected) ? onRejected : (reason) => throw(reason)
// If onFulfilled perhaps onRejected Throw an exception e , So new promise must reject e;
const fulFilledFnWitchCatch = (resolve, reject, newPromise) => {
try{
// Not a function Just directly resolve , Because there is a return value , So judgment is needed
if(!this.isFunction(onFulfilled)){
resolve(this.value)
}else{
const x = fulFilledFn(this.value);
this.resolvePromise(newPromise, x, resolve, reject);
}
}catch(e) {
reject(e)
}
}
const rejectedFnWitchCatch = (resolve, reject, newPromise) => {
try{
if(!this.isFunction(onRejected)){
reject(this.reason);
}else{
const x = rejectedFn(this.reason);
this.resolvePromise(newPromise, x, resolve, reject);
}
}catch(e) {
reject(e)
}
}
switch(this.status){
// then The return value of promise
case FULFILLED: {
const newPromise = new MPromise((resolve, reject) => fulFilledFnWitchCatch(resolve, reject, newPromise));
return newPromise;
}
case REJECTED: {
const newPromise = new MPromise((resolve, reject) => rejectedFnWitchCatch(resolve, reject, newPromise));
return newPromise;
}
case PENDING: {
const newPromise = new MPromise((resolve, reject) => {
this.FULFILLED_CALLBACK_LIST.push(() => fulFilledFnWitchCatch(resolve, reject, newPromise));
this.REJECTED_CALLBACK_LIST.push(() => rejectedFnWitchCatch(resolve, reject, newPromise));
});
return newPromise;
}
}
}
// It's defined in the specification resolvePromise Need to accept a newPromise
// resolvePromise The meaning of function , That's right promise Processing of various values
// Give Way promise You can return a result , Whether it's resolve still reject
resolvePromise(newPromise, x, resolve, reject){
}
isFunction(param){
return typeof param === 'function';
}
}8. resolvePromise The concrete implementation of the method
resolvePromise Functional significance , That's right promise Processing of various values , Give Way promise You can return a result , Whether it's resolve still reject
8.1 If promise2 and x equal
8.1 If x It's a promise ,promise Must be in pending state , until x Change of state of
If x fulfilled ,value ---> fulfilled
If x rejected ,reason ----> rejected
8.1 If x It's a object / Function
To get const then = x.then, reject reason
then It's a function ,then.call(x,resolvePromiseFn, rejectPromiseFn)
const PENDING = 'pending';
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled';
const REJECTED = 'rejected';
class MPromise{
// Just live two arrays directly , The array here will not be modified Will only be push Come in
// Status complete list
FULFILLED_CALLBACK_LIST = [];
// Status failed list
REJECTED_CALLBACK_LIST = [];
// Storage initialization status
_status = PENDING;
constructor(fn){
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = null;
this.reason = null;
// You need to call from inside , If you report an error, you need to throw it out immediately
try{
// Consider rigor , change this Point to the current environment
fn(this.resolve.bind(this), this.reject.bind(this));
} catch(e){
this.reject(e)
}
}
get status(){
// All the real status
return this._status;
}
set status(newStatus){
this._status = newStatus;
// Judge different states Execute different logic
switch(newStatus){
case FULFILLED: {
// then The method has been used to judge whether it is function So there is no need to judge
// stay status When it changes , Execute the corresponding callback .
this.FULFILLED_CALLBACK_LIST.forEach(callback=>{
callback(this.value)
});
break;
}
case REJECTED: {
this.REJECTED_CALLBACK_LIST.forEach(callback=>{
callback(this.reason)
});
break;
}
}
}
resolve(value){
// The final state cannot be changed , So we need to add a judgment
// Only when status It can only be changed when it is in the initial state
if(this.status === PENDING){
this.value = value;
this.status = FULFILLED;
}
}
reject(reason){
if(this.status === PENDING){
this.reason= reason;
this.status = REJECTED;
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected){
const fulFilledFn = this.isFunction(onFulfilled) ? onFulfilled : (value) => value
const rejectedFn = this.isFunction(onRejected) ? onRejected : (reason) => throw(reason)
// If onFulfilled perhaps onRejected Throw an exception e , So new promise must reject e;
const fulFilledFnWitchCatch = (resolve, reject, newPromise) => {
try{
// Not a function Just directly resolve , Because there is a return value , So judgment is needed
if(!this.isFunction(onFulfilled)){
resolve(this.value)
}else{
const x = fulFilledFn(this.value);
this.resolvePromise(newPromise, x, resolve, reject);
}
}catch(e) {
reject(e)
}
}
const rejectedFnWitchCatch = (resolve, reject, newPromise) => {
try{
if(!this.isFunction(onRejected)){
reject(this.reason);
}else{
const x = rejectedFn(this.reason);
this.resolvePromise(newPromise, x, resolve, reject);
}
}catch(e) {
reject(e)
}
}
switch(this.status){
// then The return value of promise
case FULFILLED: {
const newPromise = new MPromise((resolve, reject) => fulFilledFnWitchCatch(resolve, reject, newPromise));
return newPromise;
}
case REJECTED: {
const newPromise = new MPromise((resolve, reject) => rejectedFnWitchCatch(resolve, reject, newPromise));
return newPromise;
}
case PENDING: {
const newPromise = new MPromise((resolve, reject) => {
this.FULFILLED_CALLBACK_LIST.push(() => fulFilledFnWitchCatch(resolve, reject, newPromise));
this.REJECTED_CALLBACK_LIST.push(() => rejectedFnWitchCatch(resolve, reject, newPromise));
});
return newPromise;
}
}
}
// It's defined in the specification resolvePromise Need to accept a newPromise
// resolvePromise The meaning of function , That's right promise Processing of various values
// Give Way promise You can return a result , Whether it's resolve still reject
resolvePromise(newPromise, x, resolve, reject){
if(newPromise === x){
// Return an error message , Information doesn't matter. Anything can
// Why reject An error message , Because if newPromise and x Equality calls each other , Form a dead cycle
return reject(new TypeError('Type Error,Please....'))
}
if(x instanceOf MPromise){
// If it is promise There must be then Method
x.then(y =>{
this.resolvePromise(newPromise, y, resolve, reject)
}, reject);
} else if(typeof x === 'object' || this.isFunction(x)){
// typeof null It's also object, So we need to judge
if(x === null){
return resolve(x)
}
// According to the standard semantic writing
let then = null;
try{
then = x.then;
}catch(error){
return reject(error);
}
if(this.isFunction(then)){
// The specification requires then Method Can only be called once
