当前位置:网站首页>Coding style: SSM environment in MVC mode, code hierarchical management
Coding style: SSM environment in MVC mode, code hierarchical management
2020-11-10 00:28:00 【Irving the procedural ape】
In this paper, the source code :GitHub· Click here || GitEE· Click here
One 、 Layering strategy
MVC Pattern and code layering strategy ,MVC The full name is ModelViewController The model - View - controller , As a software design paradigm , Using a business logic 、 data 、 The interface displays the separated method organization code , Gather business logic into a component , While improving and personalizing the interface and user interaction , No need to rewrite business logic , It's a development model , But it's not the layered pattern of code in actual development , Usually SSM The framework's back-end code layers are as follows :
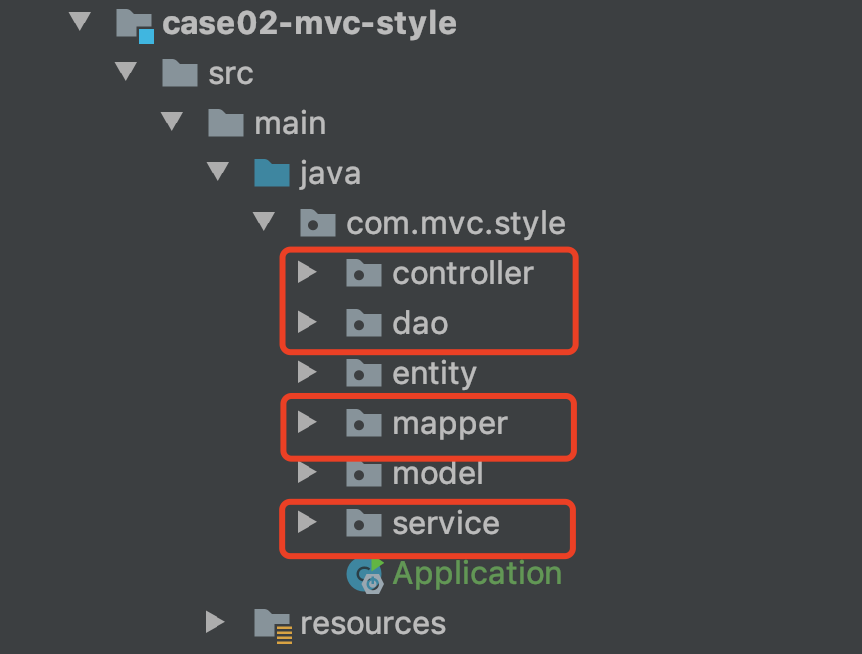
- controller Control layer : Define the server interface , In and out , And some input parameters ;
- service Business services layer : Assemble business logic , Business verification , The parameter model needed to build the control layer ;
- dao Data interaction layer : Provide the data query method needed by the service layer , Dealing with logic related to data interaction conditions ;
- mapper Persistence layer : be based on mybatis The framework needs native support , The most commonly used persistence layer component at present ;
Two 、 Control layer
1、Rest The interface style
Based on the logic of resource access and processing , Use different styles of annotations . For example, new resources , to update , Inquire about , Delete .
/** * newly added */@PostMapping("/insert")public Integer insert (@RequestBody BaseInfo baseInfo){ return baseInfoService.insert(baseInfo);}/** * to update */@PutMapping("/update/{id}")public String update(@PathVariable(value = "id") Integer id, @RequestBody BaseInfo baseInfo) { if (id<1){ return "error"; } baseInfo.setId(id); return "update="+baseInfoService.update(baseInfo);}/** * Primary key query */@GetMapping("/detail/{id}")public InfoModel detail(@PathVariable(value = "id") Integer id) { return baseInfoService.detail(id) ;}/** * Delete primary key */@DeleteMapping("/delete/{id}")public String delete(@PathVariable(value = "id") Integer id) { baseInfoService.delete(id) ; return "SUS" ;}2、 Interface reuse
High reuse of interfaces is not recommended , For example, add, delete, modify and check all the interfaces , The basic principle of , Different client side operations , For independent interfaces .
/** * List loading */@GetMapping("/list")public List<BaseInfo> list() { return baseInfoService.list(new BaseInfoExample()) ;}/** * List search */@PostMapping("/search")public List<BaseInfo> search (@RequestParam("userName") String userName, @RequestParam("phone") String phone) { return baseInfoService.search(userName,phone) ;}For example, common list Interface ,list Usually, there will be conditional loading search Mechanism , And the search criteria are complex , It is suggested that there are two interfaces , From a practical point of view , Most of the scenarios are only used list Interface , Rarely used search Search for .
3、 In and out
Verification client must be conditional , For example, a certain condition is required , If there are questions , Quickly block the request link , The program entrance control layer intercepts and returns .
@PutMapping("/update/{id}")public String update(@PathVariable(value = "id") Integer id, @RequestBody BaseInfo baseInfo) { if (id<1){ return "error"; } baseInfo.setId(id); return "update="+baseInfoService.update(baseInfo);}The parameters are less than three , It can be displayed directly into the reference , If there are three or more parameters, entity classes can be used to encapsulate them .
@PostMapping("/search")public List<BaseInfo> search (@RequestParam("userName") String userName, @RequestParam("phone") String phone) { return baseInfoService.search(userName,phone) ;}4、 Processing parameters
The basic principle of the processing degree of the output parameter format , Servers as public resources , Avoid unnecessary operations , For example, the client can judge whether the return value is empty ,null etc. , Or some common format processing , Use the client to share the server pressure properly .
3、 ... and 、 Business services layer
1、 Business verification
For example, pass in the order number , Through the database layer query , No order data , This is called a business nature exception , There's no problem with the code itself , But business logic doesn't work properly .
public InfoModel detail(Integer id){ BaseInfo baseInfo = baseInfoDao.selectByPrimaryKey(id) ; if .........版权声明
本文为[Irving the procedural ape]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
边栏推荐
- 对于程序员,那些既陌生又熟悉的计算机硬件
- 树莓派鼓捣记 - 设置 wifi
- DB-Engines 11月数据库排名:PostgreSQL坐稳同期涨幅榜冠军宝座
- 分布式文档存储数据库之MongoDB索引管理
- Python提示AttributeError 或者DeprecationWarning: This module was deprecated解决方法
- Fire knowledge online answer activity small program
- JS solves the problem of automatic pagination in browser printing
- 函数计算进阶-IP查询工具开发
- js label语法跳出多重循环
- Common settings of PLSQL developer
猜你喜欢

