当前位置:网站首页>[FreeRTOS] FreeRTOS and stm32 built-in stack occupancy
[FreeRTOS] FreeRTOS and stm32 built-in stack occupancy
2022-08-05 00:32:00 【Thank you boss for not using crabs】
In the stm32 startup file, the stack size of the microcontroller is set. In the startup file here, the stack size is set to 1024 bytes, and the heap size is set to 512 bytes.

But in the FreeRTOSConfig.h file, the configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE macro is also used to define the heap size to be used by FreeRTOS. Setting 36*1024 means that the maximum heap size used by FreeRTOS is36KB.

Obviously, 512 bytes are obviously smaller than 36 bytes, then there will be a question: why is the entire project file still able to run normally on stm32?
First of all, let's clarify the definition of stack.
Stack area (stack): It is automatically allocated and released by the compiler, and stores the parameter values of functions, the values of local variables, etc., and its operation is similar to the stack in the data structure.
heap: Generally allocated and released by the programmer, if the programmer does not release it, it may be reclaimed by the operating system at the end of the program.The allocation is similar to a linked list in a data structure.
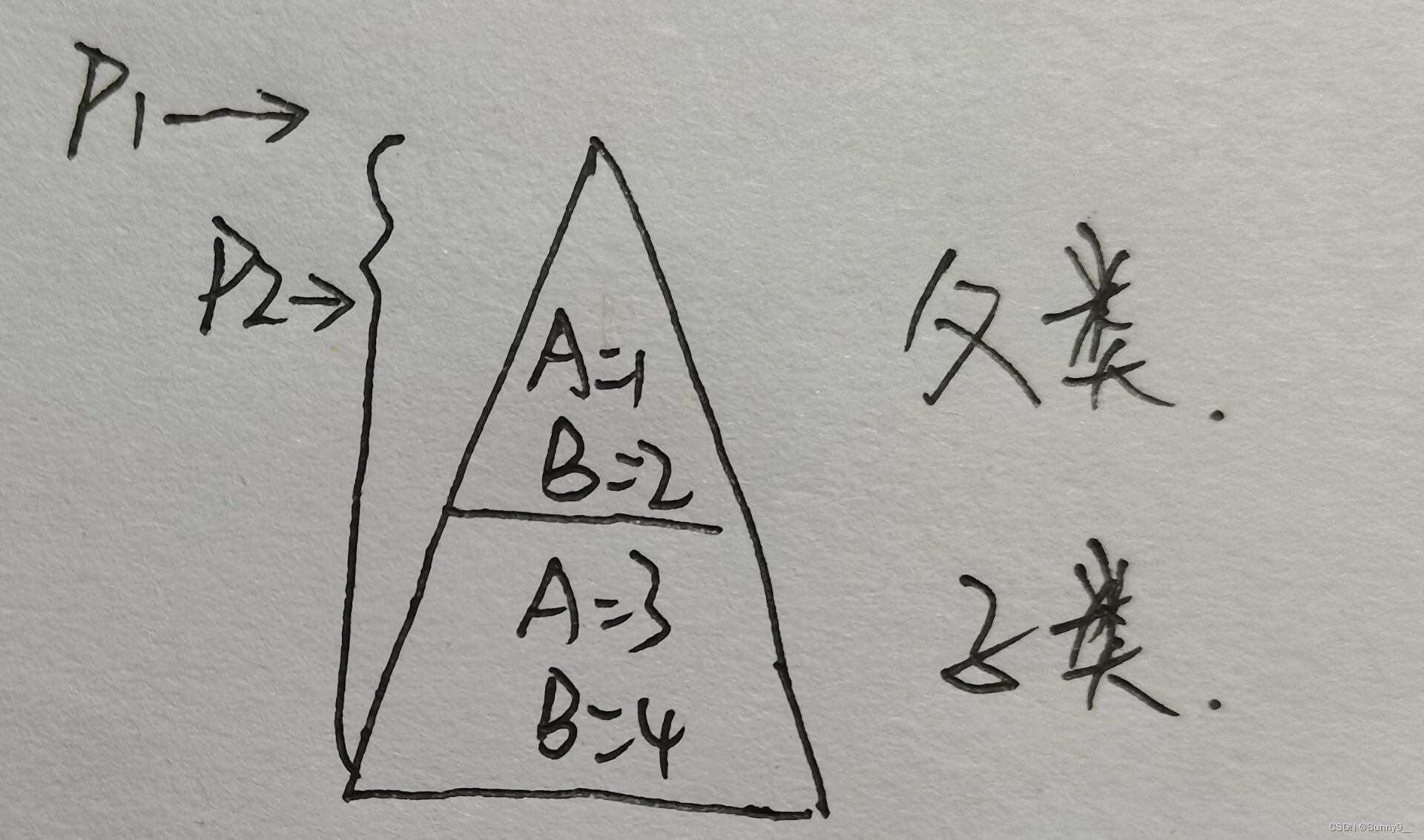
There are two stack pointers in Cortex M3. In OS, usually use MSP in interrupts and PSP in normal tasks.