// Define a called Variable , Identify whether it is called
let called = false;
try{
// In order to avoid abnormal errors , Replace then Of this Point to by x
then.call(
x,
(y) =>{
if(called){
return;
}
called = true;
// Simple recursion , The goal is to find all x
this.resolvePromise(newPromise, y, resolve, reject);
},
(r) =>{
if(called){
return;
}
called = true;
reject(r);
}
)
}catch(error){
if(called){
return;
}
reject(error);
}
}else{
resolve(x);
}
} else {
resolve(x)
}
}
isFunction(param){
return typeof param === 'function';
}
}9. onFulfilled and onRejected Is executed in a micro task
How to achieve ?
queueMicrotask(()=>{}); Pass in a function , Call in the micro task
const PENDING = 'pending';
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled';
const REJECTED = 'rejected';
class MPromise{
// Just live two arrays directly , The array here will not be modified Will only be push Come in
// Status complete list
FULFILLED_CALLBACK_LIST = [];
// Status failed list
REJECTED_CALLBACK_LIST = [];
// Storage initialization status
_status = PENDING;
constructor(fn){
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = null;
this.reason = null;
// You need to call from inside , If you report an error, you need to throw it out immediately
try{
// Consider rigor , change this Point to the current environment
fn(this.resolve.bind(this), this.reject.bind(this));
} catch(e){
this.reject(e)
}
}
get status(){
// All the real status
return this._status;
}
set status(newStatus){
this._status = newStatus;
// Judge different states Execute different logic
switch(newStatus){
case FULFILLED: {
// then The method has been used to judge whether it is function So there is no need to judge
// stay status When it changes , Execute the corresponding callback .
this.FULFILLED_CALLBACK_LIST.forEach(callback=>{
callback(this.value)
});
break;
}
case REJECTED: {
this.REJECTED_CALLBACK_LIST.forEach(callback=>{
callback(this.reason)
});
break;
}
}
}
resolve(value){
// The final state cannot be changed , So we need to add a judgment
// Only when status It can only be changed when it is in the initial state
if(this.status === PENDING){
this.value = value;
this.status = FULFILLED;
}
}
reject(reason){
if(this.status === PENDING){
this.reason= reason;
this.status = REJECTED;
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected){
const fulFilledFn = this.isFunction(onFulfilled) ? onFulfilled : (value) => value
const rejectedFn = this.isFunction(onRejected) ? onRejected : (reason) => throw(reason)
// If onFulfilled perhaps onRejected Throw an exception e , So new promise must reject e;
const fulFilledFnWitchCatch = (resolve, reject, newPromise) => {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try{
// Not a function Just directly resolve , Because there is a return value , So judgment is needed
if(!this.isFunction(onFulfilled)){
resolve(this.value)
}else{
const x = fulFilledFn(this.value);
this.resolvePromise(newPromise, x, resolve, reject);
}
}catch(e) {
reject(e)
}
});
}
const rejectedFnWitchCatch = (resolve, reject, newPromise) => {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try{
if(!this.isFunction(onRejected)){
reject(this.reason);
}else{
const x = rejectedFn(this.reason);
this.resolvePromise(newPromise, x, resolve, reject);
}
}catch(e) {
reject(e)
}
});
}
switch(this.status){
// then The return value of promise
case FULFILLED: {
const newPromise = new MPromise((resolve, reject) => fulFilledFnWitchCatch(resolve, reject, newPromise));
return newPromise;
}
case REJECTED: {
const newPromise = new MPromise((resolve, reject) => rejectedFnWitchCatch(resolve, reject, newPromise));
return newPromise;
}
case PENDING: {
const newPromise = new MPromise((resolve, reject) => {
this.FULFILLED_CALLBACK_LIST.push(() => fulFilledFnWitchCatch(resolve, reject, newPromise));
this.REJECTED_CALLBACK_LIST.push(() => rejectedFnWitchCatch(resolve, reject, newPromise));
});
return newPromise;
}
}
}
catch(onRejected){
return this.then(null, onRejected)
}
// It's defined in the specification resolvePromise Need to accept a newPromise
// resolvePromise The meaning of function , That's right promise Processing of various values
// Give Way promise You can return a result , Whether it's resolve still reject
resolvePromise(newPromise, x, resolve, reject){
if(newPromise === x){
// Return an error message , Information doesn't matter. Anything can
// Why reject An error message , Because if newPromise and x Equality calls each other , Form a dead cycle
return reject(new TypeError('Type Error,Please....'))
}
if(x instanceOf MPromise){
// If it is promise There must be then Method
x.then(y =>{
this.resolvePromise(newPromise, y, resolve, reject)
}, reject);
} else if(typeof x === 'object' || this.isFunction(x)){
// typeof null It's also object, So we need to judge
if(x === null){
return resolve(x)
}
// According to the standard semantic writing
let then = null;
try{
then = x.then;
}catch(error){
return reject(error);
}
if(this.isFunction(then)){
// The specification requires then Method Can only be called once
// Define a called Variable , Identify whether it is called
let called = false;
try{
// In order to avoid abnormal errors , Replace then Of this Point to by x
then.call(
x,
(y) =>{
if(called){
return;
}
called = true;
// Simple recursion , The goal is to find all x
this.resolvePromise(newPromise, y, resolve, reject);
},
(r) =>{
if(called){
return;
}
called = true;
reject(r);
}
)
}catch(error){
if(called){
return;
}
reject(error);
}
}else{
resolve(x);
}
} else {
resolve(x)
}
}
isFunction(param){
return typeof param === 'function';
}
}Here we are ordinary promise It's done , You can simply test
const test = new MPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve(1111);
},1000)
}).then(console.log)
const test = new MPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(()=>{
reject(1111);
},1000)
}).then((value) => {
console.log(' complete ' + value)
}).catch((reason) => {
console.log(' Report errors ' + reason)
})
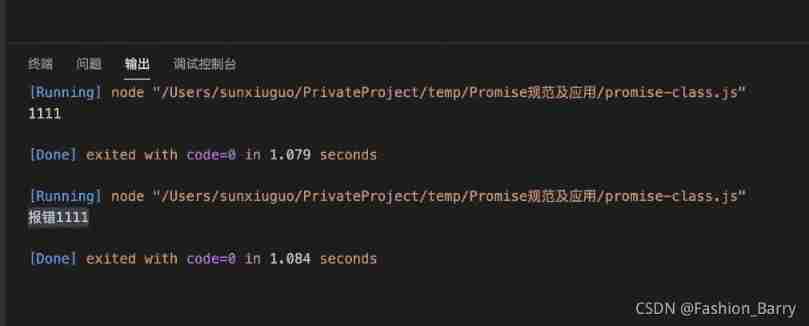
Come here Example method resolve reject already Add up , The static method will be supplemented later ;
边栏推荐
- SEO optimization of web pages
- Reasons for college students' leave
- MVC mode, encryption, jsonwebtoken
- For in and object The difference between keys()
- ITK 原图种子点经过roi、降采样后index的变化
- Shielding does not display vs warning
- 获取本机所有ipv4, ipv6地址
- Kotlin扩展函数实现原理
- C语言深度解剖篇——关键字&&补充内容
- This direction of ordinary function and arrow function
猜你喜欢