Hengxun Technology: the way to deal with server downtime
Simple use of JMeter

Hand in hand to teach you to use container service tke cluster audit troubleshooting

函数计算进阶-IP查询工具开发

mongodb内核源码实现、性能调优、最佳运维实践系列-command命令处理模块源码实现一
Prometheus installation configuration
Operation and design of rights management in ERP
CUDA_ Memory model

jt-day10

YouTube subscription: solve the problem of incomplete height display of YouTube subscription button in pop-up window
随机推荐
Make a home page
Coding style: SSM environment in MVC mode, code hierarchical management
How SSL certificate and public IP address affect SEO
Detach ()
mongodb内核源码实现、性能调优、最佳运维实践系列-command命令处理模块源码实现一
Brief analysis of LinkedList source code
Assign the corresponding key and value in the map to the object
[Python learning manual notes] 001. Preface to Python
Nodejs: handwritten koa Middleware
消防知识线上答题活动小程序复盘
YouTube subscription: solve the problem of incomplete height display of YouTube subscription button in pop-up window
sql 筛选查询重复列
分布式文档存储数据库之MongoDB索引管理
DB-Engines 11月数据库排名:PostgreSQL坐稳同期涨幅榜冠军宝座
jt-day10
Youtube订阅——解决在弹窗内使用Youtube订阅按钮高度显示不全的问题
一个名为不安全的类Unsafe
iNeuOS工业互联平台,WEB组态(iNeuView)增加工程视图导入、导出功能,及优化和修复,发布:v3.2.1版本
CUDA常用概念及注意点
pytorch训练GAN时的detach()