The stack size setting in the startup file can only change the MSP.In addition, Cortex M3 cannot set the stack size, only the stack pointer can be set!If the stack pointer is set at the last position of RAM and the stack space is set to 0, the compiler will not report an error, and the program can also run, as long as it does not conflict with the actual use area!
Summary: The stack size set in the stm32 startup file and the stack size set in FreeRTOSConfig.h usually do not interfere with each other (depending on different modelsIt depends on the size of RAM, as long as the sum of the two does not exceed the RAM size of the microcontroller, they should not interfere with each other), they are two independent memory spaces.
In addition, when looking for this problem, I found a cause and solution to the problem of insufficient allocation stack space. Here is almost the same words:
Summary of heap space usage: The heap space that the user can freely use (set in the startup file and allocated using the malloc() function) is about half of the total heap space.If it exceeds, the system will crash.
Summary of stack space usage: The functions being processed, including function nesting, recursion, etc., are allocated from this "stack".
Therefore, if aThere are too many local variables in the function. For example, if you define a u8 buf[512] in the function, this will take up 1/4 of the stack size. If you do it twice in other functions, it is very easy for the program to crash.At this time, you will usually enter hardfault....
This is a very easy mistake for beginners to make. Remember not to put N multiple local variables in the function, especially when there are large arrays!strong>
Reference:
KEIL toolThe stack 2_qrshi's blog-CSDN blog _keil stack window how to get it out
边栏推荐
- 图解 Canvas 入门
- tiup status
- Software testing interview questions: test life cycle, the test process is divided into several stages, and the meaning of each stage and the method used?
- 在线中文姓名生成工具推荐
- 典型相关分析CCA计算过程
- 软件测试面试题:系统测试的策略有?
- gorm joint table query - actual combat
- Software Testing Interview Questions: What aspects should be considered when designing test cases, i.e. what aspects should different test cases test against?
- Mysql_14 存储引擎
- [idea] idea configures sql formatting
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
The master teaches you the 3D real-time character production process, the game modeling process sharing
2022牛客多校第三场 A Ancestor
E - Many Operations (按位考虑 + dp思想记录操作后的结果
Flask框架 根据源码分析可扩展点
RK3399平台开发系列讲解(内核调试篇)2.50、嵌入式产品启动速度优化
Software Testing Interview Questions: About Automated Testing Tools?
【Valentine's Day special effects】--Canvas realizes full screen love
2022 The Third J Question Journey
canvas 高斯模糊效果
SV class virtual method of polymorphism
数据类型-整型(C语言)
僵尸进程和孤儿进程
SV 类的虚方法 多态
软件测试面试题:测试用例通常包括那些内容?
Software Testing Interview Questions: What's the Key to a Good Test Plan?
《WEB安全渗透测试》(28)Burp Collaborator-dnslog外带技术
怎样进行在不改变主线程执行的时候,进行日志的记录
leetcode:269. 火星词典
2022 Hangzhou Electric Multi-School Training Session 3 1009 Package Delivery
国内网站用香港服务器会被封吗?