Quantization and Training of Neural Networks for Efficient Integer-Arithmetic-Only Inference

itk 多分辨率图像 itk::RecursiveMultiResolutionPyramidImageFilter
El select data echo, display only value but not label

JS how to convert a string into an array object

C语言进阶篇——深度解剖数据在内存中的存储(配练习)

Left and right cases + rotating pictures of small dots + no time

点云配准--gicp原理与其在pcl中的使用

This direction of ordinary function and arrow function

In depth anatomy of C language - key words & supplementary contents

InfluxDB2.x 基准测试工具 - influxdb-comparisons
随机推荐
关系代数笛卡尔积和自然连接的例子
Rust语言学习
Bat interview & advanced, get interview materials at the end of the text
Video speed doubling in PC browser
Redis的主从复制原理
Problems encountered in installing canvas and errors encountered in running the project
ITK Examples/RegistrationITKv4/DeformableRegistration
JS built in object
MySQL 分区表介绍与测试
sublime_text使用
JS string array converted to numeric array and how to add the numbers in the array
The difference between bind, call and apply, and the encapsulation of bind()
Congratulations to splashtop for winning the 2022 it Europa "vertical application solution of the year" award
【数据库】navicat --oracle数据库创建
AGCO AI frontier promotion (6.12)
Native JS implements the copy text function
Is yuancosmos a short-term speculation or a future trend?
MySQL review
深度剖析指针的进阶——C语言的进阶篇
2021-11-16